Dynamic Low-Light Image Enhancement for Object Detection Via End-To-End Training
Haifeng Guo,
Yirui Wu,
Tong Lu

Auto-TLDR; Object Detection using Low-Light Image Enhancement for End-to-End Training
Similar papers
Automatical Enhancement and Denoising of Extremely Low-Light Images
Yuda Song, Yunfang Zhu, Xin Du

Auto-TLDR; INSNet: Illumination and Noise Separation Network for Low-Light Image Restoring
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Thermal Image Enhancement Using Generative Adversarial Network for Pedestrian Detection
Mohamed Amine Marnissi, Hajer Fradi, Anis Sahbani, Najoua Essoukri Ben Amara
Auto-TLDR; Improving Visual Quality of Infrared Images for Pedestrian Detection Using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Small Object Detection by Generative and Discriminative Learning
Yi Gu, Jie Li, Chentao Wu, Weijia Jia, Jianping Chen

Auto-TLDR; Generative and Discriminative Learning for Small Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MagnifierNet: Learning Efficient Small-Scale Pedestrian Detector towards Multiple Dense Regions
Qi Cheng, Mingqin Chen, Yingjie Wu, Fei Chen, Shiping Lin

Auto-TLDR; MagnifierNet: A Simple but Effective Small-Scale Pedestrian Detection Towards Multiple Dense Regions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Construction Worker Hardhat-Wearing Detection Based on an Improved BiFPN
Chenyang Zhang, Zhiqiang Tian, Jingyi Song, Yaoyue Zheng, Bo Xu

Auto-TLDR; A One-Stage Object Detection Method for Hardhat-Wearing in Construction Site
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SFPN: Semantic Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; SFPN: Semantic Feature Pyramid Network to Address Information Dilution Issue in FPN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Fusion of RGB and NIR Paired Images Using Convolutional Neural Networks

Auto-TLDR; Deep Fusion of RGB and NIR paired images in low light condition using convolutional neural networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Forground-Guided Vehicle Perception Framework
Kun Tian, Tong Zhou, Shiming Xiang, Chunhong Pan

Auto-TLDR; A foreground segmentation branch for vehicle detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning a Dynamic High-Resolution Network for Multi-Scale Pedestrian Detection
Mengyuan Ding, Shanshan Zhang, Jian Yang

Auto-TLDR; Learningable Dynamic HRNet for Pedestrian Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Nighttime Pedestrian Detection Based on Feature Attention and Transformation
Gang Li, Shanshan Zhang, Jian Yang

Auto-TLDR; FAM and FTM: Enhanced Feature Attention Module and Feature Transformation Module for nighttime pedestrian detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Small Object Detection Leveraging on Simultaneous Super-Resolution
Hong Ji, Zhi Gao, Xiaodong Liu, Tiancan Mei

Auto-TLDR; Super-Resolution via Generative Adversarial Network for Small Object Detection
Video Lightening with Dedicated CNN Architecture
Li-Wen Wang, Wan-Chi Siu, Zhi-Song Liu, Chu-Tak Li, P. K. Daniel Lun

Auto-TLDR; VLN: Video Lightening Network for Driving Assistant Systems in Dark Environment
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Remote Sensing Image Attribute Learning for Active Object Detection
Nuo Xu, Chunlei Huo, Chunhong Pan

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Image Attribute Learning for Active Object Detection
A Novel Region of Interest Extraction Layer for Instance Segmentation
Leonardo Rossi, Akbar Karimi, Andrea Prati

Auto-TLDR; Generic RoI Extractor for Two-Stage Neural Network for Instance Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Objects with High Object Region Percentage
Fen Fang, Qianli Xu, Liyuan Li, Ying Gu, Joo-Hwee Lim
Auto-TLDR; Faster R-CNN for High-ORP Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Detection Model Based on Scene-Level Region Proposal Self-Attention
Yu Quan, Zhixin Li, Canlong Zhang, Huifang Ma

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Semantic Informations for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boosting High-Level Vision with Joint Compression Artifacts Reduction and Super-Resolution
Xiaoyu Xiang, Qian Lin, Jan Allebach
Auto-TLDR; A Context-Aware Joint CAR and SR Neural Network for High-Resolution Text Recognition and Face Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
LFIEM: Lightweight Filter-Based Image Enhancement Model
Oktai Tatanov, Aleksei Samarin
Auto-TLDR; Image Retouching Using Semi-supervised Learning for Mobile Devices
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Detection Using Dual Graph Network
Shengjia Chen, Zhixin Li, Feicheng Huang, Canlong Zhang, Huifang Ma

Auto-TLDR; A Graph Convolutional Network for Object Detection with Key Relation Information
Triplet-Path Dilated Network for Detection and Segmentation of General Pathological Images
Jiaqi Luo, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su, Limei Guo

Auto-TLDR; Triplet-path Network for One-Stage Object Detection and Segmentation in Pathological Images
Bidirectional Matrix Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; BMFPN: Bidirectional Matrix Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchically Aggregated Residual Transformation for Single Image Super Resolution

Auto-TLDR; HARTnet: Hierarchically Aggregated Residual Transformation for Multi-Scale Super-resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamic Guided Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Xiaoxia Xing, Yinghao Cai, Yiping Yang, Dayong Wen

Auto-TLDR; DGNet: Dynamic Guidance Upsampling for Self-attention-Decoding for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PRF-Ped: Multi-Scale Pedestrian Detector with Prior-Based Receptive Field
Yuzhi Tan, Hongxun Yao, Haoran Li, Xiusheng Lu, Haozhe Xie

Auto-TLDR; Bidirectional Feature Enhancement Module for Multi-Scale Pedestrian Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient-Receptive Field Block with Group Spatial Attention Mechanism for Object Detection
Jiacheng Zhang, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; E-RFB: Efficient-Receptive Field Block for Deep Neural Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mobile Phone Surface Defect Detection Based on Improved Faster R-CNN
Tao Wang, Can Zhang, Runwei Ding, Ge Yang

Auto-TLDR; Faster R-CNN for Mobile Phone Surface Defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cascade Saliency Attention Network for Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images
Dayang Yu, Rong Zhang, Shan Qin

Auto-TLDR; Cascade Saliency Attention Network for Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DualBox: Generating BBox Pair with Strong Correspondence Via Occlusion Pattern Clustering and Proposal Refinement
Zheng Ge, Chuyu Hu, Xin Huang, Baiqiao Qiu, Osamu Yoshie

Auto-TLDR; R2NMS: Combining Full and Visible Body Bounding Box for Dense Pedestrian Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
EDD-Net: An Efficient Defect Detection Network
Tianyu Guo, Linlin Zhang, Runwei Ding, Ge Yang

Auto-TLDR; EfficientNet: Efficient Network for Mobile Phone Surface defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SyNet: An Ensemble Network for Object Detection in UAV Images
Auto-TLDR; SyNet: Combining Multi-Stage and Single-Stage Object Detection for Aerial Images
Tiny Object Detection in Aerial Images
Jinwang Wang, Wen Yang, Haowen Guo, Ruixiang Zhang, Gui-Song Xia

Auto-TLDR; Tiny Object Detection in Aerial Images Using Multiple Center Points Based Learning Network
ACRM: Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix-NMS for Metallic Surface Defect Detection
Junting Fang, Xiaoyang Tan, Yuhui Wang

Auto-TLDR; Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix Non-Maximum Suppression for Robust Metal Defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Foreground-Focused Domain Adaption for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Unsupervised Object Detection
Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Mucong Ye, Ouyang Jinpeng, Ge Chen, Jing Zhang, Xiaogang Yu
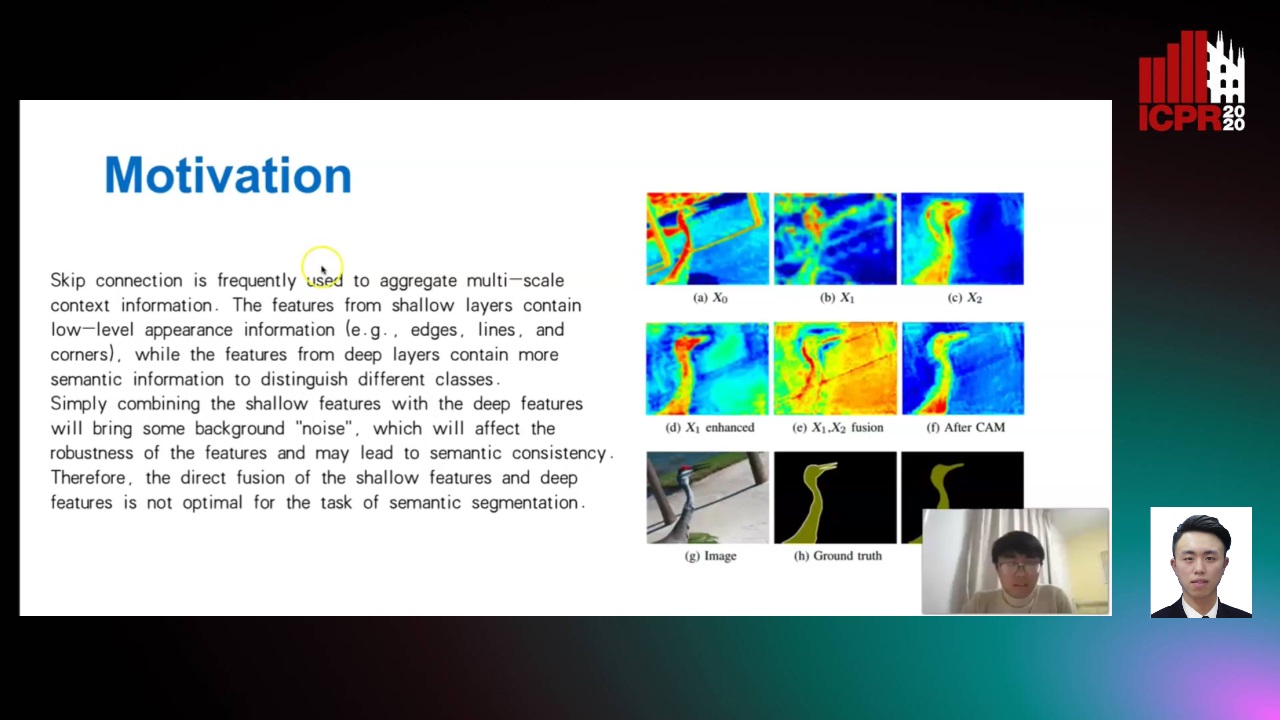
Auto-TLDR; EFPN: Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Scene Text Detection with Selected Anchors
Anna Zhu, Hang Du, Shengwu Xiong

Auto-TLDR; AS-RPN: Anchor Selection-based Region Proposal Network for Scene Text Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mutual-Supervised Feature Modulation Network for Occluded Pedestrian Detection
Auto-TLDR; A Mutual-Supervised Feature Modulation Network for Occluded Pedestrian Detection
Multiple-Step Sampling for Dense Object Detection and Counting

Auto-TLDR; Multiple-Step Sampling for Dense Objects Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Word Embedding Module for Semantic Reasoning in Large-Scale Detection
Yu Zhang, Xiaoyu Wu, Ruolin Zhu
Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Word Embedding Module for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Super-Resolution Guided Pore Detection for Fingerprint Recognition
Syeda Nyma Ferdous, Ali Dabouei, Jeremy Dawson, Nasser M. Nasarabadi

Auto-TLDR; Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network for Fingerprint Recognition Using Pore Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Neural Compression and Filtering for Edge-assisted Real-time Object Detection in Challenged Networks
Yoshitomo Matsubara, Marco Levorato

Auto-TLDR; Deep Neural Networks for Remote Object Detection Using Edge Computing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Image-Based Table Cell Detection: A New Dataset and an Improved Detection Method
Dafeng Wei, Hongtao Lu, Yi Zhou, Kai Chen

Auto-TLDR; TableCell: A Semi-supervised Dataset for Table-wise Detection and Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Modified Single-Shot Multibox Detector for Beyond Real-Time Object Detection
Georgios Orfanidis, Konstantinos Ioannidis, Stefanos Vrochidis, Anastasios Tefas, Ioannis Kompatsiaris

Auto-TLDR; Single Shot Detector in Resource-Restricted Systems with Lighter SSD Variations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hybrid Cascade Point Search Network for High Precision Bar Chart Component Detection
Junyu Luo, Jinpeng Wang, Chin-Yew Lin
Auto-TLDR; Object Detection of Chart Components in Chart Images Using Point-based and Region-Based Object Detection Framework
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Utilising Visual Attention Cues for Vehicle Detection and Tracking
Feiyan Hu, Venkatesh Gurram Munirathnam, Noel E O'Connor, Alan Smeaton, Suzanne Little
Auto-TLDR; Visual Attention for Object Detection and Tracking in Driver-Assistance Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
P2 Net: Augmented Parallel-Pyramid Net for Attention Guided Pose Estimation
Luanxuan Hou, Jie Cao, Yuan Zhao, Haifeng Shen, Jian Tang, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Parallel-Pyramid Net with Partial Attention for Human Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Point In: Counting Trees with Weakly Supervised Segmentation Network
Pinmo Tong, Shuhui Bu, Pengcheng Han
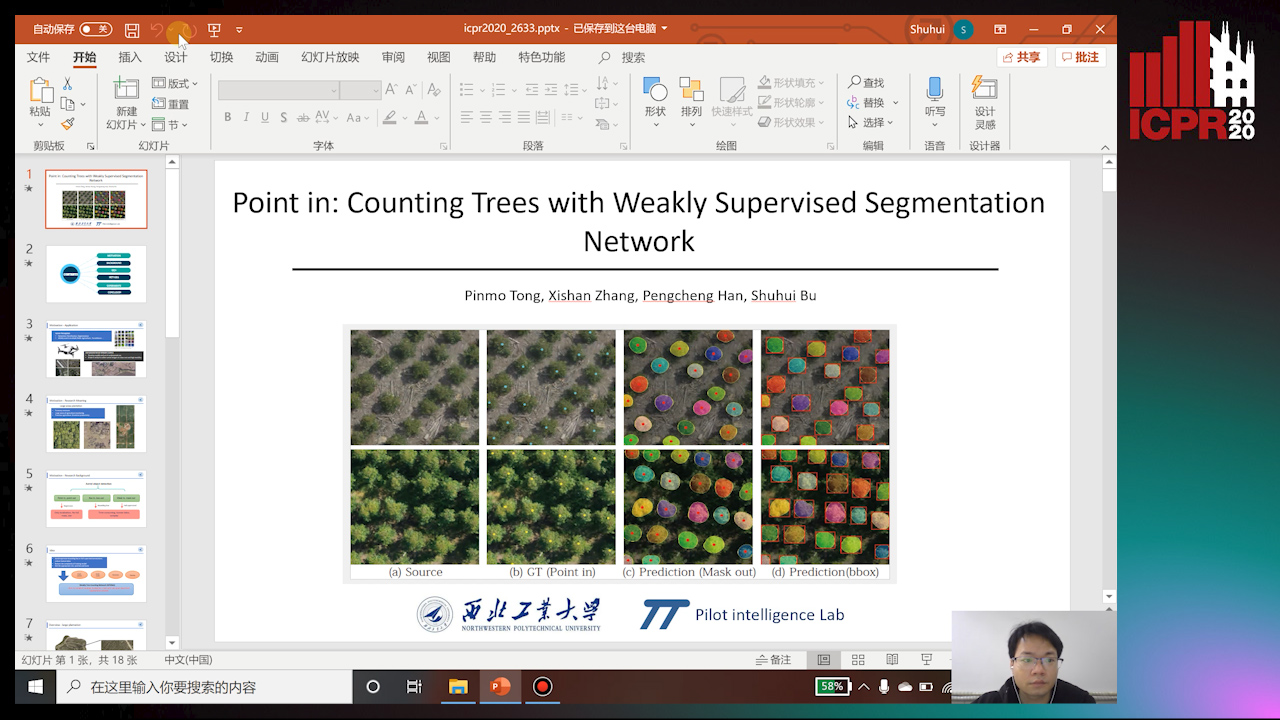
Auto-TLDR; Weakly Tree counting using Deep Segmentation Network with Localization and Mask Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SIDGAN: Single Image Dehazing without Paired Supervision
Pan Wei, Xin Wang, Lei Wang, Ji Xiang, Zihan Wang

Auto-TLDR; DehazeGAN: An End-to-End Generative Adversarial Network for Image Dehazing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PointDrop: Improving Object Detection from Sparse Point Clouds Via Adversarial Data Augmentation
Wenxin Ma, Jian Chen, Qing Du, Wei Jia

Auto-TLDR; PointDrop: Improving Robust 3D Object Detection to Sparse Point Clouds
Abstract Slides Poster Similar