Global Feature Aggregation for Accident Anticipation
Mishal Fatima,
Umar Karim Khan,
Chong Min Kyung

Auto-TLDR; Feature Aggregation for Predicting Accidents in Video Sequences
Similar papers
SAT-Net: Self-Attention and Temporal Fusion for Facial Action Unit Detection
Zhihua Li, Zheng Zhang, Lijun Yin

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Fusion and Self-Attention Network for Facial Action Unit Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
What and How? Jointly Forecasting Human Action and Pose
Yanjun Zhu, Yanxia Zhang, Qiong Liu, Andreas Girgensohn

Auto-TLDR; Forecasting Human Actions and Motion Trajectories with Joint Action Classification and Pose Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context Visual Information-Based Deliberation Network for Video Captioning
Min Lu, Xueyong Li, Caihua Liu
Auto-TLDR; Context visual information-based deliberation network for video captioning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Flow-Guided Spatial Attention Tracking for Egocentric Activity Recognition

Auto-TLDR; flow-guided spatial attention tracking for egocentric activity recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Practical Compressed Video Action Recognition: A Temporal Enhanced Multi-Stream Network
Bing Li, Longteng Kong, Dongming Zhang, Xiuguo Bao, Di Huang, Yunhong Wang

Auto-TLDR; TEMSN: Temporal Enhanced Multi-Stream Network for Compressed Video Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Modeling Long-Term Interactions to Enhance Action Recognition
Alejandro Cartas, Petia Radeva, Mariella Dimiccoli

Auto-TLDR; A Hierarchical Long Short-Term Memory Network for Action Recognition in Egocentric Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MFI: Multi-Range Feature Interchange for Video Action Recognition
Sikai Bai, Qi Wang, Xuelong Li

Auto-TLDR; Multi-range Feature Interchange Network for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentive Visual Semantic Specialized Network for Video Captioning
Jesus Perez-Martin, Benjamin Bustos, Jorge Pérez

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Visual Semantic Specialized Network for Video Captioning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learnable Higher-Order Representation for Action Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Learningable Higher-Order Operations for Spatiotemporal Dynamics in Video Recognition
RMS-Net: Regression and Masking for Soccer Event Spotting
Matteo Tomei, Lorenzo Baraldi, Simone Calderara, Simone Bronzin, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; An Action Spotting Network for Soccer Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Knowledge Distillation for Action Anticipation Via Label Smoothing
Guglielmo Camporese, Pasquale Coscia, Antonino Furnari, Giovanni Maria Farinella, Lamberto Ballan

Auto-TLDR; A Multi-Modal Framework for Action Anticipation using Long Short-Term Memory Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detective: An Attentive Recurrent Model for Sparse Object Detection
Amine Kechaou, Manuel Martinez, Monica Haurilet, Rainer Stiefelhagen

Auto-TLDR; Detective: An attentive object detector that identifies objects in images in a sequential manner
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Visual Oriented Encoder: Integrating Multimodal and Multi-Scale Contexts for Video Captioning

Auto-TLDR; Visual Oriented Encoder for Video Captioning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Joint Encoding of Motion and Appearance for First Person Action Recognition
Mirco Planamente, Andrea Bottino, Barbara Caputo

Auto-TLDR; A Single Stream Architecture for Egocentric Action Recognition from the First-Person Point of View
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Multimodal Attention for Deep Video Summarization
Melissa Sanabria, Frederic Precioso, Thomas Menguy

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Summarization of Professional Soccer Matches Using Event-Stream Data and Multi- Instance Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AG-GAN: An Attentive Group-Aware GAN for Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction
Yue Song, Niccolò Bisagno, Syed Zohaib Hassan, Nicola Conci
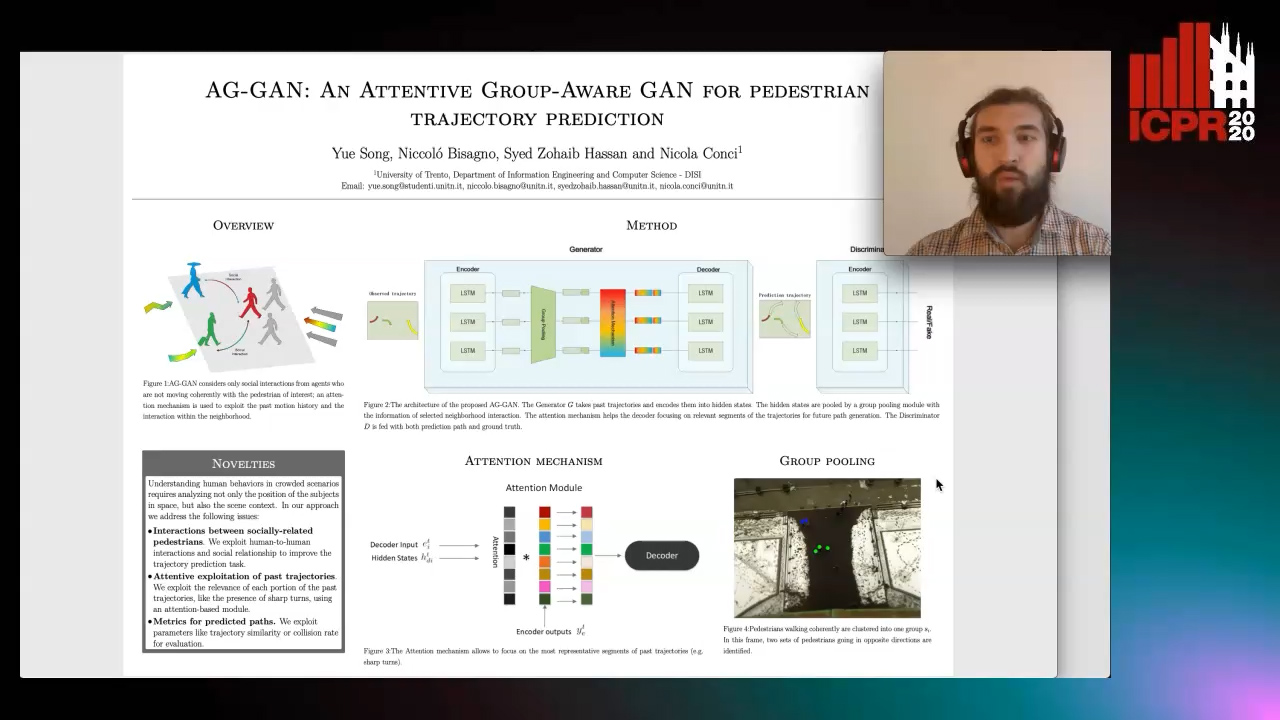
Auto-TLDR; An attentive group-aware GAN for motion prediction in crowded scenarios
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Global Context-Based Network with Transformer for Image2latex
Nuo Pang, Chun Yang, Xiaobin Zhu, Jixuan Li, Xu-Cheng Yin

Auto-TLDR; Image2latex with Global Context block and Transformer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Semantic Segmentation Using Deep Multi-View Representation Learning
Akrem Sellami, Salvatore Tabbone

Auto-TLDR; Deep Multi-view Representation Learning for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Image Sequence Based Cyclist Action Recognition Using Multi-Stream 3D Convolution
Stefan Zernetsch, Steven Schreck, Viktor Kress, Konrad Doll, Bernhard Sick
Auto-TLDR; 3D-ConvNet: A Multi-stream 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Detecting Cyclists in Real World Traffic Situations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Trajectory-User Link with Attention Recurrent Networks
Tao Sun, Yongjun Xu, Fei Wang, Lin Wu, 塘文 钱, Zezhi Shao

Auto-TLDR; TULAR: Trajectory-User Link with Attention Recurrent Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DAG-Net: Double Attentive Graph Neural Network for Trajectory Forecasting
Alessio Monti, Alessia Bertugli, Simone Calderara, Rita Cucchiara
Auto-TLDR; Recurrent Generative Model for Multi-modal Human Motion Behaviour in Urban Environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Integrating Historical States and Co-Attention Mechanism for Visual Dialog
Tianling Jiang, Yi Ji, Chunping Liu
Auto-TLDR; Integrating Historical States and Co-attention for Visual Dialog
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MAGNet: Multi-Region Attention-Assisted Grounding of Natural Language Queries at Phrase Level
Amar Shrestha, Krittaphat Pugdeethosapol, Haowen Fang, Qinru Qiu

Auto-TLDR; MAGNet: A Multi-Region Attention-Aware Grounding Network for Free-form Textual Queries
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MA-LSTM: A Multi-Attention Based LSTM for Complex Pattern Extraction
Jingjie Guo, Kelang Tian, Kejiang Ye, Cheng-Zhong Xu
Auto-TLDR; MA-LSTM: Multiple Attention based recurrent neural network for forget gate
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AttendAffectNet: Self-Attention Based Networks for Predicting Affective Responses from Movies
Thi Phuong Thao Ha, Bt Balamurali, Herremans Dorien, Roig Gemma

Auto-TLDR; AttendAffectNet: A Self-Attention Based Network for Emotion Prediction from Movies
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Manipulated Facial Videos: A Time Series Solution
Zhang Zhewei, Ma Can, Gao Meilin, Ding Bowen
Auto-TLDR; Face-Alignment Based Bi-LSTM for Fake Video Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Object Detection Using Object's Motion Context and Spatio-Temporal Feature Aggregation
Jaekyum Kim, Junho Koh, Byeongwon Lee, Seungji Yang, Jun Won Choi

Auto-TLDR; Video Object Detection Using Spatio-Temporal Aggregated Features and Gated Attention Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Revisiting Sequence-To-Sequence Video Object Segmentation with Multi-Task Loss and Skip-Memory
Fatemeh Azimi, Benjamin Bischke, Sebastian Palacio, Federico Raue, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel

Auto-TLDR; Sequence-to-Sequence Learning for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RWF-2000: An Open Large Scale Video Database for Violence Detection
Ming Cheng, Kunjing Cai, Ming Li

Auto-TLDR; Flow Gated Network for Violence Detection in Surveillance Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PrivAttNet: Predicting Privacy Risks in Images Using Visual Attention
Chen Zhang, Thivya Kandappu, Vigneshwaran Subbaraju
Auto-TLDR; PrivAttNet: A Visual Attention Based Approach for Privacy Sensitivity in Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AerialMPTNet: Multi-Pedestrian Tracking in Aerial Imagery Using Temporal and Graphical Features
Maximilian Kraus, Seyed Majid Azimi, Emec Ercelik, Reza Bahmanyar, Peter Reinartz, Alois Knoll

Auto-TLDR; AerialMPTNet: A novel approach for multi-pedestrian tracking in geo-referenced aerial imagery by fusing appearance features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Gabriella: An Online System for Real-Time Activity Detection in Untrimmed Security Videos
Mamshad Nayeem Rizve, Ugur Demir, Praveen Praveen Tirupattur, Aayush Jung Rana, Kevin Duarte, Ishan Rajendrakumar Dave, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; Gabriella: A Real-Time Online System for Activity Detection in Surveillance Videos
Audio-Visual Speech Recognition Using a Two-Step Feature Fusion Strategy

Auto-TLDR; A Two-Step Feature Fusion Network for Speech Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Forground-Guided Vehicle Perception Framework
Kun Tian, Tong Zhou, Shiming Xiang, Chunhong Pan

Auto-TLDR; A foreground segmentation branch for vehicle detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Driven Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Bappaditya Debnath, Swagat Kumar, Marry O'Brien, Ardhendu Behera

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Based Deep Metric Learning for Near-Duplicate Video Retrieval
Kuan-Hsun Wang, Chia Chun Cheng, Yi-Ling Chen, Yale Song, Shang-Hong Lai

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Deep Metric Learning for Near-duplicate Video Retrieval
A Two-Stream Recurrent Network for Skeleton-Based Human Interaction Recognition
Qianhui Men, Edmond S. L. Ho, Shum Hubert P. H., Howard Leung

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stream Recurrent Neural Network for Human-Human Interaction Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ActionSpotter: Deep Reinforcement Learning Framework for Temporal Action Spotting in Videos
Guillaume Vaudaux-Ruth, Adrien Chan-Hon-Tong, Catherine Achard

Auto-TLDR; ActionSpotter: A Reinforcement Learning Algorithm for Action Spotting in Video
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context Matters: Self-Attention for Sign Language Recognition
Fares Ben Slimane, Mohamed Bouguessa

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Network for Continuous Sign Language Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Motion U-Net: Multi-Cue Encoder-Decoder Network for Motion Segmentation
Gani Rahmon, Filiz Bunyak, Kannappan Palaniappan
Auto-TLDR; Motion U-Net: A Deep Learning Framework for Robust Moving Object Detection under Challenging Conditions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Temporal Binary Representation for Event-Based Action Recognition
Simone Undri Innocenti, Federico Becattini, Federico Pernici, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Binary Representation for Gesture Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context Aware Group Activity Recognition
Avijit Dasgupta, C. V. Jawahar, Karteek Alahari

Auto-TLDR; A Two-Stream Architecture for Group Activity Recognition in Multi-Person Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Early Wildfire Smoke Detection in Videos
Taanya Gupta, Hengyue Liu, Bir Bhanu

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Spatio-Temporal Video Object Segmentation for Automatic Detection of Smoke in Videos during Forest Fire
2D Deep Video Capsule Network with Temporal Shift for Action Recognition
Théo Voillemin, Hazem Wannous, Jean-Philippe Vandeborre

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Shift Module over Capsule Network for Action Recognition in Continuous Videos
Temporal Feature Enhancement Network with External Memory for Object Detection in Surveillance Video
Masato Fujitake, Akihiro Sugimoto

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Attention Based External Memory Network for Surveillance Object Detection
Transformer Networks for Trajectory Forecasting
Francesco Giuliari, Hasan Irtiza, Marco Cristani, Fabio Galasso

Auto-TLDR; TransformerNetworks for Trajectory Prediction of People Interactions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Anomaly Detection by Estimating Likelihood of Representations

Auto-TLDR; Video Anomaly Detection in the latent feature space using a deep probabilistic model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar