Super-Resolution Guided Pore Detection for Fingerprint Recognition
Syeda Nyma Ferdous,
Ali Dabouei,
Jeremy Dawson,
Nasser M. Nasarabadi

Auto-TLDR; Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network for Fingerprint Recognition Using Pore Features
Similar papers
Thermal Image Enhancement Using Generative Adversarial Network for Pedestrian Detection
Mohamed Amine Marnissi, Hajer Fradi, Anis Sahbani, Najoua Essoukri Ben Amara
Auto-TLDR; Improving Visual Quality of Infrared Images for Pedestrian Detection Using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Laplacian GAN with Edge Enhancement for Face Super Resolution
Auto-TLDR; Face Image Super-Resolution with Enhanced Edge Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boosting High-Level Vision with Joint Compression Artifacts Reduction and Super-Resolution
Xiaoyu Xiang, Qian Lin, Jan Allebach
Auto-TLDR; A Context-Aware Joint CAR and SR Neural Network for High-Resolution Text Recognition and Face Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Level Three Synthetic Fingerprint Generation
Andre Wyzykowski, Mauricio Pamplona Segundo, Rubisley Lemes

Auto-TLDR; Synthesis of High-Resolution Fingerprints with Pore Detection Using CycleGAN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Small Object Detection Leveraging on Simultaneous Super-Resolution
Hong Ji, Zhi Gao, Xiaodong Liu, Tiancan Mei

Auto-TLDR; Super-Resolution via Generative Adversarial Network for Small Object Detection
On-Device Text Image Super Resolution
Dhruval Jain, Arun Prabhu, Gopi Ramena, Manoj Goyal, Debi Mohanty, Naresh Purre, Sukumar Moharana
Auto-TLDR; A Novel Deep Neural Network for Super-Resolution on Low Resolution Text Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Small Object Detection by Generative and Discriminative Learning
Yi Gu, Jie Li, Chentao Wu, Weijia Jia, Jianping Chen

Auto-TLDR; Generative and Discriminative Learning for Small Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Wavelet Attention Embedding Networks for Video Super-Resolution
Young-Ju Choi, Young-Woon Lee, Byung-Gyu Kim

Auto-TLDR; Wavelet Attention Embedding Network for Video Super-Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Age Gap Reducer-GAN for Recognizing Age-Separated Faces
Daksha Yadav, Naman Kohli, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh, Afzel Noore

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Network for Age-separated Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tarsier: Evolving Noise Injection inSuper-Resolution GANs
Baptiste Roziere, Nathanaël Carraz Rakotonirina, Vlad Hosu, Rasoanaivo Andry, Hanhe Lin, Camille Couprie, Olivier Teytaud

Auto-TLDR; Evolutionary Super-Resolution using Diagonal CMA
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MBD-GAN: Model-Based Image Deblurring with a Generative Adversarial Network

Auto-TLDR; Model-Based Deblurring GAN for Inverse Imaging
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
LiNet: A Lightweight Network for Image Super Resolution
Armin Mehri, Parichehr Behjati Ardakani, Angel D. Sappa

Auto-TLDR; LiNet: A Compact Dense Network for Lightweight Super Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TinyVIRAT: Low-Resolution Video Action Recognition
Ugur Demir, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; TinyVIRAT: A Progressive Generative Approach for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchically Aggregated Residual Transformation for Single Image Super Resolution

Auto-TLDR; HARTnet: Hierarchically Aggregated Residual Transformation for Multi-Scale Super-resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
OCT Image Segmentation Using NeuralArchitecture Search and SRGAN
Saba Heidari, Omid Dehzangi, Nasser M. Nasarabadi, Ali Rezai
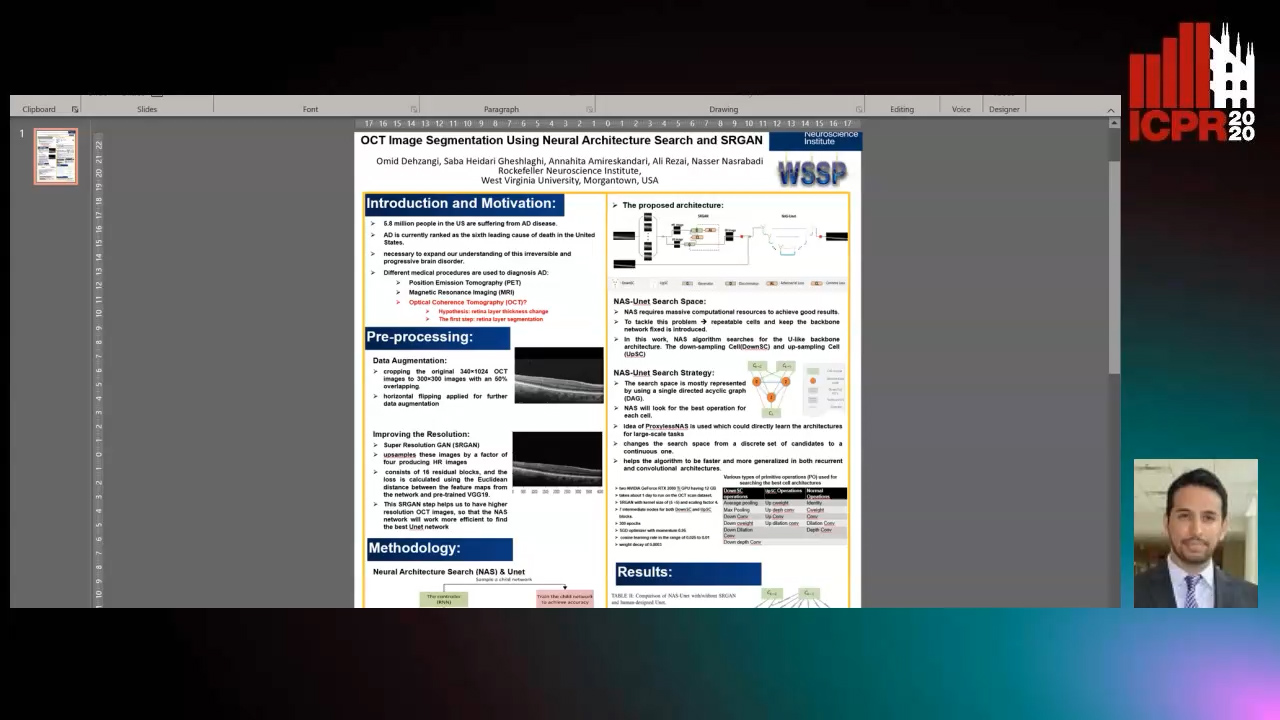
Auto-TLDR; Automatic Segmentation of Retinal Layers in Optical Coherence Tomography using Neural Architecture Search
Boundary Guided Image Translation for Pose Estimation from Ultra-Low Resolution Thermal Sensor
Kohei Kurihara, Tianren Wang, Teng Zhang, Brian Carrington Lovell
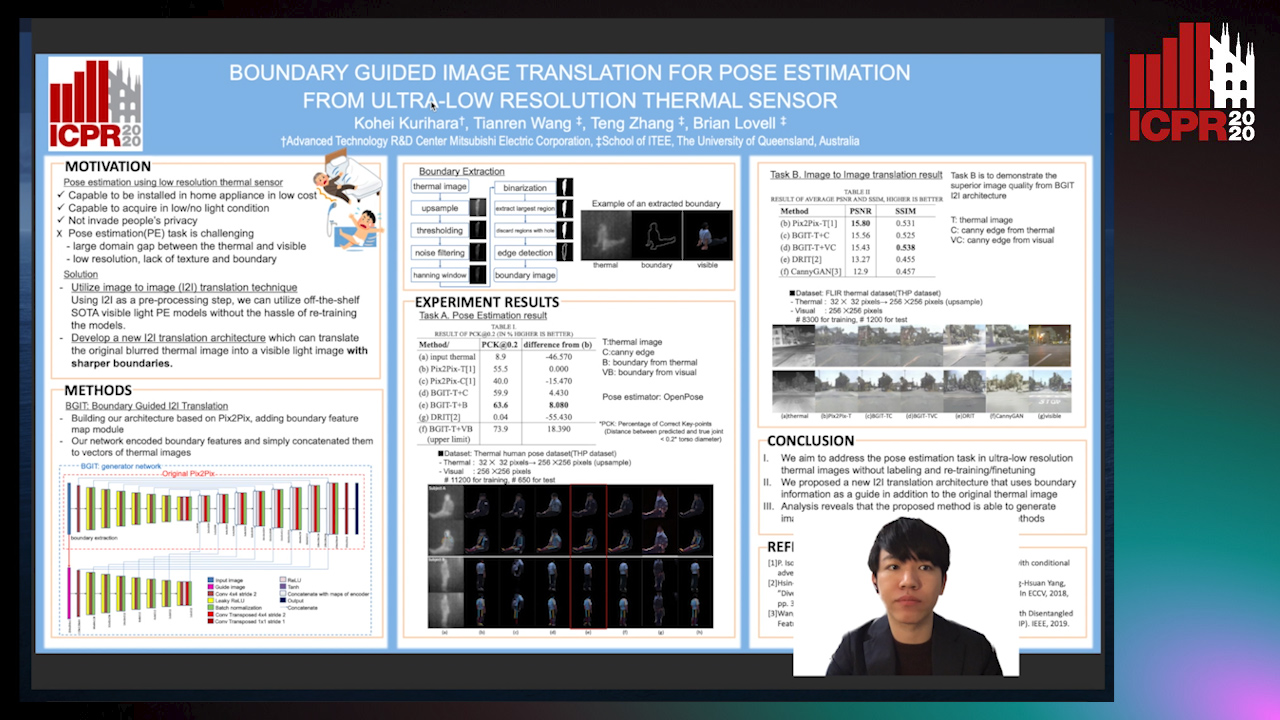
Auto-TLDR; Pose Estimation on Low-Resolution Thermal Images Using Image-to-Image Translation Architecture
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Progressive Splitting and Upscaling Structure for Super-Resolution

Auto-TLDR; PSUS: Progressive and Upscaling Layer for Single Image Super-Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Residual Fractal Network for Single Image Super Resolution by Widening and Deepening
Jiahang Gu, Zhaowei Qu, Xiaoru Wang, Jiawang Dan, Junwei Sun
Auto-TLDR; Residual fractal convolutional network for single image super-resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Machine-Learned Regularization and Polygonization of Building Segmentation Masks
Stefano Zorzi, Ksenia Bittner, Friedrich Fraundorfer

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Regularization and Polygonization of Building Segmentation masks using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention2AngioGAN: Synthesizing Fluorescein Angiography from Retinal Fundus Images Using Generative Adversarial Networks
Sharif Amit Kamran, Khondker Fariha Hossain, Alireza Tavakkoli, Stewart Lee Zuckerbrod
Auto-TLDR; Fluorescein Angiography from Fundus Images using Attention-based Generative Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detail-Revealing Deep Low-Dose CT Reconstruction
Xinchen Ye, Yuyao Xu, Rui Xu, Shoji Kido, Noriyuki Tomiyama

Auto-TLDR; A Dual-branch Aggregation Network for Low-Dose CT Reconstruction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Face Super-Resolution Network with Incremental Enhancement of Facial Parsing Information
Shuang Liu, Chengyi Xiong, Zhirong Gao

Auto-TLDR; Learning-based Face Super-Resolution with Incremental Boosting Facial Parsing Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
High Resolution Face Age Editing
Xu Yao, Gilles Puy, Alasdair Newson, Yann Gousseau, Pierre Hellier
Auto-TLDR; An Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Face Age editing on High Resolution Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Coarse to Fine: Progressive and Multi-Task Learning for Salient Object Detection
Dong-Goo Kang, Sangwoo Park, Joonki Paik
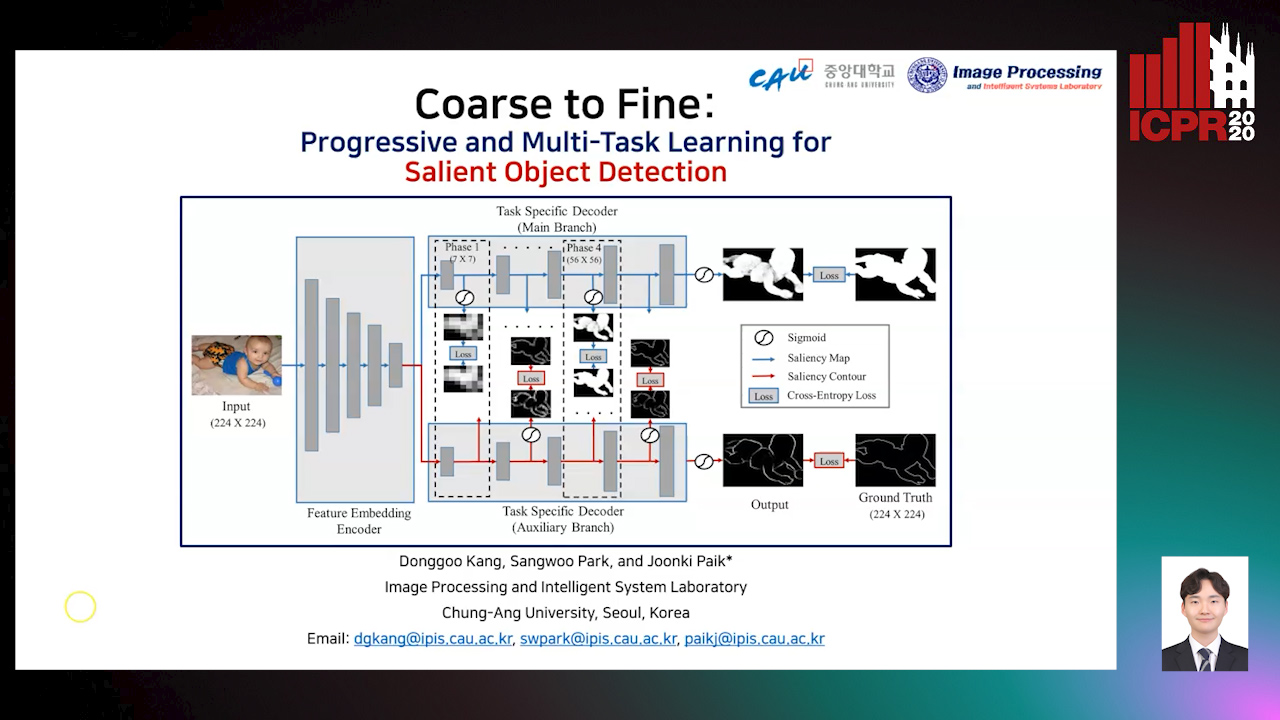
Auto-TLDR; Progressive and mutl-task learning scheme for salient object detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A NoGAN Approach for Image and Video Restoration and Compression Artifact Removal
Mameli Filippo, Marco Bertini, Leonardo Galteri, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Deep Neural Network for Image and Video Compression Artifact Removal and Restoration
Robust Pedestrian Detection in Thermal Imagery Using Synthesized Images
My Kieu, Lorenzo Berlincioni, Leonardo Galteri, Marco Bertini, Andrew Bagdanov, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Improving Pedestrian Detection in the thermal domain using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Disentangled Representations for Identity Preserving Surveillance Face Camouflage
Jingzhi Li, Lutong Han, Hua Zhang, Xiaoguang Han, Jingguo Ge, Xiaochu Cao

Auto-TLDR; Individual Face Privacy under Surveillance Scenario with Multi-task Loss Function
Deep Iterative Residual Convolutional Network for Single Image Super-Resolution
Rao Muhammad Umer, Gian Luca Foresti, Christian Micheloni

Auto-TLDR; ISRResCNet: Deep Iterative Super-Resolution Residual Convolutional Network for Single Image Super-resolution
Cross-Layer Information Refining Network for Single Image Super-Resolution
Hongyi Zhang, Wen Lu, Xiaopeng Sun

Auto-TLDR; Interlaced Spatial Attention Block for Single Image Super-Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Free-Form Image Inpainting Via Contrastive Attention Network
Xin Ma, Xiaoqiang Zhou, Huaibo Huang, Zhenhua Chai, Xiaolin Wei, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Siamese inference for image inpainting
Improving Low-Resolution Image Classification by Super-Resolution with Enhancing High-Frequency Content
Liguo Zhou, Guang Chen, Mingyue Feng, Alois Knoll

Auto-TLDR; Super-resolution for Low-Resolution Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SIDGAN: Single Image Dehazing without Paired Supervision
Pan Wei, Xin Wang, Lei Wang, Ji Xiang, Zihan Wang

Auto-TLDR; DehazeGAN: An End-to-End Generative Adversarial Network for Image Dehazing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mask-Based Style-Controlled Image Synthesis Using a Mask Style Encoder
Jaehyeong Cho, Wataru Shimoda, Keiji Yanai

Auto-TLDR; Style-controlled Image Synthesis from Semantic Segmentation masks using GANs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Facial Attribute Transfer through Inpainting
Ricard Durall, Franz-Josef Pfreundt, Janis Keuper

Auto-TLDR; Attribute Transfer Inpainting Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RSAN: Residual Subtraction and Attention Network for Single Image Super-Resolution
Shuo Wei, Xin Sun, Haoran Zhao, Junyu Dong

Auto-TLDR; RSAN: Residual subtraction and attention network for super-resolution
Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks and Fast Adaptive Bi-Dimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition for Style Transfer
Elissavet Batziou, Petros Alvanitopoulos, Konstantinos Ioannidis, Ioannis Patras, Stefanos Vrochidis, Ioannis Kompatsiaris

Auto-TLDR; FABEMD: Fast and Adaptive Bidimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition for Style Transfer on Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient Super Resolution by Recursive Aggregation
Zhengxiong Luo Zhengxiong Luo, Yan Huang, Shang Li, Liang Wang, Tieniu Tan

Auto-TLDR; Recursive Aggregation Network for Efficient Deep Super Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DFH-GAN: A Deep Face Hashing with Generative Adversarial Network
Bo Xiao, Lanxiang Zhou, Yifei Wang, Qiangfang Xu

Auto-TLDR; Deep Face Hashing with GAN for Face Image Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamic Low-Light Image Enhancement for Object Detection Via End-To-End Training
Haifeng Guo, Yirui Wu, Tong Lu

Auto-TLDR; Object Detection using Low-Light Image Enhancement for End-to-End Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Lightweight Low-Resolution Face Recognition for Surveillance Applications
Yoanna Martínez-Díaz, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Luis S. Luevano, Leonardo Chang, Miguel Gonzalez-Mendoza

Auto-TLDR; Efficiency of Lightweight Deep Face Networks on Low-Resolution Surveillance Imagery
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single Image Super-Resolution with Dynamic Residual Connection
Karam Park, Jae Woong Soh, Nam Ik Cho

Auto-TLDR; Dynamic Residual Attention Network for Lightweight Single Image Super-Residual Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Artifacts-Free Image Defogging
Gabriele Graffieti, Davide Maltoni

Auto-TLDR; CurL-Defog: Learning Based Defogging with CycleGAN and HArD
Galaxy Image Translation with Semi-Supervised Noise-Reconstructed Generative Adversarial Networks
Qiufan Lin, Dominique Fouchez, Jérôme Pasquet
Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Image Translation with Generative Adversarial Networks Using Paired and Unpaired Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient Shadow Detection and Removal Using Synthetic Data with Domain Adaptation
Rui Guo, Babajide Ayinde, Hao Sun
Auto-TLDR; Shadow Detection and Removal with Domain Adaptation and Synthetic Image Database
GarmentGAN: Photo-Realistic Adversarial Fashion Transfer
Amir Hossein Raffiee, Michael Sollami

Auto-TLDR; GarmentGAN: A Generative Adversarial Network for Image-Based Garment Transfer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Detection of Pulmonary Opacities for Computer-Aided Diagnosis of COVID-19 on CT Images
Rui Xu, Xiao Cao, Yufeng Wang, Yen-Wei Chen, Xinchen Ye, Lin Lin, Wenchao Zhu, Chao Chen, Fangyi Xu, Yong Zhou, Hongjie Hu, Shoji Kido, Noriyuki Tomiyama
Auto-TLDR; A computer-aided diagnosis of COVID-19 from CT images using unsupervised pulmonary opacity detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local-Global Interactive Network for Face Age Transformation
Jie Song, Ping Wei, Huan Li, Yongchi Zhang, Nanning Zheng

Auto-TLDR; A Novel Local-Global Interaction Framework for Long-span Face Age Transformation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A GAN-Based Blind Inpainting Method for Masonry Wall Images
Yahya Ibrahim, Balázs Nagy, Csaba Benedek

Auto-TLDR; An End-to-End Blind Inpainting Algorithm for Masonry Wall Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar