Two-Level Attention-Based Fusion Learning for RGB-D Face Recognition
Hardik Uppal,
Alireza Sepas-Moghaddam,
Michael Greenspan,
Ali Etemad

Auto-TLDR; Fused RGB-D Facial Recognition using Attention-Aware Feature Fusion
Similar papers
6D Pose Estimation with Correlation Fusion
Yi Cheng, Hongyuan Zhu, Ying Sun, Cihan Acar, Wei Jing, Yan Wu, Liyuan Li, Cheston Tan, Joo-Hwee Lim

Auto-TLDR; Intra- and Inter-modality Fusion for 6D Object Pose Estimation with Attention Mechanism
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentive Hybrid Feature Based a Two-Step Fusion for Facial Expression Recognition
Jun Weng, Yang Yang, Zichang Tan, Zhen Lei
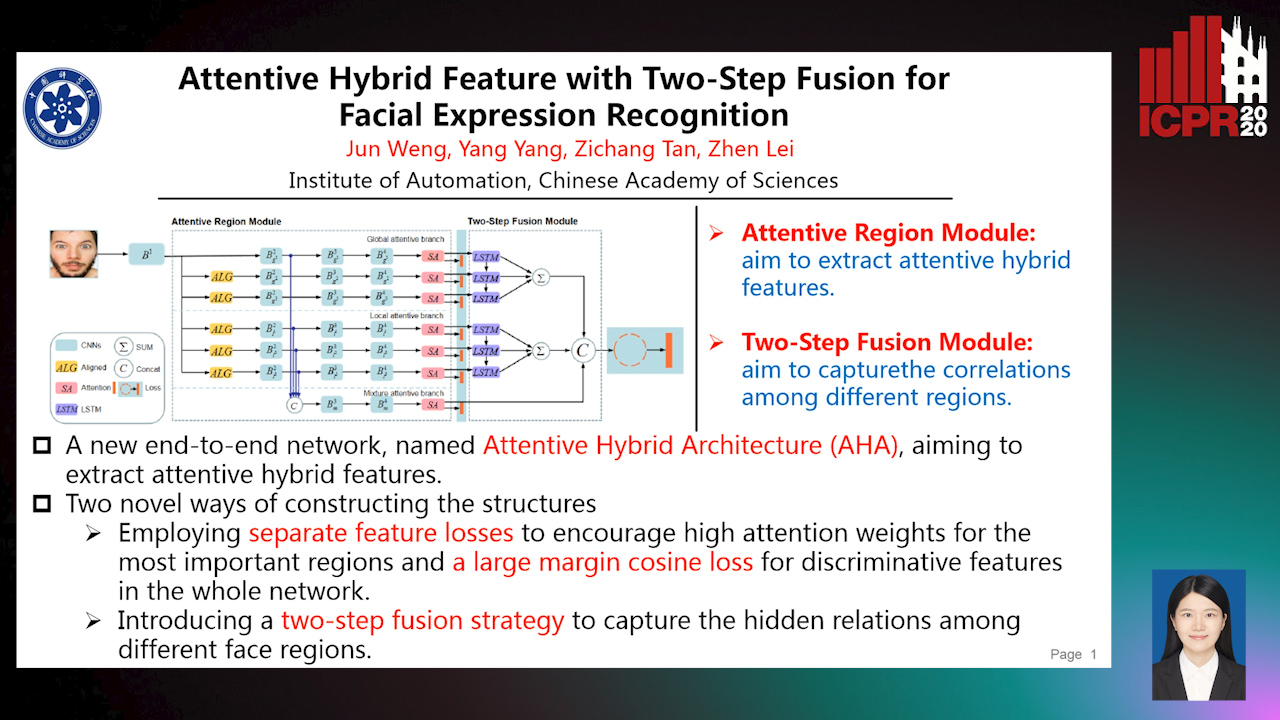
Auto-TLDR; Attentive Hybrid Architecture for Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Gait Recognition Using Multi-Scale Partial Representation Transformation with Capsules
Alireza Sepas-Moghaddam, Saeed Ghorbani, Nikolaus F. Troje, Ali Etemad
Auto-TLDR; Learning to Transfer Multi-scale Partial Gait Representations using Capsule Networks for Gait Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Stage Attention Based Visual Question Answering
Aakansha Mishra, Ashish Anand, Prithwijit Guha

Auto-TLDR; Alternative Bi-directional Attention for Visual Question Answering
MANet: Multimodal Attention Network Based Point-View Fusion for 3D Shape Recognition
Yaxin Zhao, Jichao Jiao, Ning Li
Auto-TLDR; Fusion Network for 3D Shape Recognition based on Multimodal Attention Mechanism
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Facial Expression Recognition Using Residual Masking Network
Luan Pham, Vu Huynh, Tuan Anh Tran

Auto-TLDR; Deep Residual Masking for Automatic Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Depth Videos for the Classification of Micro-Expressions
Ankith Jain Rakesh Kumar, Bir Bhanu, Christopher Casey, Sierra Cheung, Aaron Seitz

Auto-TLDR; RGB-D Dataset for the Classification of Facial Micro-expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Face Anti-Spoofing Using Spatial Pyramid Pooling
Lei Shi, Zhuo Zhou, Zhenhua Guo

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Pyramid Pooling for Face Anti-Spoofing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Driven Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Bappaditya Debnath, Swagat Kumar, Marry O'Brien, Ardhendu Behera

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Collaborative Human Machine Attention Module for Character Recognition
Chetan Ralekar, Tapan Gandhi, Santanu Chaudhury

Auto-TLDR; A Collaborative Human-Machine Attention Module for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Improved Bilinear Pooling Method for Image-Based Action Recognition

Auto-TLDR; An improved bilinear pooling method for image-based action recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Question-Agnostic Attention for Visual Question Answering
Moshiur R Farazi, Salman Hameed Khan, Nick Barnes

Auto-TLDR; Question-Agnostic Attention for Visual Question Answering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentive Part-Aware Networks for Partial Person Re-Identification
Lijuan Huo, Chunfeng Song, Zhengyi Liu, Zhaoxiang Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Part-Aware Learning for Partial Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FatNet: A Feature-Attentive Network for 3D Point Cloud Processing
Chaitanya Kaul, Nick Pears, Suresh Manandhar

Auto-TLDR; Feature-Attentive Neural Networks for Point Cloud Classification and Segmentation
A Cross Domain Multi-Modal Dataset for Robust Face Anti-Spoofing
Qiaobin Ji, Shugong Xu, Xudong Chen, Shan Cao, Shunqing Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Cross domain multi-modal FAS dataset GREAT-FASD and several evaluation protocols for academic community
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MixedFusion: 6D Object Pose Estimation from Decoupled RGB-Depth Features
Hangtao Feng, Lu Zhang, Xu Yang, Zhiyong Liu

Auto-TLDR; MixedFusion: Combining Color and Point Clouds for 6D Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PSDNet: A Balanced Architecture of Accuracy and Parameters for Semantic Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Pyramid Pooling Module with SE1Cblock and D2SUpsample Network (PSDNet)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SAT-Net: Self-Attention and Temporal Fusion for Facial Action Unit Detection
Zhihua Li, Zheng Zhang, Lijun Yin

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Fusion and Self-Attention Network for Facial Action Unit Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vision-Based Multi-Modal Framework for Action Recognition
Djamila Romaissa Beddiar, Mourad Oussalah, Brahim Nini

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Framework for Human Activity Recognition Using RGB, Depth and Skeleton Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rotation Invariant Aerial Image Retrieval with Group Convolutional Metric Learning
Hyunseung Chung, Woo-Jeoung Nam, Seong-Whan Lee

Auto-TLDR; Robust Remote Sensing Image Retrieval Using Group Convolution with Attention Mechanism and Metric Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploring Spatial-Temporal Representations for fNIRS-based Intimacy Detection via an Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
Chao Li, Qian Zhang, Ziping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Intimate Relationship Prediction by Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network Using Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PrivAttNet: Predicting Privacy Risks in Images Using Visual Attention
Chen Zhang, Thivya Kandappu, Vigneshwaran Subbaraju
Auto-TLDR; PrivAttNet: A Visual Attention Based Approach for Privacy Sensitivity in Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose-Robust Face Recognition by Deep Meta Capsule Network-Based Equivariant Embedding
Fangyu Wu, Jeremy Simon Smith, Wenjin Lu, Bailing Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Deep Meta Capsule Network-based Equivariant Embedding Model for Pose-Robust Face Recognition
Incorporating Depth Information into Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Yifei Zhang, Desire Sidibe, Olivier Morel, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; RDNet: A Deep Neural Network for Few-shot Segmentation Using Depth Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Feature Fusion Network for Gaze Tracking in Mobile Tablets
Yiwei Bao, Yihua Cheng, Yunfei Liu, Feng Lu

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Feature Fusion Network for Multi-stream Gaze Estimation in Mobile Tablets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video-Based Facial Expression Recognition Using Graph Convolutional Networks
Daizong Liu, Hongting Zhang, Pan Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Graph Convolutional Network for Video-based Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhancing Deep Semantic Segmentation of RGB-D Data with Entangled Forests
Matteo Terreran, Elia Bonetto, Stefano Ghidoni

Auto-TLDR; FuseNet: A Lighter Deep Learning Model for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Face Manipulation Detection through Ensemble of CNNs
Nicolo Bonettini, Edoardo Daniele Cannas, Sara Mandelli, Luca Bondi, Paolo Bestagini, Stefano Tubaro

Auto-TLDR; Face Manipulation Detection in Video Sequences Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock Module for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Junhui Yin, Siqing Zhang, Dongliang Chang, Zhanyu Ma, Jun Guo
Auto-TLDR; Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention Pyramid Module for Scene Recognition
Zhinan Qiao, Xiaohui Yuan, Chengyuan Zhuang, Abolfazl Meyarian

Auto-TLDR; Attention Pyramid Module for Multi-Scale Scene Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Flow-Guided Spatial Attention Tracking for Egocentric Activity Recognition

Auto-TLDR; flow-guided spatial attention tracking for egocentric activity recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Answer-Checking in Context: A Multi-Modal Fully Attention Network for Visual Question Answering
Hantao Huang, Tao Han, Wei Han, Deep Yap Deep Yap, Cheng-Ming Chiang
Auto-TLDR; Fully Attention Based Visual Question Answering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Visual Relation Detection Using Depth Maps
Sahand Sharifzadeh, Sina Moayed Baharlou, Max Berrendorf, Rajat Koner, Volker Tresp
Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Depth Maps for Visual Relation Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Scale Cascading Network with Compact Feature Learning for RGB-Infrared Person Re-Identification
Can Zhang, Hong Liu, Wei Guo, Mang Ye
Auto-TLDR; Multi-Scale Part-Aware Cascading for RGB-Infrared Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Space-Time Domain Tensor Neural Networks: An Application on Human Pose Classification
Konstantinos Makantasis, Athanasios Voulodimos, Anastasios Doulamis, Nikolaos Doulamis, Nikolaos Bakalos

Auto-TLDR; Tensor-Based Neural Network for Spatiotemporal Pose Classifiaction using Three-Dimensional Skeleton Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generalized Iris Presentation Attack Detection Algorithm under Cross-Database Settings
Mehak Gupta, Vishal Singh, Akshay Agarwal, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh

Auto-TLDR; MVNet: A Deep Learning-based PAD Network for Iris Recognition against Presentation Attacks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Scale Residual Pyramid Attention Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Jing Liu, Xiaona Zhang, Zhaoxin Li, Tianlu Mao
Auto-TLDR; Multi-scale Residual Pyramid Attention Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context-Aware Residual Module for Image Classification
Auto-TLDR; Context-Aware Residual Module for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention As Activation
Yimian Dai, Stefan Oehmcke, Fabian Gieseke, Yiquan Wu, Kobus Barnard

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Activation Units for Convolutional Networks
CSpA-DN: Channel and Spatial Attention Dense Network for Fusing PET and MRI Images
Bicao Li, Zhoufeng Liu, Shan Gao, Jenq-Neng Hwang, Jun Sun, Zongmin Wang

Auto-TLDR; CSpA-DN: Unsupervised Fusion of PET and MR Images with Channel and Spatial Attention
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient-Receptive Field Block with Group Spatial Attention Mechanism for Object Detection
Jiacheng Zhang, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; E-RFB: Efficient-Receptive Field Block for Deep Neural Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Joint Face Alignment and 3D Face Reconstruction with Efficient Convolution Neural Networks
Keqiang Li, Huaiyu Wu, Xiuqin Shang, Zhen Shen, Gang Xiong, Xisong Dong, Bin Hu, Fei-Yue Wang

Auto-TLDR; Mobile-FRNet: Efficient 3D Morphable Model Alignment and 3D Face Reconstruction from a Single 2D Facial Image
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Disentangling of Viewpoint and Residues Variations by Substituting Representations for Robust Face Recognition
Minsu Kim, Joanna Hong, Junho Kim, Hong Joo Lee, Yong Man Ro
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Disentangling of Identity, viewpoint, and Residue Representations for Robust Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Ordinal Depth Classification Using Region-Based Self-Attention
Minh Hieu Phan, Son Lam Phung, Abdesselam Bouzerdoum

Auto-TLDR; Region-based Self-Attention for Multi-scale Depth Estimation from a Single 2D Image
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Age Gap Reducer-GAN for Recognizing Age-Separated Faces
Daksha Yadav, Naman Kohli, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh, Afzel Noore

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Network for Age-separated Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Lightweight Low-Resolution Face Recognition for Surveillance Applications
Yoanna Martínez-Díaz, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Luis S. Luevano, Leonardo Chang, Miguel Gonzalez-Mendoza

Auto-TLDR; Efficiency of Lightweight Deep Face Networks on Low-Resolution Surveillance Imagery
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Attention Mechanism for Fine-Grained Classification of Table Tennis Strokes Using a Twin Spatio-Temporal Convolutional Neural Networks
Pierre-Etienne Martin, Jenny Benois-Pineau, Renaud Péteri, Julien Morlier

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Blocks for Action Recognition in Table Tennis Strokes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar