Joint Face Alignment and 3D Face Reconstruction with Efficient Convolution Neural Networks
Keqiang Li,
Huaiyu Wu,
Xiuqin Shang,
Zhen Shen,
Gang Xiong,
Xisong Dong,
Bin Hu,
Fei-Yue Wang

Auto-TLDR; Mobile-FRNet: Efficient 3D Morphable Model Alignment and 3D Face Reconstruction from a Single 2D Facial Image
Similar papers
Multi-Attribute Regression Network for Face Reconstruction

Auto-TLDR; A Multi-Attribute Regression Network for Face Reconstruction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hybrid Approach for 3D Head Reconstruction: Using Neural Networks and Visual Geometry
Oussema Bouafif, Bogdan Khomutenko, Mohammed Daoudi
Auto-TLDR; Recovering 3D Head Geometry from a Single Image using Deep Learning and Geometric Techniques
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Semantic Representations Via Joint 3D Face Reconstruction and Facial Attribute Estimation
Zichun Weng, Youjun Xiang, Xianfeng Li, Juntao Liang, Wanliang Huo, Yuli Fu

Auto-TLDR; Joint Framework for 3D Face Reconstruction with Facial Attribute Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Feature Fusion Network for Gaze Tracking in Mobile Tablets
Yiwei Bao, Yihua Cheng, Yunfei Liu, Feng Lu

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Feature Fusion Network for Multi-stream Gaze Estimation in Mobile Tablets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentive Hybrid Feature Based a Two-Step Fusion for Facial Expression Recognition
Jun Weng, Yang Yang, Zichang Tan, Zhen Lei
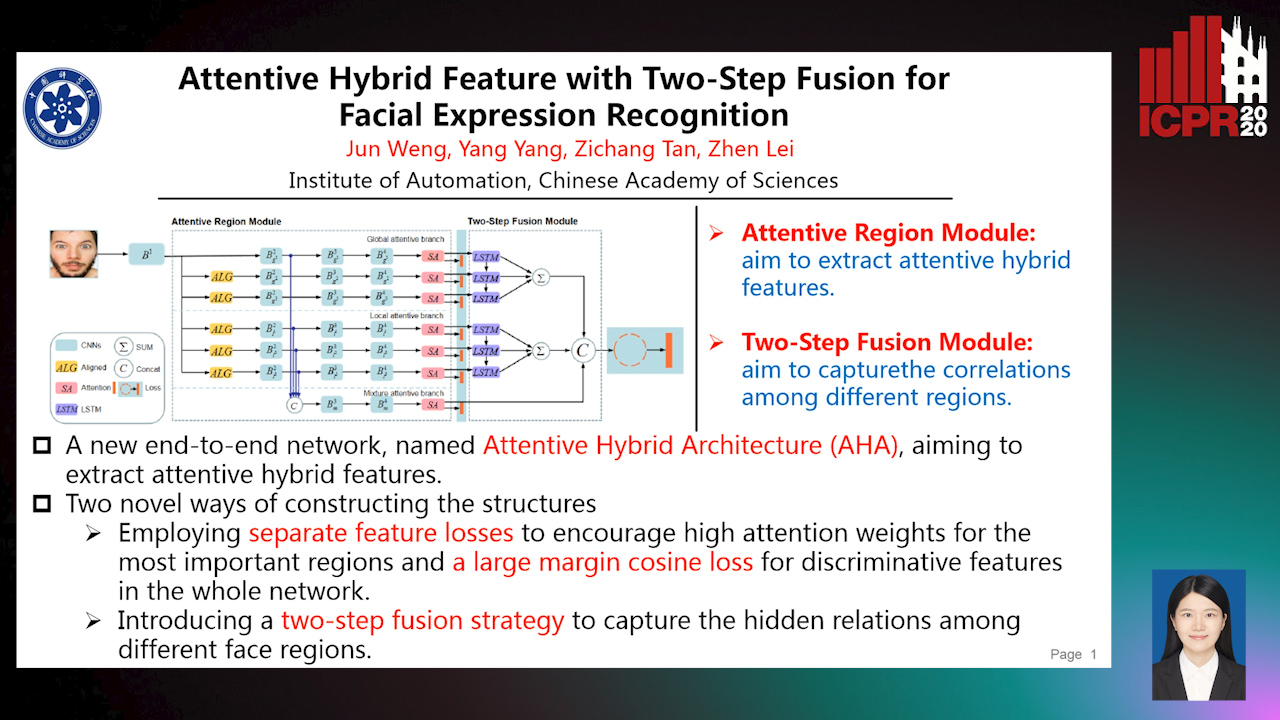
Auto-TLDR; Attentive Hybrid Architecture for Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Face Super-Resolution Network with Incremental Enhancement of Facial Parsing Information
Shuang Liu, Chengyi Xiong, Zhirong Gao

Auto-TLDR; Learning-based Face Super-Resolution with Incremental Boosting Facial Parsing Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Manipulated Facial Videos: A Time Series Solution
Zhang Zhewei, Ma Can, Gao Meilin, Ding Bowen
Auto-TLDR; Face-Alignment Based Bi-LSTM for Fake Video Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient-Receptive Field Block with Group Spatial Attention Mechanism for Object Detection
Jiacheng Zhang, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; E-RFB: Efficient-Receptive Field Block for Deep Neural Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Quality-Based Representation for Unconstrained Face Recognition
Nelson Méndez-Llanes, Katy Castillo-Rosado, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Massimo Tistarelli

Auto-TLDR; activation map for face recognition in unconstrained environments
MRP-Net: A Light Multiple Region Perception Neural Network for Multi-Label AU Detection
Yang Tang, Shuang Chen, Honggang Zhang, Gang Wang, Rui Yang

Auto-TLDR; MRP-Net: A Fast and Light Neural Network for Facial Action Unit Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PEAN: 3D Hand Pose Estimation Adversarial Network
Linhui Sun, Yifan Zhang, Jing Lu, Jian Cheng, Hanqing Lu

Auto-TLDR; PEAN: 3D Hand Pose Estimation with Adversarial Learning Framework
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Facial Expression Recognition Using Residual Masking Network
Luan Pham, Vu Huynh, Tuan Anh Tran

Auto-TLDR; Deep Residual Masking for Automatic Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Two-Stream Temporal Convolutional Network for Dynamic Facial Attractiveness Prediction
Nina Weng, Jiahao Wang, Annan Li, Yunhong Wang

Auto-TLDR; 2S-TCN: A Two-Stream Temporal Convolutional Network for Dynamic Facial Attractiveness Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MixedFusion: 6D Object Pose Estimation from Decoupled RGB-Depth Features
Hangtao Feng, Lu Zhang, Xu Yang, Zhiyong Liu

Auto-TLDR; MixedFusion: Combining Color and Point Clouds for 6D Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
LiNet: A Lightweight Network for Image Super Resolution
Armin Mehri, Parichehr Behjati Ardakani, Angel D. Sappa

Auto-TLDR; LiNet: A Compact Dense Network for Lightweight Super Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Disentangled Representations for Identity Preserving Surveillance Face Camouflage
Jingzhi Li, Lutong Han, Hua Zhang, Xiaoguang Han, Jingguo Ge, Xiaochu Cao

Auto-TLDR; Individual Face Privacy under Surveillance Scenario with Multi-task Loss Function
HP2IFS: Head Pose Estimation Exploiting Partitioned Iterated Function Systems
Carmen Bisogni, Michele Nappi, Chiara Pero, Stefano Ricciardi
Auto-TLDR; PIFS based head pose estimation using fractal coding theory and Partitioned Iterated Function Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Orthographic Projection Linear Regression for Single Image 3D Human Pose Estimation
Yahui Zhang, Shaodi You, Theo Gevers

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Neural Network for 3D Human Pose Estimation from a Single 2D Image in the Wild
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Face Anti-Spoofing Using Spatial Pyramid Pooling
Lei Shi, Zhuo Zhou, Zhenhua Guo

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Pyramid Pooling for Face Anti-Spoofing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boosting High-Level Vision with Joint Compression Artifacts Reduction and Super-Resolution
Xiaoyu Xiang, Qian Lin, Jan Allebach
Auto-TLDR; A Context-Aware Joint CAR and SR Neural Network for High-Resolution Text Recognition and Face Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exemplar Guided Cross-Spectral Face Hallucination Via Mutual Information Disentanglement
Haoxue Wu, Huaibo Huang, Aijing Yu, Jie Cao, Zhen Lei, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Exemplar Guided Cross-Spectral Face Hallucination with Structural Representation Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Talking Face Generation Via Learning Semantic and Temporal Synchronous Landmarks
Aihua Zheng, Feixia Zhu, Hao Zhu, Mandi Luo, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; A semantic and temporal synchronous landmark learning method for talking face generation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Features and Face Detection Performance: Analyses with 3D-Rendered Synthetic Data
Jian Han, Sezer Karaoglu, Hoang-An Le, Theo Gevers

Auto-TLDR; Synthetic Data for Face Detection Using 3DU Face Dataset
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Inner Eye Canthus Localization for Human Body Temperature Screening
Claudio Ferrari, Lorenzo Berlincioni, Marco Bertini, Alberto Del Bimbo
Auto-TLDR; Automatic Localization of the Inner Eye Canthus in Thermal Face Images using 3D Morphable Face Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Two-Level Attention-Based Fusion Learning for RGB-D Face Recognition
Hardik Uppal, Alireza Sepas-Moghaddam, Michael Greenspan, Ali Etemad

Auto-TLDR; Fused RGB-D Facial Recognition using Attention-Aware Feature Fusion
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Semantic Labeling of Photogrammetry Meshes Based on Active Learning
Mengqi Rong, Shuhan Shen, Zhanyi Hu

Auto-TLDR; 3D Semantic Expression of Urban Scenes Based on Active Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Selective Kernel and Motion-Emphasized Loss Based Attention-Guided Network for HDR Imaging of Dynamic Scenes
Yipeng Deng, Qin Liu, Takeshi Ikenaga

Auto-TLDR; SK-AHDRNet: A Deep Network with attention module and motion-emphasized loss function to produce ghost-free HDR images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Free-Form Image Inpainting Via Contrastive Attention Network
Xin Ma, Xiaoqiang Zhou, Huaibo Huang, Zhenhua Chai, Xiaolin Wei, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Siamese inference for image inpainting
Efficient Super Resolution by Recursive Aggregation
Zhengxiong Luo Zhengxiong Luo, Yan Huang, Shang Li, Liang Wang, Tieniu Tan

Auto-TLDR; Recursive Aggregation Network for Efficient Deep Super Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deeply-Fused Attentive Network for Stereo Matching
Zuliu Yang, Xindong Ai, Weida Yang, Yong Zhao, Qifei Dai, Fuchi Li

Auto-TLDR; DF-Net: Deep Learning-based Network for Stereo Matching
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Light3DPose: Real-Time Multi-Person 3D Pose Estimation from Multiple Views
Alessio Elmi, Davide Mazzini, Pietro Tortella

Auto-TLDR; 3D Pose Estimation of Multiple People from a Few calibrated Camera Views using Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real-Time Monocular Depth Estimation with Extremely Light-Weight Neural Network
Mian Jhong Chiu, Wei-Chen Chiu, Hua-Tsung Chen, Jen-Hui Chuang
Auto-TLDR; Real-Time Light-Weight Depth Prediction for Obstacle Avoidance and Environment Sensing with Deep Learning-based CNN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Identity-Aware Facial Expression Recognition in Compressed Video
Xiaofeng Liu, Linghao Jin, Xu Han, Jun Lu, Jonghye Woo, Jane You

Auto-TLDR; Exploring Facial Expression Representation in Compressed Video with Mutual Information Minimization
Multi-Scale Residual Pyramid Attention Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Jing Liu, Xiaona Zhang, Zhaoxin Li, Tianlu Mao
Auto-TLDR; Multi-scale Residual Pyramid Attention Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock Module for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Junhui Yin, Siqing Zhang, Dongliang Chang, Zhanyu Ma, Jun Guo
Auto-TLDR; Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PSDNet: A Balanced Architecture of Accuracy and Parameters for Semantic Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Pyramid Pooling Module with SE1Cblock and D2SUpsample Network (PSDNet)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Aggregating Object Features Based on Attention Weights for Fine-Grained Image Retrieval
Hongli Lin, Yongqi Song, Zixuan Zeng, Weisheng Wang

Auto-TLDR; DSAW: Unsupervised Dual-selection for Fine-Grained Image Retrieval
Deep Space Probing for Point Cloud Analysis
Yirong Yang, Bin Fan, Yongcheng Liu, Hua Lin, Jiyong Zhang, Xin Liu, 蔡鑫宇 蔡鑫宇, Shiming Xiang, Chunhong Pan

Auto-TLDR; SPCNN: Space Probing Convolutional Neural Network for Point Cloud Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Lightweight Low-Resolution Face Recognition for Surveillance Applications
Yoanna Martínez-Díaz, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Luis S. Luevano, Leonardo Chang, Miguel Gonzalez-Mendoza

Auto-TLDR; Efficiency of Lightweight Deep Face Networks on Low-Resolution Surveillance Imagery
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
One-Stage Multi-Task Detector for 3D Cardiac MR Imaging
Weizeng Lu, Xi Jia, Wei Chen, Nicolò Savioli, Antonio De Marvao, Linlin Shen, Declan O'Regan, Jinming Duan

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Learning for Real-Time, simultaneous landmark location and bounding box detection in 3D space
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SATGAN: Augmenting Age Biased Dataset for Cross-Age Face Recognition
Wenshuang Liu, Wenting Chen, Yuanlue Zhu, Linlin Shen

Auto-TLDR; SATGAN: Stable Age Translation GAN for Cross-Age Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Laplacian GAN with Edge Enhancement for Face Super Resolution
Auto-TLDR; Face Image Super-Resolution with Enhanced Edge Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PointSpherical: Deep Shape Context for Point Cloud Learning in Spherical Coordinates
Hua Lin, Bin Fan, Yongcheng Liu, Yirong Yang, Zheng Pan, Jianbo Shi, Chunhong Pan, Huiwen Xie

Auto-TLDR; Spherical Hierarchical Modeling of 3D Point Cloud
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fast and Efficient Neural Network for Light Field Disparity Estimation

Auto-TLDR; Improving Efficient Light Field Disparity Estimation Using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Progressive Scene Segmentation Based on Self-Attention Mechanism
Yunyi Pan, Yuan Gan, Kun Liu, Yan Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stage Semantic Scene Segmentation with Self-Attention
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
NetCalib: A Novel Approach for LiDAR-Camera Auto-Calibration Based on Deep Learning
Shan Wu, Amnir Hadachi, Damien Vivet, Yadu Prabhakar

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Calibration of LiDAR and Cameras using Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Cross Domain Multi-Modal Dataset for Robust Face Anti-Spoofing
Qiaobin Ji, Shugong Xu, Xudong Chen, Shan Cao, Shunqing Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Cross domain multi-modal FAS dataset GREAT-FASD and several evaluation protocols for academic community
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Learning of Landmarks Based on Inter-Intra Subject Consistencies
Weijian Li, Haofu Liao, Shun Miao, Le Lu, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Learning for Facial Landmark Discovery using Inter-subject Landmark consistencies