Context Visual Information-Based Deliberation Network for Video Captioning
Min Lu,
Xueyong Li,
Caihua Liu
Auto-TLDR; Context visual information-based deliberation network for video captioning
Similar papers
Visual Oriented Encoder: Integrating Multimodal and Multi-Scale Contexts for Video Captioning

Auto-TLDR; Visual Oriented Encoder for Video Captioning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentive Visual Semantic Specialized Network for Video Captioning
Jesus Perez-Martin, Benjamin Bustos, Jorge Pérez

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Visual Semantic Specialized Network for Video Captioning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enriching Video Captions with Contextual Text
Philipp Rimle, Pelin Dogan, Markus Gross
Auto-TLDR; Contextualized Video Captioning Using Contextual Text
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Text Synopsis Generation for Egocentric Videos
Aidean Sharghi, Niels Lobo, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; Egocentric Video Summarization Using Multi-task Learning for End-to-End Learning
A Novel Actor Dual-Critic Model for Remote Sensing Image Captioning
Ruchika Chavhan, Biplab Banerjee, Xiao Xiang Zhu, Subhasis Chaudhuri
Auto-TLDR; Actor Dual-Critic Training for Remote Sensing Image Captioning Using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Scale 2D Representation Learning for Weakly-Supervised Moment Retrieval
Ding Li, Rui Wu, Zhizhong Zhang, Yongqiang Tang, Wensheng Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Multi-scale 2D Representation Learning for Weakly Supervised Video Moment Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MAGNet: Multi-Region Attention-Assisted Grounding of Natural Language Queries at Phrase Level
Amar Shrestha, Krittaphat Pugdeethosapol, Haowen Fang, Qinru Qiu

Auto-TLDR; MAGNet: A Multi-Region Attention-Aware Grounding Network for Free-form Textual Queries
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Integrating Historical States and Co-Attention Mechanism for Visual Dialog
Tianling Jiang, Yi Ji, Chunping Liu
Auto-TLDR; Integrating Historical States and Co-attention for Visual Dialog
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual Path Multi-Modal High-Order Features for Textual Content Based Visual Question Answering
Yanan Li, Yuetan Lin, Hongrui Zhao, Donghui Wang

Auto-TLDR; TextVQA: An End-to-End Visual Question Answering Model for Text-Based VQA
PIN: A Novel Parallel Interactive Network for Spoken Language Understanding
Peilin Zhou, Zhiqi Huang, Fenglin Liu, Yuexian Zou

Auto-TLDR; Parallel Interactive Network for Spoken Language Understanding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tackling Contradiction Detection in German Using Machine Translation and End-To-End Recurrent Neural Networks
Maren Pielka, Rafet Sifa, Lars Patrick Hillebrand, David Biesner, Rajkumar Ramamurthy, Anna Ladi, Christian Bauckhage

Auto-TLDR; Contradiction Detection in Natural Language Inference using Recurrent Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Transformer Reasoning Network for Image-Text Matching and Retrieval
Nicola Messina, Fabrizio Falchi, Andrea Esuli, Giuseppe Amato

Auto-TLDR; A Transformer Encoder Reasoning Network for Image-Text Matching in Large-Scale Information Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Global Feature Aggregation for Accident Anticipation
Mishal Fatima, Umar Karim Khan, Chong Min Kyung

Auto-TLDR; Feature Aggregation for Predicting Accidents in Video Sequences
A Novel Attention-Based Aggregation Function to Combine Vision and Language
Matteo Stefanini, Marcella Cornia, Lorenzo Baraldi, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Fully-Attentive Reduction for Vision and Language
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-Lingual Text Image Recognition Via Multi-Task Sequence to Sequence Learning
Zhuo Chen, Fei Yin, Xu-Yao Zhang, Qing Yang, Cheng-Lin Liu

Auto-TLDR; Cross-Lingual Text Image Recognition with Multi-task Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Gaussian Constrained Attention Network for Scene Text Recognition
Zhi Qiao, Xugong Qin, Yu Zhou, Fei Yang, Weiping Wang

Auto-TLDR; Gaussian Constrained Attention Network for Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Flow-Guided Spatial Attention Tracking for Egocentric Activity Recognition

Auto-TLDR; flow-guided spatial attention tracking for egocentric activity recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Global Context-Based Network with Transformer for Image2latex
Nuo Pang, Chun Yang, Xiaobin Zhu, Jixuan Li, Xu-Cheng Yin

Auto-TLDR; Image2latex with Global Context block and Transformer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Trajectory-User Link with Attention Recurrent Networks
Tao Sun, Yongjun Xu, Fei Wang, Lin Wu, 塘文 钱, Zezhi Shao

Auto-TLDR; TULAR: Trajectory-User Link with Attention Recurrent Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Continuous Sign Language Recognition with Iterative Spatiotemporal Fine-Tuning
Kenessary Koishybay, Medet Mukushev, Anara Sandygulova

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Neural Network for Continuous Sign Language Recognition with Iterative Gloss Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AG-GAN: An Attentive Group-Aware GAN for Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction
Yue Song, Niccolò Bisagno, Syed Zohaib Hassan, Nicola Conci
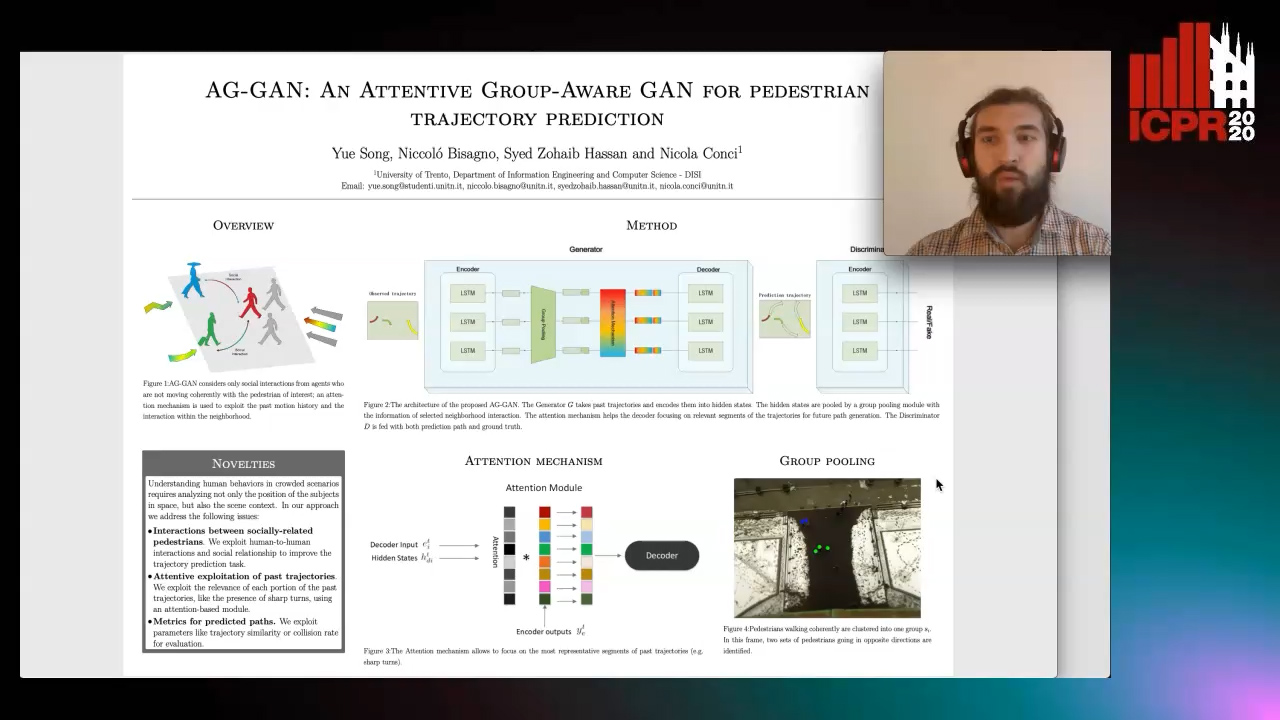
Auto-TLDR; An attentive group-aware GAN for motion prediction in crowded scenarios
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Zero-Shot Text Classification with Semantically Extended Graph Convolutional Network
Tengfei Liu, Yongli Hu, Junbin Gao, Yanfeng Sun, Baocai Yin

Auto-TLDR; Semantically Extended Graph Convolutional Network for Zero-shot Text Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PICK: Processing Key Information Extraction from Documents Using Improved Graph Learning-Convolutional Networks
Wenwen Yu, Ning Lu, Xianbiao Qi, Ping Gong, Rong Xiao

Auto-TLDR; PICK: A Graph Learning Framework for Key Information Extraction from Documents
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
What and How? Jointly Forecasting Human Action and Pose
Yanjun Zhu, Yanxia Zhang, Qiong Liu, Andreas Girgensohn

Auto-TLDR; Forecasting Human Actions and Motion Trajectories with Joint Action Classification and Pose Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MFI: Multi-Range Feature Interchange for Video Action Recognition
Sikai Bai, Qi Wang, Xuelong Li

Auto-TLDR; Multi-range Feature Interchange Network for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SAT-Net: Self-Attention and Temporal Fusion for Facial Action Unit Detection
Zhihua Li, Zheng Zhang, Lijun Yin

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Fusion and Self-Attention Network for Facial Action Unit Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RWF-2000: An Open Large Scale Video Database for Violence Detection
Ming Cheng, Kunjing Cai, Ming Li

Auto-TLDR; Flow Gated Network for Violence Detection in Surveillance Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Practical Compressed Video Action Recognition: A Temporal Enhanced Multi-Stream Network
Bing Li, Longteng Kong, Dongming Zhang, Xiuguo Bao, Di Huang, Yunhong Wang

Auto-TLDR; TEMSN: Temporal Enhanced Multi-Stream Network for Compressed Video Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Modal Contextual Graph Neural Network for Text Visual Question Answering
Yaoyuan Liang, Xin Wang, Xuguang Duan, Wenwu Zhu

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Contextual Graph Neural Network for Text Visual Question Answering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context Matters: Self-Attention for Sign Language Recognition
Fares Ben Slimane, Mohamed Bouguessa

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Network for Continuous Sign Language Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Stage Attention Based Visual Question Answering
Aakansha Mishra, Ashish Anand, Prithwijit Guha

Auto-TLDR; Alternative Bi-directional Attention for Visual Question Answering
Developing Motion Code Embedding for Action Recognition in Videos
Maxat Alibayev, David Andrea Paulius, Yu Sun
Auto-TLDR; Motion Embedding via Motion Codes for Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MA-LSTM: A Multi-Attention Based LSTM for Complex Pattern Extraction
Jingjie Guo, Kelang Tian, Kejiang Ye, Cheng-Zhong Xu
Auto-TLDR; MA-LSTM: Multiple Attention based recurrent neural network for forget gate
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Summarization with a Dual Attention Capsule Network
Hao Fu, Hongxing Wang, Jianyu Yang

Auto-TLDR; Dual Self-Attention Capsule Network for Video Summarization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Co-Segmentation for Athlete Movements and Live Commentaries Using Crossmodal Temporal Proximity
Yasunori Ohishi, Yuki Tanaka, Kunio Kashino

Auto-TLDR; A guided attention scheme for audio-visual co-segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
VSR++: Improving Visual Semantic Reasoning for Fine-Grained Image-Text Matching
Hui Yuan, Yan Huang, Dongbo Zhang, Zerui Chen, Wenlong Cheng, Liang Wang

Auto-TLDR; Improving Visual Semantic Reasoning for Fine-Grained Image-Text Matching
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient Sentence Embedding Via Semantic Subspace Analysis
Bin Wang, Fenxiao Chen, Yun Cheng Wang, C.-C. Jay Kuo

Auto-TLDR; S3E: Semantic Subspace Sentence Embedding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Evaluation of BERT and ALBERT Sentence Embedding Performance on Downstream NLP Tasks
Hyunjin Choi, Judong Kim, Seongho Joe, Youngjune Gwon

Auto-TLDR; Sentence Embedding Models for BERT and ALBERT: A Comparison and Evaluation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GCNs-Based Context-Aware Short Text Similarity Model

Auto-TLDR; Context-Aware Graph Convolutional Network for Text Similarity
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ACCLVOS: Atrous Convolution with Spatial-Temporal ConvLSTM for Video Object Segmentation
Muzhou Xu, Shan Zong, Chunping Liu, Shengrong Gong, Zhaohui Wang, Yu Xia

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Video Object Segmentation using U-shape Convolution and ConvLSTM
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ConvMath : A Convolutional Sequence Network for Mathematical Expression Recognition
Zuoyu Yan, Xiaode Zhang, Liangcai Gao, Ke Yuan, Zhi Tang
Auto-TLDR; Convolutional Sequence Modeling for Mathematical Expressions Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Moto: Enhancing Embedding with Multiple Joint Factors for Chinese Text Classification
Xunzhu Tang, Rujie Zhu, Tiezhu Sun

Auto-TLDR; Moto: Enhancing Embedding with Multiple J\textbf{o}int Fac\textBF{to}rs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-Supervised Joint-Event-Extraction with Heterogeneous Information Networks
Yue Wang, Zhuo Xu, Yao Wan, Lu Bai, Lixin Cui, Qian Zhao, Edwin Hancock, Philip Yu

Auto-TLDR; Joint-Event-extraction from Unstructured corpora using Structural Information Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Scale Relational Reasoning with Regional Attention for Visual Question Answering

Auto-TLDR; Question-Guided Relational Reasoning for Visual Question Answering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Multimodal Attention for Deep Video Summarization
Melissa Sanabria, Frederic Precioso, Thomas Menguy

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Summarization of Professional Soccer Matches Using Event-Stream Data and Multi- Instance Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Driven Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Bappaditya Debnath, Swagat Kumar, Marry O'Brien, Ardhendu Behera

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose-Based Body Language Recognition for Emotion and Psychiatric Symptom Interpretation
Zhengyuan Yang, Amanda Kay, Yuncheng Li, Wendi Cross, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; Body Language Based Emotion Recognition for Psychiatric Symptoms Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar