Collaborative Human Machine Attention Module for Character Recognition
Chetan Ralekar,
Tapan Gandhi,
Santanu Chaudhury

Auto-TLDR; A Collaborative Human-Machine Attention Module for Deep Neural Networks
Similar papers
Classifying Eye-Tracking Data Using Saliency Maps
Shafin Rahman, Sejuti Rahman, Omar Shahid, Md. Tahmeed Abdullah, Jubair Ahmed Sourov
Auto-TLDR; Saliency-based Feature Extraction for Automatic Classification of Eye-tracking Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
From Early Biological Models to CNNs: Do They Look Where Humans Look?
Marinella Iole Cadoni, Andrea Lagorio, Enrico Grosso, Jia Huei Tan, Chee Seng Chan

Auto-TLDR; Comparing Neural Networks to Human Fixations for Semantic Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Two-Level Attention-Based Fusion Learning for RGB-D Face Recognition
Hardik Uppal, Alireza Sepas-Moghaddam, Michael Greenspan, Ali Etemad

Auto-TLDR; Fused RGB-D Facial Recognition using Attention-Aware Feature Fusion
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Raw Eye Tracking Data Segmentation, Generation, and Reconstruction
Wolfgang Fuhl, Yao Rong, Enkelejda Kasneci
Auto-TLDR; Semantic Segmentation of Eye Tracking Data with Fully Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
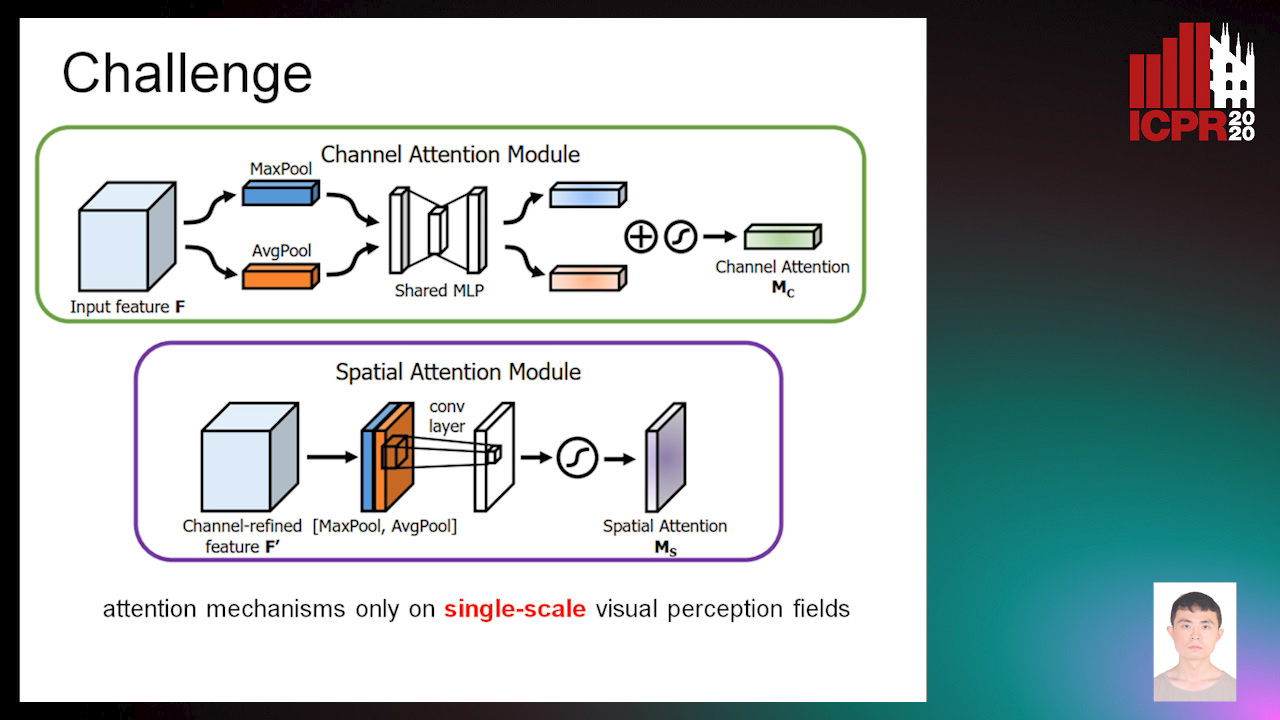
Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock Module for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Junhui Yin, Siqing Zhang, Dongliang Chang, Zhanyu Ma, Jun Guo
Auto-TLDR; Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GazeMAE: General Representations of Eye Movements Using a Micro-Macro Autoencoder
Louise Gillian C. Bautista, Prospero Naval

Auto-TLDR; Fast and Slow Eye Movement Representations for Sentiment-agnostic Eye Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context-Aware Residual Module for Image Classification
Auto-TLDR; Context-Aware Residual Module for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A General End-To-End Method for Characterizing Neuropsychiatric Disorders Using Free-Viewing Visual Scanning Tasks
Hong Yue Sean Liu, Jonathan Chung, Moshe Eizenman

Auto-TLDR; A general, data-driven, end-to-end framework that extracts relevant features of attentional bias from visual scanning behaviour and uses these features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention As Activation
Yimian Dai, Stefan Oehmcke, Fabian Gieseke, Yiquan Wu, Kobus Barnard

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Activation Units for Convolutional Networks
Arbitrary Style Transfer with Parallel Self-Attention
Tiange Zhang, Ying Gao, Feng Gao, Lin Qi, Junyu Dong

Auto-TLDR; Self-Attention-Based Arbitrary Style Transfer Using Adaptive Instance Normalization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Global-Local Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation in Aerial Images
Minglong Li, Lianlei Shan, Weiqiang Wang

Auto-TLDR; GLANet: Global-Local Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention Pyramid Module for Scene Recognition
Zhinan Qiao, Xiaohui Yuan, Chengyuan Zhuang, Abolfazl Meyarian

Auto-TLDR; Attention Pyramid Module for Multi-Scale Scene Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Question-Agnostic Attention for Visual Question Answering
Moshiur R Farazi, Salman Hameed Khan, Nick Barnes

Auto-TLDR; Question-Agnostic Attention for Visual Question Answering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Utilising Visual Attention Cues for Vehicle Detection and Tracking
Feiyan Hu, Venkatesh Gurram Munirathnam, Noel E O'Connor, Alan Smeaton, Suzanne Little
Auto-TLDR; Visual Attention for Object Detection and Tracking in Driver-Assistance Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PSDNet: A Balanced Architecture of Accuracy and Parameters for Semantic Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Pyramid Pooling Module with SE1Cblock and D2SUpsample Network (PSDNet)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FatNet: A Feature-Attentive Network for 3D Point Cloud Processing
Chaitanya Kaul, Nick Pears, Suresh Manandhar

Auto-TLDR; Feature-Attentive Neural Networks for Point Cloud Classification and Segmentation
Saliency Prediction on Omnidirectional Images with Brain-Like Shallow Neural Network
Zhu Dandan, Chen Yongqing, Min Xiongkuo, Zhao Defang, Zhu Yucheng, Zhou Qiangqiang, Yang Xiaokang, Tian Han

Auto-TLDR; A Brain-like Neural Network for Saliency Prediction of Head Fixations on Omnidirectional Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FastSal: A Computationally Efficient Network for Visual Saliency Prediction

Auto-TLDR; MobileNetV2: A Convolutional Neural Network for Saliency Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient-Receptive Field Block with Group Spatial Attention Mechanism for Object Detection
Jiacheng Zhang, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; E-RFB: Efficient-Receptive Field Block for Deep Neural Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Flow-Guided Spatial Attention Tracking for Egocentric Activity Recognition

Auto-TLDR; flow-guided spatial attention tracking for egocentric activity recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Feature Fusion Network for Gaze Tracking in Mobile Tablets
Yiwei Bao, Yihua Cheng, Yunfei Liu, Feng Lu

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Feature Fusion Network for Multi-stream Gaze Estimation in Mobile Tablets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ReADS: A Rectified Attentional Double Supervised Network for Scene Text Recognition
Qi Song, Qianyi Jiang, Xiaolin Wei, Nan Li, Rui Zhang

Auto-TLDR; ReADS: Rectified Attentional Double Supervised Network for General Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Based Selection Strategy for Weakly Supervised Object Localization

Auto-TLDR; An Attention-based Selection Strategy for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RLST: A Reinforcement Learning Approach to Scene Text Detection Refinement
Xuan Peng, Zheng Huang, Kai Chen, Jie Guo, Weidong Qiu
Auto-TLDR; Saccadic Eye Movements and Peripheral Vision for Scene Text Detection using Reinforcement Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detection and Correspondence Matching of Corneal Reflections for Eye Tracking Using Deep Learning
Soumil Chugh, Braiden Brousseau, Jonathan Rose, Moshe Eizenman

Auto-TLDR; A Fully Convolutional Neural Network for Corneal Reflection Detection and Matching in Extended Reality Eye Tracking Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Attention Mechanism for Fine-Grained Classification of Table Tennis Strokes Using a Twin Spatio-Temporal Convolutional Neural Networks
Pierre-Etienne Martin, Jenny Benois-Pineau, Renaud Péteri, Julien Morlier

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Blocks for Action Recognition in Table Tennis Strokes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SAT-Net: Self-Attention and Temporal Fusion for Facial Action Unit Detection
Zhihua Li, Zheng Zhang, Lijun Yin

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Fusion and Self-Attention Network for Facial Action Unit Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
User-Independent Gaze Estimation by Extracting Pupil Parameter and Its Mapping to the Gaze Angle

Auto-TLDR; Gaze Point Estimation using Pupil Shape for Generalization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Semantic Segmentation of Structural Elements related to the Spinal Cord in the Lumbar Region by Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Jhon Jairo Sáenz Gamboa, Maria De La Iglesia-Vaya, Jon Ander Gómez

Auto-TLDR; Semantic Segmentation of Lumbar Spine Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Second-Order Attention Guided Convolutional Activations for Visual Recognition
Shannan Chen, Qian Wang, Qiule Sun, Bin Liu, Jianxin Zhang, Qiang Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Second-order Attention Guided Network for Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Scale Residual Pyramid Attention Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Jing Liu, Xiaona Zhang, Zhaoxin Li, Tianlu Mao
Auto-TLDR; Multi-scale Residual Pyramid Attention Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Selective Kernel and Motion-Emphasized Loss Based Attention-Guided Network for HDR Imaging of Dynamic Scenes
Yipeng Deng, Qin Liu, Takeshi Ikenaga

Auto-TLDR; SK-AHDRNet: A Deep Network with attention module and motion-emphasized loss function to produce ghost-free HDR images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Joint Encoding of Motion and Appearance for First Person Action Recognition
Mirco Planamente, Andrea Bottino, Barbara Caputo

Auto-TLDR; A Single Stream Architecture for Egocentric Action Recognition from the First-Person Point of View
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Directed Variational Cross-encoder Network for Few-Shot Multi-image Co-segmentation
Sayan Banerjee, Divakar Bhat S, Subhasis Chaudhuri, Rajbabu Velmurugan
Auto-TLDR; Directed Variational Inference Cross Encoder for Class Agnostic Co-Segmentation of Multiple Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Transformer-Based Radical Analysis Network for Chinese Character Recognition
Chen Yang, Qing Wang, Jun Du, Jianshu Zhang, Changjie Wu, Jiaming Wang

Auto-TLDR; Transformer-based Radical Analysis Network for Chinese Character Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Do Not Treat Boundaries and Regions Differently: An Example on Heart Left Atrial Segmentation
Zhou Zhao, Elodie Puybareau, Nicolas Boutry, Thierry Geraud
Auto-TLDR; Attention Full Convolutional Network for Atrial Segmentation using ResNet-101 Architecture
Self and Channel Attention Network for Person Re-Identification
Asad Munir, Niki Martinel, Christian Micheloni

Auto-TLDR; SCAN: Self and Channel Attention Network for Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ACRM: Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix-NMS for Metallic Surface Defect Detection
Junting Fang, Xiaoyang Tan, Yuhui Wang

Auto-TLDR; Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix Non-Maximum Suppression for Robust Metal Defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Improved Bilinear Pooling Method for Image-Based Action Recognition

Auto-TLDR; An improved bilinear pooling method for image-based action recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhancing Semantic Segmentation of Aerial Images with Inhibitory Neurons
Ihsan Ullah, Sean Reilly, Michael Madden

Auto-TLDR; Lateral Inhibition in Deep Neural Networks for Object Recognition and Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Trainable Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations in Convolutional Neural Networks
Michele Alberti, Angela Botros, Schuetz Narayan, Rolf Ingold, Marcus Liwicki, Mathias Seuret

Auto-TLDR; Trainable and Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations for Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rotation Invariant Aerial Image Retrieval with Group Convolutional Metric Learning
Hyunseung Chung, Woo-Jeoung Nam, Seong-Whan Lee

Auto-TLDR; Robust Remote Sensing Image Retrieval Using Group Convolution with Attention Mechanism and Metric Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Image Compression Using GAN Based Semantic-Perceptual Residual Compensation
Ruojing Wang, Zitang Sun, Sei-Ichiro Kamata, Weili Chen
Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Image Compression using GAN based Semantic-Perceptual Residual Compensation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
BCAU-Net: A Novel Architecture with Binary Channel Attention Module for MRI Brain Segmentation
Yongpei Zhu, Zicong Zhou, Guojun Liao, Kehong Yuan

Auto-TLDR; BCAU-Net: Binary Channel Attention U-Net for MRI brain segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DARN: Deep Attentive Refinement Network for Liver Tumor Segmentation from 3D CT Volume
Yao Zhang, Jiang Tian, Cheng Zhong, Yang Zhang, Zhongchao Shi, Zhiqiang He

Auto-TLDR; Deep Attentive Refinement Network for Liver Tumor Segmentation from 3D Computed Tomography Using Multi-Level Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Watch Your Strokes: Improving Handwritten Text Recognition with Deformable Convolutions
Iulian Cojocaru, Silvia Cascianelli, Lorenzo Baraldi, Massimiliano Corsini, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Deformable Convolutional Neural Networks for Handwritten Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentive Hybrid Feature Based a Two-Step Fusion for Facial Expression Recognition
Jun Weng, Yang Yang, Zichang Tan, Zhen Lei
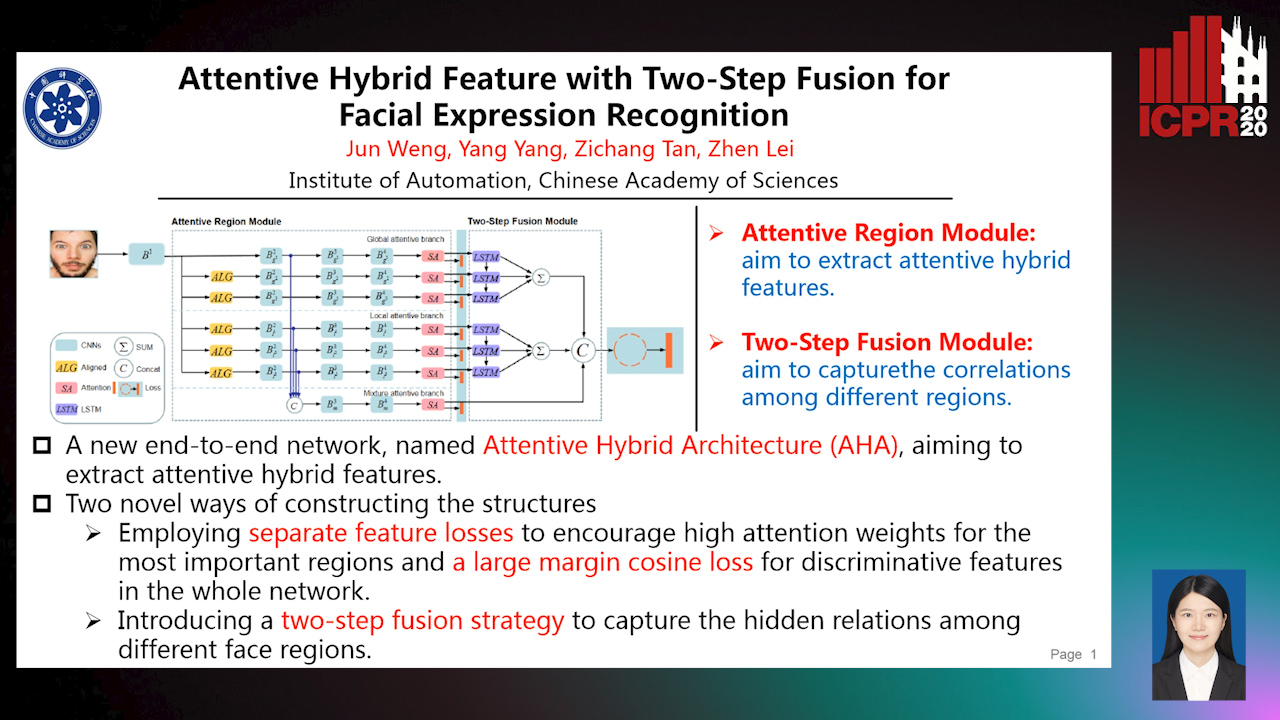
Auto-TLDR; Attentive Hybrid Architecture for Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TSMSAN: A Three-Stream Multi-Scale Attentive Network for Video Saliency Detection
Jingwen Yang, Guanwen Zhang, Wei Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Three-stream Multi-scale attentive network for video saliency detection in dynamic scenes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar