SAT-Net: Self-Attention and Temporal Fusion for Facial Action Unit Detection
Zhihua Li,
Zheng Zhang,
Lijun Yin

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Fusion and Self-Attention Network for Facial Action Unit Detection
Similar papers
MRP-Net: A Light Multiple Region Perception Neural Network for Multi-Label AU Detection
Yang Tang, Shuang Chen, Honggang Zhang, Gang Wang, Rui Yang

Auto-TLDR; MRP-Net: A Fast and Light Neural Network for Facial Action Unit Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentive Hybrid Feature Based a Two-Step Fusion for Facial Expression Recognition
Jun Weng, Yang Yang, Zichang Tan, Zhen Lei
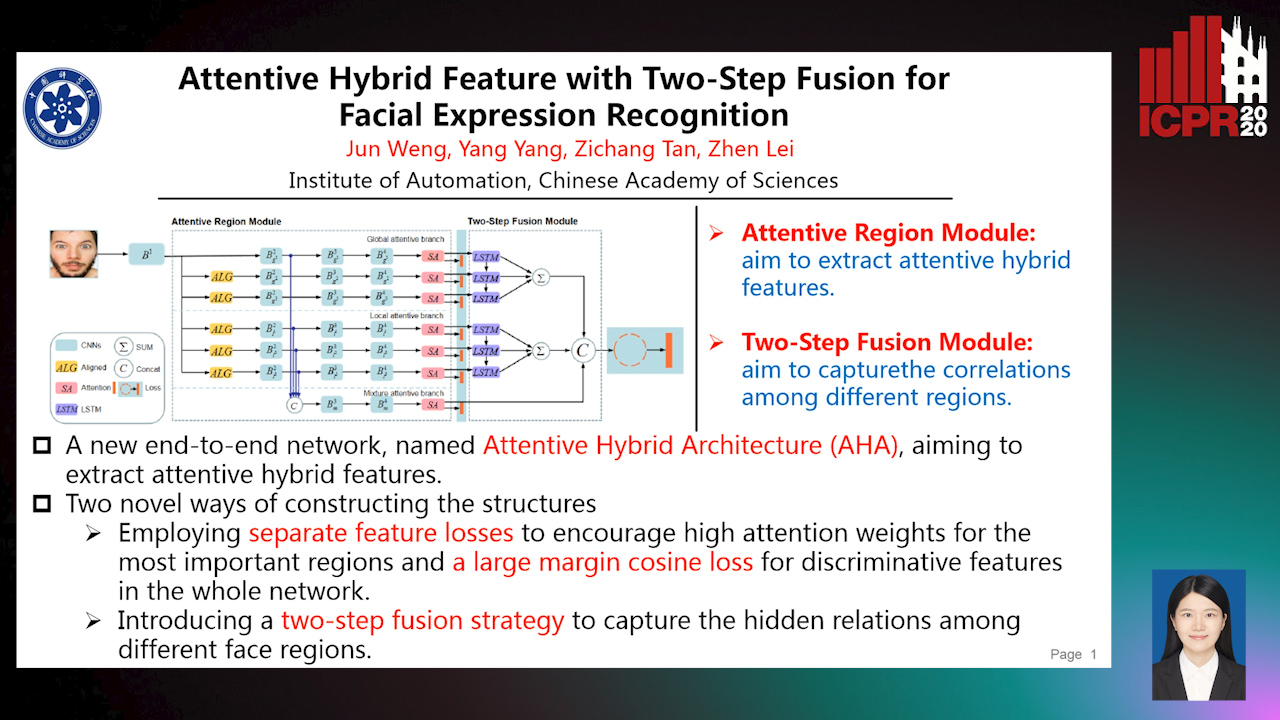
Auto-TLDR; Attentive Hybrid Architecture for Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Flow-Guided Spatial Attention Tracking for Egocentric Activity Recognition

Auto-TLDR; flow-guided spatial attention tracking for egocentric activity recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video-Based Facial Expression Recognition Using Graph Convolutional Networks
Daizong Liu, Hongting Zhang, Pan Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Graph Convolutional Network for Video-based Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Learning of Dynamic Representations for Static Images
Siyang Song, Enrique Sanchez, Linlin Shen, Michel Valstar

Auto-TLDR; Facial Action Unit Intensity Estimation and Affect Estimation from Still Images with Multiple Temporal Scale
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Interpretable Emotion Classification Using Temporal Convolutional Models
Manasi Bharat Gund, Abhiram Ravi Bharadwaj, Ifeoma Nwogu
Auto-TLDR; Understanding the Dynamics of Facial Emotion Expression with Spatiotemporal Representations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Two-Stream Temporal Convolutional Network for Dynamic Facial Attractiveness Prediction
Nina Weng, Jiahao Wang, Annan Li, Yunhong Wang

Auto-TLDR; 2S-TCN: A Two-Stream Temporal Convolutional Network for Dynamic Facial Attractiveness Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MFI: Multi-Range Feature Interchange for Video Action Recognition
Sikai Bai, Qi Wang, Xuelong Li

Auto-TLDR; Multi-range Feature Interchange Network for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Global Feature Aggregation for Accident Anticipation
Mishal Fatima, Umar Karim Khan, Chong Min Kyung

Auto-TLDR; Feature Aggregation for Predicting Accidents in Video Sequences
Self-Supervised Joint Encoding of Motion and Appearance for First Person Action Recognition
Mirco Planamente, Andrea Bottino, Barbara Caputo

Auto-TLDR; A Single Stream Architecture for Egocentric Action Recognition from the First-Person Point of View
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TSMSAN: A Three-Stream Multi-Scale Attentive Network for Video Saliency Detection
Jingwen Yang, Guanwen Zhang, Wei Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Three-stream Multi-scale attentive network for video saliency detection in dynamic scenes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Facial Expression Recognition Using Residual Masking Network
Luan Pham, Vu Huynh, Tuan Anh Tran

Auto-TLDR; Deep Residual Masking for Automatic Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Driven Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Bappaditya Debnath, Swagat Kumar, Marry O'Brien, Ardhendu Behera

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Identity-Aware Facial Expression Recognition in Compressed Video
Xiaofeng Liu, Linghao Jin, Xu Han, Jun Lu, Jonghye Woo, Jane You

Auto-TLDR; Exploring Facial Expression Representation in Compressed Video with Mutual Information Minimization
Deep Multi-Task Learning for Facial Expression Recognition and Synthesis Based on Selective Feature Sharing
Rui Zhao, Tianshan Liu, Jun Xiao, P. K. Daniel Lun, Kin-Man Lam

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Learning for Facial Expression Recognition and Synthesis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Depth Videos for the Classification of Micro-Expressions
Ankith Jain Rakesh Kumar, Bir Bhanu, Christopher Casey, Sierra Cheung, Aaron Seitz

Auto-TLDR; RGB-D Dataset for the Classification of Facial Micro-expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
What and How? Jointly Forecasting Human Action and Pose
Yanjun Zhu, Yanxia Zhang, Qiong Liu, Andreas Girgensohn

Auto-TLDR; Forecasting Human Actions and Motion Trajectories with Joint Action Classification and Pose Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Two-Stream Recurrent Network for Skeleton-Based Human Interaction Recognition
Qianhui Men, Edmond S. L. Ho, Shum Hubert P. H., Howard Leung

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stream Recurrent Neural Network for Human-Human Interaction Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
2D Deep Video Capsule Network with Temporal Shift for Action Recognition
Théo Voillemin, Hazem Wannous, Jean-Philippe Vandeborre

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Shift Module over Capsule Network for Action Recognition in Continuous Videos
ACCLVOS: Atrous Convolution with Spatial-Temporal ConvLSTM for Video Object Segmentation
Muzhou Xu, Shan Zong, Chunping Liu, Shengrong Gong, Zhaohui Wang, Yu Xia

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Video Object Segmentation using U-shape Convolution and ConvLSTM
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Two-Level Attention-Based Fusion Learning for RGB-D Face Recognition
Hardik Uppal, Alireza Sepas-Moghaddam, Michael Greenspan, Ali Etemad

Auto-TLDR; Fused RGB-D Facial Recognition using Attention-Aware Feature Fusion
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose-Based Body Language Recognition for Emotion and Psychiatric Symptom Interpretation
Zhengyuan Yang, Amanda Kay, Yuncheng Li, Wendi Cross, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; Body Language Based Emotion Recognition for Psychiatric Symptoms Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context Matters: Self-Attention for Sign Language Recognition
Fares Ben Slimane, Mohamed Bouguessa

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Network for Continuous Sign Language Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real-Time Driver Drowsiness Detection Using Facial Action Units
Malaika Vijay, Nandagopal Netrakanti Vinayak, Maanvi Nunna, Subramanyam Natarajan

Auto-TLDR; Real-Time Detection of Driver Drowsiness using Facial Action Units using Extreme Gradient Boosting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention Pyramid Module for Scene Recognition
Zhinan Qiao, Xiaohui Yuan, Chengyuan Zhuang, Abolfazl Meyarian

Auto-TLDR; Attention Pyramid Module for Multi-Scale Scene Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RWF-2000: An Open Large Scale Video Database for Violence Detection
Ming Cheng, Kunjing Cai, Ming Li

Auto-TLDR; Flow Gated Network for Violence Detection in Surveillance Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploring Spatial-Temporal Representations for fNIRS-based Intimacy Detection via an Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
Chao Li, Qian Zhang, Ziping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Intimate Relationship Prediction by Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network Using Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Attention Mechanism for Fine-Grained Classification of Table Tennis Strokes Using a Twin Spatio-Temporal Convolutional Neural Networks
Pierre-Etienne Martin, Jenny Benois-Pineau, Renaud Péteri, Julien Morlier

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Blocks for Action Recognition in Table Tennis Strokes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient-Receptive Field Block with Group Spatial Attention Mechanism for Object Detection
Jiacheng Zhang, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; E-RFB: Efficient-Receptive Field Block for Deep Neural Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Facial Expression Recognition by Using a Disentangled Identity-Invariant Expression Representation
Auto-TLDR; Transfer-based Expression Recognition Generative Adversarial Network (TER-GAN)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Channel-Wise Dense Connection Graph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition
Michael Lao Banteng, Zhiyong Wu

Auto-TLDR; Two-stream channel-wise dense connection GCN for human action recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Object Detection Using Object's Motion Context and Spatio-Temporal Feature Aggregation
Jaekyum Kim, Junho Koh, Byeongwon Lee, Seungji Yang, Jun Won Choi

Auto-TLDR; Video Object Detection Using Spatio-Temporal Aggregated Features and Gated Attention Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Practical Compressed Video Action Recognition: A Temporal Enhanced Multi-Stream Network
Bing Li, Longteng Kong, Dongming Zhang, Xiuguo Bao, Di Huang, Yunhong Wang

Auto-TLDR; TEMSN: Temporal Enhanced Multi-Stream Network for Compressed Video Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Global-Local Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation in Aerial Images
Minglong Li, Lianlei Shan, Weiqiang Wang

Auto-TLDR; GLANet: Global-Local Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TinyVIRAT: Low-Resolution Video Action Recognition
Ugur Demir, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; TinyVIRAT: A Progressive Generative Approach for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentive Visual Semantic Specialized Network for Video Captioning
Jesus Perez-Martin, Benjamin Bustos, Jorge Pérez

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Visual Semantic Specialized Network for Video Captioning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock Module for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Junhui Yin, Siqing Zhang, Dongliang Chang, Zhanyu Ma, Jun Guo
Auto-TLDR; Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context Visual Information-Based Deliberation Network for Video Captioning
Min Lu, Xueyong Li, Caihua Liu
Auto-TLDR; Context visual information-based deliberation network for video captioning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Improved Bilinear Pooling Method for Image-Based Action Recognition

Auto-TLDR; An improved bilinear pooling method for image-based action recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Audio-Visual Speech Recognition Using a Two-Step Feature Fusion Strategy

Auto-TLDR; A Two-Step Feature Fusion Network for Speech Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Semantic Representations Via Joint 3D Face Reconstruction and Facial Attribute Estimation
Zichun Weng, Youjun Xiang, Xianfeng Li, Juntao Liang, Wanliang Huo, Yuli Fu

Auto-TLDR; Joint Framework for 3D Face Reconstruction with Facial Attribute Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Wavelet Attention Embedding Networks for Video Super-Resolution
Young-Ju Choi, Young-Woon Lee, Byung-Gyu Kim

Auto-TLDR; Wavelet Attention Embedding Network for Video Super-Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Not 3D Re-ID: Simple Single Stream 2D Convolution for Robust Video Re-Identification

Auto-TLDR; ResNet50-IBN for Video-based Person Re-Identification using Single Stream 2D Convolution Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MA-LSTM: A Multi-Attention Based LSTM for Complex Pattern Extraction
Jingjie Guo, Kelang Tian, Kejiang Ye, Cheng-Zhong Xu
Auto-TLDR; MA-LSTM: Multiple Attention based recurrent neural network for forget gate
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Early Wildfire Smoke Detection in Videos
Taanya Gupta, Hengyue Liu, Bir Bhanu

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Spatio-Temporal Video Object Segmentation for Automatic Detection of Smoke in Videos during Forest Fire
RMS-Net: Regression and Masking for Soccer Event Spotting
Matteo Tomei, Lorenzo Baraldi, Simone Calderara, Simone Bronzin, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; An Action Spotting Network for Soccer Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Annotation of Corpora for Emotion Recognition through Facial Expressions Analysis
Alex Mircoli, Claudia Diamantini, Domenico Potena, Emanuele Storti

Auto-TLDR; Automatic annotation of video subtitles on the basis of facial expressions using machine learning algorithms
Abstract Slides Poster Similar