Dual Encoder Fusion U-Net (DEFU-Net) for Cross-manufacturer Chest X-Ray Segmentation
Zhang Lipei,
Aozhi Liu,
Jing Xiao
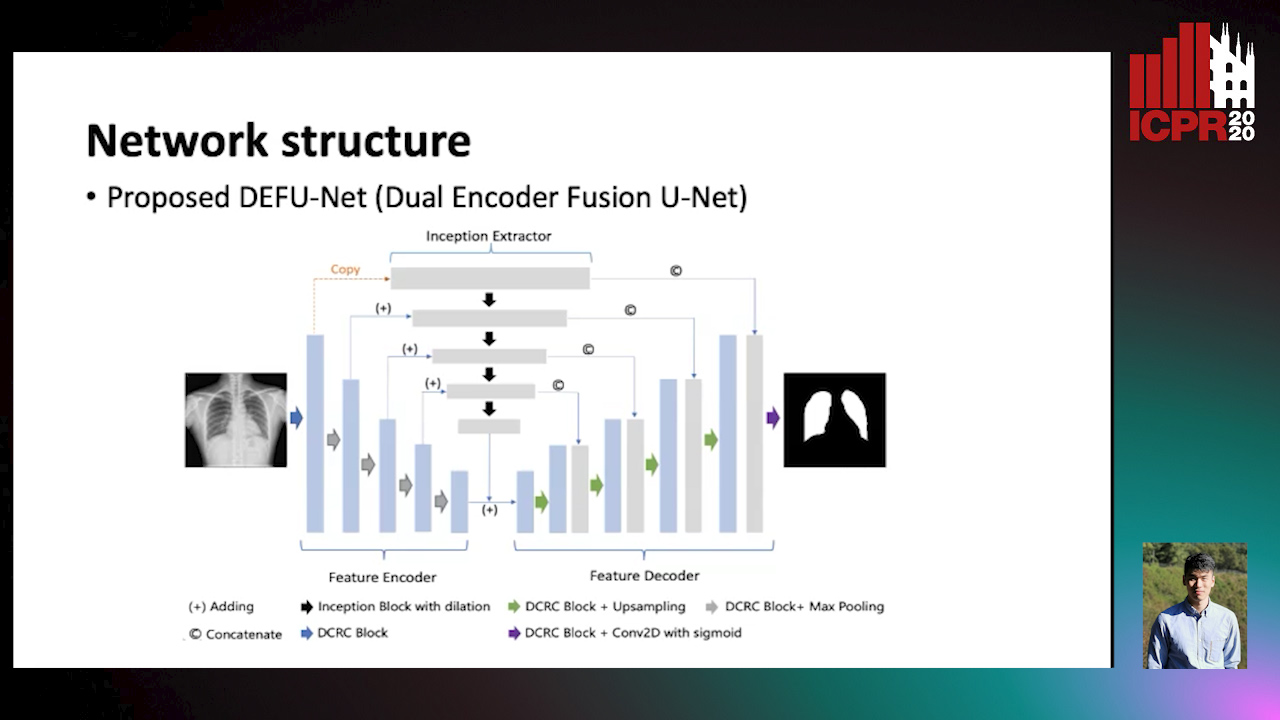
Auto-TLDR; Inception Convolutional Neural Network with Dilation for Chest X-Ray Segmentation
Similar papers
CAggNet: Crossing Aggregation Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Auto-TLDR; Crossing Aggregation Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
BCAU-Net: A Novel Architecture with Binary Channel Attention Module for MRI Brain Segmentation
Yongpei Zhu, Zicong Zhou, Guojun Liao, Kehong Yuan

Auto-TLDR; BCAU-Net: Binary Channel Attention U-Net for MRI brain segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
End-To-End Multi-Task Learning for Lung Nodule Segmentation and Diagnosis
Wei Chen, Qiuli Wang, Dan Yang, Xiaohong Zhang, Chen Liu, Yucong Li
Auto-TLDR; A novel multi-task framework for lung nodule diagnosis based on deep learning and medical features
BiLuNet: A Multi-Path Network for Semantic Segmentation on X-Ray Images
Van Luan Tran, Huei-Yung Lin, Rachel Liu, Chun-Han Tseng, Chun-Han Tseng
Auto-TLDR; BiLuNet: Multi-path Convolutional Neural Network for Semantic Segmentation of Lumbar vertebrae, sacrum,
DE-Net: Dilated Encoder Network for Automated Tongue Segmentation
Hui Tang, Bin Wang, Jun Zhou, Yongsheng Gao

Auto-TLDR; Automated Tongue Image Segmentation using De-Net
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Inception Based Deep Learning Architecture for Tuberculosis Screening of Chest X-Rays
Dipayan Das, K.C. Santosh, Umapada Pal

Auto-TLDR; End to End CNN-based Chest X-ray Screening for Tuberculosis positive patients in the severely resource constrained regions of the world
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PCANet: Pyramid Context-Aware Network for Retinal Vessel Segmentation
Yi Zhang, Yixuan Chen, Kai Zhang

Auto-TLDR; PCANet: Adaptive Context-Aware Network for Automated Retinal Vessel Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Triplet-Path Dilated Network for Detection and Segmentation of General Pathological Images
Jiaqi Luo, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su, Limei Guo

Auto-TLDR; Triplet-path Network for One-Stage Object Detection and Segmentation in Pathological Images
A Benchmark Dataset for Segmenting Liver, Vasculature and Lesions from Large-Scale Computed Tomography Data
Bo Wang, Zhengqing Xu, Wei Xu, Qingsen Yan, Liang Zhang, Zheng You

Auto-TLDR; The Biggest Treatment-Oriented Liver Cancer Dataset for Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Segmentation of Intracranial Aneurysm Remnant in MRA Using Dual-Attention Atrous Net
Subhashis Banerjee, Ashis Kumar Dhara, Johan Wikström, Robin Strand

Auto-TLDR; Dual-Attention Atrous Net for Segmentation of Intracranial Aneurysm Remnant from MRA Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Detection of Pulmonary Opacities for Computer-Aided Diagnosis of COVID-19 on CT Images
Rui Xu, Xiao Cao, Yufeng Wang, Yen-Wei Chen, Xinchen Ye, Lin Lin, Wenchao Zhu, Chao Chen, Fangyi Xu, Yong Zhou, Hongjie Hu, Shoji Kido, Noriyuki Tomiyama
Auto-TLDR; A computer-aided diagnosis of COVID-19 from CT images using unsupervised pulmonary opacity detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Recurrent-Convolutional Model for AutomatedSegmentation of Craniomaxillofacial CT Scans
Francesca Murabito, Simone Palazzo, Federica Salanitri Proietto, Francesco Rundo, Ulas Bagci, Daniela Giordano, Rosalia Leonardi, Concetto Spampinato

Auto-TLDR; Automated Segmentation of Anatomical Structures in Craniomaxillofacial CT Scans using Fully Convolutional Deep Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MTGAN: Mask and Texture-Driven Generative Adversarial Network for Lung Nodule Segmentation
Wei Chen, Qiuli Wang, Kun Wang, Dan Yang, Xiaohong Zhang, Chen Liu, Yucong Li
Auto-TLDR; Mask and Texture-driven Generative Adversarial Network for Lung Nodule Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
BG-Net: Boundary-Guided Network for Lung Segmentation on Clinical CT Images
Rui Xu, Yi Wang, Tiantian Liu, Xinchen Ye, Lin Lin, Yen-Wei Chen, Shoji Kido, Noriyuki Tomiyama

Auto-TLDR; Boundary-Guided Network for Lung Segmentation on CT Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Transitional Asymmetric Non-Local Neural Networks for Real-World Dirt Road Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Transitional Asymmetric Non-Local Neural Networks for Semantic Segmentation on Dirt Roads
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Multi-Task Contextual Atrous Residual Network for Brain Tumor Detection & Segmentation
Ngan Le, Kashu Yamazaki, Quach Kha Gia, Thanh-Dat Truong, Marios Savvides

Auto-TLDR; Contextual Brain Tumor Segmentation Using 3D atrous Residual Networks and Cascaded Structures
Learn to Segment Retinal Lesions and Beyond
Qijie Wei, Xirong Li, Weihong Yu, Xiao Zhang, Yongpeng Zhang, Bojie Hu, Bin Mo, Di Gong, Ning Chen, Dayong Ding, Youxin Chen

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Lesion Segmentation and Disease Classification for Diabetic Retinopathy Grading
Automatic Semantic Segmentation of Structural Elements related to the Spinal Cord in the Lumbar Region by Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Jhon Jairo Sáenz Gamboa, Maria De La Iglesia-Vaya, Jon Ander Gómez

Auto-TLDR; Semantic Segmentation of Lumbar Spine Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Global-Local Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation in Aerial Images
Minglong Li, Lianlei Shan, Weiqiang Wang

Auto-TLDR; GLANet: Global-Local Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CT-UNet: An Improved Neural Network Based on U-Net for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images
Huanran Ye, Sheng Liu, Kun Jin, Haohao Cheng
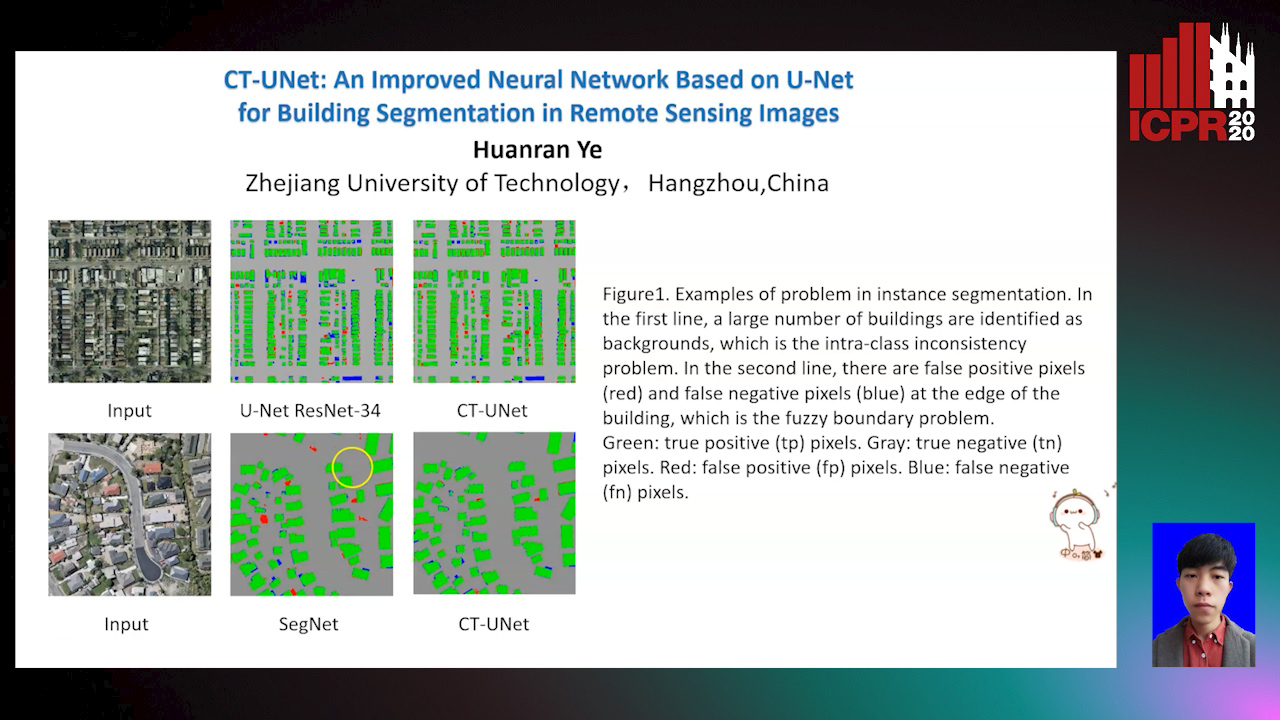
Auto-TLDR; Context-Transfer-UNet: A UNet-based Network for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DA-RefineNet: Dual-Inputs Attention RefineNet for Whole Slide Image Segmentation
Ziqiang Li, Rentuo Tao, Qianrun Wu, Bin Li

Auto-TLDR; DA-RefineNet: A dual-inputs attention network for whole slide image segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Aerial Road Segmentation in the Presence of Topological Label Noise
Corentin Henry, Friedrich Fraundorfer, Eleonora Vig

Auto-TLDR; Improving Road Segmentation with Noise-Aware U-Nets for Fine-Grained Topology delineation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fast and Accurate Real-Time Semantic Segmentation with Dilated Asymmetric Convolutions
Leonel Rosas-Arias, Gibran Benitez-Garcia, Jose Portillo-Portillo, Gabriel Sanchez-Perez, Keiji Yanai
Auto-TLDR; FASSD-Net: Dilated Asymmetric Pyramidal Fusion for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DARN: Deep Attentive Refinement Network for Liver Tumor Segmentation from 3D CT Volume
Yao Zhang, Jiang Tian, Cheng Zhong, Yang Zhang, Zhongchao Shi, Zhiqiang He

Auto-TLDR; Deep Attentive Refinement Network for Liver Tumor Segmentation from 3D Computed Tomography Using Multi-Level Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Planar 3D Transfer Learning for End to End Unimodal MRI Unbalanced Data Segmentation
Martin Kolarik, Radim Burget, Carlos M. Travieso-Gonzalez, Jan Kocica

Auto-TLDR; Planar 3D Res-U-Net Network for Unbalanced 3D Image Segmentation using Fluid Attenuation Inversion Recover
SA-UNet: Spatial Attention U-Net for Retinal Vessel Segmentation
Changlu Guo, Marton Szemenyei, Yugen Yi, Wenle Wang, Buer Chen, Changqi Fan

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Attention U-Net for Segmentation of Retinal Blood Vessels
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PSDNet: A Balanced Architecture of Accuracy and Parameters for Semantic Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Pyramid Pooling Module with SE1Cblock and D2SUpsample Network (PSDNet)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Deep Learning Approach for the Segmentation of Myocardial Diseases
Khawala Brahim, Abdull Qayyum, Alain Lalande, Arnaud Boucher, Anis Sakly, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; Segmentation of Myocardium Infarction Using Late GADEMRI and SegU-Net
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Accurate Cell Segmentation in Digital Pathology Images Via Attention Enforced Networks
Zeyi Yao, Kaiqi Li, Guanhong Zhang, Yiwen Luo, Xiaoguang Zhou, Muyi Sun

Auto-TLDR; AENet: Attention Enforced Network for Automatic Cell Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multiple Document Datasets Pre-Training Improves Text Line Detection with Deep Neural Networks
Mélodie Boillet, Christopher Kermorvant, Thierry Paquet

Auto-TLDR; A fully convolutional network for document layout analysis
Real-Time Semantic Segmentation Via Region and Pixel Context Network
Yajun Li, Yazhou Liu, Quansen Sun
Auto-TLDR; A Dual Context Network for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Medical Multi-Modal Segmentation Network Guided by Multi-Source Correlation Constraint
Tongxue Zhou, Stéphane Canu, Pierre Vera, Su Ruan
Auto-TLDR; Multi-modality Segmentation with Correlation Constrained Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FOANet: A Focus of Attention Network with Application to Myocardium Segmentation
Zhou Zhao, Elodie Puybareau, Nicolas Boutry, Thierry Geraud

Auto-TLDR; FOANet: A Hybrid Loss Function for Myocardium Segmentation of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Encoder-Decoder Based Convolutional Neural Networks with Multi-Scale-Aware Modules for Crowd Counting
Pongpisit Thanasutives, Ken-Ichi Fukui, Masayuki Numao, Boonserm Kijsirikul

Auto-TLDR; M-SFANet and M-SegNet for Crowd Counting Using Multi-Scale Fusion Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Transformer-Based Network for Anisotropic 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Guo Danfeng, Demetri Terzopoulos
Auto-TLDR; A transformer-based model to tackle the anisotropy problem in 3D medical image analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Do Not Treat Boundaries and Regions Differently: An Example on Heart Left Atrial Segmentation
Zhou Zhao, Elodie Puybareau, Nicolas Boutry, Thierry Geraud
Auto-TLDR; Attention Full Convolutional Network for Atrial Segmentation using ResNet-101 Architecture
Segmenting Kidney on Multiple Phase CT Images Using ULBNet
Yanling Chi, Yuyu Xu, Gang Feng, Jiawei Mao, Sihua Wu, Guibin Xu, Weimin Huang
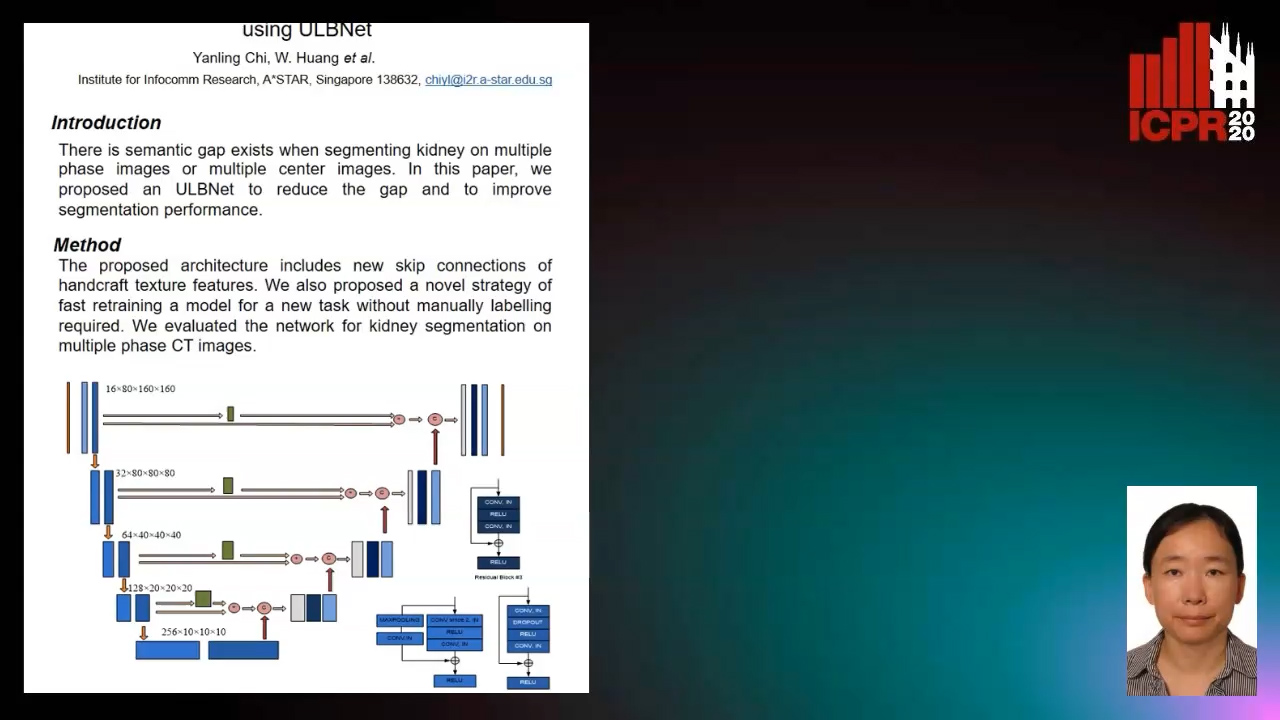
Auto-TLDR; A ULBNet network for kidney segmentation on multiple phase CT images
Enhancing Semantic Segmentation of Aerial Images with Inhibitory Neurons
Ihsan Ullah, Sean Reilly, Michael Madden

Auto-TLDR; Lateral Inhibition in Deep Neural Networks for Object Recognition and Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Lumen Segmentation Method in Ureteroscopy Images Based on a Deep Residual U-Net Architecture
Jorge Lazo, Marzullo Aldo, Sara Moccia, Michele Catellani, Benoit Rosa, Elena De Momi, Michel De Mathelin, Francesco Calimeri
Auto-TLDR; A Deep Neural Network for Ureteroscopy with Residual Units
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ResFPN: Residual Skip Connections in Multi-Resolution Feature Pyramid Networks for Accurate Dense Pixel Matching
Rishav ., René Schuster, Ramy Battrawy, Oliver Wasenmüler, Didier Stricker

Auto-TLDR; Resolution Feature Pyramid Networks for Dense Pixel Matching
EM-Net: Deep Learning for Electron Microscopy Image Segmentation
Afshin Khadangi, Thomas Boudier, Vijay Rajagopal

Auto-TLDR; EM-net: Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Electron Microscopy Image Segmentation
OCT Image Segmentation Using NeuralArchitecture Search and SRGAN
Saba Heidari, Omid Dehzangi, Nasser M. Nasarabadi, Ali Rezai
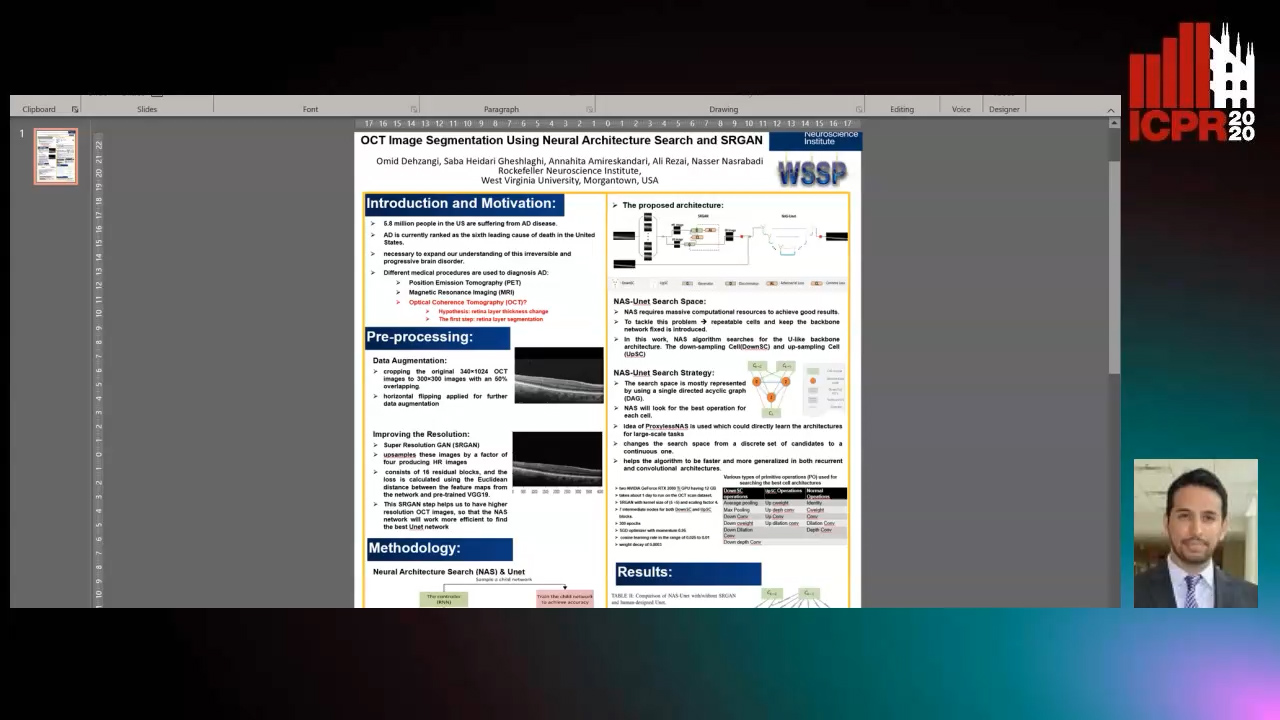
Auto-TLDR; Automatic Segmentation of Retinal Layers in Optical Coherence Tomography using Neural Architecture Search
Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Mucong Ye, Ouyang Jinpeng, Ge Chen, Jing Zhang, Xiaogang Yu
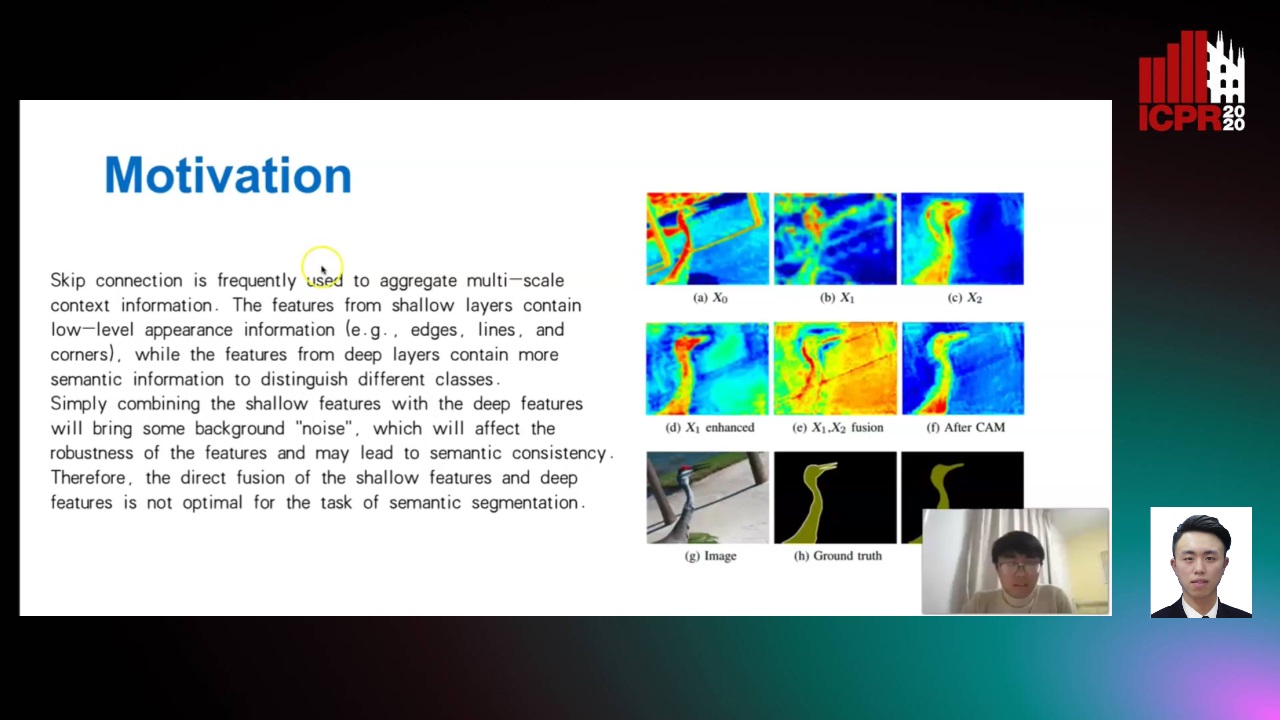
Auto-TLDR; EFPN: Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Direction Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Dehui Li, Zhiguo Cao, Ke Xian, Xinyuan Qi, Chao Zhang, Hao Lu

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Direction Convolution for Contextual Segmentation
CSpA-DN: Channel and Spatial Attention Dense Network for Fusing PET and MRI Images
Bicao Li, Zhoufeng Liu, Shan Gao, Jenq-Neng Hwang, Jun Sun, Zongmin Wang

Auto-TLDR; CSpA-DN: Unsupervised Fusion of PET and MR Images with Channel and Spatial Attention
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient-Receptive Field Block with Group Spatial Attention Mechanism for Object Detection
Jiacheng Zhang, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; E-RFB: Efficient-Receptive Field Block for Deep Neural Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Transfer Learning through Weighted Loss Function and Group Normalization for Vessel Segmentation from Retinal Images
Abdullah Sarhan, Jon Rokne, Reda Alhajj, Andrew Crichton

Auto-TLDR; Deep Learning for Segmentation of Blood Vessels in Retinal Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boundary-Aware Graph Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Hanzhe Hu, Jinshi Cui, Jinshi Hongbin Zha
Auto-TLDR; Boundary-Aware Graph Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar