Enhanced Vote Network for 3D Object Detection in Point Clouds

Auto-TLDR; A Vote Feature Enhancement Network for 3D Bounding Box Prediction
Similar papers
S-VoteNet: Deep Hough Voting with Spherical Proposal for 3D Object Detection
Yanxian Chen, Huimin Ma, Xi Li, Xiong Luo

Auto-TLDR; S-VoteNet: 3D Object Detection with Spherical Bounded Box Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Joint Semantic-Instance Segmentation of 3D Point Clouds: Instance Separation and Semantic Fusion

Auto-TLDR; Joint Semantic Segmentation and Instance Separation of 3D Point Clouds
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Yolo+FPN: 2D and 3D Fused Object Detection with an RGB-D Camera

Auto-TLDR; Yolo+FPN: Combining 2D and 3D Object Detection for Real-Time Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PointDrop: Improving Object Detection from Sparse Point Clouds Via Adversarial Data Augmentation
Wenxin Ma, Jian Chen, Qing Du, Wei Jia

Auto-TLDR; PointDrop: Improving Robust 3D Object Detection to Sparse Point Clouds
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MixedFusion: 6D Object Pose Estimation from Decoupled RGB-Depth Features
Hangtao Feng, Lu Zhang, Xu Yang, Zhiyong Liu

Auto-TLDR; MixedFusion: Combining Color and Point Clouds for 6D Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PS^2-Net: A Locally and Globally Aware Network for Point-Based Semantic Segmentation
Na Zhao, Tat Seng Chua, Gim Hee Lee

Auto-TLDR; PS2-Net: A Local and Globally Aware Deep Learning Framework for Semantic Segmentation on 3D Point Clouds
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CASNet: Common Attribute Support Network for Image Instance and Panoptic Segmentation
Xiaolong Liu, Yuqing Hou, Anbang Yao, Yurong Chen, Keqiang Li

Auto-TLDR; Common Attribute Support Network for instance segmentation and panoptic segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PointSpherical: Deep Shape Context for Point Cloud Learning in Spherical Coordinates
Hua Lin, Bin Fan, Yongcheng Liu, Yirong Yang, Zheng Pan, Jianbo Shi, Chunhong Pan, Huiwen Xie

Auto-TLDR; Spherical Hierarchical Modeling of 3D Point Cloud
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PC-Net: A Deep Network for 3D Point Clouds Analysis
Zhuo Chen, Tao Guan, Yawei Luo, Yuesong Wang
Auto-TLDR; PC-Net: A Hierarchical Neural Network for 3D Point Clouds Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
HPERL: 3D Human Pose Estimastion from RGB and LiDAR
Michael Fürst, Shriya T.P. Gupta, René Schuster, Oliver Wasenmüler, Didier Stricker
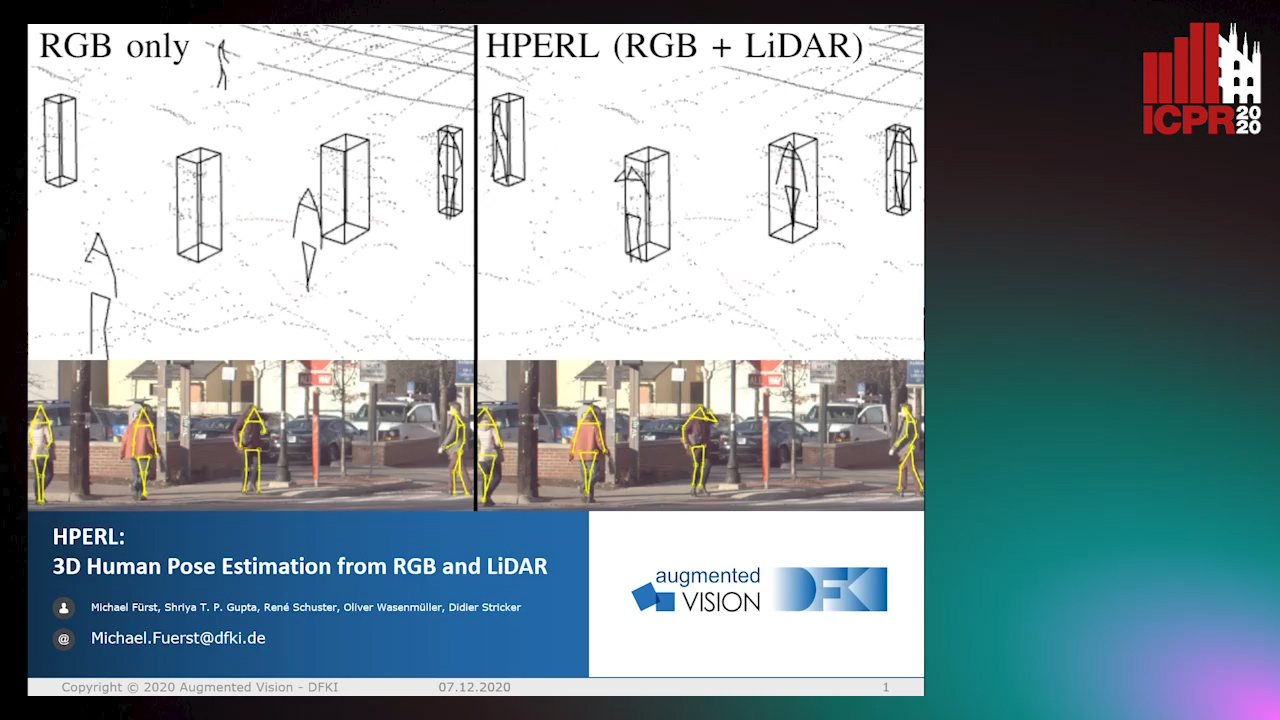
Auto-TLDR; 3D Human Pose Estimation Using RGB and LiDAR Using Weakly-Supervised Approach
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FatNet: A Feature-Attentive Network for 3D Point Cloud Processing
Chaitanya Kaul, Nick Pears, Suresh Manandhar

Auto-TLDR; Feature-Attentive Neural Networks for Point Cloud Classification and Segmentation
Cross-Regional Attention Network for Point Cloud Completion

Auto-TLDR; Learning-based Point Cloud Repair with Graph Convolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Sensor-Independent Pedestrian Detection for Personal Mobility Vehicles in Walking Space Using Dataset Generated by Simulation
Takahiro Shimizu, Kenji Koide, Shuji Oishi, Masashi Yokozuka, Atsuhiko Banno, Motoki Shino

Auto-TLDR; CosPointPillars: A 3D Object Detection Method for Pedestrian Detection in Walking Spaces
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Objects with High Object Region Percentage
Fen Fang, Qianli Xu, Liyuan Li, Ying Gu, Joo-Hwee Lim
Auto-TLDR; Faster R-CNN for High-ORP Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Space Probing for Point Cloud Analysis
Yirong Yang, Bin Fan, Yongcheng Liu, Hua Lin, Jiyong Zhang, Xin Liu, 蔡鑫宇 蔡鑫宇, Shiming Xiang, Chunhong Pan

Auto-TLDR; SPCNN: Space Probing Convolutional Neural Network for Point Cloud Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Scale Residual Pyramid Attention Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Jing Liu, Xiaona Zhang, Zhaoxin Li, Tianlu Mao
Auto-TLDR; Multi-scale Residual Pyramid Attention Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Scene Text Detection with Selected Anchors
Anna Zhu, Hang Du, Shengwu Xiong

Auto-TLDR; AS-RPN: Anchor Selection-based Region Proposal Network for Scene Text Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Detection Using Dual Graph Network
Shengjia Chen, Zhixin Li, Feicheng Huang, Canlong Zhang, Huifang Ma

Auto-TLDR; A Graph Convolutional Network for Object Detection with Key Relation Information
Progressive Scene Segmentation Based on Self-Attention Mechanism
Yunyi Pan, Yuan Gan, Kun Liu, Yan Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stage Semantic Scene Segmentation with Self-Attention
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Detection Model Based on Scene-Level Region Proposal Self-Attention
Yu Quan, Zhixin Li, Canlong Zhang, Huifang Ma

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Semantic Informations for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Forground-Guided Vehicle Perception Framework
Kun Tian, Tong Zhou, Shiming Xiang, Chunhong Pan

Auto-TLDR; A foreground segmentation branch for vehicle detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Nighttime Pedestrian Detection Based on Feature Attention and Transformation
Gang Li, Shanshan Zhang, Jian Yang

Auto-TLDR; FAM and FTM: Enhanced Feature Attention Module and Feature Transformation Module for nighttime pedestrian detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SFPN: Semantic Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; SFPN: Semantic Feature Pyramid Network to Address Information Dilution Issue in FPN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Efficient 3D Point Cloud Scene Completion Via Novel Depth View Synthesis
Haiyan Wang, Liang Yang, Xuejian Rong, Ying-Li Tian

Auto-TLDR; 3D Point Cloud Completion with Depth View Synthesis and Depth View synthesis
Object Detection on Monocular Images with Two-Dimensional Canonical Correlation Analysis

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Task Object Detection from Monocular Images Using Multimodal RGB and Depth Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Construction Worker Hardhat-Wearing Detection Based on an Improved BiFPN
Chenyang Zhang, Zhiqiang Tian, Jingyi Song, Yaoyue Zheng, Bo Xu

Auto-TLDR; A One-Stage Object Detection Method for Hardhat-Wearing in Construction Site
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Detection and Pose Estimation of Logistical Objects in 3D Sensor Data
Nikolas Müller, Jonas Stenzel, Jian-Jia Chen

Auto-TLDR; A self-supervised and fully automated deep learning approach for object pose estimation using simulated 3D data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PRF-Ped: Multi-Scale Pedestrian Detector with Prior-Based Receptive Field
Yuzhi Tan, Hongxun Yao, Haoran Li, Xiusheng Lu, Haozhe Xie

Auto-TLDR; Bidirectional Feature Enhancement Module for Multi-Scale Pedestrian Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Bidirectional Matrix Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; BMFPN: Bidirectional Matrix Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MANet: Multimodal Attention Network Based Point-View Fusion for 3D Shape Recognition
Yaxin Zhao, Jichao Jiao, Ning Li
Auto-TLDR; Fusion Network for 3D Shape Recognition based on Multimodal Attention Mechanism
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ACRM: Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix-NMS for Metallic Surface Defect Detection
Junting Fang, Xiaoyang Tan, Yuhui Wang

Auto-TLDR; Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix Non-Maximum Suppression for Robust Metal Defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning a Dynamic High-Resolution Network for Multi-Scale Pedestrian Detection
Mengyuan Ding, Shanshan Zhang, Jian Yang

Auto-TLDR; Learningable Dynamic HRNet for Pedestrian Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MagnifierNet: Learning Efficient Small-Scale Pedestrian Detector towards Multiple Dense Regions
Qi Cheng, Mingqin Chen, Yingjie Wu, Fei Chen, Shiping Lin

Auto-TLDR; MagnifierNet: A Simple but Effective Small-Scale Pedestrian Detection Towards Multiple Dense Regions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detective: An Attentive Recurrent Model for Sparse Object Detection
Amine Kechaou, Manuel Martinez, Monica Haurilet, Rainer Stiefelhagen

Auto-TLDR; Detective: An attentive object detector that identifies objects in images in a sequential manner
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Head Design for Object Detectors
Shivang Agarwal, Frederic Jurie
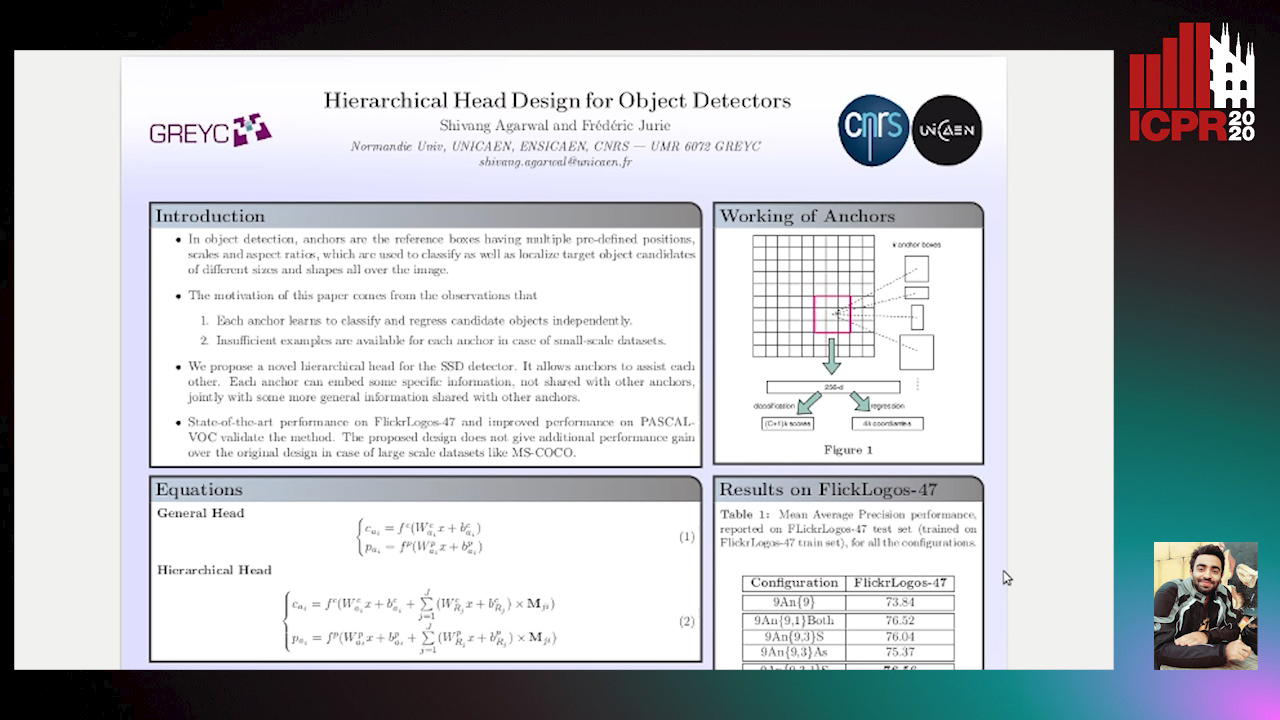
Auto-TLDR; Hierarchical Anchor for SSD Detector
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Manual-Label Free 3D Detection Via an Open-Source Simulator
Zhen Yang, Chi Zhang, Zhaoxiang Zhang, Huiming Guo

Auto-TLDR; DA-VoxelNet: A Novel Domain Adaptive VoxelNet for LIDAR-based 3D Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
6D Pose Estimation with Correlation Fusion
Yi Cheng, Hongyuan Zhu, Ying Sun, Cihan Acar, Wei Jing, Yan Wu, Liyuan Li, Cheston Tan, Joo-Hwee Lim

Auto-TLDR; Intra- and Inter-modality Fusion for 6D Object Pose Estimation with Attention Mechanism
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Joint Supervised and Self-Supervised Learning for 3D Real World Challenges
Antonio Alliegro, Davide Boscaini, Tatiana Tommasi

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervision for 3D Shape Classification and Segmentation in Point Clouds
Improving Visual Relation Detection Using Depth Maps
Sahand Sharifzadeh, Sina Moayed Baharlou, Max Berrendorf, Rajat Koner, Volker Tresp
Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Depth Maps for Visual Relation Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tiny Object Detection in Aerial Images
Jinwang Wang, Wen Yang, Haowen Guo, Ruixiang Zhang, Gui-Song Xia

Auto-TLDR; Tiny Object Detection in Aerial Images Using Multiple Center Points Based Learning Network
FeatureNMS: Non-Maximum Suppression by Learning Feature Embeddings

Auto-TLDR; FeatureNMS: Non-Maximum Suppression for Multiple Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mutually Guided Dual-Task Network for Scene Text Detection
Mengbiao Zhao, Wei Feng, Fei Yin, Xu-Yao Zhang, Cheng-Lin Liu

Auto-TLDR; A dual-task network for word-level and line-level text detection
Cascade Saliency Attention Network for Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images
Dayang Yu, Rong Zhang, Shan Qin

Auto-TLDR; Cascade Saliency Attention Network for Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
EDD-Net: An Efficient Defect Detection Network
Tianyu Guo, Linlin Zhang, Runwei Ding, Ge Yang

Auto-TLDR; EfficientNet: Efficient Network for Mobile Phone Surface defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hybrid Cascade Point Search Network for High Precision Bar Chart Component Detection
Junyu Luo, Jinpeng Wang, Chin-Yew Lin
Auto-TLDR; Object Detection of Chart Components in Chart Images Using Point-based and Region-Based Object Detection Framework
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mutual-Supervised Feature Modulation Network for Occluded Pedestrian Detection
Auto-TLDR; A Mutual-Supervised Feature Modulation Network for Occluded Pedestrian Detection
SyNet: An Ensemble Network for Object Detection in UAV Images
Auto-TLDR; SyNet: Combining Multi-Stage and Single-Stage Object Detection for Aerial Images
CenterRepp: Predict Central Representative Point Set's Distribution for Detection
Yulin He, Limeng Zhang, Wei Chen, Xin Luo, Chen Li, Xiaogang Jia

Auto-TLDR; CRPDet: CenterRepp Detector for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar