Video Semantic Segmentation Using Deep Multi-View Representation Learning
Akrem Sellami,
Salvatore Tabbone

Auto-TLDR; Deep Multi-view Representation Learning for Video Object Segmentation
Similar papers
ACCLVOS: Atrous Convolution with Spatial-Temporal ConvLSTM for Video Object Segmentation
Muzhou Xu, Shan Zong, Chunping Liu, Shengrong Gong, Zhaohui Wang, Yu Xia

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Video Object Segmentation using U-shape Convolution and ConvLSTM
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Revisiting Sequence-To-Sequence Video Object Segmentation with Multi-Task Loss and Skip-Memory
Fatemeh Azimi, Benjamin Bischke, Sebastian Palacio, Federico Raue, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel

Auto-TLDR; Sequence-to-Sequence Learning for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Object Deformation and Motion Adaption for Semi-Supervised Video Object Segmentation
Xiaoyang Zheng, Xin Tan, Jianming Guo, Lizhuang Ma

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Video Object Segmentation with Mask-propagation-based Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Segmentation Tracking from Generic Video Cues
Amirhossein Kardoost, Sabine Müller, Joachim Weickert, Margret Keuper
Auto-TLDR; A Light-Weight Variational Framework for Video Object Segmentation in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Early Wildfire Smoke Detection in Videos
Taanya Gupta, Hengyue Liu, Bir Bhanu

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Spatio-Temporal Video Object Segmentation for Automatic Detection of Smoke in Videos during Forest Fire
Siamese Dynamic Mask Estimation Network for Fast Video Object Segmentation
Dexiang Hong, Guorong Li, Kai Xu, Li Su, Qingming Huang

Auto-TLDR; Siamese Dynamic Mask Estimation for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Human Segmentation with Dynamic LiDAR Data
Tao Zhong, Wonjik Kim, Masayuki Tanaka, Masatoshi Okutomi
Auto-TLDR; Spatiotemporal Neural Network for Human Segmentation with Dynamic Point Clouds
Motion U-Net: Multi-Cue Encoder-Decoder Network for Motion Segmentation
Gani Rahmon, Filiz Bunyak, Kannappan Palaniappan
Auto-TLDR; Motion U-Net: A Deep Learning Framework for Robust Moving Object Detection under Challenging Conditions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TSMSAN: A Three-Stream Multi-Scale Attentive Network for Video Saliency Detection
Jingwen Yang, Guanwen Zhang, Wei Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Three-stream Multi-scale attentive network for video saliency detection in dynamic scenes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Residual Learning of Video Frame Interpolation Using Convolutional LSTM
Auto-TLDR; Video Frame Interpolation Using Residual Learning and Convolutional LSTMs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boundary-Aware Graph Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Hanzhe Hu, Jinshi Cui, Jinshi Hongbin Zha
Auto-TLDR; Boundary-Aware Graph Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Object Detection Using Object's Motion Context and Spatio-Temporal Feature Aggregation
Jaekyum Kim, Junho Koh, Byeongwon Lee, Seungji Yang, Jun Won Choi

Auto-TLDR; Video Object Detection Using Spatio-Temporal Aggregated Features and Gated Attention Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Siamese Fully Convolutional Tracker with Motion Correction
Mathew Francis, Prithwijit Guha

Auto-TLDR; A Siamese Ensemble for Visual Tracking with Appearance and Motion Components
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MFI: Multi-Range Feature Interchange for Video Action Recognition
Sikai Bai, Qi Wang, Xuelong Li

Auto-TLDR; Multi-range Feature Interchange Network for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multiscale Attention-Based Prototypical Network for Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Yifei Zhang, Desire Sidibe, Olivier Morel, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; Few-shot Semantic Segmentation with Multiscale Feature Attention
Global-Local Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation in Aerial Images
Minglong Li, Lianlei Shan, Weiqiang Wang

Auto-TLDR; GLANet: Global-Local Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Machine-Learned Regularization and Polygonization of Building Segmentation Masks
Stefano Zorzi, Ksenia Bittner, Friedrich Fraundorfer

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Regularization and Polygonization of Building Segmentation masks using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Motion-Supervised Co-Part Segmentation
Aliaksandr Siarohin, Subhankar Roy, Stéphane Lathuiliere, Sergey Tulyakov, Elisa Ricci, Nicu Sebe

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Co-Part Segmentation Using Motion Information from Videos
Tracking Fast Moving Objects by Segmentation Network

Auto-TLDR; Fast Moving Objects Tracking by Segmentation Using Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Joint Encoding of Motion and Appearance for First Person Action Recognition
Mirco Planamente, Andrea Bottino, Barbara Caputo

Auto-TLDR; A Single Stream Architecture for Egocentric Action Recognition from the First-Person Point of View
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Incorporating Depth Information into Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Yifei Zhang, Desire Sidibe, Olivier Morel, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; RDNet: A Deep Neural Network for Few-shot Segmentation Using Depth Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Coarse to Fine: Progressive and Multi-Task Learning for Salient Object Detection
Dong-Goo Kang, Sangwoo Park, Joonki Paik
Auto-TLDR; Progressive and mutl-task learning scheme for salient object detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Do Not Treat Boundaries and Regions Differently: An Example on Heart Left Atrial Segmentation
Zhou Zhao, Elodie Puybareau, Nicolas Boutry, Thierry Geraud
Auto-TLDR; Attention Full Convolutional Network for Atrial Segmentation using ResNet-101 Architecture
Video Reconstruction by Spatio-Temporal Fusion of Blurred-Coded Image Pair
Anupama S, Prasan Shedligeri, Abhishek Pal, Kaushik Mitr

Auto-TLDR; Recovering Video from Motion-Blurred and Coded Exposure Images Using Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention Based Coupled Framework for Road and Pothole Segmentation
Shaik Masihullah, Ritu Garg, Prerana Mukherjee, Anupama Ray
Auto-TLDR; Few Shot Learning for Road and Pothole Segmentation on KITTI and IDD
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GraphBGS: Background Subtraction Via Recovery of Graph Signals
Jhony Heriberto Giraldo Zuluaga, Thierry Bouwmans
Auto-TLDR; Graph BackGround Subtraction using Graph Signals
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Relevance Detection in Cataract Surgery Videos by Spatio-Temporal Action Localization
Negin Ghamsarian, Mario Taschwer, Doris Putzgruber, Stephanie. Sarny, Klaus Schoeffmann

Auto-TLDR; relevance-based retrieval in cataract surgery videos
Gabriella: An Online System for Real-Time Activity Detection in Untrimmed Security Videos
Mamshad Nayeem Rizve, Ugur Demir, Praveen Praveen Tirupattur, Aayush Jung Rana, Kevin Duarte, Ishan Rajendrakumar Dave, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; Gabriella: A Real-Time Online System for Activity Detection in Surveillance Videos
3D Semantic Labeling of Photogrammetry Meshes Based on Active Learning
Mengqi Rong, Shuhan Shen, Zhanyi Hu

Auto-TLDR; 3D Semantic Expression of Urban Scenes Based on Active Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PHNet: Parasite-Host Network for Video Crowd Counting
Shiqiao Meng, Jiajie Li, Weiwei Guo, Jinfeng Jiang, Lai Ye

Auto-TLDR; PHNet: A Parasite-Host Network for Video Crowd Counting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Direction Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Dehui Li, Zhiguo Cao, Ke Xian, Xinyuan Qi, Chao Zhang, Hao Lu

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Direction Convolution for Contextual Segmentation
What and How? Jointly Forecasting Human Action and Pose
Yanjun Zhu, Yanxia Zhang, Qiong Liu, Andreas Girgensohn

Auto-TLDR; Forecasting Human Actions and Motion Trajectories with Joint Action Classification and Pose Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RescueNet: Joint Building Segmentation and Damage Assessment from Satellite Imagery
Auto-TLDR; RescueNet: End-to-End Building Segmentation and Damage Classification for Humanitarian Aid and Disaster Response
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Forground-Guided Vehicle Perception Framework
Kun Tian, Tong Zhou, Shiming Xiang, Chunhong Pan

Auto-TLDR; A foreground segmentation branch for vehicle detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Directed Variational Cross-encoder Network for Few-Shot Multi-image Co-segmentation
Sayan Banerjee, Divakar Bhat S, Subhasis Chaudhuri, Rajbabu Velmurugan
Auto-TLDR; Directed Variational Inference Cross Encoder for Class Agnostic Co-Segmentation of Multiple Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Mucong Ye, Ouyang Jinpeng, Ge Chen, Jing Zhang, Xiaogang Yu
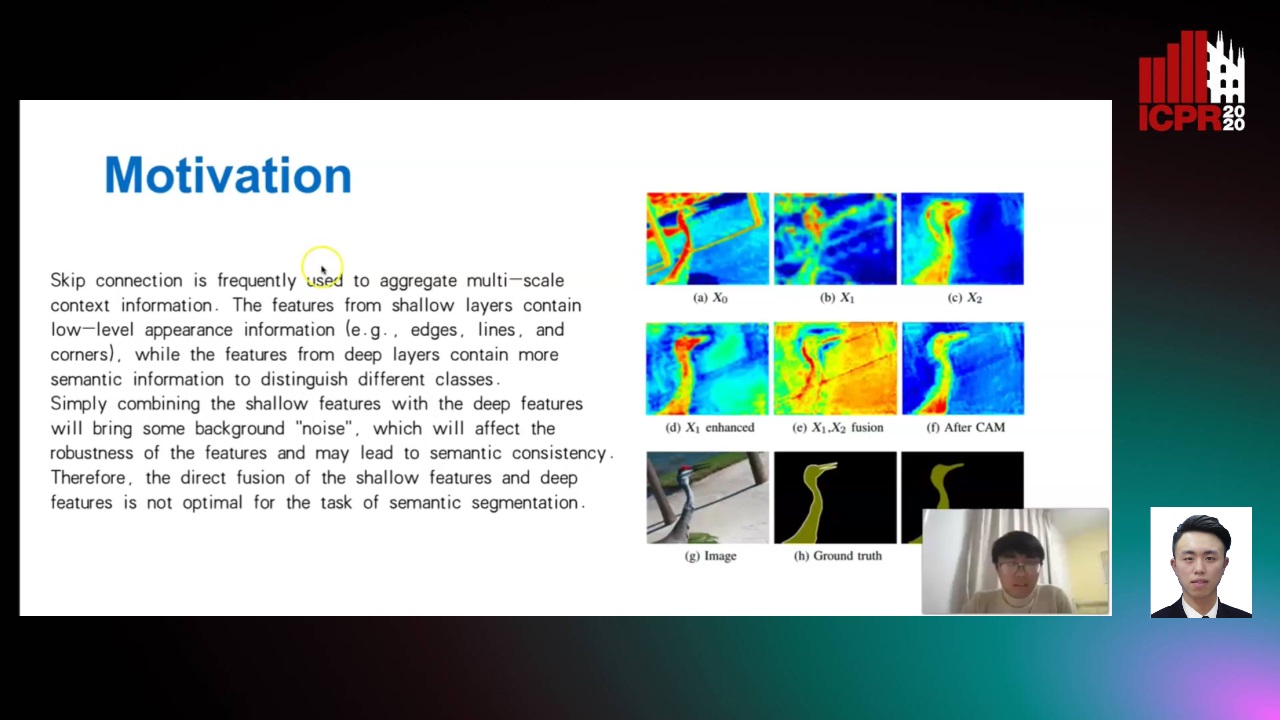
Auto-TLDR; EFPN: Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Learning of Dynamic Representations for Static Images
Siyang Song, Enrique Sanchez, Linlin Shen, Michel Valstar

Auto-TLDR; Facial Action Unit Intensity Estimation and Affect Estimation from Still Images with Multiple Temporal Scale
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Modeling Long-Term Interactions to Enhance Action Recognition
Alejandro Cartas, Petia Radeva, Mariella Dimiccoli

Auto-TLDR; A Hierarchical Long Short-Term Memory Network for Action Recognition in Egocentric Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CAggNet: Crossing Aggregation Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Auto-TLDR; Crossing Aggregation Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Future Urban Scenes Generation through Vehicles Synthesis
Alessandro Simoni, Luca Bergamini, Andrea Palazzi, Simone Calderara, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Predicting the Future of an Urban Scene with a Novel View Synthesis Paradigm
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
HMFlow: Hybrid Matching Optical Flow Network for Small and Fast-Moving Objects
Suihanjin Yu, Youmin Zhang, Chen Wang, Xiao Bai, Liang Zhang, Edwin Hancock

Auto-TLDR; Hybrid Matching Optical Flow Network with Global Matching Component
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Progressive Scene Segmentation Based on Self-Attention Mechanism
Yunyi Pan, Yuan Gan, Kun Liu, Yan Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stage Semantic Scene Segmentation with Self-Attention
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Flow-Guided Spatial Attention Tracking for Egocentric Activity Recognition

Auto-TLDR; flow-guided spatial attention tracking for egocentric activity recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Global Feature Aggregation for Accident Anticipation
Mishal Fatima, Umar Karim Khan, Chong Min Kyung

Auto-TLDR; Feature Aggregation for Predicting Accidents in Video Sequences
CASNet: Common Attribute Support Network for Image Instance and Panoptic Segmentation
Xiaolong Liu, Yuqing Hou, Anbang Yao, Yurong Chen, Keqiang Li

Auto-TLDR; Common Attribute Support Network for instance segmentation and panoptic segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TinyVIRAT: Low-Resolution Video Action Recognition
Ugur Demir, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; TinyVIRAT: A Progressive Generative Approach for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FOANet: A Focus of Attention Network with Application to Myocardium Segmentation
Zhou Zhao, Elodie Puybareau, Nicolas Boutry, Thierry Geraud

Auto-TLDR; FOANet: A Hybrid Loss Function for Myocardium Segmentation of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar