Modeling Long-Term Interactions to Enhance Action Recognition
Alejandro Cartas,
Petia Radeva,
Mariella Dimiccoli

Auto-TLDR; A Hierarchical Long Short-Term Memory Network for Action Recognition in Egocentric Videos
Similar papers
Self-Supervised Joint Encoding of Motion and Appearance for First Person Action Recognition
Mirco Planamente, Andrea Bottino, Barbara Caputo

Auto-TLDR; A Single Stream Architecture for Egocentric Action Recognition from the First-Person Point of View
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Flow-Guided Spatial Attention Tracking for Egocentric Activity Recognition

Auto-TLDR; flow-guided spatial attention tracking for egocentric activity recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Knowledge Distillation for Action Anticipation Via Label Smoothing
Guglielmo Camporese, Pasquale Coscia, Antonino Furnari, Giovanni Maria Farinella, Lamberto Ballan

Auto-TLDR; A Multi-Modal Framework for Action Anticipation using Long Short-Term Memory Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
What and How? Jointly Forecasting Human Action and Pose
Yanjun Zhu, Yanxia Zhang, Qiong Liu, Andreas Girgensohn

Auto-TLDR; Forecasting Human Actions and Motion Trajectories with Joint Action Classification and Pose Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Activity Recognition Using First-Person-View Cameras Based on Sparse Optical Flows
Peng-Yuan Kao, Yan-Jing Lei, Chia-Hao Chang, Chu-Song Chen, Ming-Sui Lee, Yi-Ping Hung

Auto-TLDR; 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Activity Recognition with FPV Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Late Fusion of Bayesian and Convolutional Models for Action Recognition
Camille Maurice, Francisco Madrigal, Frederic Lerasle

Auto-TLDR; Fusion of Deep Neural Network and Bayesian-based Approach for Temporal Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Developing Motion Code Embedding for Action Recognition in Videos
Maxat Alibayev, David Andrea Paulius, Yu Sun
Auto-TLDR; Motion Embedding via Motion Codes for Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Group Activities from Skeletons without Individual Action Labels
Fabio Zappardino, Tiberio Uricchio, Lorenzo Seidenari, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Lean Pose Only for Group Activity Recognition
Attention-Driven Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Bappaditya Debnath, Swagat Kumar, Marry O'Brien, Ardhendu Behera

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Detection-Based Approach to Multiview Action Classification in Infants
Carolina Pacheco, Effrosyni Mavroudi, Elena Kokkoni, Herbert Tanner, Rene Vidal

Auto-TLDR; Multiview Action Classification for Infants in a Pediatric Rehabilitation Environment
Gabriella: An Online System for Real-Time Activity Detection in Untrimmed Security Videos
Mamshad Nayeem Rizve, Ugur Demir, Praveen Praveen Tirupattur, Aayush Jung Rana, Kevin Duarte, Ishan Rajendrakumar Dave, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; Gabriella: A Real-Time Online System for Activity Detection in Surveillance Videos
Inferring Tasks and Fluents in Videos by Learning Causal Relations
Haowen Tang, Ping Wei, Huan Li, Nanning Zheng

Auto-TLDR; Joint Learning of Complex Task and Fluent States in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context Aware Group Activity Recognition
Avijit Dasgupta, C. V. Jawahar, Karteek Alahari

Auto-TLDR; A Two-Stream Architecture for Group Activity Recognition in Multi-Person Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learnable Higher-Order Representation for Action Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Learningable Higher-Order Operations for Spatiotemporal Dynamics in Video Recognition
RWF-2000: An Open Large Scale Video Database for Violence Detection
Ming Cheng, Kunjing Cai, Ming Li

Auto-TLDR; Flow Gated Network for Violence Detection in Surveillance Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RMS-Net: Regression and Masking for Soccer Event Spotting
Matteo Tomei, Lorenzo Baraldi, Simone Calderara, Simone Bronzin, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; An Action Spotting Network for Soccer Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single View Learning in Action Recognition
Gaurvi Goyal, Nicoletta Noceti, Francesca Odone

Auto-TLDR; Cross-View Action Recognition Using Domain Adaptation for Knowledge Transfer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vision-Based Multi-Modal Framework for Action Recognition
Djamila Romaissa Beddiar, Mourad Oussalah, Brahim Nini

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Framework for Human Activity Recognition Using RGB, Depth and Skeleton Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Attention Mechanism for Fine-Grained Classification of Table Tennis Strokes Using a Twin Spatio-Temporal Convolutional Neural Networks
Pierre-Etienne Martin, Jenny Benois-Pineau, Renaud Péteri, Julien Morlier

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Blocks for Action Recognition in Table Tennis Strokes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose-Based Body Language Recognition for Emotion and Psychiatric Symptom Interpretation
Zhengyuan Yang, Amanda Kay, Yuncheng Li, Wendi Cross, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; Body Language Based Emotion Recognition for Psychiatric Symptoms Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Relevance Detection in Cataract Surgery Videos by Spatio-Temporal Action Localization
Negin Ghamsarian, Mario Taschwer, Doris Putzgruber, Stephanie. Sarny, Klaus Schoeffmann

Auto-TLDR; relevance-based retrieval in cataract surgery videos
MFI: Multi-Range Feature Interchange for Video Action Recognition
Sikai Bai, Qi Wang, Xuelong Li

Auto-TLDR; Multi-range Feature Interchange Network for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Oriented Action Recognition for Real-Time Human-Robot Interaction
Ziyang Song, Ziyi Yin, Zejian Yuan, Chong Zhang, Wanchao Chi, Yonggen Ling, Shenghao Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Attention-Oriented Multi-Level Network for Action Recognition in Interaction Scenes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Temporal Binary Representation for Event-Based Action Recognition
Simone Undri Innocenti, Federico Becattini, Federico Pernici, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Binary Representation for Gesture Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Anticipating Activity from Multimodal Signals
Tiziana Rotondo, Giovanni Maria Farinella, Davide Giacalone, Sebastiano Mauro Strano, Valeria Tomaselli, Sebastiano Battiato

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Multimodal Signal Embedding Space for Multi-Action Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Extracting Action Hierarchies from Action Labels and their Use in Deep Action Recognition
Konstadinos Bacharidis, Antonis Argyros

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting the Information Content of Language Label Associations for Human Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Early Wildfire Smoke Detection in Videos
Taanya Gupta, Hengyue Liu, Bir Bhanu

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Spatio-Temporal Video Object Segmentation for Automatic Detection of Smoke in Videos during Forest Fire
ActionSpotter: Deep Reinforcement Learning Framework for Temporal Action Spotting in Videos
Guillaume Vaudaux-Ruth, Adrien Chan-Hon-Tong, Catherine Achard

Auto-TLDR; ActionSpotter: A Reinforcement Learning Algorithm for Action Spotting in Video
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Precise Temporal Action Localization with Quantified Temporal Structure of Actions
Chongkai Lu, Ruimin Li, Hong Fu, Bin Fu, Yihao Wang, Wai Lun Lo, Zheru Chi

Auto-TLDR; Action progression networks for temporal action detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Two-Stream Recurrent Network for Skeleton-Based Human Interaction Recognition
Qianhui Men, Edmond S. L. Ho, Shum Hubert P. H., Howard Leung

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stream Recurrent Neural Network for Human-Human Interaction Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Practical Compressed Video Action Recognition: A Temporal Enhanced Multi-Stream Network
Bing Li, Longteng Kong, Dongming Zhang, Xiuguo Bao, Di Huang, Yunhong Wang

Auto-TLDR; TEMSN: Temporal Enhanced Multi-Stream Network for Compressed Video Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TinyVIRAT: Low-Resolution Video Action Recognition
Ugur Demir, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; TinyVIRAT: A Progressive Generative Approach for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Global Feature Aggregation for Accident Anticipation
Mishal Fatima, Umar Karim Khan, Chong Min Kyung

Auto-TLDR; Feature Aggregation for Predicting Accidents in Video Sequences
You Ought to Look Around: Precise, Large Span Action Detection
Ge Pan, Zhang Han, Fan Yu, Yonghong Song, Yuanlin Zhang, Han Yuan

Auto-TLDR; YOLA: Local Feature Extraction for Action Localization with Variable receptive field
Audio-Video Detection of the Active Speaker in Meetings
Francisco Madrigal, Frederic Lerasle, Lionel Pibre, Isabelle Ferrané

Auto-TLDR; Active Speaker Detection with Visual and Contextual Information from Meeting Context
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Image Sequence Based Cyclist Action Recognition Using Multi-Stream 3D Convolution
Stefan Zernetsch, Steven Schreck, Viktor Kress, Konrad Doll, Bernhard Sick
Auto-TLDR; 3D-ConvNet: A Multi-stream 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Detecting Cyclists in Real World Traffic Situations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Pyramid Hierarchies for Multi-Scale Temporal Action Detection
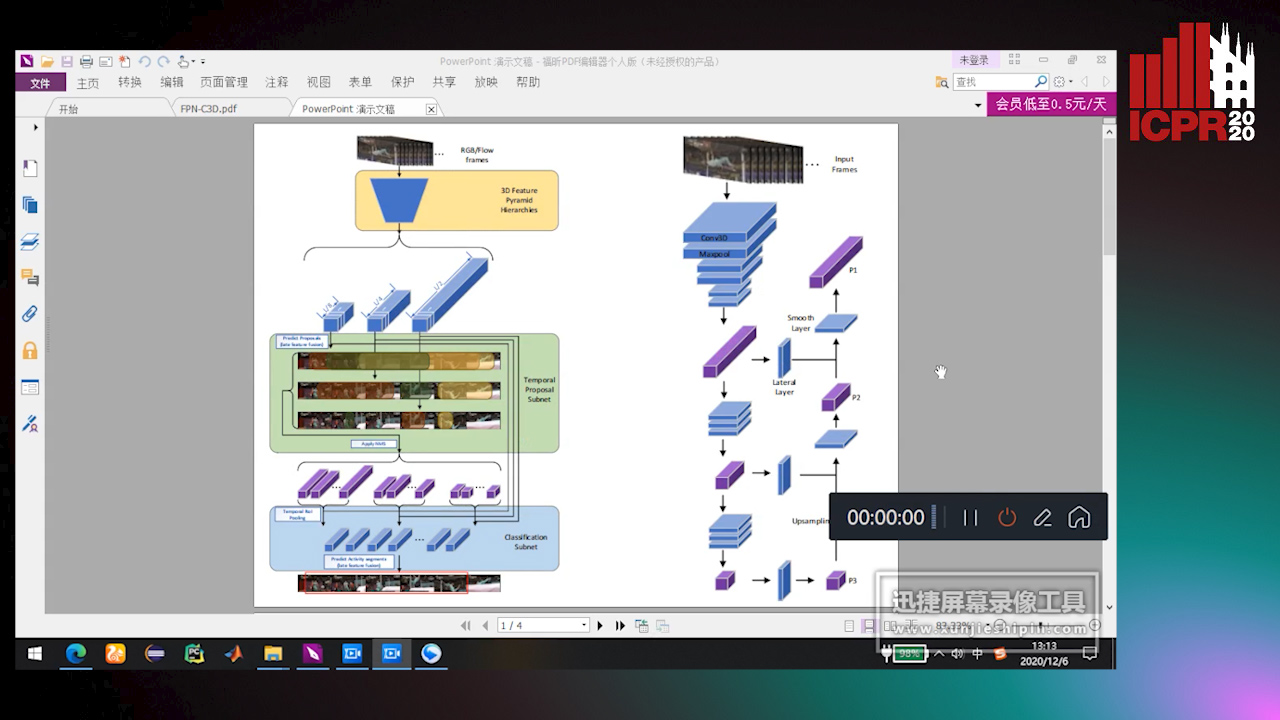
Auto-TLDR; Temporal Action Detection using Pyramid Hierarchies and Multi-scale Feature Maps
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Activity and Relationship Modeling Driven Weakly Supervised Object Detection
Yinlin Li, Yang Qian, Xu Yang, Yuren Zhang
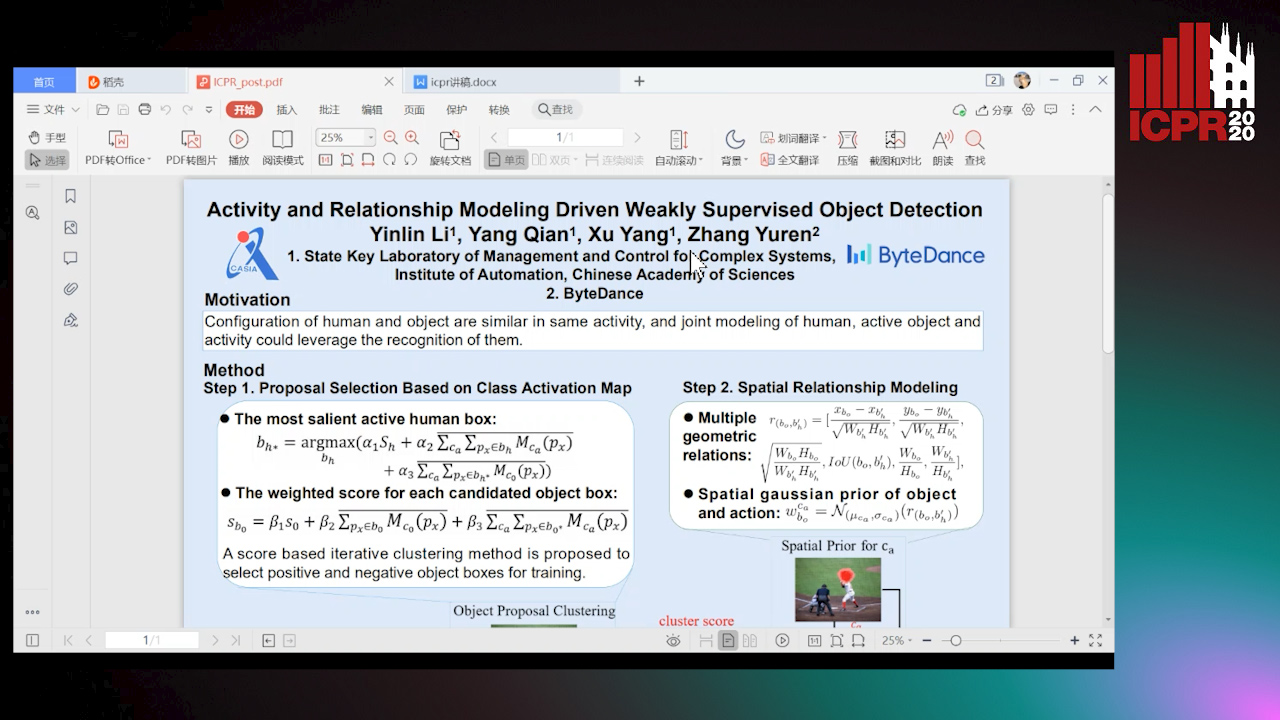
Auto-TLDR; Weakly Supervised Object Detection Using Activity Label and Relationship Modeling
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Dictionaries of Kinematic Primitives for Action Classification
Alessia Vignolo, Nicoletta Noceti, Alessandra Sciutti, Francesca Odone, Giulio Sandini

Auto-TLDR; Action Understanding using Visual Motion Primitives
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Revisiting Sequence-To-Sequence Video Object Segmentation with Multi-Task Loss and Skip-Memory
Fatemeh Azimi, Benjamin Bischke, Sebastian Palacio, Federico Raue, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel

Auto-TLDR; Sequence-to-Sequence Learning for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Semantic Segmentation Using Deep Multi-View Representation Learning
Akrem Sellami, Salvatore Tabbone

Auto-TLDR; Deep Multi-view Representation Learning for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Channel-Wise Dense Connection Graph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition
Michael Lao Banteng, Zhiyong Wu

Auto-TLDR; Two-stream channel-wise dense connection GCN for human action recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Selective Context for Interaction Recognition
Kilickaya Kilickaya, Noureldien Hussein, Efstratios Gavves, Arnold Smeulders

Auto-TLDR; Self-Selective Context for Human-Object Interaction Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Object Deformation and Motion Adaption for Semi-Supervised Video Object Segmentation
Xiaoyang Zheng, Xin Tan, Jianming Guo, Lizhuang Ma

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Video Object Segmentation with Mask-propagation-based Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vertex Feature Encoding and Hierarchical Temporal Modeling in a Spatio-Temporal Graph Convolutional Network for Action Recognition
Konstantinos Papadopoulos, Enjie Ghorbel, Djamila Aouada, Bjorn Ottersten

Auto-TLDR; Spatio-Temporal Graph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recognizing American Sign Language Nonmanual Signal Grammar Errors in Continuous Videos
Elahe Vahdani, Longlong Jing, Ying-Li Tian, Matt Huenerfauth

Auto-TLDR; ASL-HW-RGBD: Recognizing Grammatical Errors in Continuous Sign Language
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
IPN Hand: A Video Dataset and Benchmark for Real-Time Continuous Hand Gesture Recognition
Gibran Benitez-Garcia, Jesus Olivares-Mercado, Gabriel Sanchez-Perez, Keiji Yanai

Auto-TLDR; IPN Hand: A Benchmark Dataset for Continuous Hand Gesture Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar