Exploring Spatial-Temporal Representations for fNIRS-based Intimacy Detection via an Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
Chao Li,
Qian Zhang,
Ziping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Intimate Relationship Prediction by Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network Using Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Similar papers
EEG-Based Cognitive State Assessment Using Deep Ensemble Model and Filter Bank Common Spatial Pattern
Debashis Das Chakladar, Shubhashis Dey, Partha Pratim Roy, Masakazu Iwamura
Auto-TLDR; A Deep Ensemble Model for Cognitive State Assessment using EEG-based Cognitive State Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Electroencephalography Signal Processing Based on Textural Features for Monitoring the Driver’s State by a Brain-Computer Interface
Giulia Orrù, Marco Micheletto, Fabio Terranova, Gian Luca Marcialis

Auto-TLDR; One-dimensional Local Binary Pattern Algorithm for Estimating Driver Vigilance in a Brain-Computer Interface System
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The Application of Capsule Neural Network Based CNN for Speech Emotion Recognition

Auto-TLDR; CapCNN: A Capsule Neural Network for Speech Emotion Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Driven Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Bappaditya Debnath, Swagat Kumar, Marry O'Brien, Ardhendu Behera

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Two-Stream Recurrent Network for Skeleton-Based Human Interaction Recognition
Qianhui Men, Edmond S. L. Ho, Shum Hubert P. H., Howard Leung

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stream Recurrent Neural Network for Human-Human Interaction Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SAT-Net: Self-Attention and Temporal Fusion for Facial Action Unit Detection
Zhihua Li, Zheng Zhang, Lijun Yin

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Fusion and Self-Attention Network for Facial Action Unit Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
End-To-End Triplet Loss Based Emotion Embedding System for Speech Emotion Recognition
Puneet Kumar, Sidharth Jain, Balasubramanian Raman, Partha Pratim Roy, Masakazu Iwamura

Auto-TLDR; End-to-End Neural Embedding System for Speech Emotion Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Responsive Social Smile: A Machine-Learning Based Multimodal Behavior Assessment Framework towards Early Stage Autism Screening
Yueran Pan, Kunjing Cai, Ming Cheng, Xiaobing Zou, Ming Li

Auto-TLDR; Responsive Social Smile: A Machine Learningbased Assessment Framework for Early ASD Screening
Two-Level Attention-Based Fusion Learning for RGB-D Face Recognition
Hardik Uppal, Alireza Sepas-Moghaddam, Michael Greenspan, Ali Etemad

Auto-TLDR; Fused RGB-D Facial Recognition using Attention-Aware Feature Fusion
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
EasiECG: A Novel Inter-Patient Arrhythmia Classification Method Using ECG Waves
Chuanqi Han, Ruoran Huang, Fang Yu, Xi Huang, Li Cui

Auto-TLDR; EasiECG: Attention-based Convolution Factorization Machines for Arrhythmia Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-Lingual Text Image Recognition Via Multi-Task Sequence to Sequence Learning
Zhuo Chen, Fei Yin, Xu-Yao Zhang, Qing Yang, Cheng-Lin Liu

Auto-TLDR; Cross-Lingual Text Image Recognition with Multi-task Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Epileptic Seizure Prediction: A Semi-Dilated Convolutional Neural Network Architecture
Ramy Hussein, Rabab K. Ward, Soojin Lee, Martin Mckeown
Auto-TLDR; Semi-Dilated Convolutional Network for Seizure Prediction using EEG Scalograms
Hybrid Network for End-To-End Text-Independent Speaker Identification
Wajdi Ghezaiel, Luc Brun, Olivier Lezoray
Auto-TLDR; Text-Independent Speaker Identification with Scattering Wavelet Network and Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CardioGAN: An Attention-Based Generative Adversarial Network for Generation of Electrocardiograms
Subhrajyoti Dasgupta, Sudip Das, Ujjwal Bhattacharya

Auto-TLDR; CardioGAN: Generative Adversarial Network for Synthetic Electrocardiogram Signals
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Trajectory-User Link with Attention Recurrent Networks
Tao Sun, Yongjun Xu, Fei Wang, Lin Wu, 塘文 钱, Zezhi Shao

Auto-TLDR; TULAR: Trajectory-User Link with Attention Recurrent Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Constructing Geographic and Long-term Temporal Graph for Traffic Forecasting
Yiwen Sun, Yulu Wang, Kun Fu, Zheng Wang, Changshui Zhang, Jieping Ye

Auto-TLDR; GLT-GCRNN: Geographic and Long-term Temporal Graph Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network for Traffic Forecasting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Gait Recognition Using Multi-Scale Partial Representation Transformation with Capsules
Alireza Sepas-Moghaddam, Saeed Ghorbani, Nikolaus F. Troje, Ali Etemad
Auto-TLDR; Learning to Transfer Multi-scale Partial Gait Representations using Capsule Networks for Gait Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose-Based Body Language Recognition for Emotion and Psychiatric Symptom Interpretation
Zhengyuan Yang, Amanda Kay, Yuncheng Li, Wendi Cross, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; Body Language Based Emotion Recognition for Psychiatric Symptoms Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ConvMath : A Convolutional Sequence Network for Mathematical Expression Recognition
Zuoyu Yan, Xiaode Zhang, Liangcai Gao, Ke Yuan, Zhi Tang
Auto-TLDR; Convolutional Sequence Modeling for Mathematical Expressions Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AttendAffectNet: Self-Attention Based Networks for Predicting Affective Responses from Movies
Thi Phuong Thao Ha, Bt Balamurali, Herremans Dorien, Roig Gemma

Auto-TLDR; AttendAffectNet: A Self-Attention Based Network for Emotion Prediction from Movies
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context Matters: Self-Attention for Sign Language Recognition
Fares Ben Slimane, Mohamed Bouguessa

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Network for Continuous Sign Language Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Graph Convolutional Network for Relationship-Driven Stock Movement Prediction
Jiexia Ye, Juanjuan Zhao, Kejiang Ye, Cheng-Zhong Xu
Auto-TLDR; Multi-GCGRU: A Deep Learning Framework for Stock Price Prediction with Cross Effect
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Space-Time Domain Tensor Neural Networks: An Application on Human Pose Classification
Konstantinos Makantasis, Athanasios Voulodimos, Anastasios Doulamis, Nikolaos Doulamis, Nikolaos Bakalos

Auto-TLDR; Tensor-Based Neural Network for Spatiotemporal Pose Classifiaction using Three-Dimensional Skeleton Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-People Mobile-Phone Based Airwriting Character Recognition
Yunzhe Li, Hui Zheng, He Zhu, Haojun Ai, Xiaowei Dong

Auto-TLDR; Cross-People Airwriting Recognition via Motion Sensor Signal via Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Two-Stream Temporal Convolutional Network for Dynamic Facial Attractiveness Prediction
Nina Weng, Jiahao Wang, Annan Li, Yunhong Wang

Auto-TLDR; 2S-TCN: A Two-Stream Temporal Convolutional Network for Dynamic Facial Attractiveness Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Wireless Localisation in WiFi Using Novel Deep Architectures
Peizheng Li, Han Cui, Aftab Khan, Usman Raza, Robert Piechocki, Angela Doufexi, Tim Farnham
Auto-TLDR; Deep Neural Network for Indoor Localisation of WiFi Devices in Indoor Environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Engineering and Stacked Echo State Networks for Musical Onset Detection
Peter Steiner, Azarakhsh Jalalvand, Simon Stone, Peter Birkholz

Auto-TLDR; Echo State Networks for Onset Detection in Music Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MA-LSTM: A Multi-Attention Based LSTM for Complex Pattern Extraction
Jingjie Guo, Kelang Tian, Kejiang Ye, Cheng-Zhong Xu
Auto-TLDR; MA-LSTM: Multiple Attention based recurrent neural network for forget gate
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Audio-Visual Speech Recognition Using a Two-Step Feature Fusion Strategy

Auto-TLDR; A Two-Step Feature Fusion Network for Speech Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PIN: A Novel Parallel Interactive Network for Spoken Language Understanding
Peilin Zhou, Zhiqi Huang, Fenglin Liu, Yuexian Zou

Auto-TLDR; Parallel Interactive Network for Spoken Language Understanding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Annotation of Corpora for Emotion Recognition through Facial Expressions Analysis
Alex Mircoli, Claudia Diamantini, Domenico Potena, Emanuele Storti

Auto-TLDR; Automatic annotation of video subtitles on the basis of facial expressions using machine learning algorithms
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Classification of Spatially Enriched Pixel Time Series with Convolutional Neural Networks
Mohamed Chelali, Camille Kurtz, Anne Puissant, Nicole Vincent
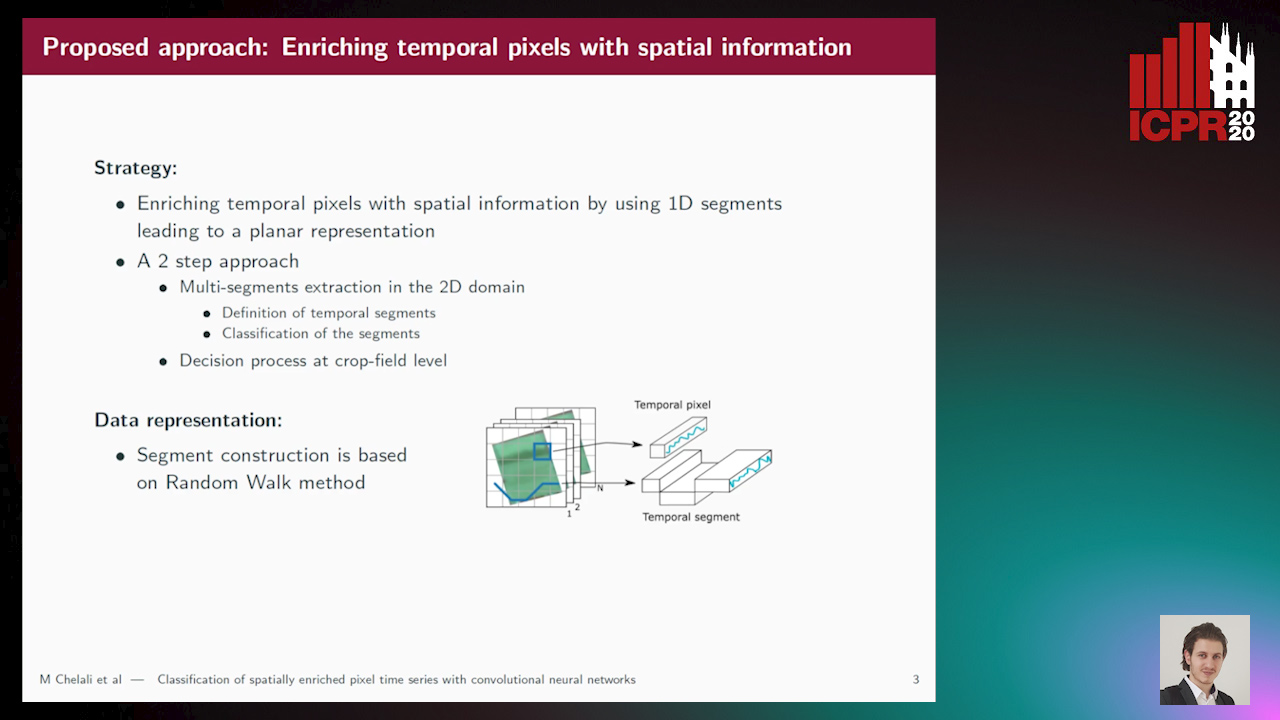
Auto-TLDR; Spatio-Temporal Features Extraction from Satellite Image Time Series Using Random Walk
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Scanning Based Recurrent Neural Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification
Weilian Zhou, Sei-Ichiro Kamata
Auto-TLDR; Spatial-Spectral Unification for Hyperspectral Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vision-Based Multi-Modal Framework for Action Recognition
Djamila Romaissa Beddiar, Mourad Oussalah, Brahim Nini

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Framework for Human Activity Recognition Using RGB, Depth and Skeleton Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Transfer Learning for Alzheimer’s Disease Detection
Nicole Cilia, Claudio De Stefano, Francesco Fontanella, Claudio Marrocco, Mario Molinara, Alessandra Scotto Di Freca

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Detection of Handwriting Alterations for Alzheimer's Disease Diagnosis using Dynamic Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Prototype-Based Generalized Zero-Shot Learning Framework for Hand Gesture Recognition
Jinting Wu, Yujia Zhang, Xiao-Guang Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Generalized Zero-Shot Learning for Hand Gesture Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Leveraging Synthetic Subject Invariant EEG Signals for Zero Calibration BCI
Nik Khadijah Nik Aznan, Amir Atapour-Abarghouei, Stephen Bonner, Jason Connolly, Toby Breckon

Auto-TLDR; SIS-GAN: Subject Invariant SSVEP Generative Adversarial Network for Brain-Computer Interface
Classifying Eye-Tracking Data Using Saliency Maps
Shafin Rahman, Sejuti Rahman, Omar Shahid, Md. Tahmeed Abdullah, Jubair Ahmed Sourov
Auto-TLDR; Saliency-based Feature Extraction for Automatic Classification of Eye-tracking Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Activity Recognition Using First-Person-View Cameras Based on Sparse Optical Flows
Peng-Yuan Kao, Yan-Jing Lei, Chia-Hao Chang, Chu-Song Chen, Ming-Sui Lee, Yi-Ping Hung

Auto-TLDR; 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Activity Recognition with FPV Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A General End-To-End Method for Characterizing Neuropsychiatric Disorders Using Free-Viewing Visual Scanning Tasks
Hong Yue Sean Liu, Jonathan Chung, Moshe Eizenman

Auto-TLDR; A general, data-driven, end-to-end framework that extracts relevant features of attentional bias from visual scanning behaviour and uses these features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Scale and Attention Based ResNet for Heartbeat Classification
Haojie Zhang, Gongping Yang, Yuwen Huang, Feng Yuan, Yilong Yin

Auto-TLDR; A Multi-Scale and Attention based ResNet for ECG heartbeat classification in intra-patient and inter-patient paradigms
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Flow-Guided Spatial Attention Tracking for Egocentric Activity Recognition

Auto-TLDR; flow-guided spatial attention tracking for egocentric activity recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Ballroom Dance Recognition from Audio Recordings
Tomas Pavlin, Jan Cech, Jiri Matas

Auto-TLDR; A CNN-based approach to classify ballroom dances given audio recordings
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RWF-2000: An Open Large Scale Video Database for Violence Detection
Ming Cheng, Kunjing Cai, Ming Li

Auto-TLDR; Flow Gated Network for Violence Detection in Surveillance Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentive Visual Semantic Specialized Network for Video Captioning
Jesus Perez-Martin, Benjamin Bustos, Jorge Pérez

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Visual Semantic Specialized Network for Video Captioning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context Visual Information-Based Deliberation Network for Video Captioning
Min Lu, Xueyong Li, Caihua Liu
Auto-TLDR; Context visual information-based deliberation network for video captioning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Personalized Models in Human Activity Recognition Using Deep Learning
Hamza Amrani, Daniela Micucci, Paolo Napoletano

Auto-TLDR; Incremental Learning for Personalized Human Activity Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar