More Correlations Better Performance: Fully Associative Networks for Multi-Label Image Classification

Auto-TLDR; Fully Associative Network for Fully Exploiting Correlation Information in Multi-Label Classification
Similar papers
Object Detection Using Dual Graph Network
Shengjia Chen, Zhixin Li, Feicheng Huang, Canlong Zhang, Huifang Ma

Auto-TLDR; A Graph Convolutional Network for Object Detection with Key Relation Information
Multi-Order Feature Statistical Model for Fine-Grained Visual Categorization
Qingtao Wang, Ke Zhang, Shaoli Huang, Lianbo Zhang, Jin Fan

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Order Feature Statistical Method for Fine-Grained Visual Categorization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boundary-Aware Graph Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Hanzhe Hu, Jinshi Cui, Jinshi Hongbin Zha
Auto-TLDR; Boundary-Aware Graph Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Zero-Shot Text Classification with Semantically Extended Graph Convolutional Network
Tengfei Liu, Yongli Hu, Junbin Gao, Yanfeng Sun, Baocai Yin

Auto-TLDR; Semantically Extended Graph Convolutional Network for Zero-shot Text Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Privacy Attributes-Aware Message Passing Neural Network for Visual Privacy Attributes Classification
Hanbin Hong, Wentao Bao, Yuan Hong, Yu Kong

Auto-TLDR; Privacy Attributes-Aware Message Passing Neural Network for Visual Privacy Attribute Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Label Incorporated Graph Neural Networks for Text Classification
Yuan Xin, Linli Xu, Junliang Guo, Jiquan Li, Xin Sheng, Yuanyuan Zhou
Auto-TLDR; Graph Neural Networks for Semi-supervised Text Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semantic Bilinear Pooling for Fine-Grained Recognition
Xinjie Li, Chun Yang, Song-Lu Chen, Chao Zhu, Xu-Cheng Yin

Auto-TLDR; Semantic bilinear pooling for fine-grained recognition with hierarchical label tree
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context for Object Detection Via Lightweight Global and Mid-Level Representations
Mesut Erhan Unal, Adriana Kovashka
Auto-TLDR; Context-Based Object Detection with Semantic Similarity
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Second-Order Attention Guided Convolutional Activations for Visual Recognition
Shannan Chen, Qian Wang, Qiule Sun, Bin Liu, Jianxin Zhang, Qiang Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Second-order Attention Guided Network for Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploiting Knowledge Embedded Soft Labels for Image Recognition
Lixian Yuan, Riquan Chen, Hefeng Wu, Tianshui Chen, Wentao Wang, Pei Chen

Auto-TLDR; A Soft Label Vector for Image Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GCNs-Based Context-Aware Short Text Similarity Model

Auto-TLDR; Context-Aware Graph Convolutional Network for Text Similarity
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Prior Knowledge about Attributes: Learning a More Effective Potential Space for Zero-Shot Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Attribute Correlation Potential Space Generation for Zero-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Word Embedding Module for Semantic Reasoning in Large-Scale Detection
Yu Zhang, Xiaoyu Wu, Ruolin Zhu
Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Word Embedding Module for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient-Receptive Field Block with Group Spatial Attention Mechanism for Object Detection
Jiacheng Zhang, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; E-RFB: Efficient-Receptive Field Block for Deep Neural Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Edge-Aware Graph Attention Network for Ratio of Edge-User Estimation in Mobile Networks
Jiehui Deng, Sheng Wan, Xiang Wang, Enmei Tu, Xiaolin Huang, Jie Yang, Chen Gong

Auto-TLDR; EAGAT: Edge-Aware Graph Attention Network for Automatic REU Estimation in Mobile Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MFI: Multi-Range Feature Interchange for Video Action Recognition
Sikai Bai, Qi Wang, Xuelong Li

Auto-TLDR; Multi-range Feature Interchange Network for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
VSR++: Improving Visual Semantic Reasoning for Fine-Grained Image-Text Matching
Hui Yuan, Yan Huang, Dongbo Zhang, Zerui Chen, Wenlong Cheng, Liang Wang

Auto-TLDR; Improving Visual Semantic Reasoning for Fine-Grained Image-Text Matching
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Sketch-SNet: Deeper Subdivision of Temporal Cues for Sketch Recognition
Yizhou Tan, Lan Yang, Honggang Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Sketch Recognition using Invariable Structural Feature and Drawing Habits Feature
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Constructing Geographic and Long-term Temporal Graph for Traffic Forecasting
Yiwen Sun, Yulu Wang, Kun Fu, Zheng Wang, Changshui Zhang, Jieping Ye

Auto-TLDR; GLT-GCRNN: Geographic and Long-term Temporal Graph Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network for Traffic Forecasting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Reinforcement Learning with Dual Attention Guided Graph Convolution for Relation Extraction
Zhixin Li, Yaru Sun, Suqin Tang, Canlong Zhang, Huifang Ma

Auto-TLDR; Dual Attention Graph Convolutional Network for Relation Extraction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
You Ought to Look Around: Precise, Large Span Action Detection
Ge Pan, Zhang Han, Fan Yu, Yonghong Song, Yuanlin Zhang, Han Yuan

Auto-TLDR; YOLA: Local Feature Extraction for Action Localization with Variable receptive field
A Novel Attention-Based Aggregation Function to Combine Vision and Language
Matteo Stefanini, Marcella Cornia, Lorenzo Baraldi, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Fully-Attentive Reduction for Vision and Language
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Graph Convolutional Network for Relationship-Driven Stock Movement Prediction
Jiexia Ye, Juanjuan Zhao, Kejiang Ye, Cheng-Zhong Xu
Auto-TLDR; Multi-GCGRU: A Deep Learning Framework for Stock Price Prediction with Cross Effect
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Open Set Domain Recognition Via Attention-Based GCN and Semantic Matching Optimization
Xinxing He, Yuan Yuan, Zhiyu Jiang

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based GCN and Semantic Matching Optimization for Open Set Domain Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Question-Agnostic Attention for Visual Question Answering
Moshiur R Farazi, Salman Hameed Khan, Nick Barnes

Auto-TLDR; Question-Agnostic Attention for Visual Question Answering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Temporal Attention-Augmented Graph Convolutional Network for Efficient Skeleton-Based Human Action Recognition
Negar Heidari, Alexandros Iosifidis

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Attention Module for Efficient Graph Convolutional Network-based Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Aggregating Object Features Based on Attention Weights for Fine-Grained Image Retrieval
Hongli Lin, Yongqi Song, Zixuan Zeng, Weisheng Wang

Auto-TLDR; DSAW: Unsupervised Dual-selection for Fine-Grained Image Retrieval
Dual Path Multi-Modal High-Order Features for Textual Content Based Visual Question Answering
Yanan Li, Yuetan Lin, Hongrui Zhao, Donghui Wang

Auto-TLDR; TextVQA: An End-to-End Visual Question Answering Model for Text-Based VQA
G-FAN: Graph-Based Feature Aggregation Network for Video Face Recognition
He Zhao, Yongjie Shi, Xin Tong, Jingsi Wen, Xianghua Ying, Jinshi Hongbin Zha

Auto-TLDR; Graph-based Feature Aggregation Network for Video Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Stage Attention Based Visual Question Answering
Aakansha Mishra, Ashish Anand, Prithwijit Guha

Auto-TLDR; Alternative Bi-directional Attention for Visual Question Answering
Video-Based Facial Expression Recognition Using Graph Convolutional Networks
Daizong Liu, Hongting Zhang, Pan Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Graph Convolutional Network for Video-based Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Kernel-based Graph Convolutional Networks
Auto-TLDR; Spatial Graph Convolutional Networks in Recurrent Kernel Hilbert Space
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
VSB^2-Net: Visual-Semantic Bi-Branch Network for Zero-Shot Hashing
Xin Li, Xiangfeng Wang, Bo Jin, Wenjie Zhang, Jun Wang, Hongyuan Zha
Auto-TLDR; VSB^2-Net: inductive zero-shot hashing for image retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recurrent Graph Convolutional Networks for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition
Guangming Zhu, Lu Yang, Liang Zhang, Peiyi Shen, Juan Song
Auto-TLDR; Recurrent Graph Convolutional Network for Human Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A CNN-RNN Framework for Image Annotation from Visual Cues and Social Network Metadata
Tobia Tesan, Pasquale Coscia, Lamberto Ballan

Auto-TLDR; Context-Based Image Annotation with Multiple Semantic Embeddings and Recurrent Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Using Scene Graphs for Detecting Visual Relationships
Anurag Tripathi, Siddharth Srivastava, Brejesh Lall, Santanu Chaudhury

Auto-TLDR; Relationship Detection using Context Aligned Scene Graph Embeddings
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Two-Stream Recurrent Network for Skeleton-Based Human Interaction Recognition
Qianhui Men, Edmond S. L. Ho, Shum Hubert P. H., Howard Leung

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stream Recurrent Neural Network for Human-Human Interaction Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Augmented Bi-Path Network for Few-Shot Learning
Baoming Yan, Chen Zhou, Bo Zhao, Kan Guo, Yang Jiang, Xiaobo Li, Zhang Ming, Yizhou Wang

Auto-TLDR; Augmented Bi-path Network for Few-shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PICK: Processing Key Information Extraction from Documents Using Improved Graph Learning-Convolutional Networks
Wenwen Yu, Ning Lu, Xianbiao Qi, Ping Gong, Rong Xiao

Auto-TLDR; PICK: A Graph Learning Framework for Key Information Extraction from Documents
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On the Global Self-attention Mechanism for Graph Convolutional Networks
Auto-TLDR; Global Self-Attention Mechanism for Graph Convolutional Networks
Human-Centric Parsing Network for Human-Object Interaction Detection
Guanyu Chen, Chong Chen, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; Human-Centric Parsing Network for Human-Object Interactions Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learnable Higher-Order Representation for Action Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Learningable Higher-Order Operations for Spatiotemporal Dynamics in Video Recognition
AOAM: Automatic Optimization of Adjacency Matrix for Graph Convolutional Network
Yuhang Zhang, Hongshuai Ren, Jiexia Ye, Xitong Gao, Yang Wang, Kejiang Ye, Cheng-Zhong Xu

Auto-TLDR; Adjacency Matrix for Graph Convolutional Network in Non-Euclidean Space
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Modal Contextual Graph Neural Network for Text Visual Question Answering
Yaoyuan Liang, Xin Wang, Xuguang Duan, Wenwu Zhu

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Contextual Graph Neural Network for Text Visual Question Answering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PrivAttNet: Predicting Privacy Risks in Images Using Visual Attention
Chen Zhang, Thivya Kandappu, Vigneshwaran Subbaraju
Auto-TLDR; PrivAttNet: A Visual Attention Based Approach for Privacy Sensitivity in Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentive Hybrid Feature Based a Two-Step Fusion for Facial Expression Recognition
Jun Weng, Yang Yang, Zichang Tan, Zhen Lei
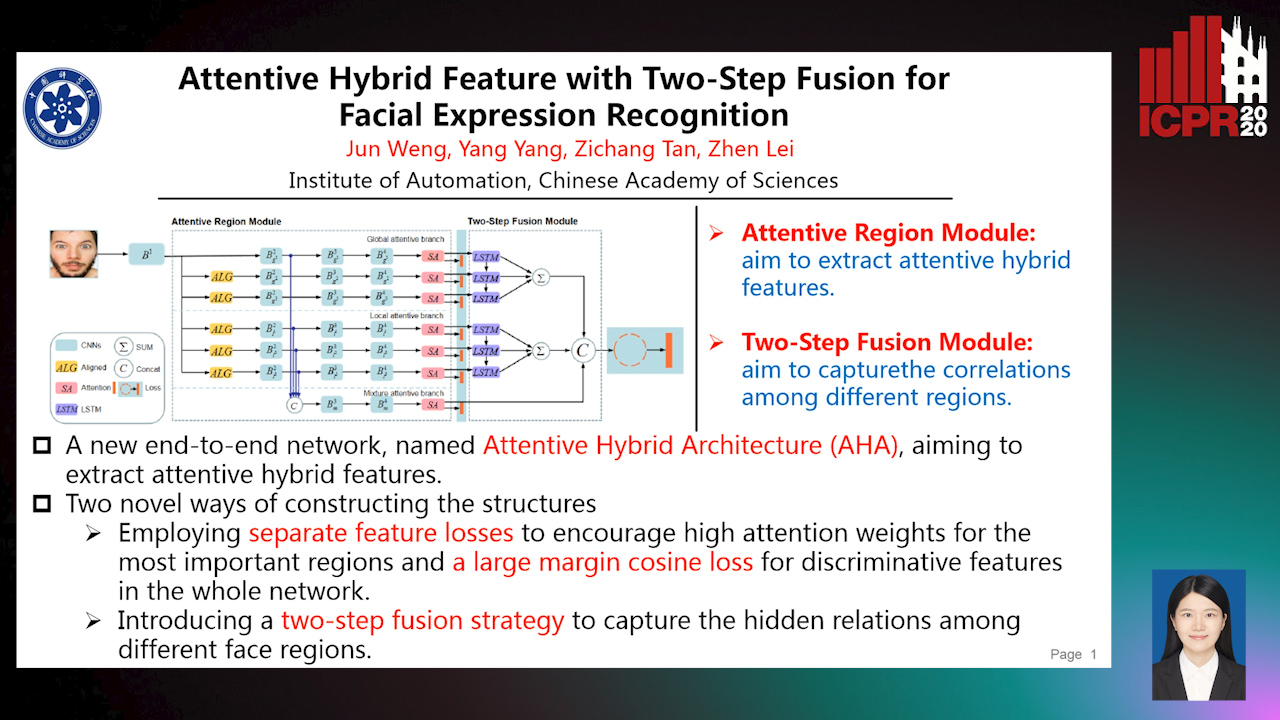
Auto-TLDR; Attentive Hybrid Architecture for Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Representation Fusion Network For Multi-Label Movie Genre Classification
Tianyu Bi, Dmitri Jarnikov, Johan Lukkien

Auto-TLDR; A Video Representation Fusion Network for Movie Genre Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Connectivity with Graph Convolutional Networks
Auto-TLDR; Learning Graph Convolutional Networks Using Topological Properties of Graphs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar