GazeMAE: General Representations of Eye Movements Using a Micro-Macro Autoencoder
Louise Gillian C. Bautista,
Prospero Naval

Auto-TLDR; Fast and Slow Eye Movement Representations for Sentiment-agnostic Eye Tracking
Similar papers
Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Raw Eye Tracking Data Segmentation, Generation, and Reconstruction
Wolfgang Fuhl, Yao Rong, Enkelejda Kasneci
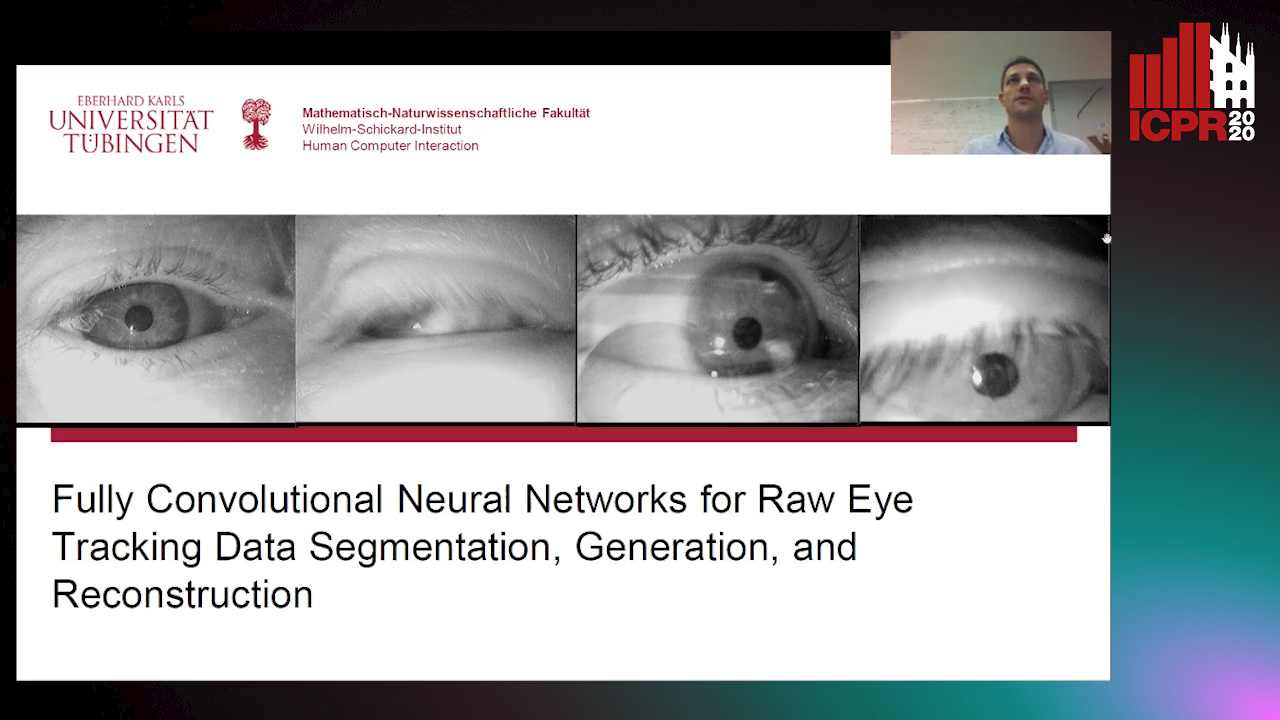
Auto-TLDR; Semantic Segmentation of Eye Tracking Data with Fully Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Classifying Eye-Tracking Data Using Saliency Maps
Shafin Rahman, Sejuti Rahman, Omar Shahid, Md. Tahmeed Abdullah, Jubair Ahmed Sourov
Auto-TLDR; Saliency-based Feature Extraction for Automatic Classification of Eye-tracking Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Collaborative Human Machine Attention Module for Character Recognition
Chetan Ralekar, Tapan Gandhi, Santanu Chaudhury

Auto-TLDR; A Collaborative Human-Machine Attention Module for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A General End-To-End Method for Characterizing Neuropsychiatric Disorders Using Free-Viewing Visual Scanning Tasks
Hong Yue Sean Liu, Jonathan Chung, Moshe Eizenman

Auto-TLDR; A general, data-driven, end-to-end framework that extracts relevant features of attentional bias from visual scanning behaviour and uses these features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Estimation of Clinical Tremor Using Spatio-Temporal Adversarial AutoEncoder
Li Zhang, Vidya Koesmahargyo, Isaac Galatzer-Levy

Auto-TLDR; ST-AAE: Spatio-temporal Adversarial Autoencoder for Clinical Assessment of Hand Tremor Frequency and Severity
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
N2D: (Not Too) Deep Clustering Via Clustering the Local Manifold of an Autoencoded Embedding
Ryan Mcconville, Raul Santos-Rodriguez, Robert Piechocki, Ian Craddock

Auto-TLDR; Local Manifold Learning for Deep Clustering on Autoencoded Embeddings
Image Representation Learning by Transformation Regression
Xifeng Guo, Jiyuan Liu, Sihang Zhou, En Zhu, Shihao Dong

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Image Representation Learning using Continuous Parameter Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Facial Matching by Spiral Convolutional Metric Learning and a Biometric Fusion-Net of Demographic Properties
Soha Sadat Mahdi, Nele Nauwelaers, Philip Joris, Giorgos Bouritsas, Imperial London, Sergiy Bokhnyak, Susan Walsh, Mark Shriver, Michael Bronstein, Peter Claes

Auto-TLDR; Multi-biometric Fusion for Biometric Verification using 3D Facial Mesures
Deep Convolutional Embedding for Digitized Painting Clustering
Giovanna Castellano, Gennaro Vessio

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Convolutional Embedding Model for Clustering Artworks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ESResNet: Environmental Sound Classification Based on Visual Domain Models
Andrey Guzhov, Federico Raue, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel
Auto-TLDR; Environmental Sound Classification with Short-Time Fourier Transform Spectrograms
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Interpretable Emotion Classification Using Temporal Convolutional Models
Manasi Bharat Gund, Abhiram Ravi Bharadwaj, Ifeoma Nwogu
Auto-TLDR; Understanding the Dynamics of Facial Emotion Expression with Spatiotemporal Representations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Handwritten Digit String Recognition Using Deep Autoencoder Based Segmentation and ResNet Based Recognition Approach
Anuran Chakraborty, Rajonya De, Samir Malakar, Friedhelm Schwenker, Ram Sarkar

Auto-TLDR; Handwritten Digit Strings Recognition Using Residual Network and Deep Autoencoder Based Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Explainable Online Validation of Machine Learning Models for Practical Applications
Wolfgang Fuhl, Yao Rong, Thomas Motz, Michael Scheidt, Andreas Markus Hartel, Andreas Koch, Enkelejda Kasneci

Auto-TLDR; A Reformulation of Regression and Classification for Machine Learning Algorithm Validation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploring Spatial-Temporal Representations for fNIRS-based Intimacy Detection via an Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
Chao Li, Qian Zhang, Ziping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Intimate Relationship Prediction by Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network Using Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
User-Independent Gaze Estimation by Extracting Pupil Parameter and Its Mapping to the Gaze Angle

Auto-TLDR; Gaze Point Estimation using Pupil Shape for Generalization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attribute-Based Quality Assessment for Demographic Estimation in Face Videos
Fabiola Becerra-Riera, Annette Morales-González, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Jean-Luc Dugelay
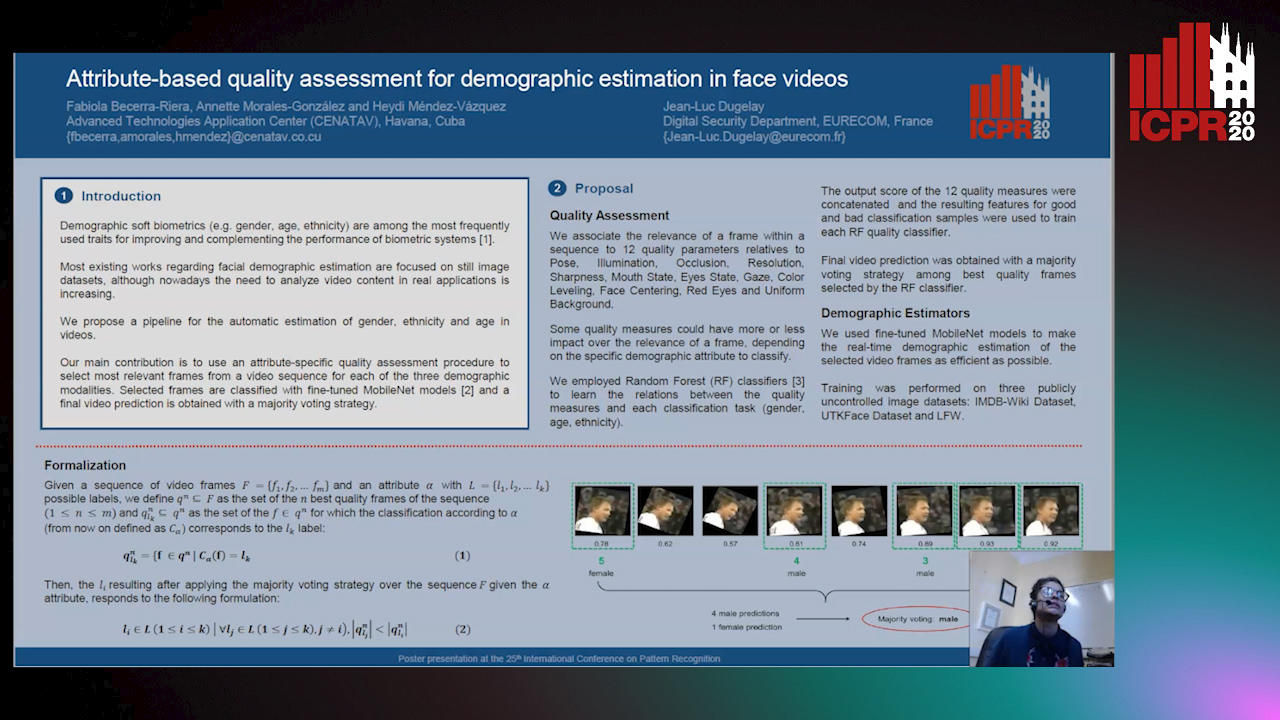
Auto-TLDR; Facial Demographic Estimation in Video Scenarios Using Quality Assessment
A Close Look at Deep Learning with Small Data

Auto-TLDR; Low-Complex Neural Networks for Small Data Conditions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Human or Machine? It Is Not What You Write, but How You Write It
Luis Leiva, Moises Diaz, M.A. Ferrer, Réjean Plamondon

Auto-TLDR; Behavioral Biometrics via Handwritten Symbols for Identification and Verification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detection and Correspondence Matching of Corneal Reflections for Eye Tracking Using Deep Learning
Soumil Chugh, Braiden Brousseau, Jonathan Rose, Moshe Eizenman

Auto-TLDR; A Fully Convolutional Neural Network for Corneal Reflection Detection and Matching in Extended Reality Eye Tracking Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real-Time Driver Drowsiness Detection Using Facial Action Units
Malaika Vijay, Nandagopal Netrakanti Vinayak, Maanvi Nunna, Subramanyam Natarajan

Auto-TLDR; Real-Time Detection of Driver Drowsiness using Facial Action Units using Extreme Gradient Boosting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Feature Fusion Network for Gaze Tracking in Mobile Tablets
Yiwei Bao, Yihua Cheng, Yunfei Liu, Feng Lu

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Feature Fusion Network for Multi-stream Gaze Estimation in Mobile Tablets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Electroencephalography Signal Processing Based on Textural Features for Monitoring the Driver’s State by a Brain-Computer Interface
Giulia Orrù, Marco Micheletto, Fabio Terranova, Gian Luca Marcialis

Auto-TLDR; One-dimensional Local Binary Pattern Algorithm for Estimating Driver Vigilance in a Brain-Computer Interface System
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FastSal: A Computationally Efficient Network for Visual Saliency Prediction

Auto-TLDR; MobileNetV2: A Convolutional Neural Network for Saliency Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Image Sequence Based Cyclist Action Recognition Using Multi-Stream 3D Convolution
Stefan Zernetsch, Steven Schreck, Viktor Kress, Konrad Doll, Bernhard Sick
Auto-TLDR; 3D-ConvNet: A Multi-stream 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Detecting Cyclists in Real World Traffic Situations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Leveraging Synthetic Subject Invariant EEG Signals for Zero Calibration BCI
Nik Khadijah Nik Aznan, Amir Atapour-Abarghouei, Stephen Bonner, Jason Connolly, Toby Breckon

Auto-TLDR; SIS-GAN: Subject Invariant SSVEP Generative Adversarial Network for Brain-Computer Interface
SECI-GAN: Semantic and Edge Completion for Dynamic Objects Removal
Francesco Pinto, Andrea Romanoni, Matteo Matteucci, Phil Torr

Auto-TLDR; SECI-GAN: Semantic and Edge Conditioned Inpainting Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploiting the Logits: Joint Sign Language Recognition and Spell-Correction
Christina Runkel, Stefan Dorenkamp, Hartmut Bauermeister, Michael Möller

Auto-TLDR; A Convolutional Neural Network for Spell-correction in Sign Language Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Wireless Localisation in WiFi Using Novel Deep Architectures
Peizheng Li, Han Cui, Aftab Khan, Usman Raza, Robert Piechocki, Angela Doufexi, Tim Farnham
Auto-TLDR; Deep Neural Network for Indoor Localisation of WiFi Devices in Indoor Environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Rare Cell Populations in Flow Cytometry Data Using UMAP
Lisa Weijler, Markus Diem, Michael Reiter

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Manifold Approximation and Projection for Small Cell Population Detection in Flow cytometry Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Engineering and Stacked Echo State Networks for Musical Onset Detection
Peter Steiner, Azarakhsh Jalalvand, Simon Stone, Peter Birkholz

Auto-TLDR; Echo State Networks for Onset Detection in Music Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Comparison of Deep Learning and Hand Crafted Features for Mining Simulation Data
Theodoros Georgiou, Sebastian Schmitt, Thomas Baeck, Nan Pu, Wei Chen, Michael Lew

Auto-TLDR; Automated Data Analysis of Flow Fields in Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Contextual Classification Using Self-Supervised Auxiliary Models for Deep Neural Networks
Sebastian Palacio, Philipp Engler, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel

Auto-TLDR; Self-Supervised Autogenous Learning for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
From Early Biological Models to CNNs: Do They Look Where Humans Look?
Marinella Iole Cadoni, Andrea Lagorio, Enrico Grosso, Jia Huei Tan, Chee Seng Chan

Auto-TLDR; Comparing Neural Networks to Human Fixations for Semantic Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Emotional Blinded Face Representations
Alejandro Peña Almansa, Julian Fierrez, Agata Lapedriza, Aythami Morales

Auto-TLDR; Blind Face Representations for Emotion Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-People Mobile-Phone Based Airwriting Character Recognition
Yunzhe Li, Hui Zheng, He Zhu, Haojun Ai, Xiaowei Dong

Auto-TLDR; Cross-People Airwriting Recognition via Motion Sensor Signal via Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Modulation Pattern Detection Using Complex Convolutions in Deep Learning
Jakob Krzyston, Rajib Bhattacharjea, Andrew Stark

Auto-TLDR; Complex Convolutional Neural Networks for Modulation Pattern Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Translating Adult's Focus of Attention to Elderly's
Onkar Krishna, Go Irie, Takahito Kawanishi, Kunio Kashino, Kiyoharu Aizawa

Auto-TLDR; Elderly Focus of Attention Prediction Using Deep Image-to-Image Translation
Trainable Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations in Convolutional Neural Networks
Michele Alberti, Angela Botros, Schuetz Narayan, Rolf Ingold, Marcus Liwicki, Mathias Seuret

Auto-TLDR; Trainable and Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations for Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Discriminative Multi-Level Reconstruction under Compact Latent Space for One-Class Novelty Detection
Jaewoo Park, Yoon Gyo Jung, Andrew Teoh

Auto-TLDR; Discriminative Compact AE for One-Class novelty detection and Adversarial Example Detection
Recognizing Bengali Word Images - A Zero-Shot Learning Perspective
Sukalpa Chanda, Daniël Arjen Willem Haitink, Prashant Kumar Prasad, Jochem Baas, Umapada Pal, Lambert Schomaker
Auto-TLDR; Zero-Shot Learning for Word Recognition in Bengali Script
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Explorable Tone Mapping Operators
Su Chien-Chuan, Yu-Lun Liu, Hung Jin Lin, Ren Wang, Chia-Ping Chen, Yu-Lin Chang, Soo-Chang Pei

Auto-TLDR; Learning-based multimodal tone-mapping from HDR images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Anomaly Detection by Estimating Likelihood of Representations

Auto-TLDR; Video Anomaly Detection in the latent feature space using a deep probabilistic model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FatNet: A Feature-Attentive Network for 3D Point Cloud Processing
Chaitanya Kaul, Nick Pears, Suresh Manandhar

Auto-TLDR; Feature-Attentive Neural Networks for Point Cloud Classification and Segmentation
Depth Videos for the Classification of Micro-Expressions
Ankith Jain Rakesh Kumar, Bir Bhanu, Christopher Casey, Sierra Cheung, Aaron Seitz

Auto-TLDR; RGB-D Dataset for the Classification of Facial Micro-expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dimensionality Reduction for Data Visualization and Linear Classification, and the Trade-Off between Robustness and Classification Accuracy
Martin Becker, Jens Lippel, Thomas Zielke

Auto-TLDR; Robustness Assessment of Deep Autoencoder for Data Visualization using Scatter Plots
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single-Modal Incremental Terrain Clustering from Self-Supervised Audio-Visual Feature Learning
Reina Ishikawa, Ryo Hachiuma, Akiyoshi Kurobe, Hideo Saito

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Variational Autoencoder for Terrain Type Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
InsideBias: Measuring Bias in Deep Networks and Application to Face Gender Biometrics
Ignacio Serna, Alejandro Peña Almansa, Aythami Morales, Julian Fierrez
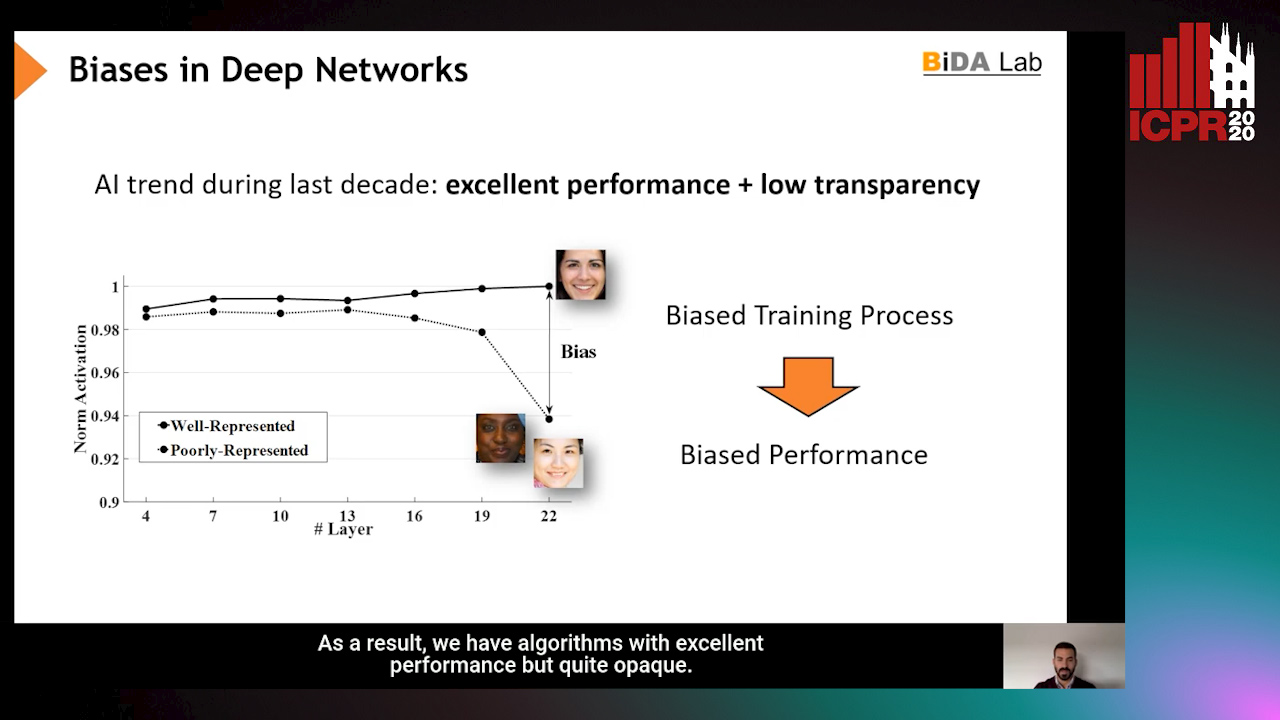
Auto-TLDR; InsideBias: Detecting Bias in Deep Neural Networks from Face Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Learning on Active Sonar Data Using Bayesian Optimization for Hyperparameter Tuning
Henrik Berg, Karl Thomas Hjelmervik

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian Optimization for Sonar Operations in Littoral Environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar