Sato Makoto
Paper download is intended for registered attendees only, and is
subjected to the IEEE Copyright Policy. Any other use is strongly forbidden.
Papers from this author
Image Defocus Analysis for Finger Detection on a Virtual Keyboard
Miwa Michio, Honda Kenji, Sato Makoto
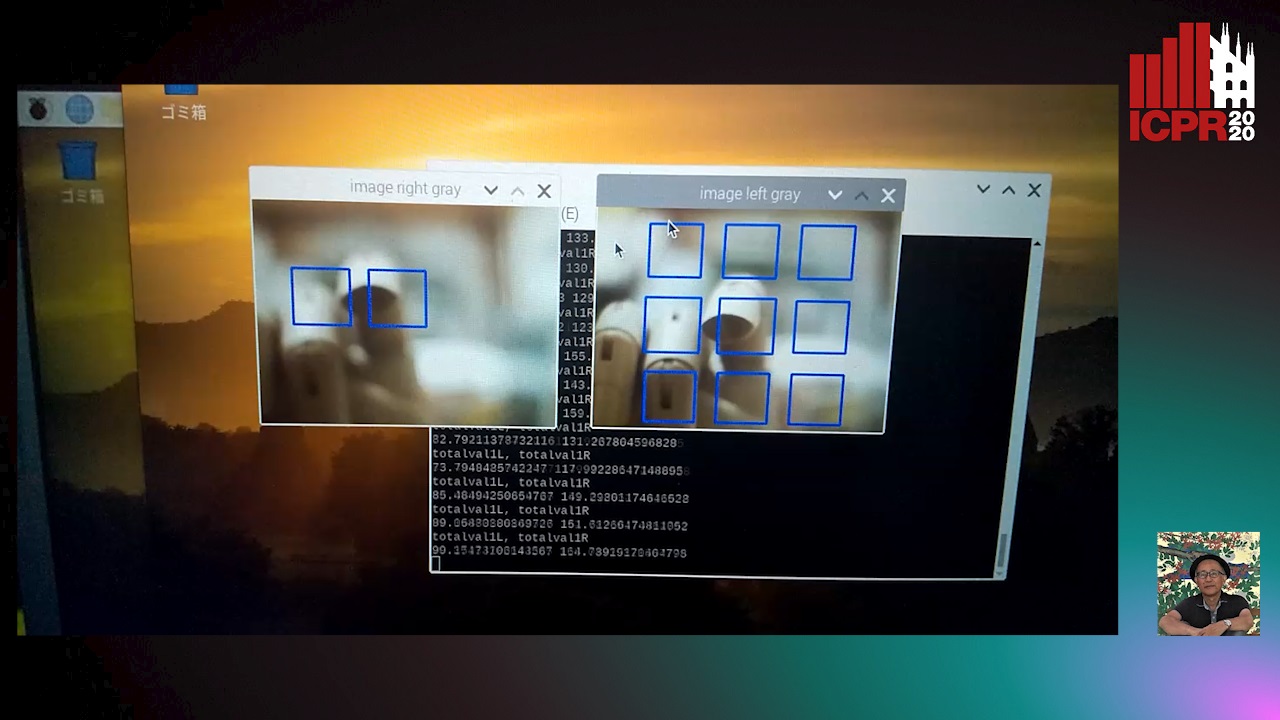
Auto-TLDR; Analysis of defocus information when a finger touching a virtual keyboard by using DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) coefficient without detecting 3D position
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
This paper describes the analysis of defocus information when a finger touching a virtual keyboard by using DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) coefficient without detecting 3D position (especially exact depth value) of thr finger. We use 2 cameras and a half mirror to get the images of the finger with same optical axis. The focal length of the two cameras are slightly different. We can know the finger touching the virtual keyboard when the finger is in the middle of the two focal length from the defocus information, because the position of the virtual keyboard is in the middle of the two focal position where the defocus information of the two cameras are same. Previous work of a virtual keyboard is realized by detecting the feature point of the finger at first. After that the finger position and the depth are checked if they are same to the position and the depth of the keyboard. A problem of the previous virtual keyboard is 3D point of the finger (feature point or edge, small region) should be detected. This is very time consuming. We overcome this problem by comparing the defocus information of the finger in the key area of virtual keyboard on the 2 images captured by the two cameras. In this paper we describe the optical system of the virtual keyboard and the resolution of the depth of the finger. Experimental result make it clear that middle range of the DCT coefficients is effective for detecting the finger. In our system, the finger touch is detected by comparing the DCT coefficients of the 2 images. The minimum distance of the detectable finger is depended on the diameter and the focal length of the lens, the resolution of the image sensor. We formulate this theoretical minimum distance and verify it by experiment. Besides finger, our system can also be generalized to detect other object touching the keyboard or not.