NetCalib: A Novel Approach for LiDAR-Camera Auto-Calibration Based on Deep Learning
Shan Wu,
Amnir Hadachi,
Damien Vivet,
Yadu Prabhakar

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Calibration of LiDAR and Cameras using Deep Neural Network
Similar papers
Extending Single Beam Lidar to Full Resolution by Fusing with Single Image Depth Estimation
Yawen Lu, Yuxing Wang, Devarth Parikh, Guoyu Lu

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised LIDAR for Low-Cost Depth Estimation
A Two-Step Approach to Lidar-Camera Calibration
Yingna Su, Yaqing Ding, Jian Yang, Hui Kong

Auto-TLDR; Closed-Form Calibration of Lidar-camera System for Ego-motion Estimation and Scene Understanding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RISEdb: A Novel Indoor Localization Dataset
Carlos Sanchez Belenguer, Erik Wolfart, Álvaro Casado Coscollá, Vitor Sequeira

Auto-TLDR; Indoor Localization Using LiDAR SLAM and Smartphones: A Benchmarking Dataset
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
P2D: A Self-Supervised Method for Depth Estimation from Polarimetry
Marc Blanchon, Desire Sidibe, Olivier Morel, Ralph Seulin, Daniel Braun, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; Polarimetric Regularization for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real-Time Monocular Depth Estimation with Extremely Light-Weight Neural Network
Mian Jhong Chiu, Wei-Chen Chiu, Hua-Tsung Chen, Jen-Hui Chuang
Auto-TLDR; Real-Time Light-Weight Depth Prediction for Obstacle Avoidance and Environment Sensing with Deep Learning-based CNN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Calibration and Absolute Pose Estimation of Trinocular Linear Camera Array for Smart City Applications
Martin Ahrnbom, Mikael Nilsson, Håkan Ardö, Kalle Åström, Oksana Yastremska-Kravchenko, Aliaksei Laureshyn

Auto-TLDR; Trinocular Linear Camera Array Calibration for Traffic Surveillance Applications
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Temporal Pulses Driven Spiking Neural Network for Time and Power Efficient Object Recognition in Autonomous Driving
Wei Wang, Shibo Zhou, Jingxi Li, Xiaohua Li, Junsong Yuan, Zhanpeng Jin

Auto-TLDR; Spiking Neural Network for Real-Time Object Recognition on Temporal LiDAR Pulses
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vehicle Lane Merge Visual Benchmark
Auto-TLDR; A Benchmark for Automated Cooperative Maneuvering Using Multi-view Video Streams and Ground Truth Vehicle Description
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Plane-Based Approach for Indoor Point Clouds Registration
Ketty Favre, Muriel Pressigout, Luce Morin, Eric Marchand

Auto-TLDR; A plane-based registration approach for indoor environments based on LiDAR data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Two-Stage Adaptive Object Scene Flow Using Hybrid CNN-CRF Model
Congcong Li, Haoyu Ma, Qingmin Liao

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive object scene flow estimation using a hybrid CNN-CRF model and adaptive iteration
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AV-SLAM: Autonomous Vehicle SLAM with Gravity Direction Initialization
Kaan Yilmaz, Baris Suslu, Sohini Roychowdhury, L. Srikar Muppirisetty

Auto-TLDR; VI-SLAM with AGI: A combination of three SLAM algorithms for autonomous vehicles
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Benchmarking Cameras for OpenVSLAM Indoors
Kevin Chappellet, Guillaume Caron, Fumio Kanehiro, Ken Sakurada, Abderrahmane Kheddar

Auto-TLDR; OpenVSLAM: Benchmarking Camera Types for Visual Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Ghost Target Detection in 3D Radar Data Using Point Cloud Based Deep Neural Network
Mahdi Chamseddine, Jason Rambach, Oliver Wasenmüler, Didier Stricker
Auto-TLDR; Point Based Deep Learning for Ghost Target Detection in 3D Radar Point Clouds
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RefiNet: 3D Human Pose Refinement with Depth Maps
Andrea D'Eusanio, Stefano Pini, Guido Borghi, Roberto Vezzani, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; RefiNet: A Multi-stage Framework for 3D Human Pose Estimation
Human Segmentation with Dynamic LiDAR Data
Tao Zhong, Wonjik Kim, Masayuki Tanaka, Masatoshi Okutomi
Auto-TLDR; Spatiotemporal Neural Network for Human Segmentation with Dynamic Point Clouds
MixedFusion: 6D Object Pose Estimation from Decoupled RGB-Depth Features
Hangtao Feng, Lu Zhang, Xu Yang, Zhiyong Liu

Auto-TLDR; MixedFusion: Combining Color and Point Clouds for 6D Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Partially Supervised Multi-Task Network for Single-View Dietary Assessment
Ya Lu, Thomai Stathopoulou, Stavroula Mougiakakou
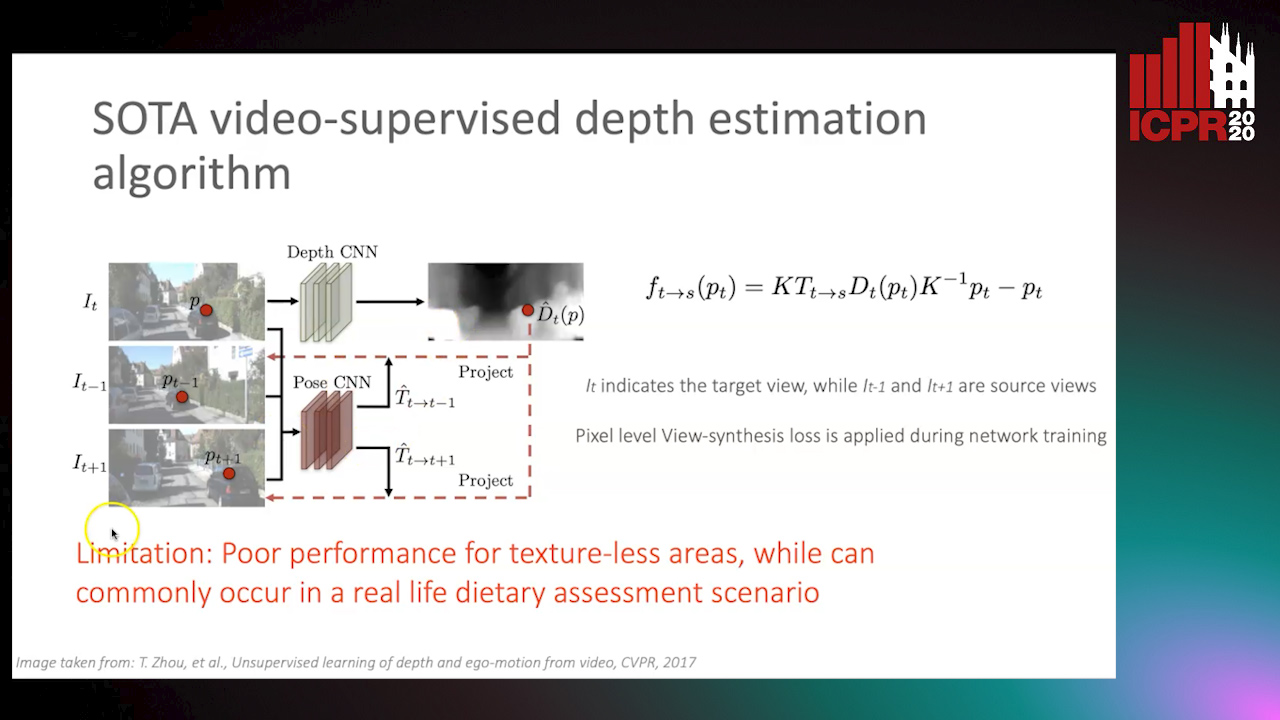
Auto-TLDR; Food Volume Estimation from a Single Food Image via Geometric Understanding and Semantic Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Movement-Induced Priors for Deep Stereo
Yuxin Hou, Muhammad Kamran Janjua, Juho Kannala, Arno Solin

Auto-TLDR; Fusing Stereo Disparity Estimation with Movement-induced Prior Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
HPERL: 3D Human Pose Estimastion from RGB and LiDAR
Michael Fürst, Shriya T.P. Gupta, René Schuster, Oliver Wasenmüler, Didier Stricker
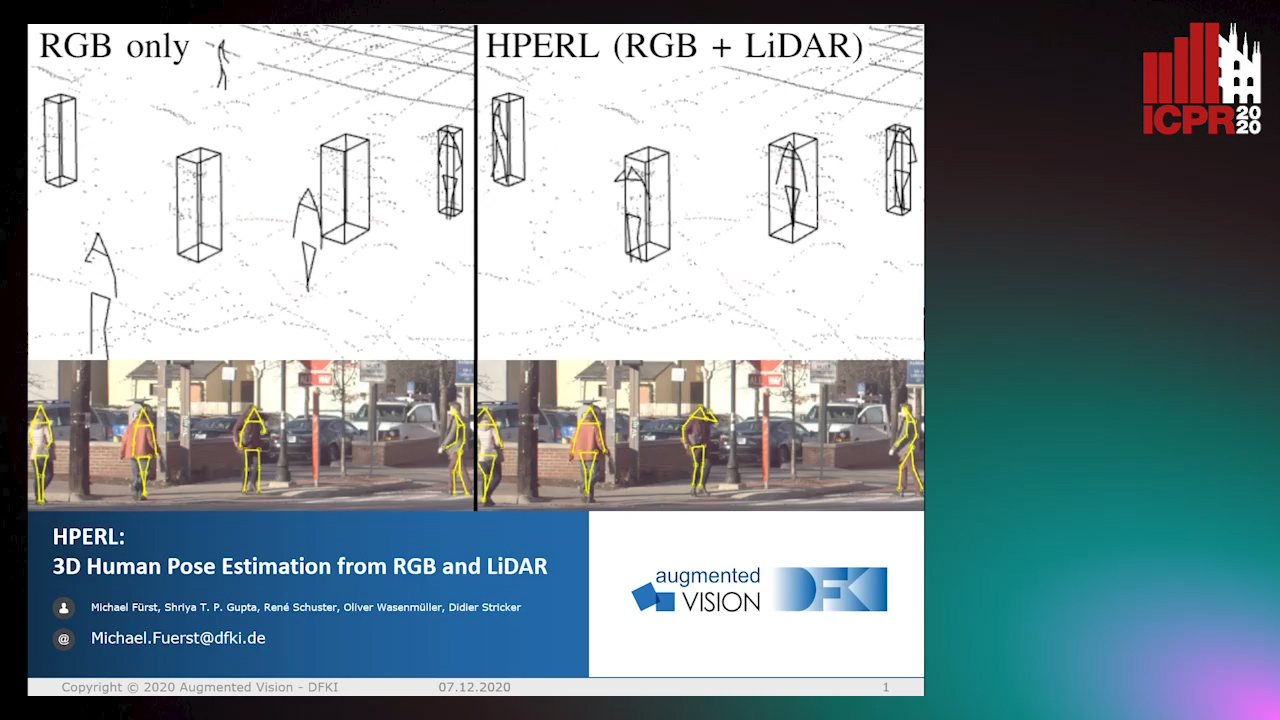
Auto-TLDR; 3D Human Pose Estimation Using RGB and LiDAR Using Weakly-Supervised Approach
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Holistic Grid Fusion Based Stop Line Estimation
Runsheng Xu, Faezeh Tafazzoli, Li Zhang, Timo Rehfeld, Gunther Krehl, Arunava Seal

Auto-TLDR; Fused Multi-Sensory Data for Stop Lines Detection in Intersection Scenarios
Better Prior Knowledge Improves Human-Pose-Based Extrinsic Camera Calibration
Olivier Moliner, Sangxia Huang, Kalle Åström

Auto-TLDR; Improving Human-pose-based Extrinsic Calibration for Multi-Camera Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Non-Rigid Surface Reconstruction from Spatio-Temporal Image Patches
Matteo Pedone, Abdelrahman Mostafa, Janne Heikkilä

Auto-TLDR; Dense Spatio-Temporal Depth Maps of Deformable Objects from Video Sequences
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cost Volume Refinement for Depth Prediction
João L. Cardoso, Nuno Goncalves, Michael Wimmer

Auto-TLDR; Refining the Cost Volume for Depth Prediction from Light Field Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention Based Coupled Framework for Road and Pothole Segmentation
Shaik Masihullah, Ritu Garg, Prerana Mukherjee, Anupama Ray
Auto-TLDR; Few Shot Learning for Road and Pothole Segmentation on KITTI and IDD
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deeply-Fused Attentive Network for Stereo Matching
Zuliu Yang, Xindong Ai, Weida Yang, Yong Zhao, Qifei Dai, Fuchi Li

Auto-TLDR; DF-Net: Deep Learning-based Network for Stereo Matching
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FC-DCNN: A Densely Connected Neural Network for Stereo Estimation
Dominik Hirner, Friedrich Fraundorfer

Auto-TLDR; FC-DCNN: A Lightweight Network for Stereo Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Manual-Label Free 3D Detection Via an Open-Source Simulator
Zhen Yang, Chi Zhang, Zhaoxiang Zhang, Huiming Guo

Auto-TLDR; DA-VoxelNet: A Novel Domain Adaptive VoxelNet for LIDAR-based 3D Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Detection and Pose Estimation of Logistical Objects in 3D Sensor Data
Nikolas Müller, Jonas Stenzel, Jian-Jia Chen

Auto-TLDR; A self-supervised and fully automated deep learning approach for object pose estimation using simulated 3D data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Yolo+FPN: 2D and 3D Fused Object Detection with an RGB-D Camera

Auto-TLDR; Yolo+FPN: Combining 2D and 3D Object Detection for Real-Time Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Sensor-Independent Pedestrian Detection for Personal Mobility Vehicles in Walking Space Using Dataset Generated by Simulation
Takahiro Shimizu, Kenji Koide, Shuji Oishi, Masashi Yokozuka, Atsuhiko Banno, Motoki Shino

Auto-TLDR; CosPointPillars: A 3D Object Detection Method for Pedestrian Detection in Walking Spaces
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CARRADA Dataset: Camera and Automotive Radar with Range-Angle-Doppler Annotations
Arthur Ouaknine, Alasdair Newson, Julien Rebut, Florence Tupin, Patrick Pérez
Auto-TLDR; CARRADA: A dataset of synchronized camera and radar recordings with range-angle-Doppler annotations for autonomous driving
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Efficient 3D Point Cloud Scene Completion Via Novel Depth View Synthesis
Haiyan Wang, Liang Yang, Xuejian Rong, Ying-Li Tian

Auto-TLDR; 3D Point Cloud Completion with Depth View Synthesis and Depth View synthesis
Enhancing Deep Semantic Segmentation of RGB-D Data with Entangled Forests
Matteo Terreran, Elia Bonetto, Stefano Ghidoni

Auto-TLDR; FuseNet: A Lighter Deep Learning Model for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semantic Segmentation for Pedestrian Detection from Motion in Temporal Domain

Auto-TLDR; Motion Profile: Recognizing Pedestrians along with their Motion Directions in a Temporal Way
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multimodal End-To-End Learning for Autonomous Steering in Adverse Road and Weather Conditions
Jyri Sakari Maanpää, Josef Taher, Petri Manninen, Leo Pakola, Iaroslav Melekhov, Juha Hyyppä

Auto-TLDR; End-to-End Learning for Autonomous Steering in Adverse Road and Weather Conditions with Lidar Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Leveraging a Weakly Adversarial Paradigm for Joint Learning of Disparity and Confidence Estimation
Matteo Poggi, Fabio Tosi, Filippo Aleotti, Stefano Mattoccia

Auto-TLDR; Joint Training of Deep-Networks for Outlier Detection from Stereo Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Map-Based Temporally Consistent Geolocalization through Learning Motion Trajectories

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Motion Trajectories for Geolocalization of Object on Topological Map using Recurrent Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Domain Siamese CNNs for Sparse Multispectral Disparity Estimation
David-Alexandre Beaupre, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau

Auto-TLDR; Multispectral Disparity Estimation between Thermal and Visible Images using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Derivation of Geometrically and Semantically Annotated UAV Datasets at Large Scales from 3D City Models
Sidi Wu, Lukas Liebel, Marco Körner
Auto-TLDR; Large-Scale Dataset of Synthetic UAV Imagery for Geometric and Semantic Annotation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Detection on Monocular Images with Two-Dimensional Canonical Correlation Analysis

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Task Object Detection from Monocular Images Using Multimodal RGB and Depth Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Camera Calibration Using Parallel Line Segments

Auto-TLDR; Closed-Form Calibration of Surveillance Cameras using Parallel 3D Line Segment Projections
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multiple Future Prediction Leveraging Synthetic Trajectories
Lorenzo Berlincioni, Federico Becattini, Lorenzo Seidenari, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Synthetic Trajectory Prediction using Markov Chains
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generic Merging of Structure from Motion Maps with a Low Memory Footprint
Gabrielle Flood, David Gillsjö, Patrik Persson, Anders Heyden, Kalle Åström

Auto-TLDR; A Low-Memory Footprint Representation for Robust Map Merge
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Knowledge-Rich Sequential Model for Planar Homography Estimation in Aerial Video

Auto-TLDR; Sequential Estimation of Planar Homographic Transformations over Aerial Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Stereo Matchability in Disparity Regression Networks
Jingyang Zhang, Yao Yao, Zixin Luo, Shiwei Li, Tianwei Shen, Tian Fang, Long Quan

Auto-TLDR; Deep Stereo Matchability for Weakly Matchable Regions
Polarimetric Image Augmentation
Marc Blanchon, Fabrice Meriaudeau, Olivier Morel, Ralph Seulin, Desire Sidibe
Auto-TLDR; Polarimetric Augmentation for Deep Learning in Robotics Applications
Enhancing Depth Quality of Stereo Vision Using Deep Learning-Based Prior Information of the Driving Environment
Weifu Li, Vijay John, Seiichi Mita

Auto-TLDR; A Novel Post-processing Mathematical Framework for Stereo Vision
Abstract Slides Poster Similar