Activity Recognition Using First-Person-View Cameras Based on Sparse Optical Flows
Peng-Yuan Kao,
Yan-Jing Lei,
Chia-Hao Chang,
Chu-Song Chen,
Ming-Sui Lee,
Yi-Ping Hung

Auto-TLDR; 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Activity Recognition with FPV Videos
Similar papers
RWF-2000: An Open Large Scale Video Database for Violence Detection
Ming Cheng, Kunjing Cai, Ming Li

Auto-TLDR; Flow Gated Network for Violence Detection in Surveillance Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Modeling Long-Term Interactions to Enhance Action Recognition
Alejandro Cartas, Petia Radeva, Mariella Dimiccoli

Auto-TLDR; A Hierarchical Long Short-Term Memory Network for Action Recognition in Egocentric Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Flow-Guided Spatial Attention Tracking for Egocentric Activity Recognition

Auto-TLDR; flow-guided spatial attention tracking for egocentric activity recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
What and How? Jointly Forecasting Human Action and Pose
Yanjun Zhu, Yanxia Zhang, Qiong Liu, Andreas Girgensohn

Auto-TLDR; Forecasting Human Actions and Motion Trajectories with Joint Action Classification and Pose Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Joint Encoding of Motion and Appearance for First Person Action Recognition
Mirco Planamente, Andrea Bottino, Barbara Caputo

Auto-TLDR; A Single Stream Architecture for Egocentric Action Recognition from the First-Person Point of View
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Late Fusion of Bayesian and Convolutional Models for Action Recognition
Camille Maurice, Francisco Madrigal, Frederic Lerasle

Auto-TLDR; Fusion of Deep Neural Network and Bayesian-based Approach for Temporal Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Driven Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Bappaditya Debnath, Swagat Kumar, Marry O'Brien, Ardhendu Behera

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learnable Higher-Order Representation for Action Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Learningable Higher-Order Operations for Spatiotemporal Dynamics in Video Recognition
MFI: Multi-Range Feature Interchange for Video Action Recognition
Sikai Bai, Qi Wang, Xuelong Li

Auto-TLDR; Multi-range Feature Interchange Network for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vision-Based Multi-Modal Framework for Action Recognition
Djamila Romaissa Beddiar, Mourad Oussalah, Brahim Nini

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Framework for Human Activity Recognition Using RGB, Depth and Skeleton Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Group Activities from Skeletons without Individual Action Labels
Fabio Zappardino, Tiberio Uricchio, Lorenzo Seidenari, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Lean Pose Only for Group Activity Recognition
Single View Learning in Action Recognition
Gaurvi Goyal, Nicoletta Noceti, Francesca Odone

Auto-TLDR; Cross-View Action Recognition Using Domain Adaptation for Knowledge Transfer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TinyVIRAT: Low-Resolution Video Action Recognition
Ugur Demir, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; TinyVIRAT: A Progressive Generative Approach for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Anticipating Activity from Multimodal Signals
Tiziana Rotondo, Giovanni Maria Farinella, Davide Giacalone, Sebastiano Mauro Strano, Valeria Tomaselli, Sebastiano Battiato

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Multimodal Signal Embedding Space for Multi-Action Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DeepPear: Deep Pose Estimation and Action Recognition
Wen-Jiin Tsai, You-Ying Jhuang

Auto-TLDR; Human Action Recognition Using RGB Video Using 3D Human Pose and Appearance Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RMS-Net: Regression and Masking for Soccer Event Spotting
Matteo Tomei, Lorenzo Baraldi, Simone Calderara, Simone Bronzin, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; An Action Spotting Network for Soccer Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Gabriella: An Online System for Real-Time Activity Detection in Untrimmed Security Videos
Mamshad Nayeem Rizve, Ugur Demir, Praveen Praveen Tirupattur, Aayush Jung Rana, Kevin Duarte, Ishan Rajendrakumar Dave, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; Gabriella: A Real-Time Online System for Activity Detection in Surveillance Videos
A Two-Stream Recurrent Network for Skeleton-Based Human Interaction Recognition
Qianhui Men, Edmond S. L. Ho, Shum Hubert P. H., Howard Leung

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stream Recurrent Neural Network for Human-Human Interaction Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
IPN Hand: A Video Dataset and Benchmark for Real-Time Continuous Hand Gesture Recognition
Gibran Benitez-Garcia, Jesus Olivares-Mercado, Gabriel Sanchez-Perez, Keiji Yanai

Auto-TLDR; IPN Hand: A Benchmark Dataset for Continuous Hand Gesture Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Pyramid Hierarchies for Multi-Scale Temporal Action Detection
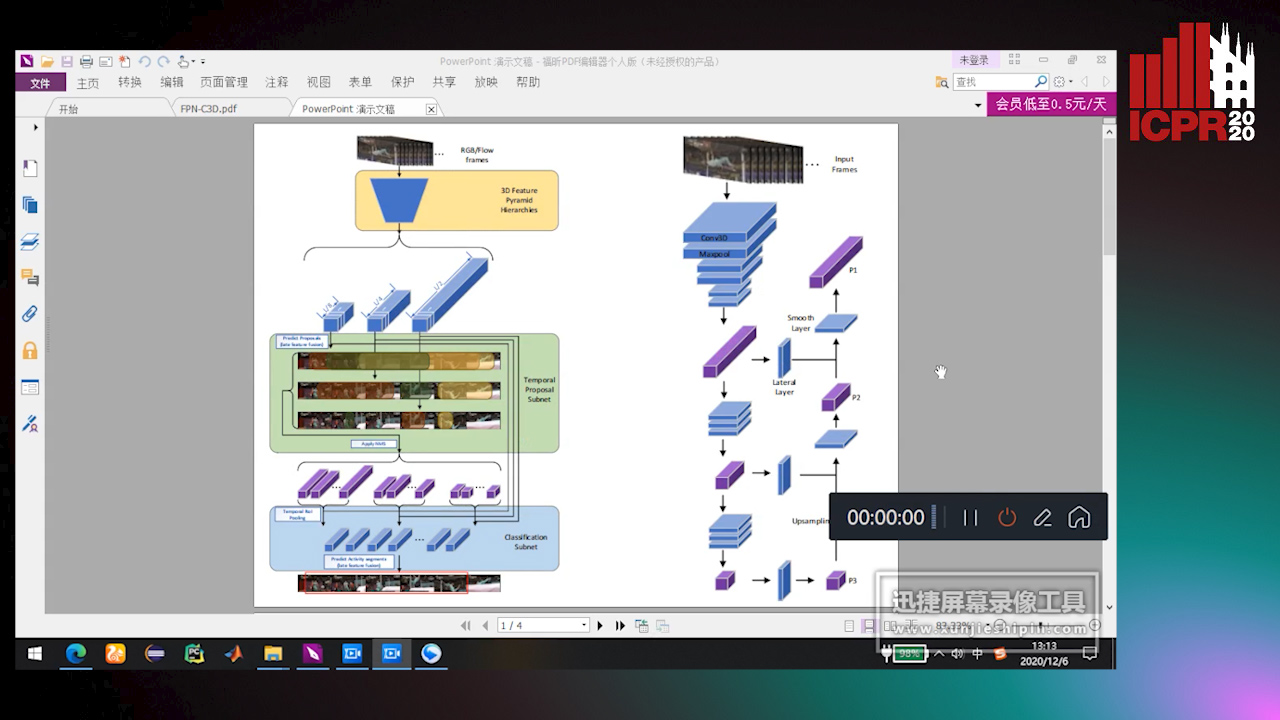
Auto-TLDR; Temporal Action Detection using Pyramid Hierarchies and Multi-scale Feature Maps
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
From Human Pose to On-Body Devices for Human-Activity Recognition
Fernando Moya Rueda, Gernot Fink
Auto-TLDR; Transfer Learning from Human Pose Estimation for Human Activity Recognition using Inertial Measurements from On-Body Devices
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Temporal Binary Representation for Event-Based Action Recognition
Simone Undri Innocenti, Federico Becattini, Federico Pernici, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Binary Representation for Gesture Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Estimation of Clinical Tremor Using Spatio-Temporal Adversarial AutoEncoder
Li Zhang, Vidya Koesmahargyo, Isaac Galatzer-Levy

Auto-TLDR; ST-AAE: Spatio-temporal Adversarial Autoencoder for Clinical Assessment of Hand Tremor Frequency and Severity
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Space-Time Domain Tensor Neural Networks: An Application on Human Pose Classification
Konstantinos Makantasis, Athanasios Voulodimos, Anastasios Doulamis, Nikolaos Doulamis, Nikolaos Bakalos

Auto-TLDR; Tensor-Based Neural Network for Spatiotemporal Pose Classifiaction using Three-Dimensional Skeleton Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose-Aware Multi-Feature Fusion Network for Driver Distraction Recognition
Mingyan Wu, Xi Zhang, Linlin Shen, Hang Yu

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Feature Fusion Network for Distracted Driving Detection using Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SL-DML: Signal Level Deep Metric Learning for Multimodal One-Shot Action Recognition
Raphael Memmesheimer, Nick Theisen, Dietrich Paulus

Auto-TLDR; One-Shot Action Recognition using Metric Learning
3D Attention Mechanism for Fine-Grained Classification of Table Tennis Strokes Using a Twin Spatio-Temporal Convolutional Neural Networks
Pierre-Etienne Martin, Jenny Benois-Pineau, Renaud Péteri, Julien Morlier

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Blocks for Action Recognition in Table Tennis Strokes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Detection-Based Approach to Multiview Action Classification in Infants
Carolina Pacheco, Effrosyni Mavroudi, Elena Kokkoni, Herbert Tanner, Rene Vidal

Auto-TLDR; Multiview Action Classification for Infants in a Pediatric Rehabilitation Environment
Residual Learning of Video Frame Interpolation Using Convolutional LSTM
Auto-TLDR; Video Frame Interpolation Using Residual Learning and Convolutional LSTMs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context Aware Group Activity Recognition
Avijit Dasgupta, C. V. Jawahar, Karteek Alahari

Auto-TLDR; A Two-Stream Architecture for Group Activity Recognition in Multi-Person Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Multi-Task Neural Network for Action Recognition with 3D Key-Points
Rongxiao Tang, Wang Luyang, Zhenhua Guo

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Neural Network for Action Recognition and 3D Human Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vertex Feature Encoding and Hierarchical Temporal Modeling in a Spatio-Temporal Graph Convolutional Network for Action Recognition
Konstantinos Papadopoulos, Enjie Ghorbel, Djamila Aouada, Bjorn Ottersten

Auto-TLDR; Spatio-Temporal Graph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Inferring Tasks and Fluents in Videos by Learning Causal Relations
Haowen Tang, Ping Wei, Huan Li, Nanning Zheng

Auto-TLDR; Joint Learning of Complex Task and Fluent States in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Developing Motion Code Embedding for Action Recognition in Videos
Maxat Alibayev, David Andrea Paulius, Yu Sun
Auto-TLDR; Motion Embedding via Motion Codes for Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Channel-Wise Dense Connection Graph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition
Michael Lao Banteng, Zhiyong Wu

Auto-TLDR; Two-stream channel-wise dense connection GCN for human action recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PHNet: Parasite-Host Network for Video Crowd Counting
Shiqiao Meng, Jiajie Li, Weiwei Guo, Jinfeng Jiang, Lai Ye

Auto-TLDR; PHNet: A Parasite-Host Network for Video Crowd Counting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Feature Fusion Network for Gaze Tracking in Mobile Tablets
Yiwei Bao, Yihua Cheng, Yunfei Liu, Feng Lu

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Feature Fusion Network for Multi-stream Gaze Estimation in Mobile Tablets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Practical Compressed Video Action Recognition: A Temporal Enhanced Multi-Stream Network
Bing Li, Longteng Kong, Dongming Zhang, Xiuguo Bao, Di Huang, Yunhong Wang

Auto-TLDR; TEMSN: Temporal Enhanced Multi-Stream Network for Compressed Video Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TSMSAN: A Three-Stream Multi-Scale Attentive Network for Video Saliency Detection
Jingwen Yang, Guanwen Zhang, Wei Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Three-stream Multi-scale attentive network for video saliency detection in dynamic scenes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SAT-Net: Self-Attention and Temporal Fusion for Facial Action Unit Detection
Zhihua Li, Zheng Zhang, Lijun Yin

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Fusion and Self-Attention Network for Facial Action Unit Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Motion Complementary Network for Efficient Action Recognition
Ke Cheng, Yifan Zhang, Chenghua Li, Jian Cheng, Hanqing Lu

Auto-TLDR; Efficient Motion Complementary Network for Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Text Synopsis Generation for Egocentric Videos
Aidean Sharghi, Niels Lobo, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; Egocentric Video Summarization Using Multi-task Learning for End-to-End Learning
Knowledge Distillation for Action Anticipation Via Label Smoothing
Guglielmo Camporese, Pasquale Coscia, Antonino Furnari, Giovanni Maria Farinella, Lamberto Ballan

Auto-TLDR; A Multi-Modal Framework for Action Anticipation using Long Short-Term Memory Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploring Severe Occlusion: Multi-Person 3D Pose Estimation with Gated Convolution
Renshu Gu, Gaoang Wang, Jenq-Neng Hwang

Auto-TLDR; 3D Human Pose Estimation for Multi-Human Videos with Occlusion
Exploring Spatial-Temporal Representations for fNIRS-based Intimacy Detection via an Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
Chao Li, Qian Zhang, Ziping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Intimate Relationship Prediction by Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network Using Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Depth Videos for the Classification of Micro-Expressions
Ankith Jain Rakesh Kumar, Bir Bhanu, Christopher Casey, Sierra Cheung, Aaron Seitz

Auto-TLDR; RGB-D Dataset for the Classification of Facial Micro-expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar