Detail Fusion GAN: High-Quality Translation for Unpaired Images with GAN-Based Data Augmentation
Ling Li,
Yaochen Li,
Chuan Wu,
Hang Dong,
Peilin Jiang,
Fei Wang

Auto-TLDR; Data Augmentation with GAN-based Generative Adversarial Network
Similar papers
Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks and Fast Adaptive Bi-Dimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition for Style Transfer
Elissavet Batziou, Petros Alvanitopoulos, Konstantinos Ioannidis, Ioannis Patras, Stefanos Vrochidis, Ioannis Kompatsiaris

Auto-TLDR; FABEMD: Fast and Adaptive Bidimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition for Style Transfer on Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation of Urban Scenes Via Multi-Level Feature Alignment
Bin Zhang, Shengjie Zhao, Rongqing Zhang
Auto-TLDR; Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation Using Generative Adversarial Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Facial Attribute Transfer through Inpainting
Ricard Durall, Franz-Josef Pfreundt, Janis Keuper

Auto-TLDR; Attribute Transfer Inpainting Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boundary Guided Image Translation for Pose Estimation from Ultra-Low Resolution Thermal Sensor
Kohei Kurihara, Tianren Wang, Teng Zhang, Brian Carrington Lovell
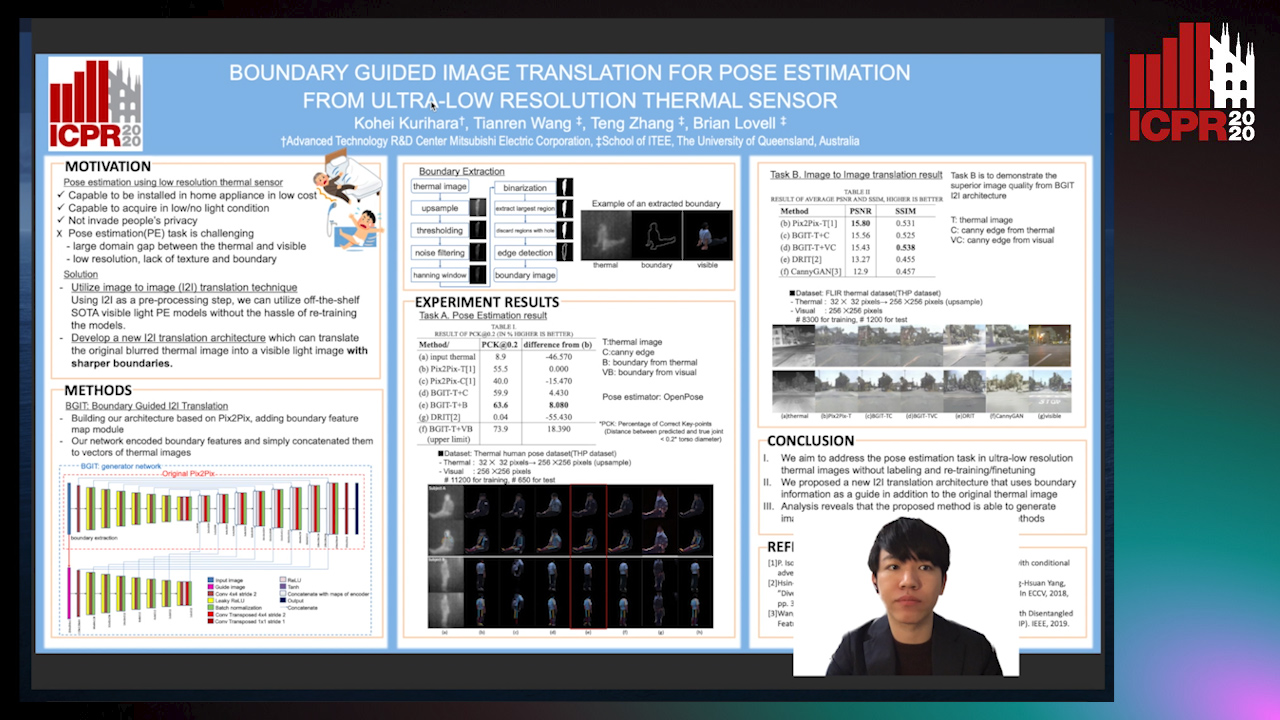
Auto-TLDR; Pose Estimation on Low-Resolution Thermal Images Using Image-to-Image Translation Architecture
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Augmented Cyclic Consistency Regularization for Unpaired Image-To-Image Translation
Takehiko Ohkawa, Naoto Inoue, Hirokatsu Kataoka, Nakamasa Inoue
Auto-TLDR; Augmented Cyclic Consistency Regularization for Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Galaxy Image Translation with Semi-Supervised Noise-Reconstructed Generative Adversarial Networks
Qiufan Lin, Dominique Fouchez, Jérôme Pasquet
Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Image Translation with Generative Adversarial Networks Using Paired and Unpaired Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Small Object Detection Leveraging on Simultaneous Super-Resolution
Hong Ji, Zhi Gao, Xiaodong Liu, Tiancan Mei

Auto-TLDR; Super-Resolution via Generative Adversarial Network for Small Object Detection
Mask-Based Style-Controlled Image Synthesis Using a Mask Style Encoder
Jaehyeong Cho, Wataru Shimoda, Keiji Yanai

Auto-TLDR; Style-controlled Image Synthesis from Semantic Segmentation masks using GANs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Domain Image-To-Image Translation with Adaptive Inference Graph
The Phuc Nguyen, Stéphane Lathuiliere, Elisa Ricci
Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Graph Structure for Multi-Domain Image-to-Image Translation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DAPC: Domain Adaptation People Counting Via Style-Level Transfer Learning and Scene-Aware Estimation
Na Jiang, Xingsen Wen, Zhiping Shi

Auto-TLDR; Domain Adaptation People counting via Style-Level Transfer Learning and Scene-Aware Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose Variation Adaptation for Person Re-Identification
Lei Zhang, Na Jiang, Qishuai Diao, Yue Xu, Zhong Zhou, Wei Wu

Auto-TLDR; Pose Transfer Generative Adversarial Network for Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SIDGAN: Single Image Dehazing without Paired Supervision
Pan Wei, Xin Wang, Lei Wang, Ji Xiang, Zihan Wang

Auto-TLDR; DehazeGAN: An End-to-End Generative Adversarial Network for Image Dehazing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Contrastive Photo-To-Caricature Translation Based on Auto-Distortion
Yuhe Ding, Xin Ma, Mandi Luo, Aihua Zheng, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised contrastive photo-to-caricature translation with style loss
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Stylized-Colorization for Line Arts
Tzu-Ting Fang, Minh Duc Vo, Akihiro Sugimoto, Shang-Hong Lai

Auto-TLDR; Stylized-colorization using GAN-based End-to-End Model for Anime
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Disentangled Representations for Identity Preserving Surveillance Face Camouflage
Jingzhi Li, Lutong Han, Hua Zhang, Xiaoguang Han, Jingguo Ge, Xiaochu Cao

Auto-TLDR; Individual Face Privacy under Surveillance Scenario with Multi-task Loss Function
Towards Artifacts-Free Image Defogging
Gabriele Graffieti, Davide Maltoni

Auto-TLDR; CurL-Defog: Learning Based Defogging with CycleGAN and HArD
Robust Pedestrian Detection in Thermal Imagery Using Synthesized Images
My Kieu, Lorenzo Berlincioni, Leonardo Galteri, Marco Bertini, Andrew Bagdanov, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Improving Pedestrian Detection in the thermal domain using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Multi-Task Domain Adaptation

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Multi-task Learning for Image Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SATGAN: Augmenting Age Biased Dataset for Cross-Age Face Recognition
Wenshuang Liu, Wenting Chen, Yuanlue Zhu, Linlin Shen

Auto-TLDR; SATGAN: Stable Age Translation GAN for Cross-Age Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentional Wavelet Network for Traditional Chinese Painting Transfer
Rui Wang, Huaibo Huang, Aihua Zheng, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Wavelet Network for Photo to Chinese Painting Transfer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Thermal Image Enhancement Using Generative Adversarial Network for Pedestrian Detection
Mohamed Amine Marnissi, Hajer Fradi, Anis Sahbani, Najoua Essoukri Ben Amara
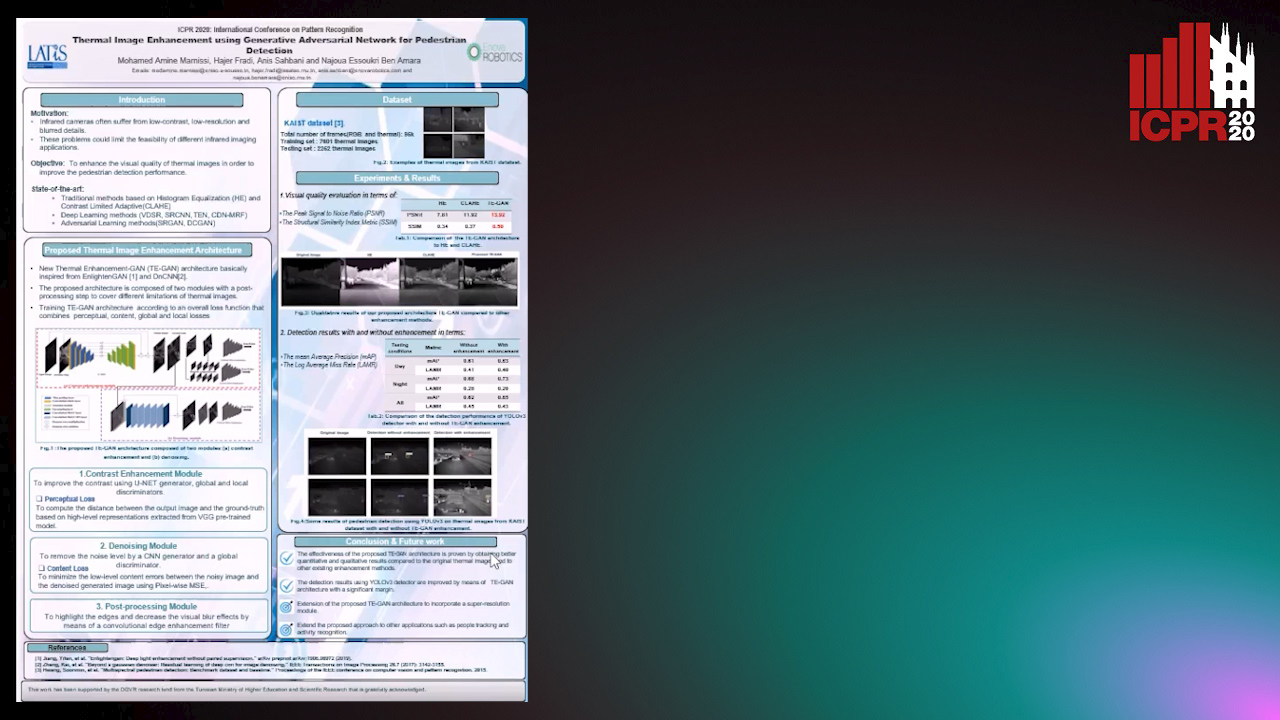
Auto-TLDR; Improving Visual Quality of Infrared Images for Pedestrian Detection Using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Laplacian GAN with Edge Enhancement for Face Super Resolution
Auto-TLDR; Face Image Super-Resolution with Enhanced Edge Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Spatial-Aware GAN for Unsupervised Person Re-Identification
Fangneng Zhan, Changgong Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Person Re-Identification
Cascade Attention Guided Residue Learning GAN for Cross-Modal Translation
Bin Duan, Wei Wang, Hao Tang, Hugo Latapie, Yan Yan

Auto-TLDR; Cascade Attention-Guided Residue GAN for Cross-modal Audio-Visual Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GarmentGAN: Photo-Realistic Adversarial Fashion Transfer
Amir Hossein Raffiee, Michael Sollami

Auto-TLDR; GarmentGAN: A Generative Adversarial Network for Image-Based Garment Transfer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Small Object Detection by Generative and Discriminative Learning
Yi Gu, Jie Li, Chentao Wu, Weijia Jia, Jianping Chen

Auto-TLDR; Generative and Discriminative Learning for Small Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The Role of Cycle Consistency for Generating Better Human Action Videos from a Single Frame

Auto-TLDR; Generating Videos with Human Action Semantics using Cycle Constraints
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Makeup Style Transfer on Low-Quality Images with Weighted Multi-Scale Attention
Daniel Organisciak, Edmond S. L. Ho, Shum Hubert P. H.

Auto-TLDR; Facial Makeup Style Transfer for Low-Resolution Images Using Multi-Scale Spatial Attention
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual-MTGAN: Stochastic and Deterministic Motion Transfer for Image-To-Video Synthesis
Fu-En Yang, Jing-Cheng Chang, Yuan-Hao Lee, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang
Auto-TLDR; Dual Motion Transfer GAN for Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
High Resolution Face Age Editing
Xu Yao, Gilles Puy, Alasdair Newson, Yann Gousseau, Pierre Hellier
Auto-TLDR; An Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Face Age editing on High Resolution Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Data Augmentation Via Mixed Class Interpolation Using Cycle-Consistent Generative Adversarial Networks Applied to Cross-Domain Imagery
Hiroshi Sasaki, Chris G. Willcocks, Toby Breckon
Auto-TLDR; C2GMA: A Generative Domain Transfer Model for Non-visible Domain Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Driving by Transferring Visual Features
Hongli Zhou, Guanwen Zhang, Wei Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Deep Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Driving by Transferring Visual Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient Shadow Detection and Removal Using Synthetic Data with Domain Adaptation
Rui Guo, Babajide Ayinde, Hao Sun
Auto-TLDR; Shadow Detection and Removal with Domain Adaptation and Synthetic Image Database
Learning Low-Shot Generative Networks for Cross-Domain Data
Hsuan-Kai Kao, Cheng-Che Lee, Wei-Chen Chiu
Auto-TLDR; Learning Generators for Cross-Domain Data under Low-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semantic-Guided Inpainting Network for Complex Urban Scenes Manipulation
Pierfrancesco Ardino, Yahui Liu, Elisa Ricci, Bruno Lepri, Marco De Nadai

Auto-TLDR; Semantic-Guided Inpainting of Complex Urban Scene Using Semantic Segmentation and Generation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The Surprising Effectiveness of Linear Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation

Auto-TLDR; linear encoder-decoder architectures for unsupervised image-to-image translation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exemplar Guided Cross-Spectral Face Hallucination Via Mutual Information Disentanglement
Haoxue Wu, Huaibo Huang, Aijing Yu, Jie Cao, Zhen Lei, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Exemplar Guided Cross-Spectral Face Hallucination with Structural Representation Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MBD-GAN: Model-Based Image Deblurring with a Generative Adversarial Network

Auto-TLDR; Model-Based Deblurring GAN for Inverse Imaging
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Controllable Face Aging

Auto-TLDR; A controllable face aging method via attribute disentanglement generative adversarial network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boosting High-Level Vision with Joint Compression Artifacts Reduction and Super-Resolution
Xiaoyu Xiang, Qian Lin, Jan Allebach
Auto-TLDR; A Context-Aware Joint CAR and SR Neural Network for High-Resolution Text Recognition and Face Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Identity-Preserved Face Beauty Transformation with Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks

Auto-TLDR; Identity-preserved face beauty transformation using conditional GANs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
UCCTGAN: Unsupervised Clothing Color Transformation Generative Adversarial Network
Shuming Sun, Xiaoqiang Li, Jide Li

Auto-TLDR; An Unsupervised Clothing Color Transformation Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A GAN-Based Blind Inpainting Method for Masonry Wall Images
Yahya Ibrahim, Balázs Nagy, Csaba Benedek

Auto-TLDR; An End-to-End Blind Inpainting Algorithm for Masonry Wall Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Free-Form Image Inpainting Via Contrastive Attention Network
Xin Ma, Xiaoqiang Zhou, Huaibo Huang, Zhenhua Chai, Xiaolin Wei, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Siamese inference for image inpainting
Image Inpainting with Contrastive Relation Network
Xiaoqiang Zhou, Junjie Li, Zilei Wang, Ran He, Tieniu Tan

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stage Inpainting with Graph-based Relation Network
Detail-Revealing Deep Low-Dose CT Reconstruction
Xinchen Ye, Yuyao Xu, Rui Xu, Shoji Kido, Noriyuki Tomiyama

Auto-TLDR; A Dual-branch Aggregation Network for Low-Dose CT Reconstruction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Progressive Splitting and Upscaling Structure for Super-Resolution

Auto-TLDR; PSUS: Progressive and Upscaling Layer for Single Image Super-Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Multiple Domain Discriminators and Adaptive Self-Training
Teo Spadotto, Marco Toldo, Umberto Michieli, Pietro Zanuttigh

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Scenes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar