Human Segmentation with Dynamic LiDAR Data
Tao Zhong,
Wonjik Kim,
Masayuki Tanaka,
Masatoshi Okutomi
Auto-TLDR; Spatiotemporal Neural Network for Human Segmentation with Dynamic Point Clouds
Similar papers
PC-Net: A Deep Network for 3D Point Clouds Analysis
Zhuo Chen, Tao Guan, Yawei Luo, Yuesong Wang
Auto-TLDR; PC-Net: A Hierarchical Neural Network for 3D Point Clouds Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Semantic Segmentation Using Deep Multi-View Representation Learning
Akrem Sellami, Salvatore Tabbone

Auto-TLDR; Deep Multi-view Representation Learning for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Ghost Target Detection in 3D Radar Data Using Point Cloud Based Deep Neural Network
Mahdi Chamseddine, Jason Rambach, Oliver Wasenmüler, Didier Stricker
Auto-TLDR; Point Based Deep Learning for Ghost Target Detection in 3D Radar Point Clouds
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Early Wildfire Smoke Detection in Videos
Taanya Gupta, Hengyue Liu, Bir Bhanu

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Spatio-Temporal Video Object Segmentation for Automatic Detection of Smoke in Videos during Forest Fire
Semantic Segmentation for Pedestrian Detection from Motion in Temporal Domain

Auto-TLDR; Motion Profile: Recognizing Pedestrians along with their Motion Directions in a Temporal Way
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Sensor-Independent Pedestrian Detection for Personal Mobility Vehicles in Walking Space Using Dataset Generated by Simulation
Takahiro Shimizu, Kenji Koide, Shuji Oishi, Masashi Yokozuka, Atsuhiko Banno, Motoki Shino

Auto-TLDR; CosPointPillars: A 3D Object Detection Method for Pedestrian Detection in Walking Spaces
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Progressive Scene Segmentation Based on Self-Attention Mechanism
Yunyi Pan, Yuan Gan, Kun Liu, Yan Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stage Semantic Scene Segmentation with Self-Attention
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Segmentation Tracking from Generic Video Cues
Amirhossein Kardoost, Sabine Müller, Joachim Weickert, Margret Keuper
Auto-TLDR; A Light-Weight Variational Framework for Video Object Segmentation in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Residual Learning of Video Frame Interpolation Using Convolutional LSTM
Auto-TLDR; Video Frame Interpolation Using Residual Learning and Convolutional LSTMs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
NetCalib: A Novel Approach for LiDAR-Camera Auto-Calibration Based on Deep Learning
Shan Wu, Amnir Hadachi, Damien Vivet, Yadu Prabhakar

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Calibration of LiDAR and Cameras using Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ACCLVOS: Atrous Convolution with Spatial-Temporal ConvLSTM for Video Object Segmentation
Muzhou Xu, Shan Zong, Chunping Liu, Shengrong Gong, Zhaohui Wang, Yu Xia

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Video Object Segmentation using U-shape Convolution and ConvLSTM
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MixedFusion: 6D Object Pose Estimation from Decoupled RGB-Depth Features
Hangtao Feng, Lu Zhang, Xu Yang, Zhiyong Liu

Auto-TLDR; MixedFusion: Combining Color and Point Clouds for 6D Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-Regional Attention Network for Point Cloud Completion

Auto-TLDR; Learning-based Point Cloud Repair with Graph Convolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PointDrop: Improving Object Detection from Sparse Point Clouds Via Adversarial Data Augmentation
Wenxin Ma, Jian Chen, Qing Du, Wei Jia

Auto-TLDR; PointDrop: Improving Robust 3D Object Detection to Sparse Point Clouds
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MANet: Multimodal Attention Network Based Point-View Fusion for 3D Shape Recognition
Yaxin Zhao, Jichao Jiao, Ning Li
Auto-TLDR; Fusion Network for 3D Shape Recognition based on Multimodal Attention Mechanism
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Revisiting Sequence-To-Sequence Video Object Segmentation with Multi-Task Loss and Skip-Memory
Fatemeh Azimi, Benjamin Bischke, Sebastian Palacio, Federico Raue, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel

Auto-TLDR; Sequence-to-Sequence Learning for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Motion U-Net: Multi-Cue Encoder-Decoder Network for Motion Segmentation
Gani Rahmon, Filiz Bunyak, Kannappan Palaniappan
Auto-TLDR; Motion U-Net: A Deep Learning Framework for Robust Moving Object Detection under Challenging Conditions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Two-Stage Adaptive Object Scene Flow Using Hybrid CNN-CRF Model
Congcong Li, Haoyu Ma, Qingmin Liao

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive object scene flow estimation using a hybrid CNN-CRF model and adaptive iteration
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PointSpherical: Deep Shape Context for Point Cloud Learning in Spherical Coordinates
Hua Lin, Bin Fan, Yongcheng Liu, Yirong Yang, Zheng Pan, Jianbo Shi, Chunhong Pan, Huiwen Xie

Auto-TLDR; Spherical Hierarchical Modeling of 3D Point Cloud
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Object Deformation and Motion Adaption for Semi-Supervised Video Object Segmentation
Xiaoyang Zheng, Xin Tan, Jianming Guo, Lizhuang Ma

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Video Object Segmentation with Mask-propagation-based Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FatNet: A Feature-Attentive Network for 3D Point Cloud Processing
Chaitanya Kaul, Nick Pears, Suresh Manandhar

Auto-TLDR; Feature-Attentive Neural Networks for Point Cloud Classification and Segmentation
Holistic Grid Fusion Based Stop Line Estimation
Runsheng Xu, Faezeh Tafazzoli, Li Zhang, Timo Rehfeld, Gunther Krehl, Arunava Seal

Auto-TLDR; Fused Multi-Sensory Data for Stop Lines Detection in Intersection Scenarios
Real-Time Monocular Depth Estimation with Extremely Light-Weight Neural Network
Mian Jhong Chiu, Wei-Chen Chiu, Hua-Tsung Chen, Jen-Hui Chuang
Auto-TLDR; Real-Time Light-Weight Depth Prediction for Obstacle Avoidance and Environment Sensing with Deep Learning-based CNN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Siamese Dynamic Mask Estimation Network for Fast Video Object Segmentation
Dexiang Hong, Guorong Li, Kai Xu, Li Su, Qingming Huang

Auto-TLDR; Siamese Dynamic Mask Estimation for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CARRADA Dataset: Camera and Automotive Radar with Range-Angle-Doppler Annotations
Arthur Ouaknine, Alasdair Newson, Julien Rebut, Florence Tupin, Patrick Pérez
Auto-TLDR; CARRADA: A dataset of synchronized camera and radar recordings with range-angle-Doppler annotations for autonomous driving
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PS^2-Net: A Locally and Globally Aware Network for Point-Based Semantic Segmentation
Na Zhao, Tat Seng Chua, Gim Hee Lee

Auto-TLDR; PS2-Net: A Local and Globally Aware Deep Learning Framework for Semantic Segmentation on 3D Point Clouds
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Extending Single Beam Lidar to Full Resolution by Fusing with Single Image Depth Estimation
Yawen Lu, Yuxing Wang, Devarth Parikh, Guoyu Lu

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised LIDAR for Low-Cost Depth Estimation
PHNet: Parasite-Host Network for Video Crowd Counting
Shiqiao Meng, Jiajie Li, Weiwei Guo, Jinfeng Jiang, Lai Ye

Auto-TLDR; PHNet: A Parasite-Host Network for Video Crowd Counting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Detection and Pose Estimation of Logistical Objects in 3D Sensor Data
Nikolas Müller, Jonas Stenzel, Jian-Jia Chen

Auto-TLDR; A self-supervised and fully automated deep learning approach for object pose estimation using simulated 3D data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention Based Coupled Framework for Road and Pothole Segmentation
Shaik Masihullah, Ritu Garg, Prerana Mukherjee, Anupama Ray
Auto-TLDR; Few Shot Learning for Road and Pothole Segmentation on KITTI and IDD
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Manual-Label Free 3D Detection Via an Open-Source Simulator
Zhen Yang, Chi Zhang, Zhaoxiang Zhang, Huiming Guo

Auto-TLDR; DA-VoxelNet: A Novel Domain Adaptive VoxelNet for LIDAR-based 3D Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Semantic Labeling of Photogrammetry Meshes Based on Active Learning
Mengqi Rong, Shuhan Shen, Zhanyi Hu

Auto-TLDR; 3D Semantic Expression of Urban Scenes Based on Active Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Space Probing for Point Cloud Analysis
Yirong Yang, Bin Fan, Yongcheng Liu, Hua Lin, Jiyong Zhang, Xin Liu, 蔡鑫宇 蔡鑫宇, Shiming Xiang, Chunhong Pan

Auto-TLDR; SPCNN: Space Probing Convolutional Neural Network for Point Cloud Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Lightweight Network to Learn Optical Flow from Event Data

Auto-TLDR; A lightweight pyramid network with attention mechanism to learn optical flow from events data
MFI: Multi-Range Feature Interchange for Video Action Recognition
Sikai Bai, Qi Wang, Xuelong Li

Auto-TLDR; Multi-range Feature Interchange Network for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Efficient 3D Point Cloud Scene Completion Via Novel Depth View Synthesis
Haiyan Wang, Liang Yang, Xuejian Rong, Ying-Li Tian

Auto-TLDR; 3D Point Cloud Completion with Depth View Synthesis and Depth View synthesis
Temporal Pulses Driven Spiking Neural Network for Time and Power Efficient Object Recognition in Autonomous Driving
Wei Wang, Shibo Zhou, Jingxi Li, Xiaohua Li, Junsong Yuan, Zhanpeng Jin

Auto-TLDR; Spiking Neural Network for Real-Time Object Recognition on Temporal LiDAR Pulses
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Yolo+FPN: 2D and 3D Fused Object Detection with an RGB-D Camera

Auto-TLDR; Yolo+FPN: Combining 2D and 3D Object Detection for Real-Time Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Incorporating Depth Information into Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Yifei Zhang, Desire Sidibe, Olivier Morel, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; RDNet: A Deep Neural Network for Few-shot Segmentation Using Depth Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
S-VoteNet: Deep Hough Voting with Spherical Proposal for 3D Object Detection
Yanxian Chen, Huimin Ma, Xi Li, Xiong Luo

Auto-TLDR; S-VoteNet: 3D Object Detection with Spherical Bounded Box Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Object Detection Using Object's Motion Context and Spatio-Temporal Feature Aggregation
Jaekyum Kim, Junho Koh, Byeongwon Lee, Seungji Yang, Jun Won Choi

Auto-TLDR; Video Object Detection Using Spatio-Temporal Aggregated Features and Gated Attention Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhancing Deep Semantic Segmentation of RGB-D Data with Entangled Forests
Matteo Terreran, Elia Bonetto, Stefano Ghidoni

Auto-TLDR; FuseNet: A Lighter Deep Learning Model for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
What and How? Jointly Forecasting Human Action and Pose
Yanjun Zhu, Yanxia Zhang, Qiong Liu, Andreas Girgensohn

Auto-TLDR; Forecasting Human Actions and Motion Trajectories with Joint Action Classification and Pose Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Movement-Induced Priors for Deep Stereo
Yuxin Hou, Muhammad Kamran Janjua, Juho Kannala, Arno Solin

Auto-TLDR; Fusing Stereo Disparity Estimation with Movement-induced Prior Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
HPERL: 3D Human Pose Estimastion from RGB and LiDAR
Michael Fürst, Shriya T.P. Gupta, René Schuster, Oliver Wasenmüler, Didier Stricker
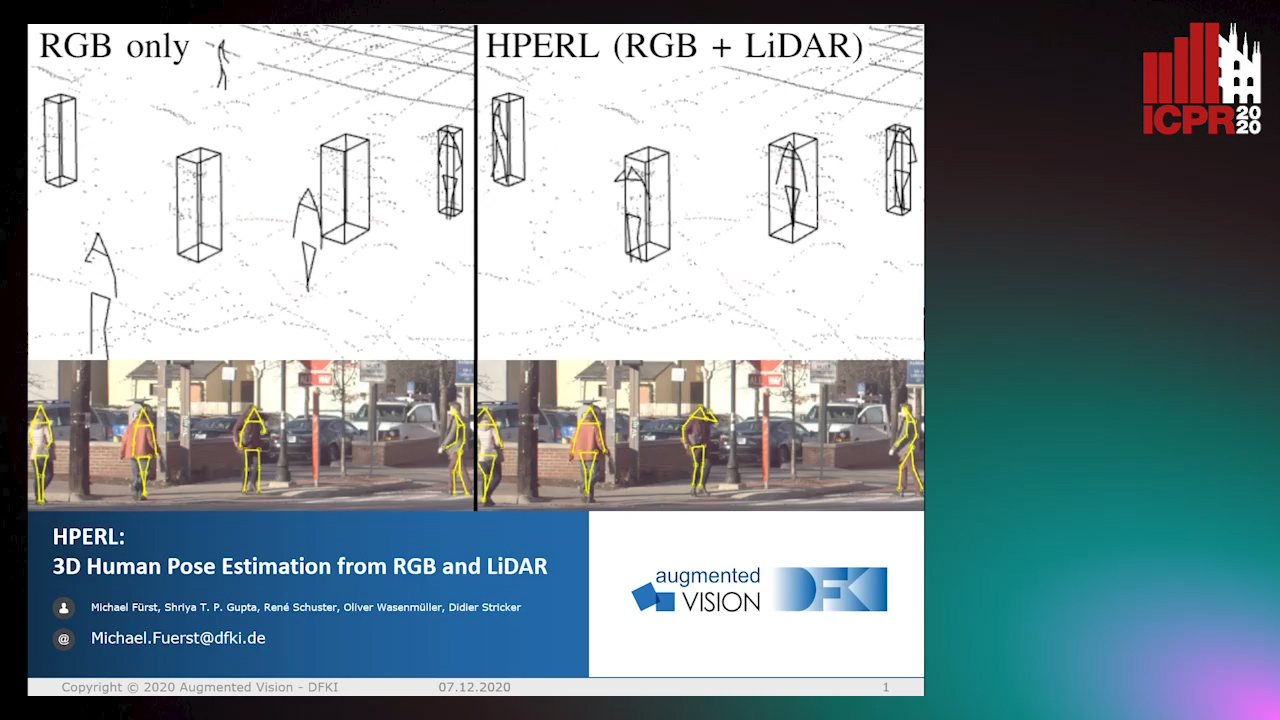
Auto-TLDR; 3D Human Pose Estimation Using RGB and LiDAR Using Weakly-Supervised Approach
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vehicle Classification from Profile Measures
Auto-TLDR; SliceNets: Convolutional Neural Networks for 3D Object Classification of Planar Slices
Delivering Meaningful Representation for Monocular Depth Estimation
Doyeon Kim, Donggyu Joo, Junmo Kim

Auto-TLDR; Monocular Depth Estimation by Bridging the Context between Encoding and Decoding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar