Fall Detection by Human Pose Estimation and Kinematic Theory
Vincenzo Dentamaro,
Donato Impedovo,
Giuseppe Pirlo

Auto-TLDR; A Decision Support System for Automatic Fall Detection on Le2i and URFD Datasets
Similar papers
Video Analytics Gait Trend Measurement for Fall Prevention and Health Monitoring
Lawrence O'Gorman, Xinyi Liu, Md Imran Sarker, Mariofanna Milanova

Auto-TLDR; Towards Health Monitoring of Gait with Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Transfer Learning for Alzheimer’s Disease Detection
Nicole Cilia, Claudio De Stefano, Francesco Fontanella, Claudio Marrocco, Mario Molinara, Alessandra Scotto Di Freca

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Detection of Handwriting Alterations for Alzheimer's Disease Diagnosis using Dynamic Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
IPT: A Dataset for Identity Preserved Tracking in Closed Domains
Thomas Heitzinger, Martin Kampel
Auto-TLDR; Identity Preserved Tracking Using Depth Data for Privacy and Privacy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Dictionaries of Kinematic Primitives for Action Classification
Alessia Vignolo, Nicoletta Noceti, Alessandra Sciutti, Francesca Odone, Giulio Sandini

Auto-TLDR; Action Understanding using Visual Motion Primitives
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Classification of Human Granulosa Cells in Assisted Reproductive Technology Using Vibrational Spectroscopy Imaging
Marina Paolanti, Emanuele Frontoni, Giorgia Gioacchini, Giorgini Elisabetta, Notarstefano Valentina, Zacà Carlotta, Carnevali Oliana, Andrea Borini, Marco Mameli

Auto-TLDR; Predicting Oocyte Quality in Assisted Reproductive Technology Using Machine Learning Techniques
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Anomalies from Video-Sequences: A Novel Descriptor
Giulia Orrù, Davide Ghiani, Maura Pintor, Gian Luca Marcialis, Fabio Roli

Auto-TLDR; Trit-based Measurement of Group Dynamics for Crowd Behavior Analysis and Anomaly Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rotational Adjoint Methods for Learning-Free 3D Human Pose Estimation from IMU Data
Caterina Emilia Agelide Buizza, Yiannis Demiris
Auto-TLDR; Learning-free 3D Human Pose Estimation from Inertial Measurement Unit Data
Anticipating Activity from Multimodal Signals
Tiziana Rotondo, Giovanni Maria Farinella, Davide Giacalone, Sebastiano Mauro Strano, Valeria Tomaselli, Sebastiano Battiato

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Multimodal Signal Embedding Space for Multi-Action Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose-Based Body Language Recognition for Emotion and Psychiatric Symptom Interpretation
Zhengyuan Yang, Amanda Kay, Yuncheng Li, Wendi Cross, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; Body Language Based Emotion Recognition for Psychiatric Symptoms Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RefiNet: 3D Human Pose Refinement with Depth Maps
Andrea D'Eusanio, Stefano Pini, Guido Borghi, Roberto Vezzani, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; RefiNet: A Multi-stage Framework for 3D Human Pose Estimation
What and How? Jointly Forecasting Human Action and Pose
Yanjun Zhu, Yanxia Zhang, Qiong Liu, Andreas Girgensohn

Auto-TLDR; Forecasting Human Actions and Motion Trajectories with Joint Action Classification and Pose Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Raw Eye Tracking Data Segmentation, Generation, and Reconstruction
Wolfgang Fuhl, Yao Rong, Enkelejda Kasneci
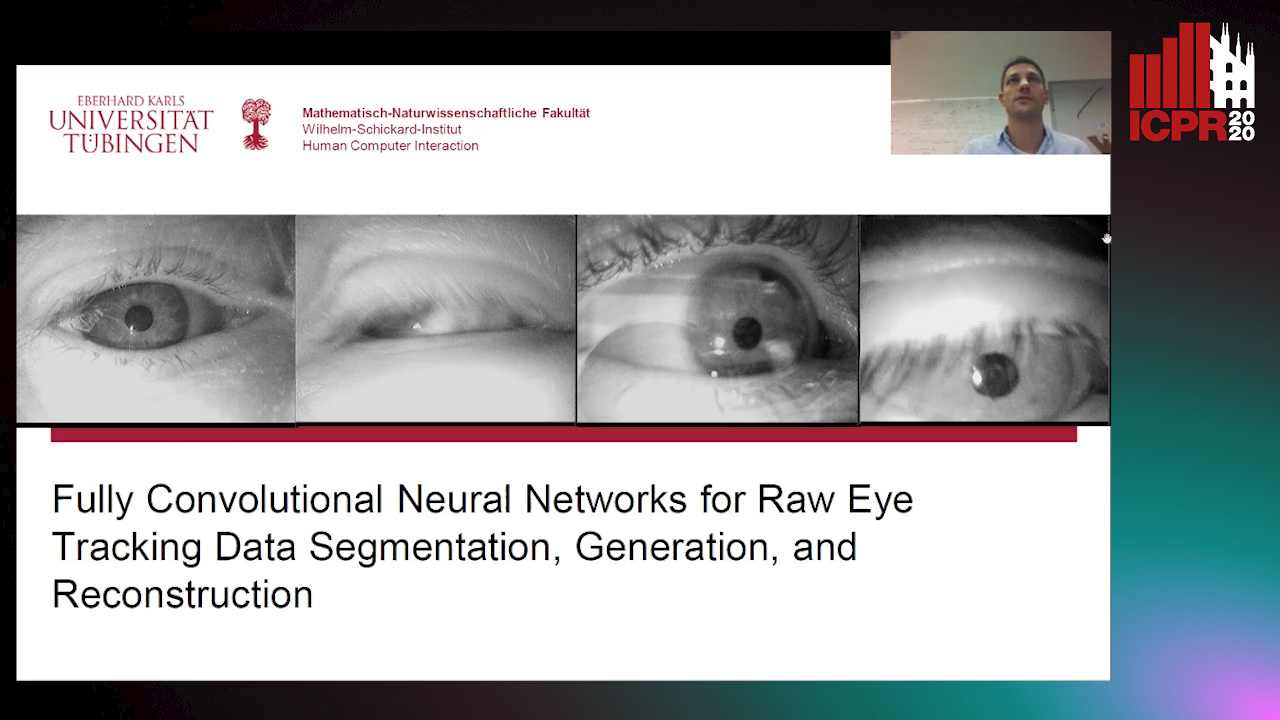
Auto-TLDR; Semantic Segmentation of Eye Tracking Data with Fully Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Depth Videos for the Classification of Micro-Expressions
Ankith Jain Rakesh Kumar, Bir Bhanu, Christopher Casey, Sierra Cheung, Aaron Seitz

Auto-TLDR; RGB-D Dataset for the Classification of Facial Micro-expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Early Wildfire Smoke Detection in Videos
Taanya Gupta, Hengyue Liu, Bir Bhanu

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Spatio-Temporal Video Object Segmentation for Automatic Detection of Smoke in Videos during Forest Fire
Electroencephalography Signal Processing Based on Textural Features for Monitoring the Driver’s State by a Brain-Computer Interface
Giulia Orrù, Marco Micheletto, Fabio Terranova, Gian Luca Marcialis

Auto-TLDR; One-dimensional Local Binary Pattern Algorithm for Estimating Driver Vigilance in a Brain-Computer Interface System
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Tuberculosis Detection Using Chest X-Ray Analysis with Position Enhanced Structural Information
Hermann Jepdjio Nkouanga, Szilard Vajda
Auto-TLDR; Automatic Chest X-ray Screening for Tuberculosis in Rural Population using Localized Region on Interest
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Gender Classification Using Video Sequences of Body Sway Recorded by Overhead Camera
Takuya Kamitani, Yuta Yamaguchi, Shintaro Nakatani, Masashi Nishiyama, Yoshio Iwai

Auto-TLDR; Spatio-Temporal Feature for Gender Classification of a Standing Person Using Body Stance Using Time-Series Signals
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Motion and Region Aware Adversarial Learning for Fall Detection with Thermal Imaging
Vineet Mehta, Abhinav Dhall, Sujata Pal, Shehroz Khan

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Fall Detection with Adversarial Network using Thermal Imaging Camera
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vision-Based Multi-Modal Framework for Action Recognition
Djamila Romaissa Beddiar, Mourad Oussalah, Brahim Nini

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Framework for Human Activity Recognition Using RGB, Depth and Skeleton Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Location Prediction in Real Homes of Older Adults based on K-Means in Low-Resolution Depth Videos
Simon Simonsson, Flávia Dias Casagrande, Evi Zouganeli

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Learning for Location Recognition and Prediction in Smart Homes using Depth Video Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Space-Time Domain Tensor Neural Networks: An Application on Human Pose Classification
Konstantinos Makantasis, Athanasios Voulodimos, Anastasios Doulamis, Nikolaos Doulamis, Nikolaos Bakalos

Auto-TLDR; Tensor-Based Neural Network for Spatiotemporal Pose Classifiaction using Three-Dimensional Skeleton Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Influence of Event Duration on Automatic Wheeze Classification
Bruno M Rocha, Diogo Pessoa, Alda Marques, Paulo Carvalho, Rui Pedro Paiva

Auto-TLDR; Experimental Design of the Non-wheeze Class for Wheeze Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RWF-2000: An Open Large Scale Video Database for Violence Detection
Ming Cheng, Kunjing Cai, Ming Li

Auto-TLDR; Flow Gated Network for Violence Detection in Surveillance Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Late Fusion of Bayesian and Convolutional Models for Action Recognition
Camille Maurice, Francisco Madrigal, Frederic Lerasle

Auto-TLDR; Fusion of Deep Neural Network and Bayesian-based Approach for Temporal Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Systematic Investigation on Deep Architectures for Automatic Skin Lesions Classification
Pierluigi Carcagni, Marco Leo, Andrea Cuna, Giuseppe Celeste, Cosimo Distante

Auto-TLDR; RegNet: Deep Investigation of Convolutional Neural Networks for Automatic Classification of Skin Lesions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real-Time Driver Drowsiness Detection Using Facial Action Units
Malaika Vijay, Nandagopal Netrakanti Vinayak, Maanvi Nunna, Subramanyam Natarajan

Auto-TLDR; Real-Time Detection of Driver Drowsiness using Facial Action Units using Extreme Gradient Boosting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Better Prior Knowledge Improves Human-Pose-Based Extrinsic Camera Calibration
Olivier Moliner, Sangxia Huang, Kalle Åström

Auto-TLDR; Improving Human-pose-based Extrinsic Calibration for Multi-Camera Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Detection-Based Approach to Multiview Action Classification in Infants
Carolina Pacheco, Effrosyni Mavroudi, Elena Kokkoni, Herbert Tanner, Rene Vidal

Auto-TLDR; Multiview Action Classification for Infants in a Pediatric Rehabilitation Environment
Extraction and Analysis of 3D Kinematic Parameters of Table Tennis Ball from a Single Camera
Jordan Calandre, Renaud Péteri, Laurent Mascarilla, Benoit Tremblais
Auto-TLDR; 3D Ball Trajectories Analysis using a Single Camera for Sport Gesture Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
JT-MGCN: Joint-Temporal Motion Graph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Joint-temporal Motion Graph Convolutional Networks for Action Recognition
Conditional-UNet: A Condition-Aware Deep Model for Coherent Human Activity Recognition from Wearables
Liming Zhang, Wenbin Zhang, Nathalie Japkowicz

Auto-TLDR; Coherent Human Activity Recognition from Multi-Channel Time Series Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
VR Sickness Assessment with Perception Prior and Hybrid Temporal Features
Po-Chen Kuo, Li-Chung Chuang, Dong-Yi Lin, Ming-Sui Lee

Auto-TLDR; A novel content-based VR sickness assessment method which considers both the perception prior and hybrid temporal features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
LFIR2Pose: Pose Estimation from an Extremely Low-Resolution FIR Image Sequence
Saki Iwata, Yasutomo Kawanishi, Daisuke Deguchi, Ichiro Ide, Hiroshi Murase, Tomoyoshi Aizawa
Auto-TLDR; LFIR2Pose: Human Pose Estimation from a Low-Resolution Far-InfraRed Image Sequence
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Personalized Models in Human Activity Recognition Using Deep Learning
Hamza Amrani, Daniela Micucci, Paolo Napoletano

Auto-TLDR; Incremental Learning for Personalized Human Activity Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Human or Machine? It Is Not What You Write, but How You Write It
Luis Leiva, Moises Diaz, M.A. Ferrer, Réjean Plamondon

Auto-TLDR; Behavioral Biometrics via Handwritten Symbols for Identification and Verification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Spatial Bias in Vision-Based Voice Activity Detection
Kalin Stefanov, Mohammad Adiban, Giampiero Salvi
Auto-TLDR; Spatial Bias in Vision-based Voice Activity Detection in Multiparty Human-Human Interactions
From Human Pose to On-Body Devices for Human-Activity Recognition
Fernando Moya Rueda, Gernot Fink
Auto-TLDR; Transfer Learning from Human Pose Estimation for Human Activity Recognition using Inertial Measurements from On-Body Devices
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploring Spatial-Temporal Representations for fNIRS-based Intimacy Detection via an Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
Chao Li, Qian Zhang, Ziping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Intimate Relationship Prediction by Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network Using Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real Time Fencing Move Classification and Detection at Touch Time During a Fencing Match
Cem Ekin Sunal, Chris G. Willcocks, Boguslaw Obara

Auto-TLDR; Fencing Body Move Classification and Detection Using Deep Learning
Modeling Long-Term Interactions to Enhance Action Recognition
Alejandro Cartas, Petia Radeva, Mariella Dimiccoli

Auto-TLDR; A Hierarchical Long Short-Term Memory Network for Action Recognition in Egocentric Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Gait Relative Attribute Using a Signed Quadratic Contrastive Loss
Yuta Hayashi, Shehata Allam, Yasushi Makihara, Daigo Muramatsu, Yasushi Yagi

Auto-TLDR; Signal-Contrastive Loss for Gait Attributes Estimation
Recognizing Bengali Word Images - A Zero-Shot Learning Perspective
Sukalpa Chanda, Daniël Arjen Willem Haitink, Prashant Kumar Prasad, Jochem Baas, Umapada Pal, Lambert Schomaker
Auto-TLDR; Zero-Shot Learning for Word Recognition in Bengali Script
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Estimation of Clinical Tremor Using Spatio-Temporal Adversarial AutoEncoder
Li Zhang, Vidya Koesmahargyo, Isaac Galatzer-Levy

Auto-TLDR; ST-AAE: Spatio-temporal Adversarial Autoencoder for Clinical Assessment of Hand Tremor Frequency and Severity
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
StrongPose: Bottom-up and Strong Keypoint Heat Map Based Pose Estimation

Auto-TLDR; StrongPose: A bottom-up box-free approach for human pose estimation and action recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Classifying Eye-Tracking Data Using Saliency Maps
Shafin Rahman, Sejuti Rahman, Omar Shahid, Md. Tahmeed Abdullah, Jubair Ahmed Sourov
Auto-TLDR; Saliency-based Feature Extraction for Automatic Classification of Eye-tracking Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Anomaly Detection, Localization and Classification for Railway Inspection
Riccardo Gasparini, Andrea D'Eusanio, Guido Borghi, Stefano Pini, Giuseppe Scaglione, Simone Calderara, Eugenio Fedeli, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Anomaly Detection and Localization using thermal images in the lowlight environment