Progressive Scene Segmentation Based on Self-Attention Mechanism
Yunyi Pan,
Yuan Gan,
Kun Liu,
Yan Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stage Semantic Scene Segmentation with Self-Attention
Similar papers
Boundary-Aware Graph Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Hanzhe Hu, Jinshi Cui, Jinshi Hongbin Zha
Auto-TLDR; Boundary-Aware Graph Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Transitional Asymmetric Non-Local Neural Networks for Real-World Dirt Road Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Transitional Asymmetric Non-Local Neural Networks for Semantic Segmentation on Dirt Roads
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Global-Local Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation in Aerial Images
Minglong Li, Lianlei Shan, Weiqiang Wang

Auto-TLDR; GLANet: Global-Local Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PS^2-Net: A Locally and Globally Aware Network for Point-Based Semantic Segmentation
Na Zhao, Tat Seng Chua, Gim Hee Lee

Auto-TLDR; PS2-Net: A Local and Globally Aware Deep Learning Framework for Semantic Segmentation on 3D Point Clouds
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PointSpherical: Deep Shape Context for Point Cloud Learning in Spherical Coordinates
Hua Lin, Bin Fan, Yongcheng Liu, Yirong Yang, Zheng Pan, Jianbo Shi, Chunhong Pan, Huiwen Xie

Auto-TLDR; Spherical Hierarchical Modeling of 3D Point Cloud
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PC-Net: A Deep Network for 3D Point Clouds Analysis
Zhuo Chen, Tao Guan, Yawei Luo, Yuesong Wang
Auto-TLDR; PC-Net: A Hierarchical Neural Network for 3D Point Clouds Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real-Time Semantic Segmentation Via Region and Pixel Context Network
Yajun Li, Yazhou Liu, Quansen Sun
Auto-TLDR; A Dual Context Network for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FatNet: A Feature-Attentive Network for 3D Point Cloud Processing
Chaitanya Kaul, Nick Pears, Suresh Manandhar

Auto-TLDR; Feature-Attentive Neural Networks for Point Cloud Classification and Segmentation
MANet: Multimodal Attention Network Based Point-View Fusion for 3D Shape Recognition
Yaxin Zhao, Jichao Jiao, Ning Li
Auto-TLDR; Fusion Network for 3D Shape Recognition based on Multimodal Attention Mechanism
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Joint Semantic-Instance Segmentation of 3D Point Clouds: Instance Separation and Semantic Fusion

Auto-TLDR; Joint Semantic Segmentation and Instance Separation of 3D Point Clouds
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Space Probing for Point Cloud Analysis
Yirong Yang, Bin Fan, Yongcheng Liu, Hua Lin, Jiyong Zhang, Xin Liu, 蔡鑫宇 蔡鑫宇, Shiming Xiang, Chunhong Pan

Auto-TLDR; SPCNN: Space Probing Convolutional Neural Network for Point Cloud Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PSDNet: A Balanced Architecture of Accuracy and Parameters for Semantic Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Pyramid Pooling Module with SE1Cblock and D2SUpsample Network (PSDNet)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamic Guided Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Xiaoxia Xing, Yinghao Cai, Yiping Yang, Dayong Wen

Auto-TLDR; DGNet: Dynamic Guidance Upsampling for Self-attention-Decoding for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deeply-Fused Attentive Network for Stereo Matching
Zuliu Yang, Xindong Ai, Weida Yang, Yong Zhao, Qifei Dai, Fuchi Li

Auto-TLDR; DF-Net: Deep Learning-based Network for Stereo Matching
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single Image Deblurring Using Bi-Attention Network

Auto-TLDR; Bi-Attention Neural Network for Single Image Deblurring
CT-UNet: An Improved Neural Network Based on U-Net for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images
Huanran Ye, Sheng Liu, Kun Jin, Haohao Cheng
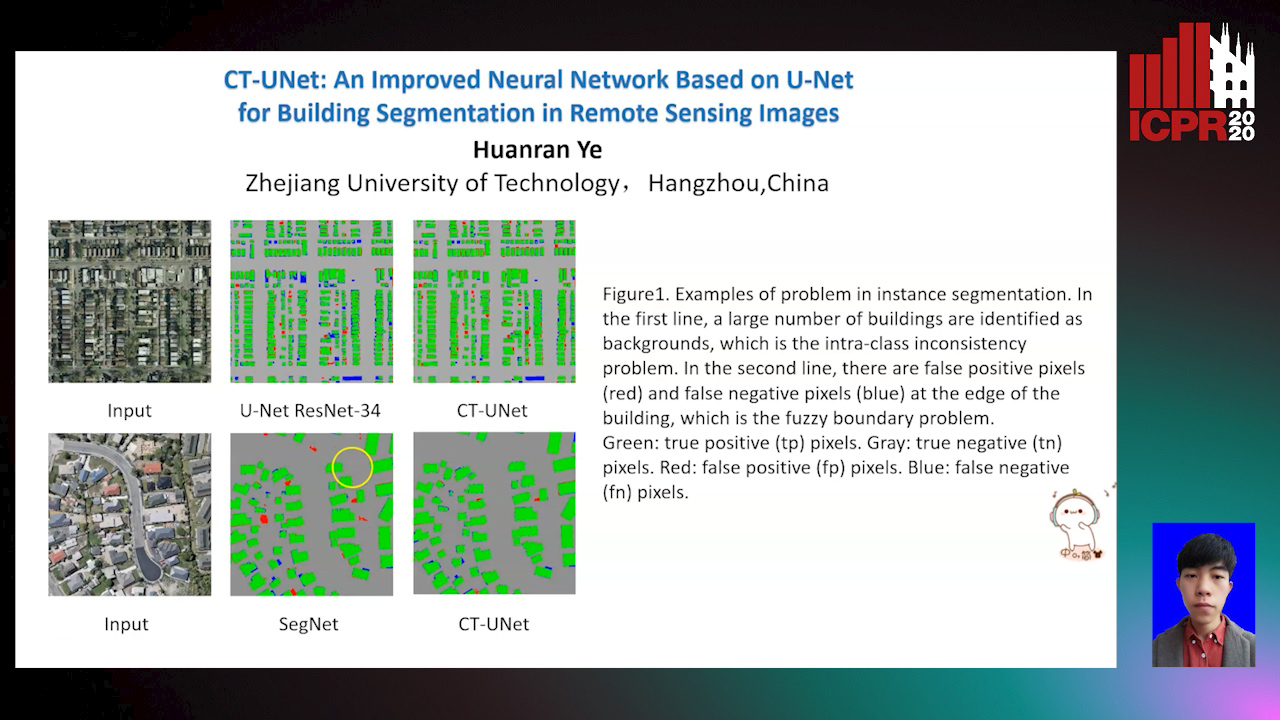
Auto-TLDR; Context-Transfer-UNet: A UNet-based Network for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Mucong Ye, Ouyang Jinpeng, Ge Chen, Jing Zhang, Xiaogang Yu
Auto-TLDR; EFPN: Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Scale Residual Pyramid Attention Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Jing Liu, Xiaona Zhang, Zhaoxin Li, Tianlu Mao
Auto-TLDR; Multi-scale Residual Pyramid Attention Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Do Not Treat Boundaries and Regions Differently: An Example on Heart Left Atrial Segmentation
Zhou Zhao, Elodie Puybareau, Nicolas Boutry, Thierry Geraud
Auto-TLDR; Attention Full Convolutional Network for Atrial Segmentation using ResNet-101 Architecture
Attention Pyramid Module for Scene Recognition
Zhinan Qiao, Xiaohui Yuan, Chengyuan Zhuang, Abolfazl Meyarian

Auto-TLDR; Attention Pyramid Module for Multi-Scale Scene Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Accurate Cell Segmentation in Digital Pathology Images Via Attention Enforced Networks
Zeyi Yao, Kaiqi Li, Guanhong Zhang, Yiwen Luo, Xiaoguang Zhou, Muyi Sun

Auto-TLDR; AENet: Attention Enforced Network for Automatic Cell Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-Regional Attention Network for Point Cloud Completion

Auto-TLDR; Learning-based Point Cloud Repair with Graph Convolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Human Segmentation with Dynamic LiDAR Data
Tao Zhong, Wonjik Kim, Masayuki Tanaka, Masatoshi Okutomi
Auto-TLDR; Spatiotemporal Neural Network for Human Segmentation with Dynamic Point Clouds
Multi-Direction Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Dehui Li, Zhiguo Cao, Ke Xian, Xinyuan Qi, Chao Zhang, Hao Lu

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Direction Convolution for Contextual Segmentation
3D Semantic Labeling of Photogrammetry Meshes Based on Active Learning
Mengqi Rong, Shuhan Shen, Zhanyi Hu

Auto-TLDR; 3D Semantic Expression of Urban Scenes Based on Active Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CSpA-DN: Channel and Spatial Attention Dense Network for Fusing PET and MRI Images
Bicao Li, Zhoufeng Liu, Shan Gao, Jenq-Neng Hwang, Jun Sun, Zongmin Wang

Auto-TLDR; CSpA-DN: Unsupervised Fusion of PET and MR Images with Channel and Spatial Attention
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self and Channel Attention Network for Person Re-Identification
Asad Munir, Niki Martinel, Christian Micheloni

Auto-TLDR; SCAN: Self and Channel Attention Network for Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GSTO: Gated Scale-Transfer Operation for Multi-Scale Feature Learning in Semantic Segmentation
Zhuoying Wang, Yongtao Wang, Zhi Tang, Yangyan Li, Ying Chen, Haibin Ling, Weisi Lin

Auto-TLDR; Gated Scale-Transfer Operation for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Ordinal Depth Classification Using Region-Based Self-Attention
Minh Hieu Phan, Son Lam Phung, Abdesselam Bouzerdoum

Auto-TLDR; Region-based Self-Attention for Multi-scale Depth Estimation from a Single 2D Image
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CAggNet: Crossing Aggregation Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Auto-TLDR; Crossing Aggregation Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient-Receptive Field Block with Group Spatial Attention Mechanism for Object Detection
Jiacheng Zhang, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; E-RFB: Efficient-Receptive Field Block for Deep Neural Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PointDrop: Improving Object Detection from Sparse Point Clouds Via Adversarial Data Augmentation
Wenxin Ma, Jian Chen, Qing Du, Wei Jia

Auto-TLDR; PointDrop: Improving Robust 3D Object Detection to Sparse Point Clouds
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ACRM: Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix-NMS for Metallic Surface Defect Detection
Junting Fang, Xiaoyang Tan, Yuhui Wang

Auto-TLDR; Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix Non-Maximum Suppression for Robust Metal Defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Segmentation of Intracranial Aneurysm Remnant in MRA Using Dual-Attention Atrous Net
Subhashis Banerjee, Ashis Kumar Dhara, Johan Wikström, Robin Strand

Auto-TLDR; Dual-Attention Atrous Net for Segmentation of Intracranial Aneurysm Remnant from MRA Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MixedFusion: 6D Object Pose Estimation from Decoupled RGB-Depth Features
Hangtao Feng, Lu Zhang, Xu Yang, Zhiyong Liu

Auto-TLDR; MixedFusion: Combining Color and Point Clouds for 6D Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhancing Deep Semantic Segmentation of RGB-D Data with Entangled Forests
Matteo Terreran, Elia Bonetto, Stefano Ghidoni

Auto-TLDR; FuseNet: A Lighter Deep Learning Model for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock Module for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Junhui Yin, Siqing Zhang, Dongliang Chang, Zhanyu Ma, Jun Guo
Auto-TLDR; Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DA-RefineNet: Dual-Inputs Attention RefineNet for Whole Slide Image Segmentation
Ziqiang Li, Rentuo Tao, Qianrun Wu, Bin Li

Auto-TLDR; DA-RefineNet: A dual-inputs attention network for whole slide image segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Efficient 3D Point Cloud Scene Completion Via Novel Depth View Synthesis
Haiyan Wang, Liang Yang, Xuejian Rong, Ying-Li Tian

Auto-TLDR; 3D Point Cloud Completion with Depth View Synthesis and Depth View synthesis
MFI: Multi-Range Feature Interchange for Video Action Recognition
Sikai Bai, Qi Wang, Xuelong Li

Auto-TLDR; Multi-range Feature Interchange Network for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Improved Bilinear Pooling Method for Image-Based Action Recognition

Auto-TLDR; An improved bilinear pooling method for image-based action recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Joint Supervised and Self-Supervised Learning for 3D Real World Challenges
Antonio Alliegro, Davide Boscaini, Tatiana Tommasi

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervision for 3D Shape Classification and Segmentation in Point Clouds
Global Context-Based Network with Transformer for Image2latex
Nuo Pang, Chun Yang, Xiaobin Zhu, Jixuan Li, Xu-Cheng Yin

Auto-TLDR; Image2latex with Global Context block and Transformer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-Layer Information Refining Network for Single Image Super-Resolution
Hongyi Zhang, Wen Lu, Xiaopeng Sun

Auto-TLDR; Interlaced Spatial Attention Block for Single Image Super-Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Free-Form Image Inpainting Via Contrastive Attention Network
Xin Ma, Xiaoqiang Zhou, Huaibo Huang, Zhenhua Chai, Xiaolin Wei, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Siamese inference for image inpainting
Directional Graph Networks with Hard Weight Assignments
Miguel Dominguez, Raymond Ptucha

Auto-TLDR; Hard Directional Graph Networks for Point Cloud Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fast and Accurate Real-Time Semantic Segmentation with Dilated Asymmetric Convolutions
Leonel Rosas-Arias, Gibran Benitez-Garcia, Jose Portillo-Portillo, Gabriel Sanchez-Perez, Keiji Yanai
Auto-TLDR; FASSD-Net: Dilated Asymmetric Pyramidal Fusion for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhanced Vote Network for 3D Object Detection in Point Clouds

Auto-TLDR; A Vote Feature Enhancement Network for 3D Bounding Box Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar