Exemplar Guided Cross-Spectral Face Hallucination Via Mutual Information Disentanglement
Haoxue Wu,
Huaibo Huang,
Aijing Yu,
Jie Cao,
Zhen Lei,
Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Exemplar Guided Cross-Spectral Face Hallucination with Structural Representation Learning
Similar papers
Unsupervised Disentangling of Viewpoint and Residues Variations by Substituting Representations for Robust Face Recognition
Minsu Kim, Joanna Hong, Junho Kim, Hong Joo Lee, Yong Man Ro
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Disentangling of Identity, viewpoint, and Residue Representations for Robust Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Disentangled Representations for Identity Preserving Surveillance Face Camouflage
Jingzhi Li, Lutong Han, Hua Zhang, Xiaoguang Han, Jingguo Ge, Xiaochu Cao

Auto-TLDR; Individual Face Privacy under Surveillance Scenario with Multi-task Loss Function
SATGAN: Augmenting Age Biased Dataset for Cross-Age Face Recognition
Wenshuang Liu, Wenting Chen, Yuanlue Zhu, Linlin Shen

Auto-TLDR; SATGAN: Stable Age Translation GAN for Cross-Age Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Contrastive Data Learning for Facial Pose and Illumination Normalization

Auto-TLDR; Pose and Illumination Normalization with Contrast Data Learning for Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Age Gap Reducer-GAN for Recognizing Age-Separated Faces
Daksha Yadav, Naman Kohli, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh, Afzel Noore

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Network for Age-separated Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
High Resolution Face Age Editing
Xu Yao, Gilles Puy, Alasdair Newson, Yann Gousseau, Pierre Hellier
Auto-TLDR; An Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Face Age editing on High Resolution Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Contrastive Photo-To-Caricature Translation Based on Auto-Distortion
Yuhe Ding, Xin Ma, Mandi Luo, Aihua Zheng, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised contrastive photo-to-caricature translation with style loss
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Controllable Face Aging

Auto-TLDR; A controllable face aging method via attribute disentanglement generative adversarial network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-spectrum Face Recognition Using Subspace Projection Hashing
Hanrui Wang, Xingbo Dong, Jin Zhe, Jean-Luc Dugelay, Massimo Tistarelli

Auto-TLDR; Subspace Projection Hashing for Cross-Spectrum Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DAIL: Dataset-Aware and Invariant Learning for Face Recognition
Gaoang Wang, Chen Lin, Tianqiang Liu, Mingwei He, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; DAIL: Dataset-Aware and Invariant Learning for Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boundary Guided Image Translation for Pose Estimation from Ultra-Low Resolution Thermal Sensor
Kohei Kurihara, Tianren Wang, Teng Zhang, Brian Carrington Lovell
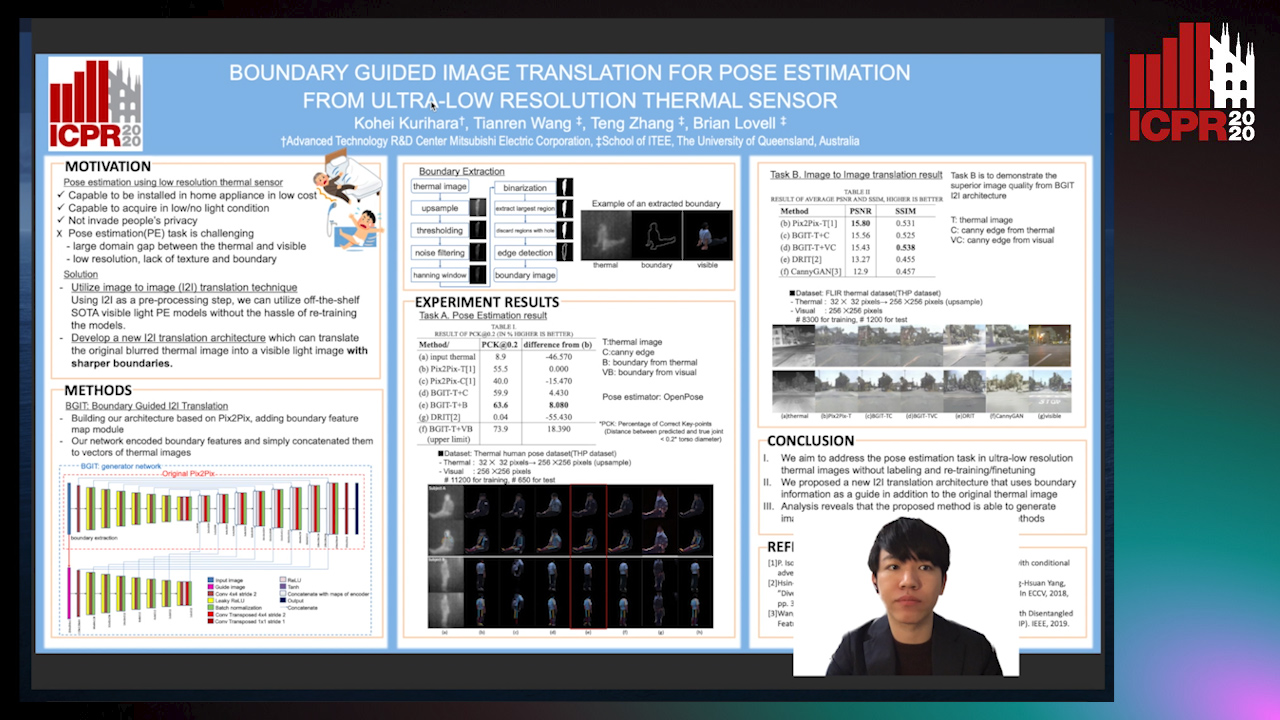
Auto-TLDR; Pose Estimation on Low-Resolution Thermal Images Using Image-to-Image Translation Architecture
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Face Manipulation Via Hallucination
Keerthy Kusumam, Enrique Sanchez, Georgios Tzimiropoulos

Auto-TLDR; Unpaired Face Image Manipulation using Autoencoders
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual-MTGAN: Stochastic and Deterministic Motion Transfer for Image-To-Video Synthesis
Fu-En Yang, Jing-Cheng Chang, Yuan-Hao Lee, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang
Auto-TLDR; Dual Motion Transfer GAN for Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Facial Attribute Transfer through Inpainting
Ricard Durall, Franz-Josef Pfreundt, Janis Keuper

Auto-TLDR; Attribute Transfer Inpainting Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Facial Expression Recognition by Using a Disentangled Identity-Invariant Expression Representation
Auto-TLDR; Transfer-based Expression Recognition Generative Adversarial Network (TER-GAN)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GarmentGAN: Photo-Realistic Adversarial Fashion Transfer
Amir Hossein Raffiee, Michael Sollami

Auto-TLDR; GarmentGAN: A Generative Adversarial Network for Image-Based Garment Transfer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Talking Face Generation Via Learning Semantic and Temporal Synchronous Landmarks
Aihua Zheng, Feixia Zhu, Hao Zhu, Mandi Luo, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; A semantic and temporal synchronous landmark learning method for talking face generation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks and Fast Adaptive Bi-Dimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition for Style Transfer
Elissavet Batziou, Petros Alvanitopoulos, Konstantinos Ioannidis, Ioannis Patras, Stefanos Vrochidis, Ioannis Kompatsiaris

Auto-TLDR; FABEMD: Fast and Adaptive Bidimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition for Style Transfer on Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Let's Play Music: Audio-Driven Performance Video Generation
Hao Zhu, Yi Li, Feixia Zhu, Aihua Zheng, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; APVG: Audio-driven Performance Video Generation Using Structured Temporal UNet
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Multi-Task Learning for Facial Expression Recognition and Synthesis Based on Selective Feature Sharing
Rui Zhao, Tianshan Liu, Jun Xiao, P. K. Daniel Lun, Kin-Man Lam

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Learning for Facial Expression Recognition and Synthesis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Lightweight Low-Resolution Face Recognition for Surveillance Applications
Yoanna Martínez-Díaz, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Luis S. Luevano, Leonardo Chang, Miguel Gonzalez-Mendoza

Auto-TLDR; Efficiency of Lightweight Deep Face Networks on Low-Resolution Surveillance Imagery
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detail Fusion GAN: High-Quality Translation for Unpaired Images with GAN-Based Data Augmentation
Ling Li, Yaochen Li, Chuan Wu, Hang Dong, Peilin Jiang, Fei Wang

Auto-TLDR; Data Augmentation with GAN-based Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local-Global Interactive Network for Face Age Transformation
Jie Song, Ping Wei, Huan Li, Yongchi Zhang, Nanning Zheng

Auto-TLDR; A Novel Local-Global Interaction Framework for Long-span Face Age Transformation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Low-Shot Generative Networks for Cross-Domain Data
Hsuan-Kai Kao, Cheng-Che Lee, Wei-Chen Chiu
Auto-TLDR; Learning Generators for Cross-Domain Data under Low-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Free-Form Image Inpainting Via Contrastive Attention Network
Xin Ma, Xiaoqiang Zhou, Huaibo Huang, Zhenhua Chai, Xiaolin Wei, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Siamese inference for image inpainting
Identity-Preserved Face Beauty Transformation with Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks

Auto-TLDR; Identity-preserved face beauty transformation using conditional GANs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Disentangled Representation Based Face Anti-Spoofing
Zhao Liu, Zunlei Feng, Yong Li, Zeyu Zou, Rong Zhang, Mingli Song, Jianping Shen

Auto-TLDR; Face Anti-Spoofing using Motion Information and Disentangled Frame Work
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RGB-Infrared Person Re-Identification Via Image Modality Conversion
Huangpeng Dai, Qing Xie, Yanchun Ma, Yongjian Liu, Shengwu Xiong

Auto-TLDR; CE2L: A Novel Network for Cross-Modality Re-identification with Feature Alignment
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Identifying Missing Children: Face Age-Progression Via Deep Feature Aging
Debayan Deb, Divyansh Aggarwal, Anil Jain

Auto-TLDR; Aging Face Features for Missing Children Identification
DEN: Disentangling and Exchanging Network for Depth Completion
You-Feng Wu, Vu-Hoang Tran, Ting-Wei Chang, Wei-Chen Chiu, Ching-Chun Huang

Auto-TLDR; Disentangling and Exchanging Network for Depth Completion
Disentangled Representation Learning for Controllable Image Synthesis: An Information-Theoretic Perspective
Shichang Tang, Xu Zhou, Xuming He, Yi Ma
Auto-TLDR; Controllable Image Synthesis in Deep Generative Models using Variational Auto-Encoder
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Attribute Regression Network for Face Reconstruction

Auto-TLDR; A Multi-Attribute Regression Network for Face Reconstruction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose Variation Adaptation for Person Re-Identification
Lei Zhang, Na Jiang, Qishuai Diao, Yue Xu, Zhong Zhou, Wei Wu

Auto-TLDR; Pose Transfer Generative Adversarial Network for Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose-Robust Face Recognition by Deep Meta Capsule Network-Based Equivariant Embedding
Fangyu Wu, Jeremy Simon Smith, Wenjin Lu, Bailing Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Deep Meta Capsule Network-based Equivariant Embedding Model for Pose-Robust Face Recognition
Makeup Style Transfer on Low-Quality Images with Weighted Multi-Scale Attention
Daniel Organisciak, Edmond S. L. Ho, Shum Hubert P. H.

Auto-TLDR; Facial Makeup Style Transfer for Low-Resolution Images Using Multi-Scale Spatial Attention
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mutual Information Based Method for Unsupervised Disentanglement of Video Representation
Aditya Sreekar P, Ujjwal Tiwari, Anoop Namboodiri

Auto-TLDR; MIPAE: Mutual Information Predictive Auto-Encoder for Video Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Reducing the Variance of Variational Estimates of Mutual Information by Limiting the Critic's Hypothesis Space to RKHS
Aditya Sreekar P, Ujjwal Tiwari, Anoop Namboodiri

Auto-TLDR; Mutual Information Estimation from Variational Lower Bounds Using a Critic's Hypothesis Space
Pixel-based Facial Expression Synthesis
Auto-TLDR; pixel-based facial expression synthesis using GANs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Joint Face Alignment and 3D Face Reconstruction with Efficient Convolution Neural Networks
Keqiang Li, Huaiyu Wu, Xiuqin Shang, Zhen Shen, Gang Xiong, Xisong Dong, Bin Hu, Fei-Yue Wang

Auto-TLDR; Mobile-FRNet: Efficient 3D Morphable Model Alignment and 3D Face Reconstruction from a Single 2D Facial Image
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mask-Based Style-Controlled Image Synthesis Using a Mask Style Encoder
Jaehyeong Cho, Wataru Shimoda, Keiji Yanai

Auto-TLDR; Style-controlled Image Synthesis from Semantic Segmentation masks using GANs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hybrid Approach for 3D Head Reconstruction: Using Neural Networks and Visual Geometry
Oussema Bouafif, Bogdan Khomutenko, Mohammed Daoudi
Auto-TLDR; Recovering 3D Head Geometry from a Single Image using Deep Learning and Geometric Techniques
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Coherence and Identity Learning for Arbitrary-Length Face Video Generation
Shuquan Ye, Chu Han, Jiaying Lin, Guoqiang Han, Shengfeng He

Auto-TLDR; Face Video Synthesis Using Identity-Aware GAN and Face Coherence Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cascade Attention Guided Residue Learning GAN for Cross-Modal Translation
Bin Duan, Wei Wang, Hao Tang, Hugo Latapie, Yan Yan

Auto-TLDR; Cascade Attention-Guided Residue GAN for Cross-modal Audio-Visual Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Laplacian GAN with Edge Enhancement for Face Super Resolution
Auto-TLDR; Face Image Super-Resolution with Enhanced Edge Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DFH-GAN: A Deep Face Hashing with Generative Adversarial Network
Bo Xiao, Lanxiang Zhou, Yifei Wang, Qiangfang Xu

Auto-TLDR; Deep Face Hashing with GAN for Face Image Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Galaxy Image Translation with Semi-Supervised Noise-Reconstructed Generative Adversarial Networks
Qiufan Lin, Dominique Fouchez, Jérôme Pasquet
Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Image Translation with Generative Adversarial Networks Using Paired and Unpaired Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Super-Resolution Guided Pore Detection for Fingerprint Recognition
Syeda Nyma Ferdous, Ali Dabouei, Jeremy Dawson, Nasser M. Nasarabadi

Auto-TLDR; Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network for Fingerprint Recognition Using Pore Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Continuous Learning of Face Attribute Synthesis
Ning Xin, Shaohui Xu, Fangzhe Nan, Xiaoli Dong, Weijun Li, Yuanzhou Yao

Auto-TLDR; Continuous Learning for Face Attribute Synthesis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar