Small Object Detection Leveraging on Simultaneous Super-Resolution
Hong Ji,
Zhi Gao,
Xiaodong Liu,
Tiancan Mei

Auto-TLDR; Super-Resolution via Generative Adversarial Network for Small Object Detection
Similar papers
Small Object Detection by Generative and Discriminative Learning
Yi Gu, Jie Li, Chentao Wu, Weijia Jia, Jianping Chen

Auto-TLDR; Generative and Discriminative Learning for Small Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boosting High-Level Vision with Joint Compression Artifacts Reduction and Super-Resolution
Xiaoyu Xiang, Qian Lin, Jan Allebach
Auto-TLDR; A Context-Aware Joint CAR and SR Neural Network for High-Resolution Text Recognition and Face Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Thermal Image Enhancement Using Generative Adversarial Network for Pedestrian Detection
Mohamed Amine Marnissi, Hajer Fradi, Anis Sahbani, Najoua Essoukri Ben Amara
Auto-TLDR; Improving Visual Quality of Infrared Images for Pedestrian Detection Using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tiny Object Detection in Aerial Images
Jinwang Wang, Wen Yang, Haowen Guo, Ruixiang Zhang, Gui-Song Xia

Auto-TLDR; Tiny Object Detection in Aerial Images Using Multiple Center Points Based Learning Network
Detail Fusion GAN: High-Quality Translation for Unpaired Images with GAN-Based Data Augmentation
Ling Li, Yaochen Li, Chuan Wu, Hang Dong, Peilin Jiang, Fei Wang

Auto-TLDR; Data Augmentation with GAN-based Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Progressive Splitting and Upscaling Structure for Super-Resolution

Auto-TLDR; PSUS: Progressive and Upscaling Layer for Single Image Super-Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Super-Resolution Guided Pore Detection for Fingerprint Recognition
Syeda Nyma Ferdous, Ali Dabouei, Jeremy Dawson, Nasser M. Nasarabadi

Auto-TLDR; Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network for Fingerprint Recognition Using Pore Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Residual Fractal Network for Single Image Super Resolution by Widening and Deepening
Jiahang Gu, Zhaowei Qu, Xiaoru Wang, Jiawang Dan, Junwei Sun
Auto-TLDR; Residual fractal convolutional network for single image super-resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Laplacian GAN with Edge Enhancement for Face Super Resolution
Auto-TLDR; Face Image Super-Resolution with Enhanced Edge Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchically Aggregated Residual Transformation for Single Image Super Resolution

Auto-TLDR; HARTnet: Hierarchically Aggregated Residual Transformation for Multi-Scale Super-resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On-Device Text Image Super Resolution
Dhruval Jain, Arun Prabhu, Gopi Ramena, Manoj Goyal, Debi Mohanty, Naresh Purre, Sukumar Moharana
Auto-TLDR; A Novel Deep Neural Network for Super-Resolution on Low Resolution Text Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
LiNet: A Lightweight Network for Image Super Resolution
Armin Mehri, Parichehr Behjati Ardakani, Angel D. Sappa

Auto-TLDR; LiNet: A Compact Dense Network for Lightweight Super Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamic Low-Light Image Enhancement for Object Detection Via End-To-End Training
Haifeng Guo, Yirui Wu, Tong Lu

Auto-TLDR; Object Detection using Low-Light Image Enhancement for End-to-End Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MagnifierNet: Learning Efficient Small-Scale Pedestrian Detector towards Multiple Dense Regions
Qi Cheng, Mingqin Chen, Yingjie Wu, Fei Chen, Shiping Lin

Auto-TLDR; MagnifierNet: A Simple but Effective Small-Scale Pedestrian Detection Towards Multiple Dense Regions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Objects with High Object Region Percentage
Fen Fang, Qianli Xu, Liyuan Li, Ying Gu, Joo-Hwee Lim
Auto-TLDR; Faster R-CNN for High-ORP Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Modified Single-Shot Multibox Detector for Beyond Real-Time Object Detection
Georgios Orfanidis, Konstantinos Ioannidis, Stefanos Vrochidis, Anastasios Tefas, Ioannis Kompatsiaris

Auto-TLDR; Single Shot Detector in Resource-Restricted Systems with Lighter SSD Variations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Wavelet Attention Embedding Networks for Video Super-Resolution
Young-Ju Choi, Young-Woon Lee, Byung-Gyu Kim

Auto-TLDR; Wavelet Attention Embedding Network for Video Super-Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SFPN: Semantic Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; SFPN: Semantic Feature Pyramid Network to Address Information Dilution Issue in FPN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Low-Resolution Image Classification by Super-Resolution with Enhancing High-Frequency Content
Liguo Zhou, Guang Chen, Mingyue Feng, Alois Knoll

Auto-TLDR; Super-resolution for Low-Resolution Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Robust Pedestrian Detection in Thermal Imagery Using Synthesized Images
My Kieu, Lorenzo Berlincioni, Leonardo Galteri, Marco Bertini, Andrew Bagdanov, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Improving Pedestrian Detection in the thermal domain using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boundary Guided Image Translation for Pose Estimation from Ultra-Low Resolution Thermal Sensor
Kohei Kurihara, Tianren Wang, Teng Zhang, Brian Carrington Lovell
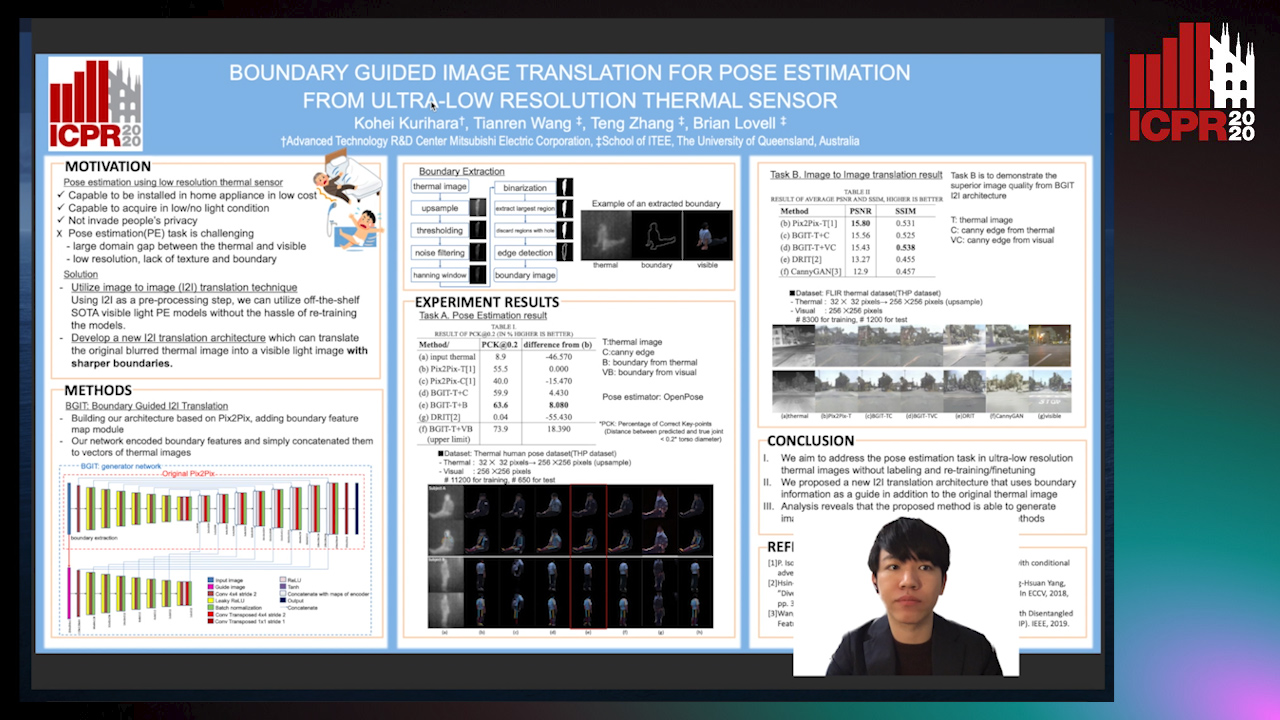
Auto-TLDR; Pose Estimation on Low-Resolution Thermal Images Using Image-to-Image Translation Architecture
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Detection Using Dual Graph Network
Shengjia Chen, Zhixin Li, Feicheng Huang, Canlong Zhang, Huifang Ma

Auto-TLDR; A Graph Convolutional Network for Object Detection with Key Relation Information
SyNet: An Ensemble Network for Object Detection in UAV Images
Auto-TLDR; SyNet: Combining Multi-Stage and Single-Stage Object Detection for Aerial Images
Tarsier: Evolving Noise Injection inSuper-Resolution GANs
Baptiste Roziere, Nathanaël Carraz Rakotonirina, Vlad Hosu, Rasoanaivo Andry, Hanhe Lin, Camille Couprie, Olivier Teytaud

Auto-TLDR; Evolutionary Super-Resolution using Diagonal CMA
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Iterative Residual Convolutional Network for Single Image Super-Resolution
Rao Muhammad Umer, Gian Luca Foresti, Christian Micheloni

Auto-TLDR; ISRResCNet: Deep Iterative Super-Resolution Residual Convolutional Network for Single Image Super-resolution
Efficient Super Resolution by Recursive Aggregation
Zhengxiong Luo Zhengxiong Luo, Yan Huang, Shang Li, Liang Wang, Tieniu Tan

Auto-TLDR; Recursive Aggregation Network for Efficient Deep Super Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ScarfNet: Multi-Scale Features with Deeply Fused and Redistributed Semantics for Enhanced Object Detection
Jin Hyeok Yoo, Dongsuk Kum, Jun Won Choi
Auto-TLDR; Semantic Fusion of Multi-scale Feature Maps for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Bidirectional Matrix Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; BMFPN: Bidirectional Matrix Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single Image Super-Resolution with Dynamic Residual Connection
Karam Park, Jae Woong Soh, Nam Ik Cho

Auto-TLDR; Dynamic Residual Attention Network for Lightweight Single Image Super-Residual Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cascade Saliency Attention Network for Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images
Dayang Yu, Rong Zhang, Shan Qin

Auto-TLDR; Cascade Saliency Attention Network for Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Forground-Guided Vehicle Perception Framework
Kun Tian, Tong Zhou, Shiming Xiang, Chunhong Pan

Auto-TLDR; A foreground segmentation branch for vehicle detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning a Dynamic High-Resolution Network for Multi-Scale Pedestrian Detection
Mengyuan Ding, Shanshan Zhang, Jian Yang

Auto-TLDR; Learningable Dynamic HRNet for Pedestrian Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Novel Region of Interest Extraction Layer for Instance Segmentation
Leonardo Rossi, Akbar Karimi, Andrea Prati

Auto-TLDR; Generic RoI Extractor for Two-Stage Neural Network for Instance Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Face Super-Resolution Network with Incremental Enhancement of Facial Parsing Information
Shuang Liu, Chengyi Xiong, Zhirong Gao

Auto-TLDR; Learning-based Face Super-Resolution with Incremental Boosting Facial Parsing Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RSAN: Residual Subtraction and Attention Network for Single Image Super-Resolution
Shuo Wei, Xin Sun, Haoran Zhao, Junyu Dong

Auto-TLDR; RSAN: Residual subtraction and attention network for super-resolution
Efficient-Receptive Field Block with Group Spatial Attention Mechanism for Object Detection
Jiacheng Zhang, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; E-RFB: Efficient-Receptive Field Block for Deep Neural Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TinyVIRAT: Low-Resolution Video Action Recognition
Ugur Demir, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; TinyVIRAT: A Progressive Generative Approach for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
EAGLE: Large-Scale Vehicle Detection Dataset in Real-World Scenarios Using Aerial Imagery
Seyed Majid Azimi, Reza Bahmanyar, Corentin Henry, Kurz Franz

Auto-TLDR; EAGLE: A Large-Scale Dataset for Multi-class Vehicle Detection with Object Orientation Information in Airborne Imagery
Construction Worker Hardhat-Wearing Detection Based on an Improved BiFPN
Chenyang Zhang, Zhiqiang Tian, Jingyi Song, Yaoyue Zheng, Bo Xu

Auto-TLDR; A One-Stage Object Detection Method for Hardhat-Wearing in Construction Site
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Galaxy Image Translation with Semi-Supervised Noise-Reconstructed Generative Adversarial Networks
Qiufan Lin, Dominique Fouchez, Jérôme Pasquet
Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Image Translation with Generative Adversarial Networks Using Paired and Unpaired Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Foreground-Focused Domain Adaption for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Unsupervised Object Detection
Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks and Fast Adaptive Bi-Dimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition for Style Transfer
Elissavet Batziou, Petros Alvanitopoulos, Konstantinos Ioannidis, Ioannis Patras, Stefanos Vrochidis, Ioannis Kompatsiaris

Auto-TLDR; FABEMD: Fast and Adaptive Bidimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition for Style Transfer on Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Triplet-Path Dilated Network for Detection and Segmentation of General Pathological Images
Jiaqi Luo, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su, Limei Guo

Auto-TLDR; Triplet-path Network for One-Stage Object Detection and Segmentation in Pathological Images
Point In: Counting Trees with Weakly Supervised Segmentation Network
Pinmo Tong, Shuhui Bu, Pengcheng Han
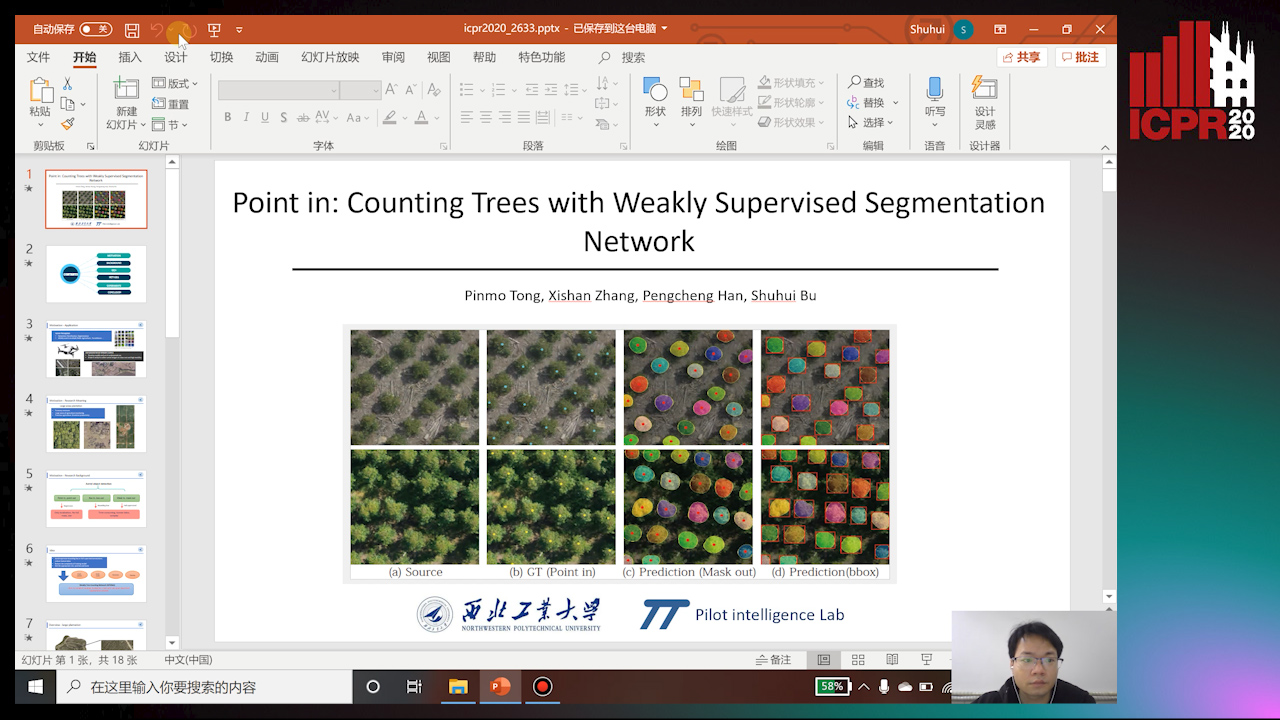
Auto-TLDR; Weakly Tree counting using Deep Segmentation Network with Localization and Mask Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Detection Model Based on Scene-Level Region Proposal Self-Attention
Yu Quan, Zhixin Li, Canlong Zhang, Huifang Ma

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Semantic Informations for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Neural Architecture Search for Image Super-Resolution Using Densely Connected Search Space: DeCoNAS

Auto-TLDR; DeCoNASNet: Automated Neural Architecture Search for Super-Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multiple-Step Sampling for Dense Object Detection and Counting

Auto-TLDR; Multiple-Step Sampling for Dense Objects Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Features and Face Detection Performance: Analyses with 3D-Rendered Synthetic Data
Jian Han, Sezer Karaoglu, Hoang-An Le, Theo Gevers

Auto-TLDR; Synthetic Data for Face Detection Using 3DU Face Dataset
Abstract Slides Poster Similar