Anticipating Activity from Multimodal Signals
Tiziana Rotondo,
Giovanni Maria Farinella,
Davide Giacalone,
Sebastiano Mauro Strano,
Valeria Tomaselli,
Sebastiano Battiato

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Multimodal Signal Embedding Space for Multi-Action Prediction
Similar papers
Knowledge Distillation for Action Anticipation Via Label Smoothing
Guglielmo Camporese, Pasquale Coscia, Antonino Furnari, Giovanni Maria Farinella, Lamberto Ballan

Auto-TLDR; A Multi-Modal Framework for Action Anticipation using Long Short-Term Memory Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vision-Based Multi-Modal Framework for Action Recognition
Djamila Romaissa Beddiar, Mourad Oussalah, Brahim Nini

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Framework for Human Activity Recognition Using RGB, Depth and Skeleton Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
What and How? Jointly Forecasting Human Action and Pose
Yanjun Zhu, Yanxia Zhang, Qiong Liu, Andreas Girgensohn

Auto-TLDR; Forecasting Human Actions and Motion Trajectories with Joint Action Classification and Pose Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SL-DML: Signal Level Deep Metric Learning for Multimodal One-Shot Action Recognition
Raphael Memmesheimer, Nick Theisen, Dietrich Paulus

Auto-TLDR; One-Shot Action Recognition using Metric Learning
From Human Pose to On-Body Devices for Human-Activity Recognition
Fernando Moya Rueda, Gernot Fink
Auto-TLDR; Transfer Learning from Human Pose Estimation for Human Activity Recognition using Inertial Measurements from On-Body Devices
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Modeling Long-Term Interactions to Enhance Action Recognition
Alejandro Cartas, Petia Radeva, Mariella Dimiccoli

Auto-TLDR; A Hierarchical Long Short-Term Memory Network for Action Recognition in Egocentric Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Activity Recognition Using First-Person-View Cameras Based on Sparse Optical Flows
Peng-Yuan Kao, Yan-Jing Lei, Chia-Hao Chang, Chu-Song Chen, Ming-Sui Lee, Yi-Ping Hung

Auto-TLDR; 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Activity Recognition with FPV Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Personalized Models in Human Activity Recognition Using Deep Learning
Hamza Amrani, Daniela Micucci, Paolo Napoletano

Auto-TLDR; Incremental Learning for Personalized Human Activity Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Joint Encoding of Motion and Appearance for First Person Action Recognition
Mirco Planamente, Andrea Bottino, Barbara Caputo

Auto-TLDR; A Single Stream Architecture for Egocentric Action Recognition from the First-Person Point of View
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Dictionaries of Kinematic Primitives for Action Classification
Alessia Vignolo, Nicoletta Noceti, Alessandra Sciutti, Francesca Odone, Giulio Sandini

Auto-TLDR; Action Understanding using Visual Motion Primitives
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Space-Time Domain Tensor Neural Networks: An Application on Human Pose Classification
Konstantinos Makantasis, Athanasios Voulodimos, Anastasios Doulamis, Nikolaos Doulamis, Nikolaos Bakalos

Auto-TLDR; Tensor-Based Neural Network for Spatiotemporal Pose Classifiaction using Three-Dimensional Skeleton Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Detection-Based Approach to Multiview Action Classification in Infants
Carolina Pacheco, Effrosyni Mavroudi, Elena Kokkoni, Herbert Tanner, Rene Vidal

Auto-TLDR; Multiview Action Classification for Infants in a Pediatric Rehabilitation Environment
Pose-Based Body Language Recognition for Emotion and Psychiatric Symptom Interpretation
Zhengyuan Yang, Amanda Kay, Yuncheng Li, Wendi Cross, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; Body Language Based Emotion Recognition for Psychiatric Symptoms Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Translation Resilient Opportunistic WiFi Sensing
Mohammud Junaid Bocus, Wenda Li, Jonas Paulavičius, Ryan Mcconville, Raul Santos-Rodriguez, Kevin Chetty, Robert Piechocki
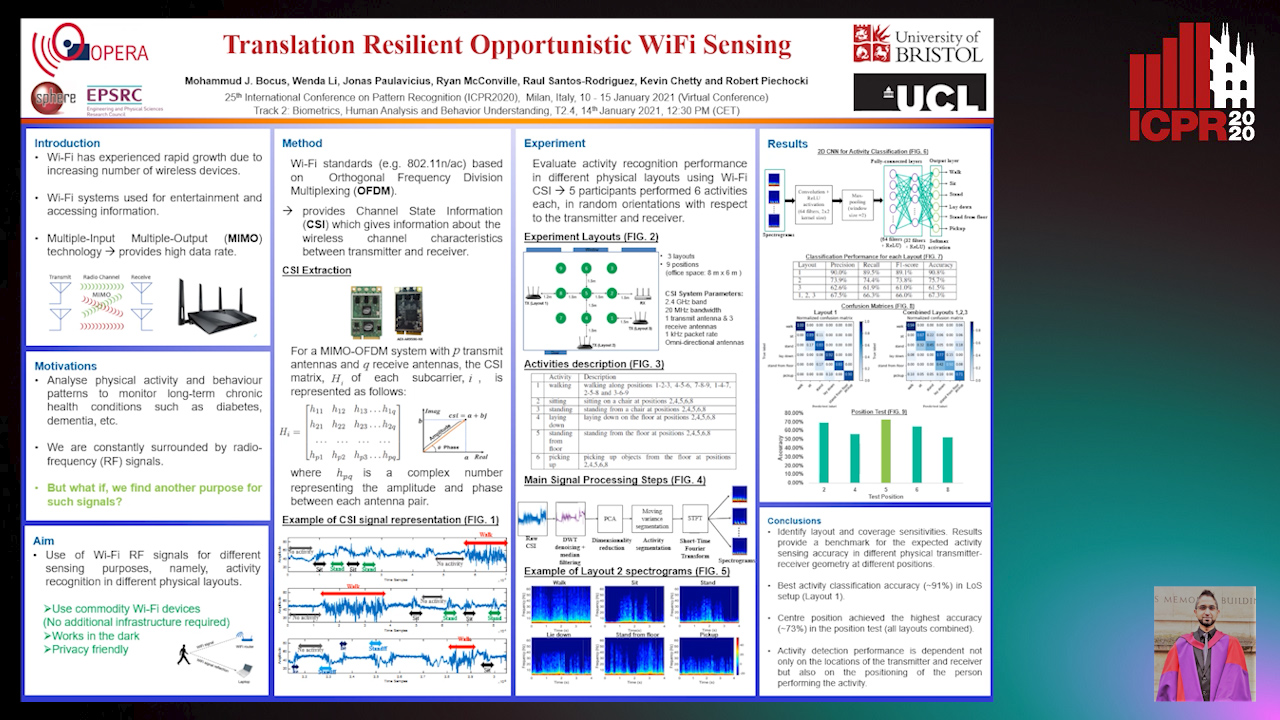
Auto-TLDR; Activity Recognition using Fine-Grained WiFi Channel State Information using WiFi CSI
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Inferring Tasks and Fluents in Videos by Learning Causal Relations
Haowen Tang, Ping Wei, Huan Li, Nanning Zheng

Auto-TLDR; Joint Learning of Complex Task and Fluent States in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Co-Segmentation for Athlete Movements and Live Commentaries Using Crossmodal Temporal Proximity
Yasunori Ohishi, Yuki Tanaka, Kunio Kashino

Auto-TLDR; A guided attention scheme for audio-visual co-segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Conditional-UNet: A Condition-Aware Deep Model for Coherent Human Activity Recognition from Wearables
Liming Zhang, Wenbin Zhang, Nathalie Japkowicz

Auto-TLDR; Coherent Human Activity Recognition from Multi-Channel Time Series Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Electroencephalography Signal Processing Based on Textural Features for Monitoring the Driver’s State by a Brain-Computer Interface
Giulia Orrù, Marco Micheletto, Fabio Terranova, Gian Luca Marcialis

Auto-TLDR; One-dimensional Local Binary Pattern Algorithm for Estimating Driver Vigilance in a Brain-Computer Interface System
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Audio-Video Detection of the Active Speaker in Meetings
Francisco Madrigal, Frederic Lerasle, Lionel Pibre, Isabelle Ferrané

Auto-TLDR; Active Speaker Detection with Visual and Contextual Information from Meeting Context
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Developing Motion Code Embedding for Action Recognition in Videos
Maxat Alibayev, David Andrea Paulius, Yu Sun
Auto-TLDR; Motion Embedding via Motion Codes for Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single View Learning in Action Recognition
Gaurvi Goyal, Nicoletta Noceti, Francesca Odone

Auto-TLDR; Cross-View Action Recognition Using Domain Adaptation for Knowledge Transfer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ESResNet: Environmental Sound Classification Based on Visual Domain Models
Andrey Guzhov, Federico Raue, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel
Auto-TLDR; Environmental Sound Classification with Short-Time Fourier Transform Spectrograms
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Late Fusion of Bayesian and Convolutional Models for Action Recognition
Camille Maurice, Francisco Madrigal, Frederic Lerasle

Auto-TLDR; Fusion of Deep Neural Network and Bayesian-based Approach for Temporal Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Spatial Bias in Vision-Based Voice Activity Detection
Kalin Stefanov, Mohammad Adiban, Giampiero Salvi
Auto-TLDR; Spatial Bias in Vision-based Voice Activity Detection in Multiparty Human-Human Interactions
RWF-2000: An Open Large Scale Video Database for Violence Detection
Ming Cheng, Kunjing Cai, Ming Li

Auto-TLDR; Flow Gated Network for Violence Detection in Surveillance Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fall Detection by Human Pose Estimation and Kinematic Theory
Vincenzo Dentamaro, Donato Impedovo, Giuseppe Pirlo

Auto-TLDR; A Decision Support System for Automatic Fall Detection on Le2i and URFD Datasets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Multimodal Attention for Deep Video Summarization
Melissa Sanabria, Frederic Precioso, Thomas Menguy

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Summarization of Professional Soccer Matches Using Event-Stream Data and Multi- Instance Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single-Modal Incremental Terrain Clustering from Self-Supervised Audio-Visual Feature Learning
Reina Ishikawa, Ryo Hachiuma, Akiyoshi Kurobe, Hideo Saito

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Variational Autoencoder for Terrain Type Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Flow-Guided Spatial Attention Tracking for Egocentric Activity Recognition

Auto-TLDR; flow-guided spatial attention tracking for egocentric activity recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DenseRecognition of Spoken Languages
Jaybrata Chakraborty, Bappaditya Chakraborty, Ujjwal Bhattacharya

Auto-TLDR; DenseNet: A Dense Convolutional Network Architecture for Speech Recognition in Indian Languages
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Location Prediction in Real Homes of Older Adults based on K-Means in Low-Resolution Depth Videos
Simon Simonsson, Flávia Dias Casagrande, Evi Zouganeli

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Learning for Location Recognition and Prediction in Smart Homes using Depth Video Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
One-Shot Representational Learning for Joint Biometric and Device Authentication

Auto-TLDR; Joint Biometric and Device Recognition from a Single Biometric Image
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
IPN Hand: A Video Dataset and Benchmark for Real-Time Continuous Hand Gesture Recognition
Gibran Benitez-Garcia, Jesus Olivares-Mercado, Gabriel Sanchez-Perez, Keiji Yanai

Auto-TLDR; IPN Hand: A Benchmark Dataset for Continuous Hand Gesture Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploring Spatial-Temporal Representations for fNIRS-based Intimacy Detection via an Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
Chao Li, Qian Zhang, Ziping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Intimate Relationship Prediction by Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network Using Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Ballroom Dance Recognition from Audio Recordings
Tomas Pavlin, Jan Cech, Jiri Matas

Auto-TLDR; A CNN-based approach to classify ballroom dances given audio recordings
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Driven Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Bappaditya Debnath, Swagat Kumar, Marry O'Brien, Ardhendu Behera

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Visual Oriented Encoder: Integrating Multimodal and Multi-Scale Contexts for Video Captioning

Auto-TLDR; Visual Oriented Encoder for Video Captioning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Person Recognition with HGR Maximal Correlation on Multimodal Data
Yihua Liang, Fei Ma, Yang Li, Shao-Lun Huang
Auto-TLDR; A correlation-based multimodal person recognition framework that learns discriminative embeddings of persons by joint learning visual features and audio features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AttendAffectNet: Self-Attention Based Networks for Predicting Affective Responses from Movies
Thi Phuong Thao Ha, Bt Balamurali, Herremans Dorien, Roig Gemma

Auto-TLDR; AttendAffectNet: A Self-Attention Based Network for Emotion Prediction from Movies
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Better Prior Knowledge Improves Human-Pose-Based Extrinsic Camera Calibration
Olivier Moliner, Sangxia Huang, Kalle Åström

Auto-TLDR; Improving Human-pose-based Extrinsic Calibration for Multi-Camera Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Subspace Clustering for Action Recognition with Covariance Representations and Temporal Pruning
Giancarlo Paoletti, Jacopo Cavazza, Cigdem Beyan, Alessio Del Bue

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Learning for Human Action Recognition from Skeletal Data
Improving Mix-And-Separate Training in Audio-Visual Sound Source Separation with an Object Prior
Quan Nguyen, Simone Frintrop, Timo Gerkmann, Mikko Lauri, Julius Richter
Auto-TLDR; Object-Prior: Learning the 1-to-1 correspondence between visual and audio signals by audio- visual sound source methods
Mutual Alignment between Audiovisual Features for End-To-End Audiovisual Speech Recognition
Hong Liu, Yawei Wang, Bing Yang

Auto-TLDR; Mutual Iterative Attention for Audio Visual Speech Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
End-To-End Triplet Loss Based Emotion Embedding System for Speech Emotion Recognition
Puneet Kumar, Sidharth Jain, Balasubramanian Raman, Partha Pratim Roy, Masakazu Iwamura

Auto-TLDR; End-to-End Neural Embedding System for Speech Emotion Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Which are the factors affecting the performance of audio surveillance systems?
Antonio Greco, Antonio Roberto, Alessia Saggese, Mario Vento

Auto-TLDR; Sound Event Recognition Using Convolutional Neural Networks and Visual Representations on MIVIA Audio Events
Temporal Binary Representation for Event-Based Action Recognition
Simone Undri Innocenti, Federico Becattini, Federico Pernici, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Binary Representation for Gesture Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar