Leveraging Synthetic Subject Invariant EEG Signals for Zero Calibration BCI
Nik Khadijah Nik Aznan,
Amir Atapour-Abarghouei,
Stephen Bonner,
Jason Connolly,
Toby Breckon

Auto-TLDR; SIS-GAN: Subject Invariant SSVEP Generative Adversarial Network for Brain-Computer Interface
Similar papers
Signal Generation Using 1d Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks for Fault Diagnosis of Electrical Machines
Russell Sabir, Daniele Rosato, Sven Hartmann, Clemens Gühmann

Auto-TLDR; Large Dataset Generation from Faulty AC Machines using Deep Convolutional GAN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Augmentation of Small Training Data Using GANs for Enhancing the Performance of Image Classification

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Network for Image Training Data Augmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Data Augmentation Via Mixed Class Interpolation Using Cycle-Consistent Generative Adversarial Networks Applied to Cross-Domain Imagery
Hiroshi Sasaki, Chris G. Willcocks, Toby Breckon
Auto-TLDR; C2GMA: A Generative Domain Transfer Model for Non-visible Domain Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SAGE: Sequential Attribute Generator for Analyzing Glioblastomas Using Limited Dataset
Padmaja Jonnalagedda, Brent Weinberg, Jason Allen, Taejin Min, Shiv Bhanu, Bir Bhanu

Auto-TLDR; SAGE: Generative Adversarial Networks for Imaging Biomarker Detection and Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GAP: Quantifying the Generative Adversarial Set and Class Feature Applicability of Deep Neural Networks
Edward Collier, Supratik Mukhopadhyay
Auto-TLDR; Approximating Adversarial Learning in Deep Neural Networks Using Set and Class Adversaries
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Facial Attribute Transfer through Inpainting
Ricard Durall, Franz-Josef Pfreundt, Janis Keuper

Auto-TLDR; Attribute Transfer Inpainting Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Quantifying the Use of Domain Randomization
Mohammad Ani, Hector Basevi, Ales Leonardis

Auto-TLDR; Evaluating Domain Randomization for Synthetic Image Generation by directly measuring the difference between realistic and synthetic data distributions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Estimation of Clinical Tremor Using Spatio-Temporal Adversarial AutoEncoder
Li Zhang, Vidya Koesmahargyo, Isaac Galatzer-Levy

Auto-TLDR; ST-AAE: Spatio-temporal Adversarial Autoencoder for Clinical Assessment of Hand Tremor Frequency and Severity
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On the Evaluation of Generative Adversarial Networks by Discriminative Models
Amirsina Torfi, Mohammadreza Beyki, Edward Alan Fox
Auto-TLDR; Domain-agnostic GAN Evaluation with Siamese Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Galaxy Image Translation with Semi-Supervised Noise-Reconstructed Generative Adversarial Networks
Qiufan Lin, Dominique Fouchez, Jérôme Pasquet
Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Image Translation with Generative Adversarial Networks Using Paired and Unpaired Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Uncertainty-Aware Data Augmentation for Food Recognition
Eduardo Aguilar, Bhalaji Nagarajan, Rupali Khatun, Marc Bolaños, Petia Radeva

Auto-TLDR; Data Augmentation for Food Recognition Using Epistemic Uncertainty
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Electroencephalography Signal Processing Based on Textural Features for Monitoring the Driver’s State by a Brain-Computer Interface
Giulia Orrù, Marco Micheletto, Fabio Terranova, Gian Luca Marcialis

Auto-TLDR; One-dimensional Local Binary Pattern Algorithm for Estimating Driver Vigilance in a Brain-Computer Interface System
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CardioGAN: An Attention-Based Generative Adversarial Network for Generation of Electrocardiograms
Subhrajyoti Dasgupta, Sudip Das, Ujjwal Bhattacharya

Auto-TLDR; CardioGAN: Generative Adversarial Network for Synthetic Electrocardiogram Signals
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient Shadow Detection and Removal Using Synthetic Data with Domain Adaptation
Rui Guo, Babajide Ayinde, Hao Sun
Auto-TLDR; Shadow Detection and Removal with Domain Adaptation and Synthetic Image Database
DeepBEV: A Conditional Adversarial Network for Bird’s Eye View Generation

Auto-TLDR; A Generative Adversarial Network for Semantic Object Representation in Autonomous Vehicles
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semi-Supervised Generative Adversarial Networks with a Pair of Complementary Generators for Retinopathy Screening
Yingpeng Xie, Qiwei Wan, Hai Xie, En-Leng Tan, Yanwu Xu, Baiying Lei

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Networks for Retinopathy Diagnosis via Fundus Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
IDA-GAN: A Novel Imbalanced Data Augmentation GAN
Auto-TLDR; IDA-GAN: Generative Adversarial Networks for Imbalanced Data Augmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploring Spatial-Temporal Representations for fNIRS-based Intimacy Detection via an Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
Chao Li, Qian Zhang, Ziping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Intimate Relationship Prediction by Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network Using Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A GAN-Based Blind Inpainting Method for Masonry Wall Images
Yahya Ibrahim, Balázs Nagy, Csaba Benedek

Auto-TLDR; An End-to-End Blind Inpainting Algorithm for Masonry Wall Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Digit Recognition Applied to Reconstructed Audio Signals Using Deep Learning
Anastasia-Sotiria Toufa, Constantine Kotropoulos
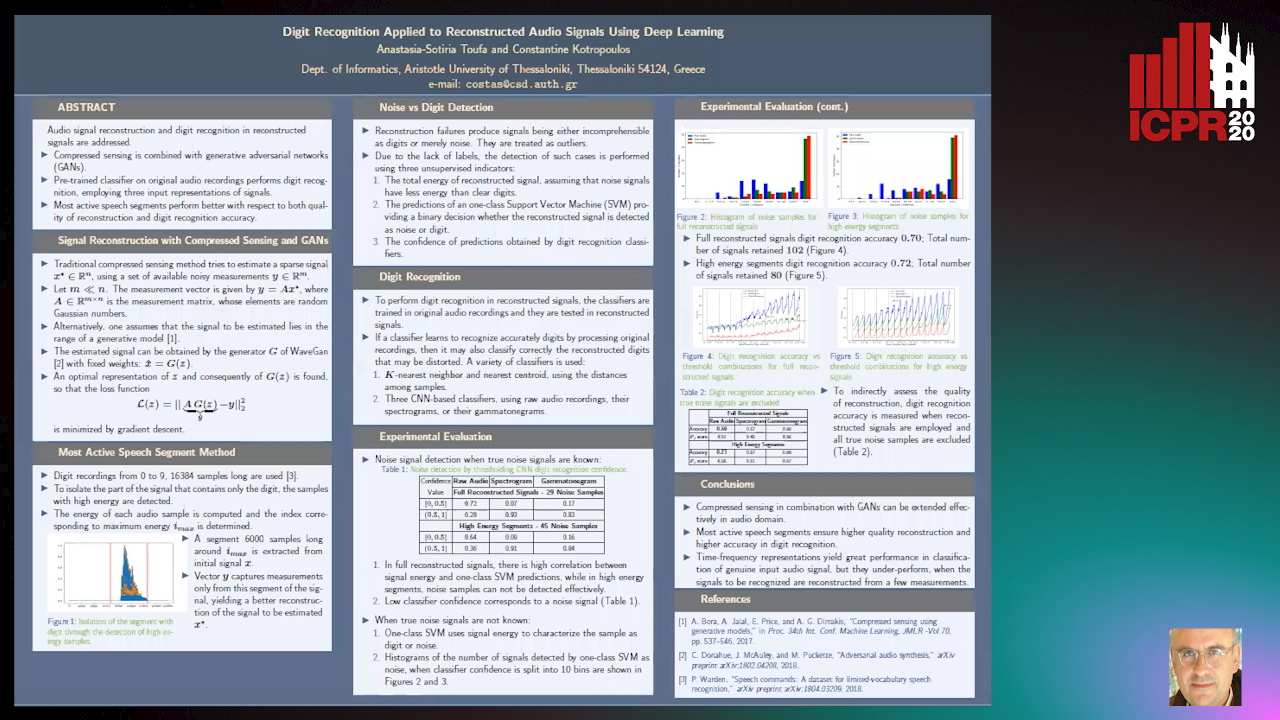
Auto-TLDR; Compressed Sensing for Digit Recognition in Audio Reconstruction
Learning Low-Shot Generative Networks for Cross-Domain Data
Hsuan-Kai Kao, Cheng-Che Lee, Wei-Chen Chiu
Auto-TLDR; Learning Generators for Cross-Domain Data under Low-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GAN-Based Gaussian Mixture Model Responsibility Learning
Wanming Huang, Yi Da Xu, Shuai Jiang, Xuan Liang, Ian Oppermann

Auto-TLDR; Posterior Consistency Module for Gaussian Mixture Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generative Latent Implicit Conditional Optimization When Learning from Small Sample
Auto-TLDR; GLICO: Generative Latent Implicit Conditional Optimization for Small Sample Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
High Resolution Face Age Editing
Xu Yao, Gilles Puy, Alasdair Newson, Yann Gousseau, Pierre Hellier
Auto-TLDR; An Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Face Age editing on High Resolution Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
S2I-Bird: Sound-To-Image Generation of Bird Species Using Generative Adversarial Networks
Joo Yong Shim, Joongheon Kim, Jong-Kook Kim

Auto-TLDR; Generating bird images from sound using conditional generative adversarial networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Background Invariance by Adversarial Learning
Ricardo Cruz, Ricardo M. Prates, Eduardo F. Simas Filho, Joaquim F. Pinto Costa, Jaime S. Cardoso
Auto-TLDR; Improving Convolutional Neural Networks for Overhead Power Line Insulators Detection using a Drone
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Robotic Grasping on Monocular Images Via Multi-Task Learning and Positional Loss
William Prew, Toby Breckon, Magnus Bordewich, Ulrik Beierholm
Auto-TLDR; Improving grasping performance from monocularcolour images in an end-to-end CNN architecture with multi-task learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Robust Pedestrian Detection in Thermal Imagery Using Synthesized Images
My Kieu, Lorenzo Berlincioni, Leonardo Galteri, Marco Bertini, Andrew Bagdanov, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Improving Pedestrian Detection in the thermal domain using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generating Private Data Surrogates for Vision Related Tasks
Ryan Webster, Julien Rabin, Loic Simon, Frederic Jurie

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Networks for Membership Inference Attacks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Lightweight Low-Resolution Face Recognition for Surveillance Applications
Yoanna Martínez-Díaz, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Luis S. Luevano, Leonardo Chang, Miguel Gonzalez-Mendoza

Auto-TLDR; Efficiency of Lightweight Deep Face Networks on Low-Resolution Surveillance Imagery
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Simple Domain Shifting Network for Generating Low Quality Images
Guruprasad Hegde, Avinash Nittur Ramesh, Kanchana Vaishnavi Gandikota, Michael Möller, Roman Obermaisser
Auto-TLDR; Robotic Image Classification Using Quality degrading networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
End-To-End Multi-Task Learning of Missing Value Imputation and Forecasting in Time-Series Data
Jinhee Kim, Taesung Kim, Jang-Ho Choi, Jaegul Choo

Auto-TLDR; Time-Series Prediction with Denoising and Imputation of Missing Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Age Gap Reducer-GAN for Recognizing Age-Separated Faces
Daksha Yadav, Naman Kohli, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh, Afzel Noore

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Network for Age-separated Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
EEG-Based Cognitive State Assessment Using Deep Ensemble Model and Filter Bank Common Spatial Pattern
Debashis Das Chakladar, Shubhashis Dey, Partha Pratim Roy, Masakazu Iwamura
Auto-TLDR; A Deep Ensemble Model for Cognitive State Assessment using EEG-based Cognitive State Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multiple Future Prediction Leveraging Synthetic Trajectories
Lorenzo Berlincioni, Federico Becattini, Lorenzo Seidenari, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Synthetic Trajectory Prediction using Markov Chains
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Multiple Domain Discriminators and Adaptive Self-Training
Teo Spadotto, Marco Toldo, Umberto Michieli, Pietro Zanuttigh

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Scenes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enlarging Discriminative Power by Adding an Extra Class in Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Hai Tran, Sumyeong Ahn, Taeyoung Lee, Yung Yi

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation using Artificial Classes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Unsupervised Approach towards Varying Human Skin Tone Using Generative Adversarial Networks
Debapriya Roy, Diganta Mukherjee, Bhabatosh Chanda

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Skin Tone Change Using Augmented Reality Based Models
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GazeMAE: General Representations of Eye Movements Using a Micro-Macro Autoencoder
Louise Gillian C. Bautista, Prospero Naval

Auto-TLDR; Fast and Slow Eye Movement Representations for Sentiment-agnostic Eye Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pseudo Rehearsal Using Non Photo-Realistic Images
Bhasker Sri Harsha Suri, Kalidas Yeturu

Auto-TLDR; Pseudo-Rehearsing for Catastrophic Forgetting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semantic Object Segmentation in Cultural Sites Using Real and Synthetic Data
Francesco Ragusa, Daniele Di Mauro, Alfio Palermo, Antonino Furnari, Giovanni Maria Farinella

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Synthetic Data for Object Segmentation in Cultural Sites
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Effective Deployment of CNNs for 3DoF Pose Estimation and Grasping in Industrial Settings
Daniele De Gregorio, Riccardo Zanella, Gianluca Palli, Luigi Di Stefano
Auto-TLDR; Automated Deep Learning for Robotic Grasping Applications
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Face Manipulation Via Hallucination
Keerthy Kusumam, Enrique Sanchez, Georgios Tzimiropoulos

Auto-TLDR; Unpaired Face Image Manipulation using Autoencoders
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Mixtures of Generators for Adversarial Learning
Alper Ahmetoğlu, Ethem Alpaydin

Auto-TLDR; Hierarchical Mixture of Generative Adversarial Networks
Learning Disentangled Representations for Identity Preserving Surveillance Face Camouflage
Jingzhi Li, Lutong Han, Hua Zhang, Xiaoguang Han, Jingguo Ge, Xiaochu Cao

Auto-TLDR; Individual Face Privacy under Surveillance Scenario with Multi-task Loss Function
Stylized-Colorization for Line Arts
Tzu-Ting Fang, Minh Duc Vo, Akihiro Sugimoto, Shang-Hong Lai

Auto-TLDR; Stylized-colorization using GAN-based End-to-End Model for Anime
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Thermal Image Enhancement Using Generative Adversarial Network for Pedestrian Detection
Mohamed Amine Marnissi, Hajer Fradi, Anis Sahbani, Najoua Essoukri Ben Amara
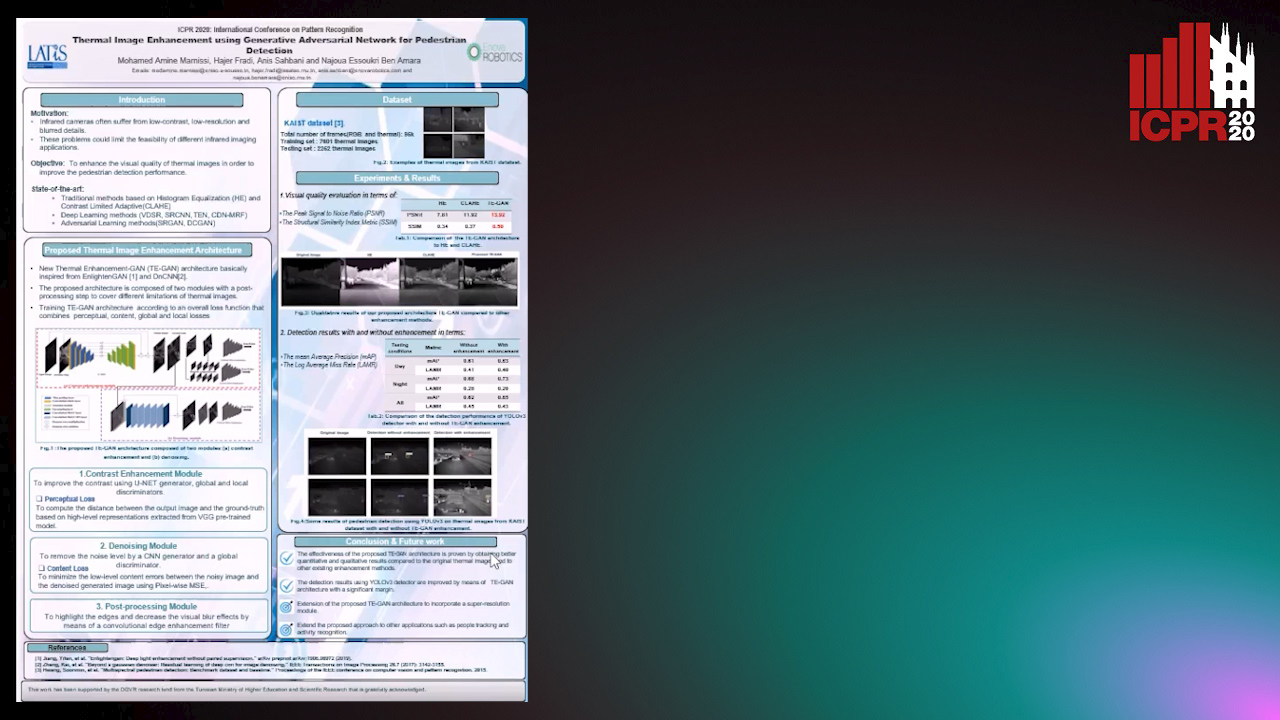
Auto-TLDR; Improving Visual Quality of Infrared Images for Pedestrian Detection Using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Super-Resolution Guided Pore Detection for Fingerprint Recognition
Syeda Nyma Ferdous, Ali Dabouei, Jeremy Dawson, Nasser M. Nasarabadi

Auto-TLDR; Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network for Fingerprint Recognition Using Pore Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar