Improving Visual Relation Detection Using Depth Maps
Sahand Sharifzadeh,
Sina Moayed Baharlou,
Max Berrendorf,
Rajat Koner,
Volker Tresp
Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Depth Maps for Visual Relation Detection
Similar papers
Using Scene Graphs for Detecting Visual Relationships
Anurag Tripathi, Siddharth Srivastava, Brejesh Lall, Santanu Chaudhury

Auto-TLDR; Relationship Detection using Context Aligned Scene Graph Embeddings
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
EdgeNet: Semantic Scene Completion from a Single RGB-D Image
Aloisio Dourado, Teofilo De Campos, Adrian Hilton, Hansung Kim

Auto-TLDR; Semantic Scene Completion using 3D Depth and RGB Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Detection on Monocular Images with Two-Dimensional Canonical Correlation Analysis

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Task Object Detection from Monocular Images Using Multimodal RGB and Depth Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context for Object Detection Via Lightweight Global and Mid-Level Representations
Mesut Erhan Unal, Adriana Kovashka
Auto-TLDR; Context-Based Object Detection with Semantic Similarity
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Incorporating Depth Information into Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Yifei Zhang, Desire Sidibe, Olivier Morel, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; RDNet: A Deep Neural Network for Few-shot Segmentation Using Depth Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Modal Contextual Graph Neural Network for Text Visual Question Answering
Yaoyuan Liang, Xin Wang, Xuguang Duan, Wenwu Zhu

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Contextual Graph Neural Network for Text Visual Question Answering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MAGNet: Multi-Region Attention-Assisted Grounding of Natural Language Queries at Phrase Level
Amar Shrestha, Krittaphat Pugdeethosapol, Haowen Fang, Qinru Qiu

Auto-TLDR; MAGNet: A Multi-Region Attention-Aware Grounding Network for Free-form Textual Queries
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-View Relation Networks for Mammogram Mass Detection
Ma Jiechao, Xiang Li, Hongwei Li, Ruixuan Wang, Bjoern Menze, Wei-Shi Zheng
Auto-TLDR; Multi-view Modeling for Mass Detection in Mammogram
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
6D Pose Estimation with Correlation Fusion
Yi Cheng, Hongyuan Zhu, Ying Sun, Cihan Acar, Wei Jing, Yan Wu, Liyuan Li, Cheston Tan, Joo-Hwee Lim

Auto-TLDR; Intra- and Inter-modality Fusion for 6D Object Pose Estimation with Attention Mechanism
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploring and Exploiting the Hierarchical Structure of a Scene for Scene Graph Generation
Ikuto Kurosawa, Tetsunori Kobayashi, Yoshihiko Hayashi
Auto-TLDR; A Hierarchical Model for Scene Graph Generation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Visual Style Extraction from Chart Images for Chart Restyling
Danqing Huang, Jinpeng Wang, Guoxin Wang, Chin-Yew Lin

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Visual Properties from Reference Chart Images for Chart Restyling
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detective: An Attentive Recurrent Model for Sparse Object Detection
Amine Kechaou, Manuel Martinez, Monica Haurilet, Rainer Stiefelhagen

Auto-TLDR; Detective: An attentive object detector that identifies objects in images in a sequential manner
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Two-Level Attention-Based Fusion Learning for RGB-D Face Recognition
Hardik Uppal, Alireza Sepas-Moghaddam, Michael Greenspan, Ali Etemad

Auto-TLDR; Fused RGB-D Facial Recognition using Attention-Aware Feature Fusion
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semantics to Space(S2S): Embedding Semantics into Spatial Space for Zero-Shot Verb-Object Query Inferencing

Auto-TLDR; Semantics-to-Space: Deep Zero-Shot Learning for Verb-Object Interaction with Vectors
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FashionGraph: Understanding Fashion Data Using Scene Graph Generation
Shabnam Sadegharmaki, Marc A. Kastner, Shin'Ichi Satoh
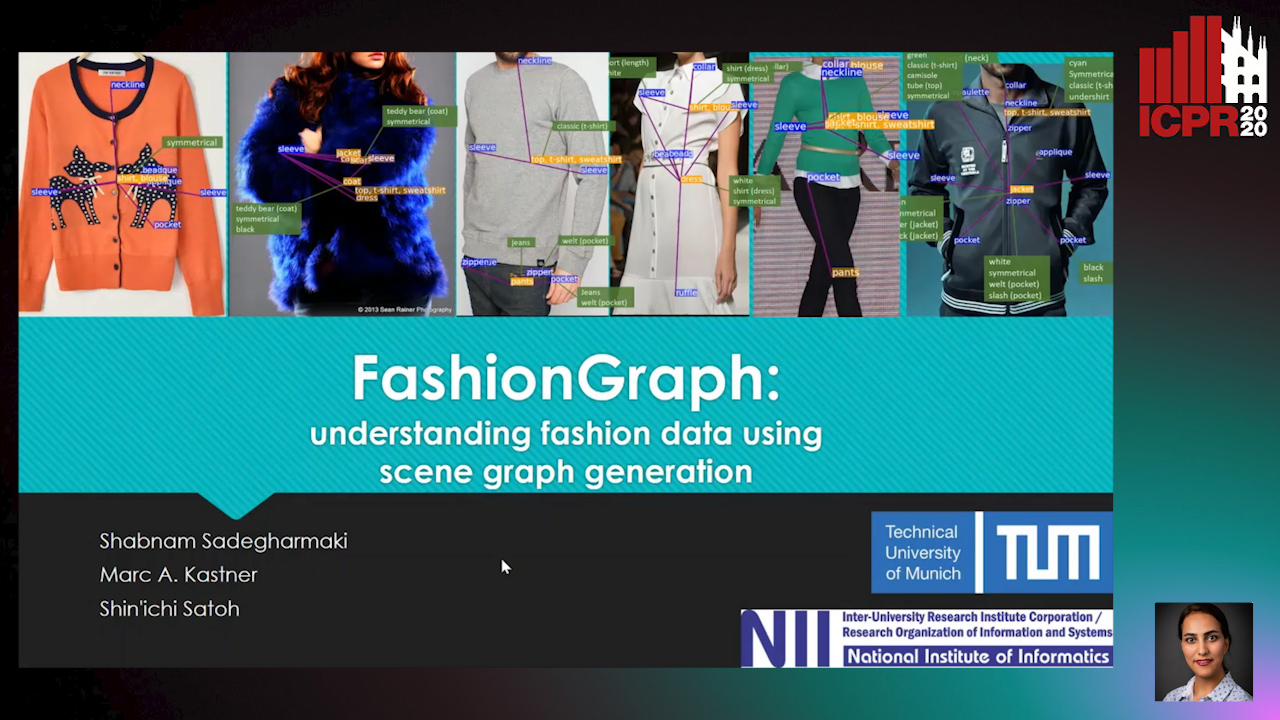
Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Scene Graph Knowledge for Fashion Applications
Detecting Objects with High Object Region Percentage
Fen Fang, Qianli Xu, Liyuan Li, Ying Gu, Joo-Hwee Lim
Auto-TLDR; Faster R-CNN for High-ORP Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
HPERL: 3D Human Pose Estimastion from RGB and LiDAR
Michael Fürst, Shriya T.P. Gupta, René Schuster, Oliver Wasenmüler, Didier Stricker
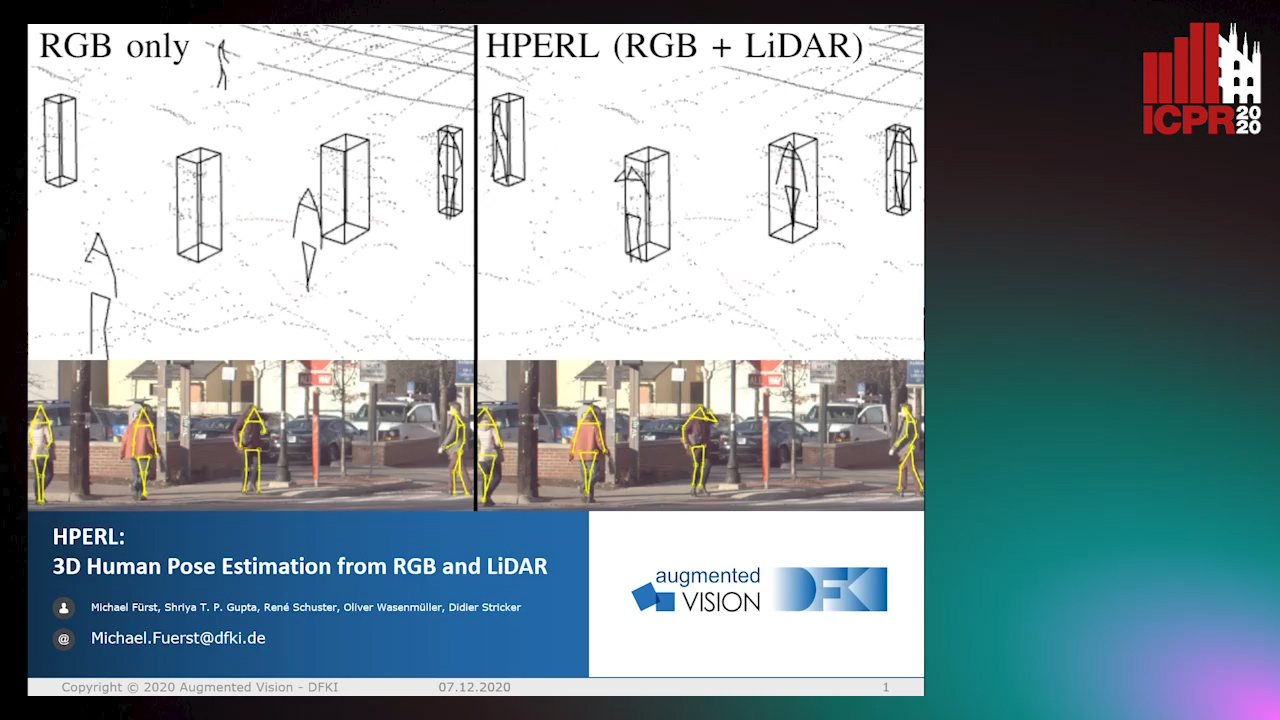
Auto-TLDR; 3D Human Pose Estimation Using RGB and LiDAR Using Weakly-Supervised Approach
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Scale Relational Reasoning with Regional Attention for Visual Question Answering

Auto-TLDR; Question-Guided Relational Reasoning for Visual Question Answering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhanced Vote Network for 3D Object Detection in Point Clouds

Auto-TLDR; A Vote Feature Enhancement Network for 3D Bounding Box Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Yolo+FPN: 2D and 3D Fused Object Detection with an RGB-D Camera

Auto-TLDR; Yolo+FPN: Combining 2D and 3D Object Detection for Real-Time Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Detection Using Dual Graph Network
Shengjia Chen, Zhixin Li, Feicheng Huang, Canlong Zhang, Huifang Ma

Auto-TLDR; A Graph Convolutional Network for Object Detection with Key Relation Information
Question-Agnostic Attention for Visual Question Answering
Moshiur R Farazi, Salman Hameed Khan, Nick Barnes

Auto-TLDR; Question-Agnostic Attention for Visual Question Answering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Stage Attention Based Visual Question Answering
Aakansha Mishra, Ashish Anand, Prithwijit Guha

Auto-TLDR; Alternative Bi-directional Attention for Visual Question Answering
Hierarchical Head Design for Object Detectors
Shivang Agarwal, Frederic Jurie
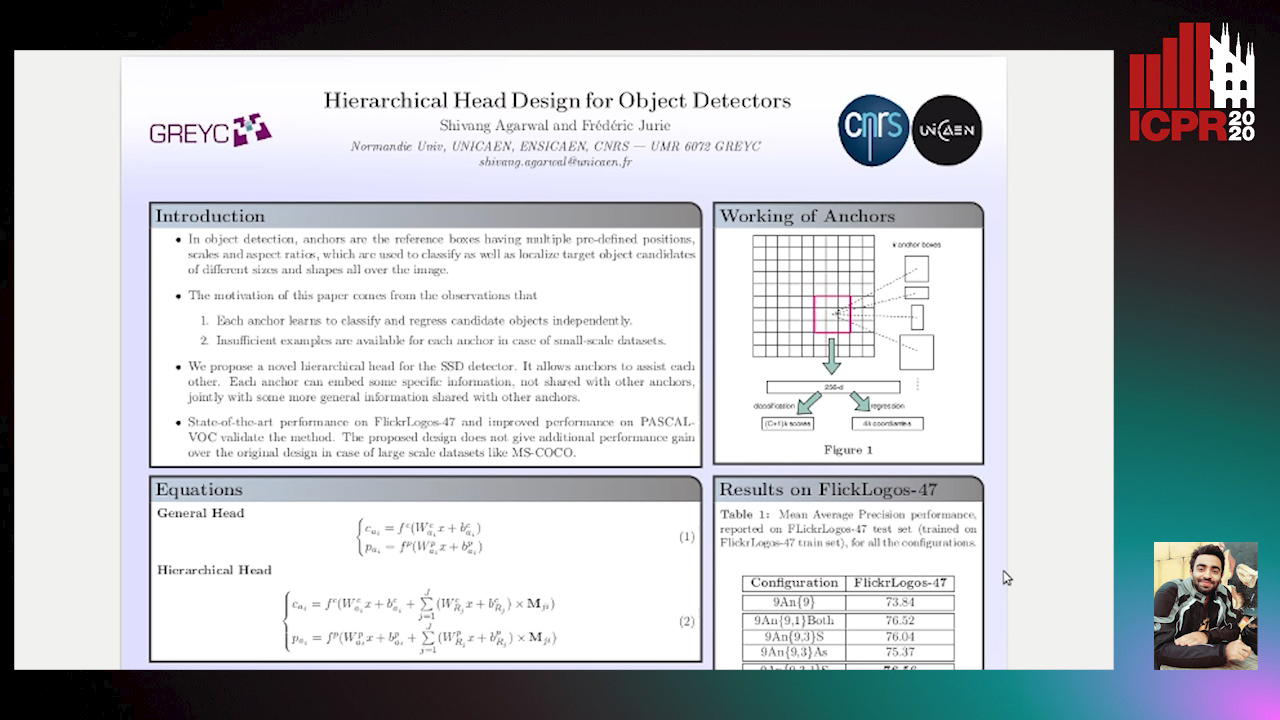
Auto-TLDR; Hierarchical Anchor for SSD Detector
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual Path Multi-Modal High-Order Features for Textual Content Based Visual Question Answering
Yanan Li, Yuetan Lin, Hongrui Zhao, Donghui Wang

Auto-TLDR; TextVQA: An End-to-End Visual Question Answering Model for Text-Based VQA
Adaptive Word Embedding Module for Semantic Reasoning in Large-Scale Detection
Yu Zhang, Xiaoyu Wu, Ruolin Zhu
Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Word Embedding Module for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Human-Centric Parsing Network for Human-Object Interaction Detection
Guanyu Chen, Chong Chen, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; Human-Centric Parsing Network for Human-Object Interactions Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real-Time Monocular Depth Estimation with Extremely Light-Weight Neural Network
Mian Jhong Chiu, Wei-Chen Chiu, Hua-Tsung Chen, Jen-Hui Chuang
Auto-TLDR; Real-Time Light-Weight Depth Prediction for Obstacle Avoidance and Environment Sensing with Deep Learning-based CNN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamic Guided Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Xiaoxia Xing, Yinghao Cai, Yiping Yang, Dayong Wen

Auto-TLDR; DGNet: Dynamic Guidance Upsampling for Self-attention-Decoding for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SyNet: An Ensemble Network for Object Detection in UAV Images
Auto-TLDR; SyNet: Combining Multi-Stage and Single-Stage Object Detection for Aerial Images
A Novel Attention-Based Aggregation Function to Combine Vision and Language
Matteo Stefanini, Marcella Cornia, Lorenzo Baraldi, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Fully-Attentive Reduction for Vision and Language
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Extending Single Beam Lidar to Full Resolution by Fusing with Single Image Depth Estimation
Yawen Lu, Yuxing Wang, Devarth Parikh, Guoyu Lu

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised LIDAR for Low-Cost Depth Estimation
Enhancing Deep Semantic Segmentation of RGB-D Data with Entangled Forests
Matteo Terreran, Elia Bonetto, Stefano Ghidoni

Auto-TLDR; FuseNet: A Lighter Deep Learning Model for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MixedFusion: 6D Object Pose Estimation from Decoupled RGB-Depth Features
Hangtao Feng, Lu Zhang, Xu Yang, Zhiyong Liu

Auto-TLDR; MixedFusion: Combining Color and Point Clouds for 6D Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context Aware Group Activity Recognition
Avijit Dasgupta, C. V. Jawahar, Karteek Alahari

Auto-TLDR; A Two-Stream Architecture for Group Activity Recognition in Multi-Person Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FatNet: A Feature-Attentive Network for 3D Point Cloud Processing
Chaitanya Kaul, Nick Pears, Suresh Manandhar

Auto-TLDR; Feature-Attentive Neural Networks for Point Cloud Classification and Segmentation
Transformer Reasoning Network for Image-Text Matching and Retrieval
Nicola Messina, Fabrizio Falchi, Andrea Esuli, Giuseppe Amato

Auto-TLDR; A Transformer Encoder Reasoning Network for Image-Text Matching in Large-Scale Information Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DEN: Disentangling and Exchanging Network for Depth Completion
You-Feng Wu, Vu-Hoang Tran, Ting-Wei Chang, Wei-Chen Chiu, Ching-Chun Huang

Auto-TLDR; Disentangling and Exchanging Network for Depth Completion
Delivering Meaningful Representation for Monocular Depth Estimation
Doyeon Kim, Donggyu Joo, Junmo Kim

Auto-TLDR; Monocular Depth Estimation by Bridging the Context between Encoding and Decoding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
More Correlations Better Performance: Fully Associative Networks for Multi-Label Image Classification

Auto-TLDR; Fully Associative Network for Fully Exploiting Correlation Information in Multi-Label Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Efficient 3D Point Cloud Scene Completion Via Novel Depth View Synthesis
Haiyan Wang, Liang Yang, Xuejian Rong, Ying-Li Tian

Auto-TLDR; 3D Point Cloud Completion with Depth View Synthesis and Depth View synthesis
Named Entity Recognition and Relation Extraction with Graph Neural Networks in Semi Structured Documents
Manuel Carbonell, Pau Riba, Mauricio Villegas, Alicia Fornés, Josep Llados

Auto-TLDR; Graph Neural Network for Entity Recognition and Relation Extraction in Semi-Structured Documents
End-To-End Hierarchical Relation Extraction for Generic Form Understanding
Tuan Anh Nguyen Dang, Duc-Thanh Hoang, Quang Bach Tran, Chih-Wei Pan, Thanh-Dat Nguyen

Auto-TLDR; Joint Entity Labeling and Link Prediction for Form Understanding in Noisy Scanned Documents
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Point In: Counting Trees with Weakly Supervised Segmentation Network
Pinmo Tong, Shuhui Bu, Pengcheng Han
Auto-TLDR; Weakly Tree counting using Deep Segmentation Network with Localization and Mask Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multiscale Attention-Based Prototypical Network for Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Yifei Zhang, Desire Sidibe, Olivier Morel, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; Few-shot Semantic Segmentation with Multiscale Feature Attention
Domain Siamese CNNs for Sparse Multispectral Disparity Estimation
David-Alexandre Beaupre, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau

Auto-TLDR; Multispectral Disparity Estimation between Thermal and Visible Images using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Fine-Grained Dataset and Its Efficient Semantic Segmentation for Unstructured Driving Scenarios
Kai Andreas Metzger, Peter Mortimer, Hans J "Joe" Wuensche

Auto-TLDR; TAS500: A Semantic Segmentation Dataset for Autonomous Driving in Unstructured Environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar