IPN Hand: A Video Dataset and Benchmark for Real-Time Continuous Hand Gesture Recognition
Gibran Benitez-Garcia,
Jesus Olivares-Mercado,
Gabriel Sanchez-Perez,
Keiji Yanai

Auto-TLDR; IPN Hand: A Benchmark Dataset for Continuous Hand Gesture Recognition
Similar papers
Recognizing American Sign Language Nonmanual Signal Grammar Errors in Continuous Videos
Elahe Vahdani, Longlong Jing, Ying-Li Tian, Matt Huenerfauth

Auto-TLDR; ASL-HW-RGBD: Recognizing Grammatical Errors in Continuous Sign Language
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RWF-2000: An Open Large Scale Video Database for Violence Detection
Ming Cheng, Kunjing Cai, Ming Li

Auto-TLDR; Flow Gated Network for Violence Detection in Surveillance Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose-Based Body Language Recognition for Emotion and Psychiatric Symptom Interpretation
Zhengyuan Yang, Amanda Kay, Yuncheng Li, Wendi Cross, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; Body Language Based Emotion Recognition for Psychiatric Symptoms Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Continuous Sign Language Recognition with Iterative Spatiotemporal Fine-Tuning
Kenessary Koishybay, Medet Mukushev, Anara Sandygulova

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Neural Network for Continuous Sign Language Recognition with Iterative Gloss Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
What and How? Jointly Forecasting Human Action and Pose
Yanjun Zhu, Yanxia Zhang, Qiong Liu, Andreas Girgensohn

Auto-TLDR; Forecasting Human Actions and Motion Trajectories with Joint Action Classification and Pose Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Temporal Binary Representation for Event-Based Action Recognition
Simone Undri Innocenti, Federico Becattini, Federico Pernici, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Binary Representation for Gesture Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Depth Videos for the Classification of Micro-Expressions
Ankith Jain Rakesh Kumar, Bir Bhanu, Christopher Casey, Sierra Cheung, Aaron Seitz

Auto-TLDR; RGB-D Dataset for the Classification of Facial Micro-expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Joint Encoding of Motion and Appearance for First Person Action Recognition
Mirco Planamente, Andrea Bottino, Barbara Caputo

Auto-TLDR; A Single Stream Architecture for Egocentric Action Recognition from the First-Person Point of View
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Oriented Action Recognition for Real-Time Human-Robot Interaction
Ziyang Song, Ziyi Yin, Zejian Yuan, Chong Zhang, Wanchao Chi, Yonggen Ling, Shenghao Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Attention-Oriented Multi-Level Network for Action Recognition in Interaction Scenes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Activity Recognition Using First-Person-View Cameras Based on Sparse Optical Flows
Peng-Yuan Kao, Yan-Jing Lei, Chia-Hao Chang, Chu-Song Chen, Ming-Sui Lee, Yi-Ping Hung

Auto-TLDR; 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Activity Recognition with FPV Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Late Fusion of Bayesian and Convolutional Models for Action Recognition
Camille Maurice, Francisco Madrigal, Frederic Lerasle

Auto-TLDR; Fusion of Deep Neural Network and Bayesian-based Approach for Temporal Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Audio-Video Detection of the Active Speaker in Meetings
Francisco Madrigal, Frederic Lerasle, Lionel Pibre, Isabelle Ferrané

Auto-TLDR; Active Speaker Detection with Visual and Contextual Information from Meeting Context
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Motion Complementary Network for Efficient Action Recognition
Ke Cheng, Yifan Zhang, Chenghua Li, Jian Cheng, Hanqing Lu

Auto-TLDR; Efficient Motion Complementary Network for Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vision-Based Multi-Modal Framework for Action Recognition
Djamila Romaissa Beddiar, Mourad Oussalah, Brahim Nini

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Framework for Human Activity Recognition Using RGB, Depth and Skeleton Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Modeling Long-Term Interactions to Enhance Action Recognition
Alejandro Cartas, Petia Radeva, Mariella Dimiccoli

Auto-TLDR; A Hierarchical Long Short-Term Memory Network for Action Recognition in Egocentric Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single View Learning in Action Recognition
Gaurvi Goyal, Nicoletta Noceti, Francesca Odone

Auto-TLDR; Cross-View Action Recognition Using Domain Adaptation for Knowledge Transfer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature-Supervised Action Modality Transfer
Fida Mohammad Thoker, Cees Snoek

Auto-TLDR; Cross-Modal Action Recognition and Detection in Non-RGB Video Modalities by Learning from Large-Scale Labeled RGB Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Estimation of Clinical Tremor Using Spatio-Temporal Adversarial AutoEncoder
Li Zhang, Vidya Koesmahargyo, Isaac Galatzer-Levy

Auto-TLDR; ST-AAE: Spatio-temporal Adversarial Autoencoder for Clinical Assessment of Hand Tremor Frequency and Severity
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Real-Time Hand Detection Using CFPN on Embedded Systems
Pirdiansyah Hendri, Jun-Wei Hsieh, Ping Yang Chen

Auto-TLDR; Concatenated Feature Pyramid Network for Small Hand Detection on Embedded Devices
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TinyVIRAT: Low-Resolution Video Action Recognition
Ugur Demir, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; TinyVIRAT: A Progressive Generative Approach for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feasibility Study of Using MyoBand for Learning Electronic Keyboard

Auto-TLDR; Autonomous Finger-Based Music Instrument Learning using Electromyography Using MyoBand and Machine Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploiting the Logits: Joint Sign Language Recognition and Spell-Correction
Christina Runkel, Stefan Dorenkamp, Hartmut Bauermeister, Michael Möller

Auto-TLDR; A Convolutional Neural Network for Spell-correction in Sign Language Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Dictionaries of Kinematic Primitives for Action Classification
Alessia Vignolo, Nicoletta Noceti, Alessandra Sciutti, Francesca Odone, Giulio Sandini

Auto-TLDR; Action Understanding using Visual Motion Primitives
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
2D Deep Video Capsule Network with Temporal Shift for Action Recognition
Théo Voillemin, Hazem Wannous, Jean-Philippe Vandeborre

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Shift Module over Capsule Network for Action Recognition in Continuous Videos
Towards Practical Compressed Video Action Recognition: A Temporal Enhanced Multi-Stream Network
Bing Li, Longteng Kong, Dongming Zhang, Xiuguo Bao, Di Huang, Yunhong Wang

Auto-TLDR; TEMSN: Temporal Enhanced Multi-Stream Network for Compressed Video Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Image Sequence Based Cyclist Action Recognition Using Multi-Stream 3D Convolution
Stefan Zernetsch, Steven Schreck, Viktor Kress, Konrad Doll, Bernhard Sick
Auto-TLDR; 3D-ConvNet: A Multi-stream 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Detecting Cyclists in Real World Traffic Situations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Identity-Aware Facial Expression Recognition in Compressed Video
Xiaofeng Liu, Linghao Jin, Xu Han, Jun Lu, Jonghye Woo, Jane You

Auto-TLDR; Exploring Facial Expression Representation in Compressed Video with Mutual Information Minimization
MixTConv: Mixed Temporal Convolutional Kernels for Efficient Action Recognition
Kaiyu Shan, Yongtao Wang, Zhi Tang, Ying Chen, Yangyan Li

Auto-TLDR; Mixed Temporal Convolution for Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Anomaly Detection, Localization and Classification for Railway Inspection
Riccardo Gasparini, Andrea D'Eusanio, Guido Borghi, Stefano Pini, Giuseppe Scaglione, Simone Calderara, Eugenio Fedeli, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Anomaly Detection and Localization using thermal images in the lowlight environment
Human or Machine? It Is Not What You Write, but How You Write It
Luis Leiva, Moises Diaz, M.A. Ferrer, Réjean Plamondon

Auto-TLDR; Behavioral Biometrics via Handwritten Symbols for Identification and Verification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Attention Mechanism for Fine-Grained Classification of Table Tennis Strokes Using a Twin Spatio-Temporal Convolutional Neural Networks
Pierre-Etienne Martin, Jenny Benois-Pineau, Renaud Péteri, Julien Morlier

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Blocks for Action Recognition in Table Tennis Strokes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Developing Motion Code Embedding for Action Recognition in Videos
Maxat Alibayev, David Andrea Paulius, Yu Sun
Auto-TLDR; Motion Embedding via Motion Codes for Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Spatial Bias in Vision-Based Voice Activity Detection
Kalin Stefanov, Mohammad Adiban, Giampiero Salvi
Auto-TLDR; Spatial Bias in Vision-based Voice Activity Detection in Multiparty Human-Human Interactions
A Detection-Based Approach to Multiview Action Classification in Infants
Carolina Pacheco, Effrosyni Mavroudi, Elena Kokkoni, Herbert Tanner, Rene Vidal

Auto-TLDR; Multiview Action Classification for Infants in a Pediatric Rehabilitation Environment
IPT: A Dataset for Identity Preserved Tracking in Closed Domains
Thomas Heitzinger, Martin Kampel
Auto-TLDR; Identity Preserved Tracking Using Depth Data for Privacy and Privacy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Concept Embedding through Canonical Forms: A Case Study on Zero-Shot ASL Recognition
Azamat Kamzin, Apurupa Amperyani, Prasanth Sukhapalli, Ayan Banerjee, Sandeep Gupta

Auto-TLDR; A canonical form of gestures in American Sign Language
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attribute-Based Quality Assessment for Demographic Estimation in Face Videos
Fabiola Becerra-Riera, Annette Morales-González, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Jean-Luc Dugelay
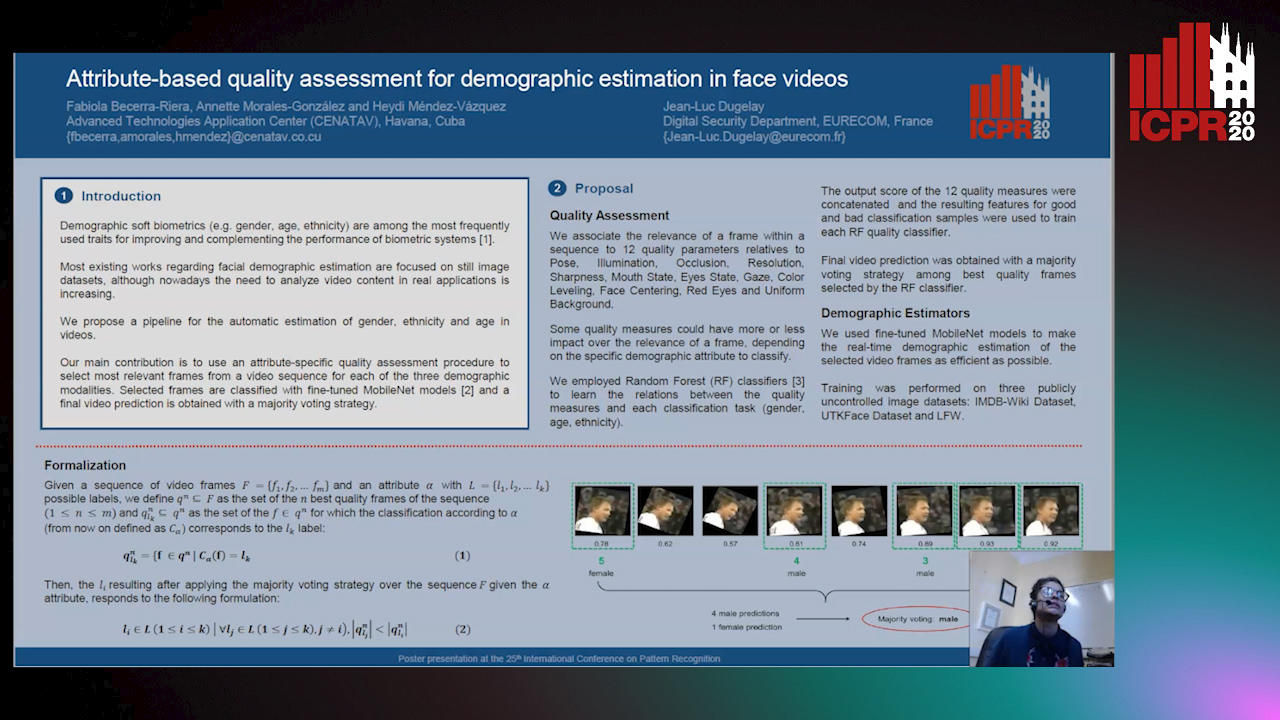
Auto-TLDR; Facial Demographic Estimation in Video Scenarios Using Quality Assessment
Conditional-UNet: A Condition-Aware Deep Model for Coherent Human Activity Recognition from Wearables
Liming Zhang, Wenbin Zhang, Nathalie Japkowicz

Auto-TLDR; Coherent Human Activity Recognition from Multi-Channel Time Series Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Motion U-Net: Multi-Cue Encoder-Decoder Network for Motion Segmentation
Gani Rahmon, Filiz Bunyak, Kannappan Palaniappan
Auto-TLDR; Motion U-Net: A Deep Learning Framework for Robust Moving Object Detection under Challenging Conditions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Driven Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Bappaditya Debnath, Swagat Kumar, Marry O'Brien, Ardhendu Behera

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Prototype-Based Generalized Zero-Shot Learning Framework for Hand Gesture Recognition
Jinting Wu, Yujia Zhang, Xiao-Guang Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Generalized Zero-Shot Learning for Hand Gesture Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Gabriella: An Online System for Real-Time Activity Detection in Untrimmed Security Videos
Mamshad Nayeem Rizve, Ugur Demir, Praveen Praveen Tirupattur, Aayush Jung Rana, Kevin Duarte, Ishan Rajendrakumar Dave, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; Gabriella: A Real-Time Online System for Activity Detection in Surveillance Videos
SL-DML: Signal Level Deep Metric Learning for Multimodal One-Shot Action Recognition
Raphael Memmesheimer, Nick Theisen, Dietrich Paulus

Auto-TLDR; One-Shot Action Recognition using Metric Learning
Learnable Higher-Order Representation for Action Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Learningable Higher-Order Operations for Spatiotemporal Dynamics in Video Recognition
Real Time Fencing Move Classification and Detection at Touch Time During a Fencing Match
Cem Ekin Sunal, Chris G. Willcocks, Boguslaw Obara

Auto-TLDR; Fencing Body Move Classification and Detection Using Deep Learning
A Systematic Investigation on End-To-End Deep Recognition of Grocery Products in the Wild
Marco Leo, Pierluigi Carcagni, Cosimo Distante

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Recognition of Products on grocery shelf images using Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar