Automatic Semantic Segmentation of Structural Elements related to the Spinal Cord in the Lumbar Region by Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Jhon Jairo Sáenz Gamboa,
Maria De La Iglesia-Vaya,
Jon Ander Gómez

Auto-TLDR; Semantic Segmentation of Lumbar Spine Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Similar papers
FOANet: A Focus of Attention Network with Application to Myocardium Segmentation
Zhou Zhao, Elodie Puybareau, Nicolas Boutry, Thierry Geraud

Auto-TLDR; FOANet: A Hybrid Loss Function for Myocardium Segmentation of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Planar 3D Transfer Learning for End to End Unimodal MRI Unbalanced Data Segmentation
Martin Kolarik, Radim Burget, Carlos M. Travieso-Gonzalez, Jan Kocica

Auto-TLDR; Planar 3D Res-U-Net Network for Unbalanced 3D Image Segmentation using Fluid Attenuation Inversion Recover
A Benchmark Dataset for Segmenting Liver, Vasculature and Lesions from Large-Scale Computed Tomography Data
Bo Wang, Zhengqing Xu, Wei Xu, Qingsen Yan, Liang Zhang, Zheng You

Auto-TLDR; The Biggest Treatment-Oriented Liver Cancer Dataset for Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Segmentation of Intracranial Aneurysm Remnant in MRA Using Dual-Attention Atrous Net
Subhashis Banerjee, Ashis Kumar Dhara, Johan Wikström, Robin Strand

Auto-TLDR; Dual-Attention Atrous Net for Segmentation of Intracranial Aneurysm Remnant from MRA Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Recurrent-Convolutional Model for AutomatedSegmentation of Craniomaxillofacial CT Scans
Francesca Murabito, Simone Palazzo, Federica Salanitri Proietto, Francesco Rundo, Ulas Bagci, Daniela Giordano, Rosalia Leonardi, Concetto Spampinato

Auto-TLDR; Automated Segmentation of Anatomical Structures in Craniomaxillofacial CT Scans using Fully Convolutional Deep Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Deep Learning Approach for the Segmentation of Myocardial Diseases
Khawala Brahim, Abdull Qayyum, Alain Lalande, Arnaud Boucher, Anis Sakly, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; Segmentation of Myocardium Infarction Using Late GADEMRI and SegU-Net
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
BiLuNet: A Multi-Path Network for Semantic Segmentation on X-Ray Images
Van Luan Tran, Huei-Yung Lin, Rachel Liu, Chun-Han Tseng, Chun-Han Tseng
Auto-TLDR; BiLuNet: Multi-path Convolutional Neural Network for Semantic Segmentation of Lumbar vertebrae, sacrum,
Deep Learning-Based Type Identification of Volumetric MRI Sequences
Jean Pablo De Mello, Thiago Paixão, Rodrigo Berriel, Mauricio Reyes, Alberto F. De Souza, Claudine Badue, Thiago Oliveira-Santos

Auto-TLDR; Deep Learning for Brain MRI Sequences Identification Using Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Do Not Treat Boundaries and Regions Differently: An Example on Heart Left Atrial Segmentation
Zhou Zhao, Elodie Puybareau, Nicolas Boutry, Thierry Geraud
Auto-TLDR; Attention Full Convolutional Network for Atrial Segmentation using ResNet-101 Architecture
A Multi-Task Contextual Atrous Residual Network for Brain Tumor Detection & Segmentation
Ngan Le, Kashu Yamazaki, Quach Kha Gia, Thanh-Dat Truong, Marios Savvides

Auto-TLDR; Contextual Brain Tumor Segmentation Using 3D atrous Residual Networks and Cascaded Structures
3D Medical Multi-Modal Segmentation Network Guided by Multi-Source Correlation Constraint
Tongxue Zhou, Stéphane Canu, Pierre Vera, Su Ruan
Auto-TLDR; Multi-modality Segmentation with Correlation Constrained Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Segmenting Kidney on Multiple Phase CT Images Using ULBNet
Yanling Chi, Yuyu Xu, Gang Feng, Jiawei Mao, Sihua Wu, Guibin Xu, Weimin Huang
Auto-TLDR; A ULBNet network for kidney segmentation on multiple phase CT images
BCAU-Net: A Novel Architecture with Binary Channel Attention Module for MRI Brain Segmentation
Yongpei Zhu, Zicong Zhou, Guojun Liao, Kehong Yuan

Auto-TLDR; BCAU-Net: Binary Channel Attention U-Net for MRI brain segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DA-RefineNet: Dual-Inputs Attention RefineNet for Whole Slide Image Segmentation
Ziqiang Li, Rentuo Tao, Qianrun Wu, Bin Li

Auto-TLDR; DA-RefineNet: A dual-inputs attention network for whole slide image segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
End-To-End Multi-Task Learning for Lung Nodule Segmentation and Diagnosis
Wei Chen, Qiuli Wang, Dan Yang, Xiaohong Zhang, Chen Liu, Yucong Li
Auto-TLDR; A novel multi-task framework for lung nodule diagnosis based on deep learning and medical features
A Transformer-Based Network for Anisotropic 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Guo Danfeng, Demetri Terzopoulos
Auto-TLDR; A transformer-based model to tackle the anisotropy problem in 3D medical image analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Lumen Segmentation Method in Ureteroscopy Images Based on a Deep Residual U-Net Architecture
Jorge Lazo, Marzullo Aldo, Sara Moccia, Michele Catellani, Benoit Rosa, Elena De Momi, Michel De Mathelin, Francesco Calimeri
Auto-TLDR; A Deep Neural Network for Ureteroscopy with Residual Units
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learn to Segment Retinal Lesions and Beyond
Qijie Wei, Xirong Li, Weihong Yu, Xiao Zhang, Yongpeng Zhang, Bojie Hu, Bin Mo, Di Gong, Ning Chen, Dayong Ding, Youxin Chen

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Lesion Segmentation and Disease Classification for Diabetic Retinopathy Grading
CAggNet: Crossing Aggregation Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Auto-TLDR; Crossing Aggregation Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DARN: Deep Attentive Refinement Network for Liver Tumor Segmentation from 3D CT Volume
Yao Zhang, Jiang Tian, Cheng Zhong, Yang Zhang, Zhongchao Shi, Zhiqiang He

Auto-TLDR; Deep Attentive Refinement Network for Liver Tumor Segmentation from 3D Computed Tomography Using Multi-Level Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MTGAN: Mask and Texture-Driven Generative Adversarial Network for Lung Nodule Segmentation
Wei Chen, Qiuli Wang, Kun Wang, Dan Yang, Xiaohong Zhang, Chen Liu, Yucong Li
Auto-TLDR; Mask and Texture-driven Generative Adversarial Network for Lung Nodule Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
One-Stage Multi-Task Detector for 3D Cardiac MR Imaging
Weizeng Lu, Xi Jia, Wei Chen, Nicolò Savioli, Antonio De Marvao, Linlin Shen, Declan O'Regan, Jinming Duan

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Learning for Real-Time, simultaneous landmark location and bounding box detection in 3D space
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
EM-Net: Deep Learning for Electron Microscopy Image Segmentation
Afshin Khadangi, Thomas Boudier, Vijay Rajagopal

Auto-TLDR; EM-net: Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Electron Microscopy Image Segmentation
DE-Net: Dilated Encoder Network for Automated Tongue Segmentation
Hui Tang, Bin Wang, Jun Zhou, Yongsheng Gao

Auto-TLDR; Automated Tongue Image Segmentation using De-Net
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhancing Semantic Segmentation of Aerial Images with Inhibitory Neurons
Ihsan Ullah, Sean Reilly, Michael Madden

Auto-TLDR; Lateral Inhibition in Deep Neural Networks for Object Recognition and Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Transfer Learning through Weighted Loss Function and Group Normalization for Vessel Segmentation from Retinal Images
Abdullah Sarhan, Jon Rokne, Reda Alhajj, Andrew Crichton

Auto-TLDR; Deep Learning for Segmentation of Blood Vessels in Retinal Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Systematic Investigation on Deep Architectures for Automatic Skin Lesions Classification
Pierluigi Carcagni, Marco Leo, Andrea Cuna, Giuseppe Celeste, Cosimo Distante

Auto-TLDR; RegNet: Deep Investigation of Convolutional Neural Networks for Automatic Classification of Skin Lesions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhancing Deep Semantic Segmentation of RGB-D Data with Entangled Forests
Matteo Terreran, Elia Bonetto, Stefano Ghidoni

Auto-TLDR; FuseNet: A Lighter Deep Learning Model for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
BG-Net: Boundary-Guided Network for Lung Segmentation on Clinical CT Images
Rui Xu, Yi Wang, Tiantian Liu, Xinchen Ye, Lin Lin, Yen-Wei Chen, Shoji Kido, Noriyuki Tomiyama

Auto-TLDR; Boundary-Guided Network for Lung Segmentation on CT Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
NephCNN: A Deep-Learning Framework for Vessel Segmentation in Nephrectomy Laparoscopic Videos
Alessandro Casella, Sara Moccia, Chiara Carlini, Emanuele Frontoni, Elena De Momi, Leonardo Mattos

Auto-TLDR; Adversarial Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for kidney vessel segmentation from nephrectomy laparoscopic videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual Encoder Fusion U-Net (DEFU-Net) for Cross-manufacturer Chest X-Ray Segmentation
Zhang Lipei, Aozhi Liu, Jing Xiao
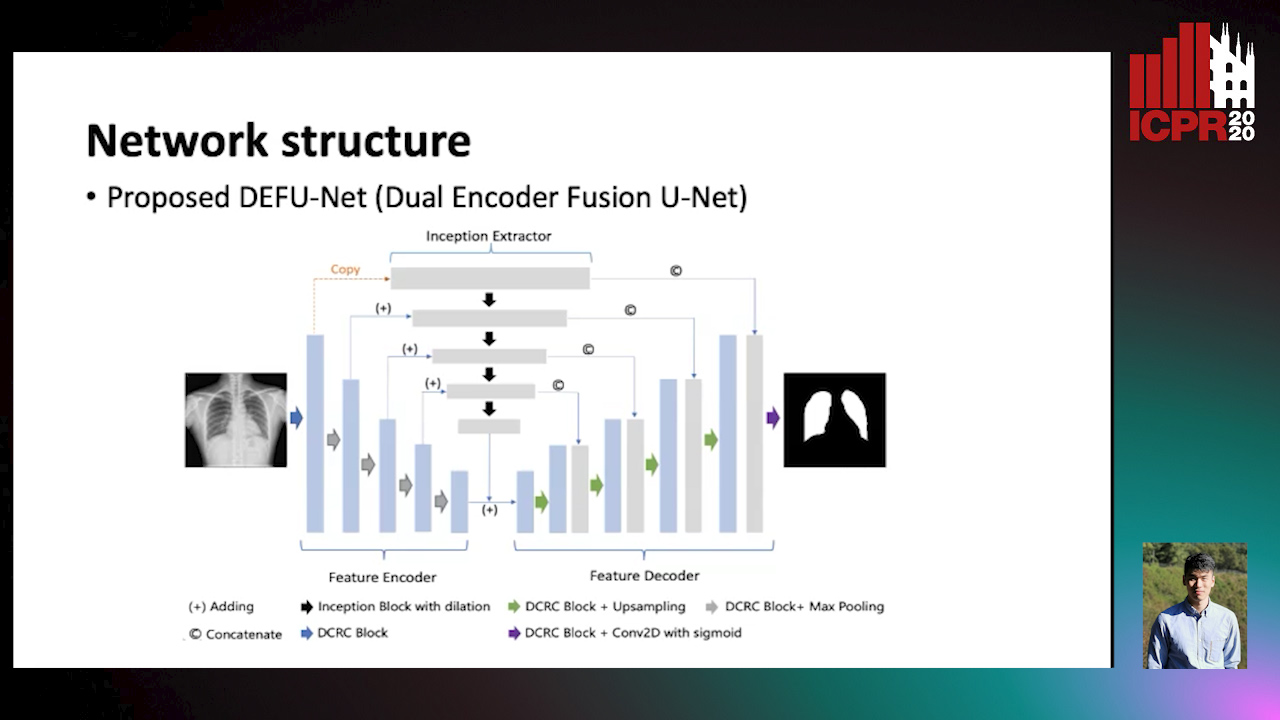
Auto-TLDR; Inception Convolutional Neural Network with Dilation for Chest X-Ray Segmentation
Triplet-Path Dilated Network for Detection and Segmentation of General Pathological Images
Jiaqi Luo, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su, Limei Guo

Auto-TLDR; Triplet-path Network for One-Stage Object Detection and Segmentation in Pathological Images
Fine-Tuning Convolutional Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Guide and Benchmark Analysis for Glaucoma Screening
Amed Mvoulana, Rostom Kachouri, Mohamed Akil
Auto-TLDR; Fine-tuning Convolutional Neural Networks for Glaucoma Screening
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Comparison of Neural Network Approaches for Melanoma Classification
Maria Frasca, Michele Nappi, Michele Risi, Genoveffa Tortora, Alessia Auriemma Citarella
Auto-TLDR; Classification of Melanoma Using Deep Neural Network Methodologies
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Multi-Stage Model for Automated Landmarking of Craniomaxillofacial CT Scans
Simone Palazzo, Giovanni Bellitto, Luca Prezzavento, Francesco Rundo, Ulas Bagci, Daniela Giordano, Rosalia Leonardi, Concetto Spampinato

Auto-TLDR; Automated Landmarking of Craniomaxillofacial CT Images Using Deep Multi-Stage Architecture
Progressive Adversarial Semantic Segmentation
Abdullah-Al-Zubaer Imran, Demetri Terzopoulos

Auto-TLDR; Progressive Adversarial Semantic Segmentation for End-to-End Medical Image Segmenting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Segmentation of Axillary and Supraclavicular Tumoral Lymph Nodes in PET/CT: A Hybrid CNN/Component-Tree Approach
Diana Lucia Farfan Cabrera, Nicolas Gogin, David Morland, Benoît Naegel, Dimitri Papathanassiou, Nicolas Passat

Auto-TLDR; Coupling Convolutional Neural Networks and Component-Trees for Lymph node Segmentation from PET/CT Images
Transitional Asymmetric Non-Local Neural Networks for Real-World Dirt Road Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Transitional Asymmetric Non-Local Neural Networks for Semantic Segmentation on Dirt Roads
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Leveraging Unlabeled Data for Glioma Molecular Subtype and Survival Prediction
Nicholas Nuechterlein, Beibin Li, Mehmet Saygin Seyfioglu, Sachin Mehta, Patrick Cimino, Linda Shapiro

Auto-TLDR; Multimodal Brain Tumor Segmentation Using Unlabeled MR Data and Genomic Data for Cancer Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Revisiting Sequence-To-Sequence Video Object Segmentation with Multi-Task Loss and Skip-Memory
Fatemeh Azimi, Benjamin Bischke, Sebastian Palacio, Federico Raue, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel

Auto-TLDR; Sequence-to-Sequence Learning for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PCANet: Pyramid Context-Aware Network for Retinal Vessel Segmentation
Yi Zhang, Yixuan Chen, Kai Zhang

Auto-TLDR; PCANet: Adaptive Context-Aware Network for Automated Retinal Vessel Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PSDNet: A Balanced Architecture of Accuracy and Parameters for Semantic Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Pyramid Pooling Module with SE1Cblock and D2SUpsample Network (PSDNet)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semantic Segmentation Refinement Using Entropy and Boundary-guided Monte Carlo Sampling and Directed Regional Search
Zitang Sun, Sei-Ichiro Kamata, Ruojing Wang, Weili Chen
Auto-TLDR; Directed Region Search and Refinement for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multiscale Attention-Based Prototypical Network for Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Yifei Zhang, Desire Sidibe, Olivier Morel, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; Few-shot Semantic Segmentation with Multiscale Feature Attention
Accurate Cell Segmentation in Digital Pathology Images Via Attention Enforced Networks
Zeyi Yao, Kaiqi Li, Guanhong Zhang, Yiwen Luo, Xiaoguang Zhou, Muyi Sun

Auto-TLDR; AENet: Attention Enforced Network for Automatic Cell Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Trainable Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations in Convolutional Neural Networks
Michele Alberti, Angela Botros, Schuetz Narayan, Rolf Ingold, Marcus Liwicki, Mathias Seuret

Auto-TLDR; Trainable and Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations for Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Novel Computer-Aided Diagnostic System for Early Assessment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Ahmed Alksas, Mohamed Shehata, Gehad Saleh, Ahmed Shaffie, Ahmed Soliman, Mohammed Ghazal, Hadil Abukhalifeh, Abdel Razek Ahmed, Ayman El-Baz

Auto-TLDR; Classification of Liver Tumor Lesions from CE-MRI Using Structured Structural Features and Functional Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar