Lokesh Nandanwar
Papers from this author
Chebyshev-Harmonic-Fourier-Moments and Deep CNNs for Detecting Forged Handwriting
Lokesh Nandanwar, Shivakumara Palaiahnakote, Kundu Sayani, Umapada Pal, Tong Lu, Daniel Lopresti

Auto-TLDR; Chebyshev-Harmonic-Fourier-Moments and Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for forged handwriting detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Gradient Difference Based Mass Features for Classification of 2D-3D Natural Scene Text Images
Lokesh Nandanwar, Shivakumara Palaiahnakote, Raghavendra Ramachandra, Tong Lu, Umapada Pal, Daniel Lopresti, Nor Badrul Anuar
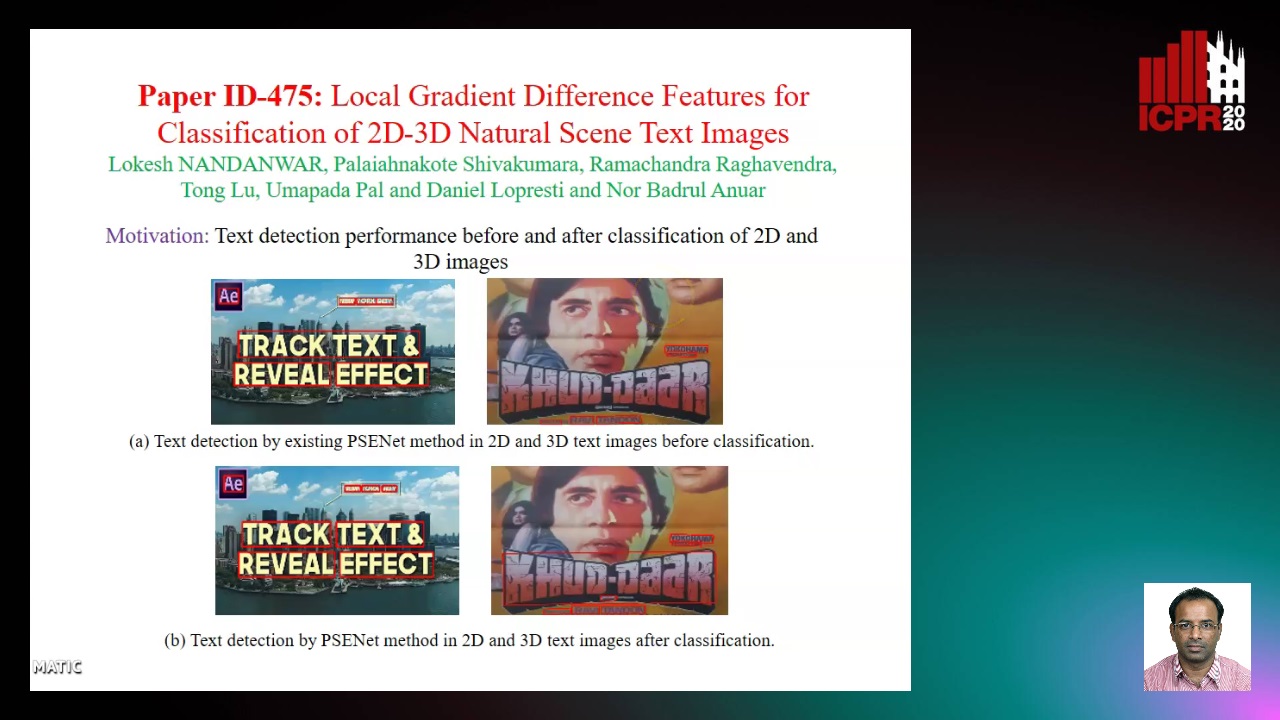
Auto-TLDR; Classification of 2D and 3D Natural Scene Images Using COLD
Abstract Slides Poster Similar