Tong Lu
Papers from this author
Chebyshev-Harmonic-Fourier-Moments and Deep CNNs for Detecting Forged Handwriting
Lokesh Nandanwar, Shivakumara Palaiahnakote, Kundu Sayani, Umapada Pal, Tong Lu, Daniel Lopresti

Auto-TLDR; Chebyshev-Harmonic-Fourier-Moments and Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for forged handwriting detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamic Low-Light Image Enhancement for Object Detection Via End-To-End Training
Haifeng Guo, Yirui Wu, Tong Lu

Auto-TLDR; Object Detection using Low-Light Image Enhancement for End-to-End Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
IFSM: An Iterative Feature Selection Mechanism for Few-Shot Image Classification
Chunhao Cai, Minglei Yuan, Tong Lu

Auto-TLDR; Iterative Feature Selection Mechanism for Few-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Gradient Difference Based Mass Features for Classification of 2D-3D Natural Scene Text Images
Lokesh Nandanwar, Shivakumara Palaiahnakote, Raghavendra Ramachandra, Tong Lu, Umapada Pal, Daniel Lopresti, Nor Badrul Anuar
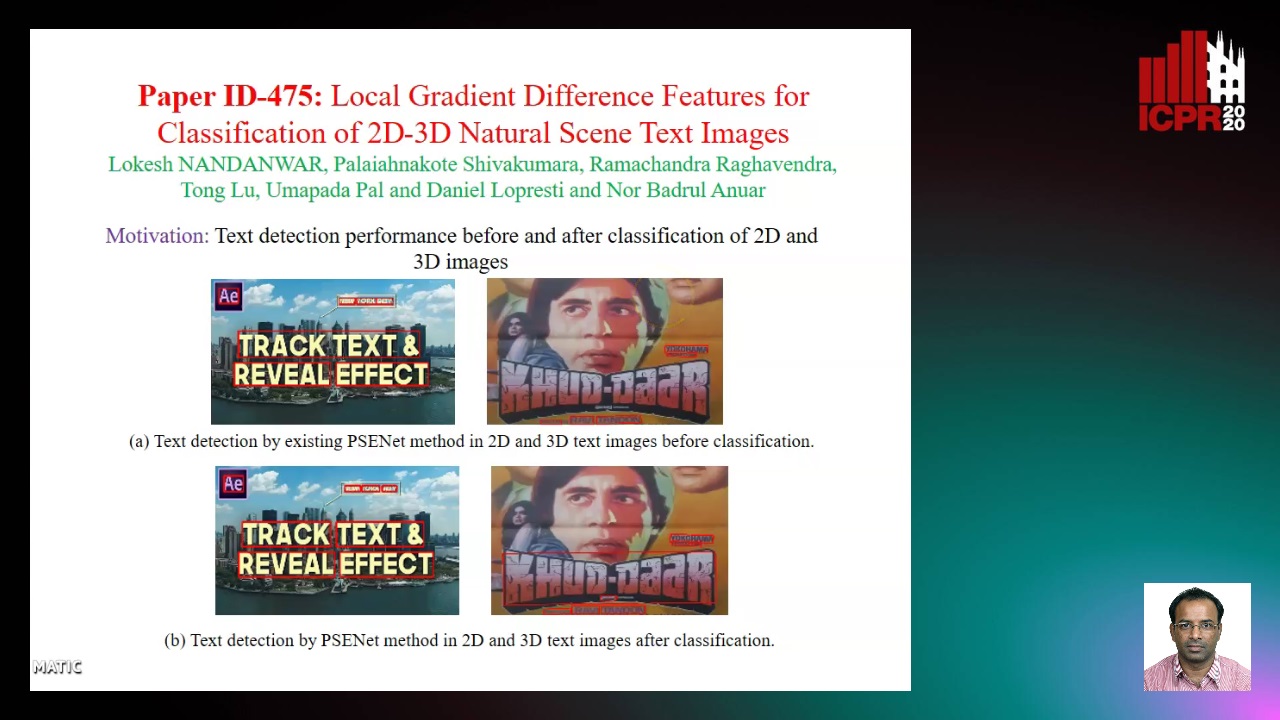
Auto-TLDR; Classification of 2D and 3D Natural Scene Images Using COLD
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Scale Relational Reasoning with Regional Attention for Visual Question Answering

Auto-TLDR; Question-Guided Relational Reasoning for Visual Question Answering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar