Encoder-Decoder Based Convolutional Neural Networks with Multi-Scale-Aware Modules for Crowd Counting
Pongpisit Thanasutives,
Ken-Ichi Fukui,
Masayuki Numao,
Boonserm Kijsirikul

Auto-TLDR; M-SFANet and M-SegNet for Crowd Counting Using Multi-Scale Fusion Networks
Similar papers
Spatial-Related and Scale-Aware Network for Crowd Counting
Lei Li, Yuan Dong, Hongliang Bai

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Attention for Crowd Counting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
VGG-Embedded Adaptive Layer-Normalized Crowd Counting Net with Scale-Shuffling Modules
Dewen Guo, Jie Feng, Bingfeng Zhou
Auto-TLDR; VadaLN: VGG-embedded Adaptive Layer Normalization for Crowd Counting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
HANet: Hybrid Attention-Aware Network for Crowd Counting
Xinxing Su, Yuchen Yuan, Xiangbo Su, Zhikang Zou, Shilei Wen, Pan Zhou

Auto-TLDR; HANet: Hybrid Attention-Aware Network for Crowd Counting with Adaptive Compensation Loss
Multi-Resolution Fusion and Multi-Scale Input Priors Based Crowd Counting
Usman Sajid, Wenchi Ma, Guanghui Wang

Auto-TLDR; Multi-resolution Fusion Based End-to-End Crowd Counting in Still Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PHNet: Parasite-Host Network for Video Crowd Counting
Shiqiao Meng, Jiajie Li, Weiwei Guo, Jinfeng Jiang, Lai Ye

Auto-TLDR; PHNet: A Parasite-Host Network for Video Crowd Counting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Error-Driven Curriculum for Crowd Counting
Wenxi Li, Zhuoqun Cao, Qian Wang, Songjian Chen, Rui Feng

Auto-TLDR; Learning Error-Driven Curriculum for Crowd Counting with TutorNet
Learning from Web Data: Improving Crowd Counting Via Semi-Supervised Learning

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Crowd Counting Baseline for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DAPC: Domain Adaptation People Counting Via Style-Level Transfer Learning and Scene-Aware Estimation
Na Jiang, Xingsen Wen, Zhiping Shi

Auto-TLDR; Domain Adaptation People counting via Style-Level Transfer Learning and Scene-Aware Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Point In: Counting Trees with Weakly Supervised Segmentation Network
Pinmo Tong, Shuhui Bu, Pengcheng Han
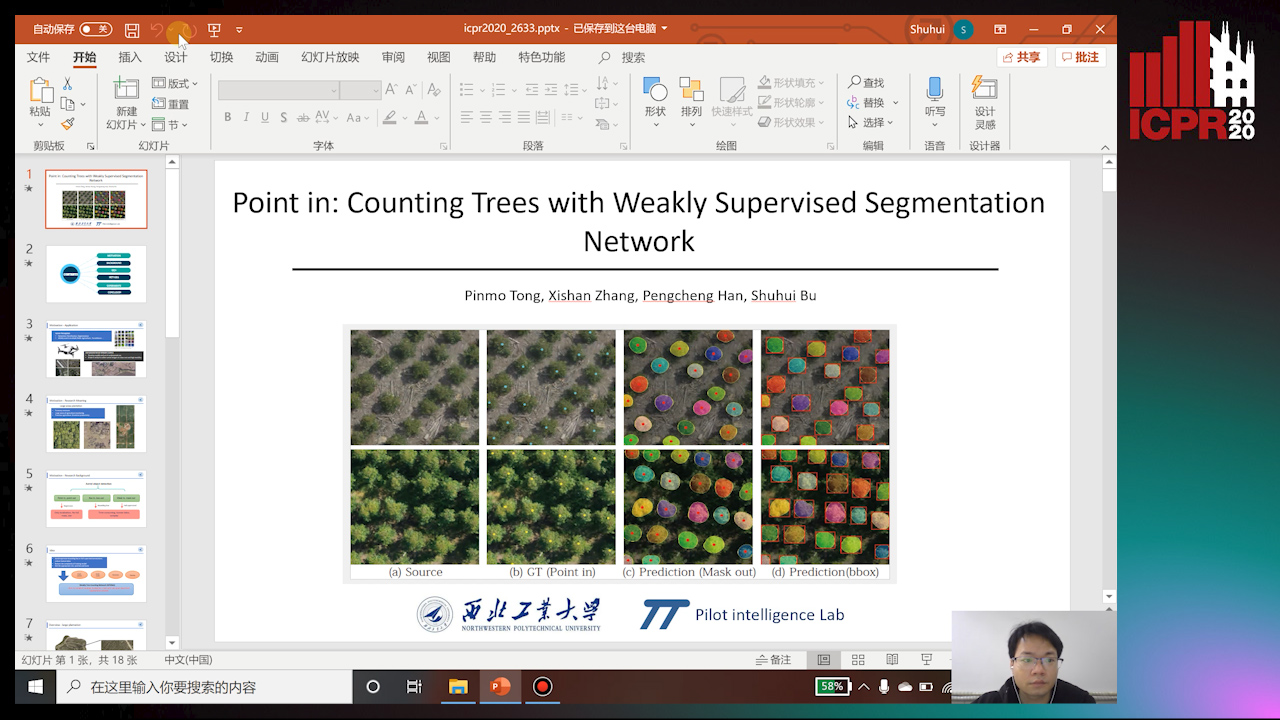
Auto-TLDR; Weakly Tree counting using Deep Segmentation Network with Localization and Mask Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Mucong Ye, Ouyang Jinpeng, Ge Chen, Jing Zhang, Xiaogang Yu
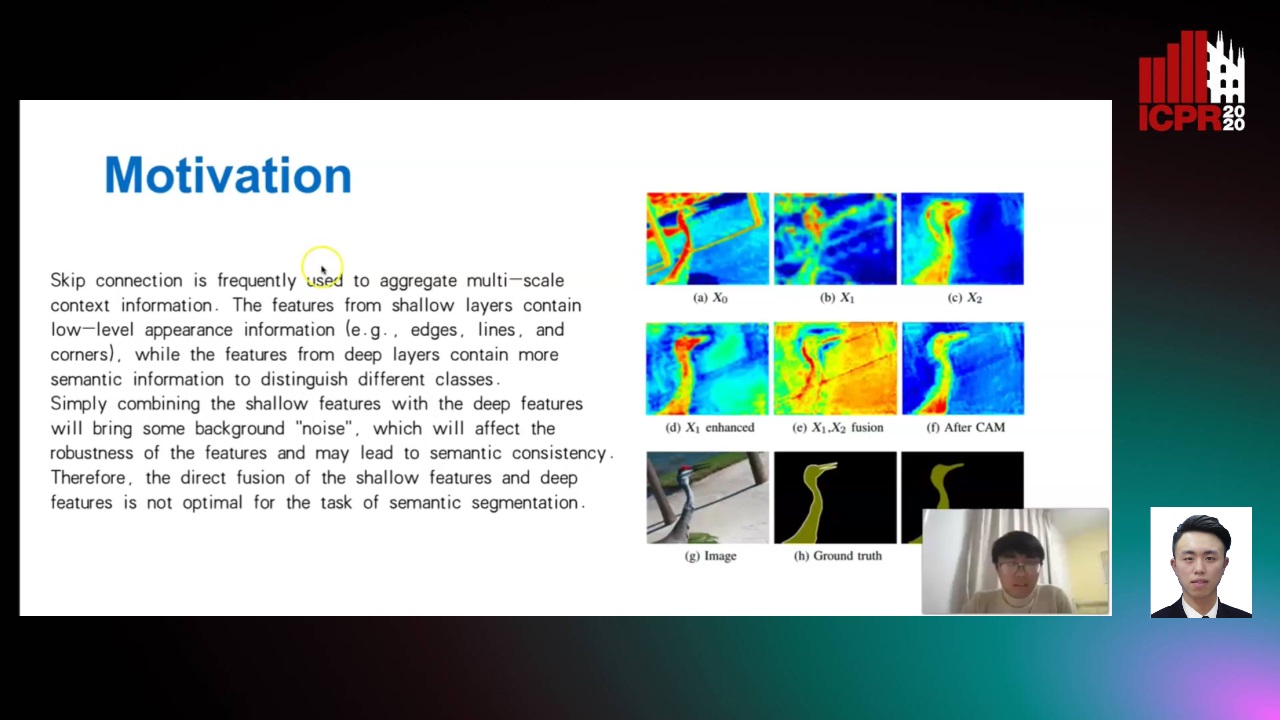
Auto-TLDR; EFPN: Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamic Guided Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Xiaoxia Xing, Yinghao Cai, Yiping Yang, Dayong Wen

Auto-TLDR; DGNet: Dynamic Guidance Upsampling for Self-attention-Decoding for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Transitional Asymmetric Non-Local Neural Networks for Real-World Dirt Road Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Transitional Asymmetric Non-Local Neural Networks for Semantic Segmentation on Dirt Roads
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DARN: Deep Attentive Refinement Network for Liver Tumor Segmentation from 3D CT Volume
Yao Zhang, Jiang Tian, Cheng Zhong, Yang Zhang, Zhongchao Shi, Zhiqiang He

Auto-TLDR; Deep Attentive Refinement Network for Liver Tumor Segmentation from 3D Computed Tomography Using Multi-Level Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real-Time Semantic Segmentation Via Region and Pixel Context Network
Yajun Li, Yazhou Liu, Quansen Sun
Auto-TLDR; A Dual Context Network for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Scale Residual Pyramid Attention Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Jing Liu, Xiaona Zhang, Zhaoxin Li, Tianlu Mao
Auto-TLDR; Multi-scale Residual Pyramid Attention Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PSDNet: A Balanced Architecture of Accuracy and Parameters for Semantic Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Pyramid Pooling Module with SE1Cblock and D2SUpsample Network (PSDNet)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GSTO: Gated Scale-Transfer Operation for Multi-Scale Feature Learning in Semantic Segmentation
Zhuoying Wang, Yongtao Wang, Zhi Tang, Yangyan Li, Ying Chen, Haibin Ling, Weisi Lin

Auto-TLDR; Gated Scale-Transfer Operation for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boundary-Aware Graph Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Hanzhe Hu, Jinshi Cui, Jinshi Hongbin Zha
Auto-TLDR; Boundary-Aware Graph Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention Pyramid Module for Scene Recognition
Zhinan Qiao, Xiaohui Yuan, Chengyuan Zhuang, Abolfazl Meyarian

Auto-TLDR; Attention Pyramid Module for Multi-Scale Scene Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Delivering Meaningful Representation for Monocular Depth Estimation
Doyeon Kim, Donggyu Joo, Junmo Kim

Auto-TLDR; Monocular Depth Estimation by Bridging the Context between Encoding and Decoding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Distortion-Adaptive Grape Bunch Counting for Omnidirectional Images
Ryota Akai, Yuzuko Utsumi, Yuka Miwa, Masakazu Iwamura, Koichi Kise
Auto-TLDR; Object Counting for Omnidirectional Images Using Stereographic Projection
Efficient-Receptive Field Block with Group Spatial Attention Mechanism for Object Detection
Jiacheng Zhang, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; E-RFB: Efficient-Receptive Field Block for Deep Neural Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Global-Local Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation in Aerial Images
Minglong Li, Lianlei Shan, Weiqiang Wang

Auto-TLDR; GLANet: Global-Local Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DE-Net: Dilated Encoder Network for Automated Tongue Segmentation
Hui Tang, Bin Wang, Jun Zhou, Yongsheng Gao

Auto-TLDR; Automated Tongue Image Segmentation using De-Net
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Coarse to Fine: Progressive and Multi-Task Learning for Salient Object Detection
Dong-Goo Kang, Sangwoo Park, Joonki Paik
Auto-TLDR; Progressive and mutl-task learning scheme for salient object detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fast and Accurate Real-Time Semantic Segmentation with Dilated Asymmetric Convolutions
Leonel Rosas-Arias, Gibran Benitez-Garcia, Jose Portillo-Portillo, Gabriel Sanchez-Perez, Keiji Yanai
Auto-TLDR; FASSD-Net: Dilated Asymmetric Pyramidal Fusion for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Ordinal Depth Classification Using Region-Based Self-Attention
Minh Hieu Phan, Son Lam Phung, Abdesselam Bouzerdoum

Auto-TLDR; Region-based Self-Attention for Multi-scale Depth Estimation from a Single 2D Image
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Segmentation of Intracranial Aneurysm Remnant in MRA Using Dual-Attention Atrous Net
Subhashis Banerjee, Ashis Kumar Dhara, Johan Wikström, Robin Strand

Auto-TLDR; Dual-Attention Atrous Net for Segmentation of Intracranial Aneurysm Remnant from MRA Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Do Not Treat Boundaries and Regions Differently: An Example on Heart Left Atrial Segmentation
Zhou Zhao, Elodie Puybareau, Nicolas Boutry, Thierry Geraud
Auto-TLDR; Attention Full Convolutional Network for Atrial Segmentation using ResNet-101 Architecture
Learning a Dynamic High-Resolution Network for Multi-Scale Pedestrian Detection
Mengyuan Ding, Shanshan Zhang, Jian Yang

Auto-TLDR; Learningable Dynamic HRNet for Pedestrian Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Accurate Cell Segmentation in Digital Pathology Images Via Attention Enforced Networks
Zeyi Yao, Kaiqi Li, Guanhong Zhang, Yiwen Luo, Xiaoguang Zhou, Muyi Sun

Auto-TLDR; AENet: Attention Enforced Network for Automatic Cell Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PRF-Ped: Multi-Scale Pedestrian Detector with Prior-Based Receptive Field
Yuzhi Tan, Hongxun Yao, Haoran Li, Xiusheng Lu, Haozhe Xie

Auto-TLDR; Bidirectional Feature Enhancement Module for Multi-Scale Pedestrian Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SFPN: Semantic Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; SFPN: Semantic Feature Pyramid Network to Address Information Dilution Issue in FPN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CAggNet: Crossing Aggregation Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Auto-TLDR; Crossing Aggregation Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Triplet-Path Dilated Network for Detection and Segmentation of General Pathological Images
Jiaqi Luo, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su, Limei Guo

Auto-TLDR; Triplet-path Network for One-Stage Object Detection and Segmentation in Pathological Images
Hierarchically Aggregated Residual Transformation for Single Image Super Resolution

Auto-TLDR; HARTnet: Hierarchically Aggregated Residual Transformation for Multi-Scale Super-resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CT-UNet: An Improved Neural Network Based on U-Net for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images
Huanran Ye, Sheng Liu, Kun Jin, Haohao Cheng
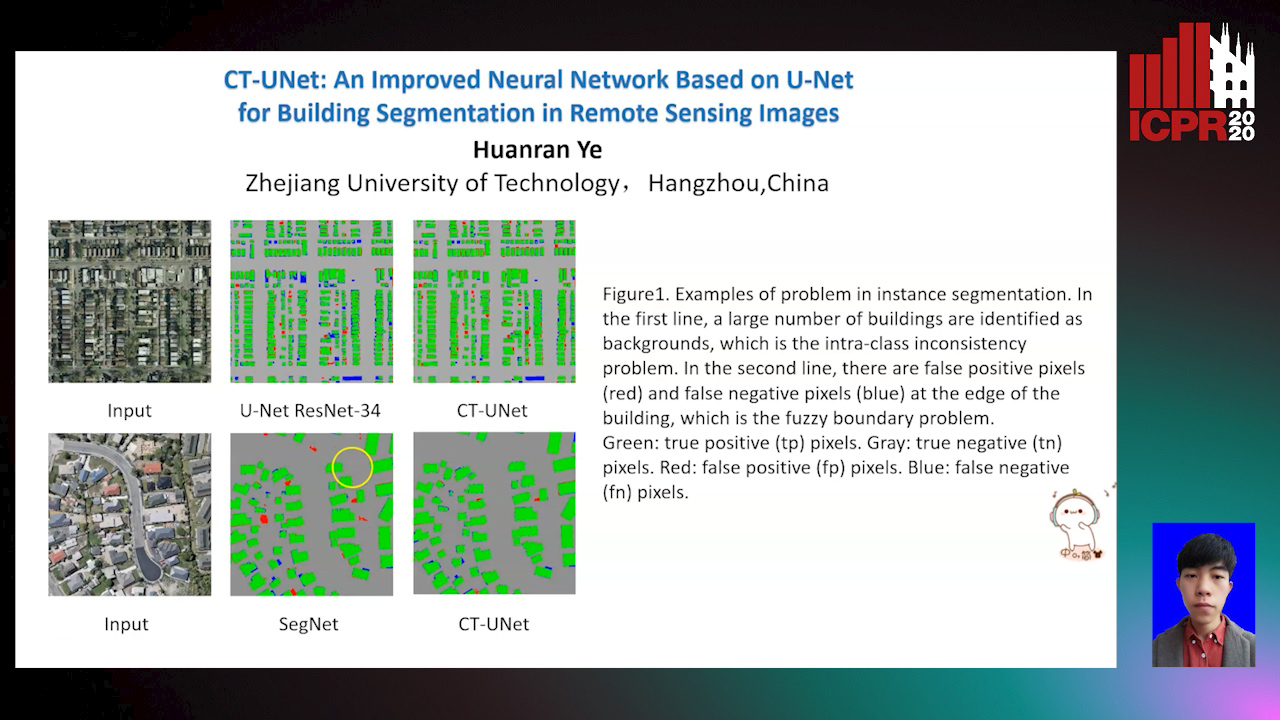
Auto-TLDR; Context-Transfer-UNet: A UNet-based Network for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DA-RefineNet: Dual-Inputs Attention RefineNet for Whole Slide Image Segmentation
Ziqiang Li, Rentuo Tao, Qianrun Wu, Bin Li

Auto-TLDR; DA-RefineNet: A dual-inputs attention network for whole slide image segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deeply-Fused Attentive Network for Stereo Matching
Zuliu Yang, Xindong Ai, Weida Yang, Yong Zhao, Qifei Dai, Fuchi Li

Auto-TLDR; DF-Net: Deep Learning-based Network for Stereo Matching
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Bidirectional Matrix Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; BMFPN: Bidirectional Matrix Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhancing Semantic Segmentation of Aerial Images with Inhibitory Neurons
Ihsan Ullah, Sean Reilly, Michael Madden

Auto-TLDR; Lateral Inhibition in Deep Neural Networks for Object Recognition and Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
UHRSNet: A Semantic Segmentation Network Specifically for Ultra-High-Resolution Images

Auto-TLDR; Ultra-High-Resolution Segmentation with Local and Global Feature Fusion
Multi-Direction Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Dehui Li, Zhiguo Cao, Ke Xian, Xinyuan Qi, Chao Zhang, Hao Lu

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Direction Convolution for Contextual Segmentation
BiLuNet: A Multi-Path Network for Semantic Segmentation on X-Ray Images
Van Luan Tran, Huei-Yung Lin, Rachel Liu, Chun-Han Tseng, Chun-Han Tseng
Auto-TLDR; BiLuNet: Multi-path Convolutional Neural Network for Semantic Segmentation of Lumbar vertebrae, sacrum,
Multiscale Attention-Based Prototypical Network for Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Yifei Zhang, Desire Sidibe, Olivier Morel, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; Few-shot Semantic Segmentation with Multiscale Feature Attention
Nighttime Pedestrian Detection Based on Feature Attention and Transformation
Gang Li, Shanshan Zhang, Jian Yang

Auto-TLDR; FAM and FTM: Enhanced Feature Attention Module and Feature Transformation Module for nighttime pedestrian detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context-Aware Residual Module for Image Classification
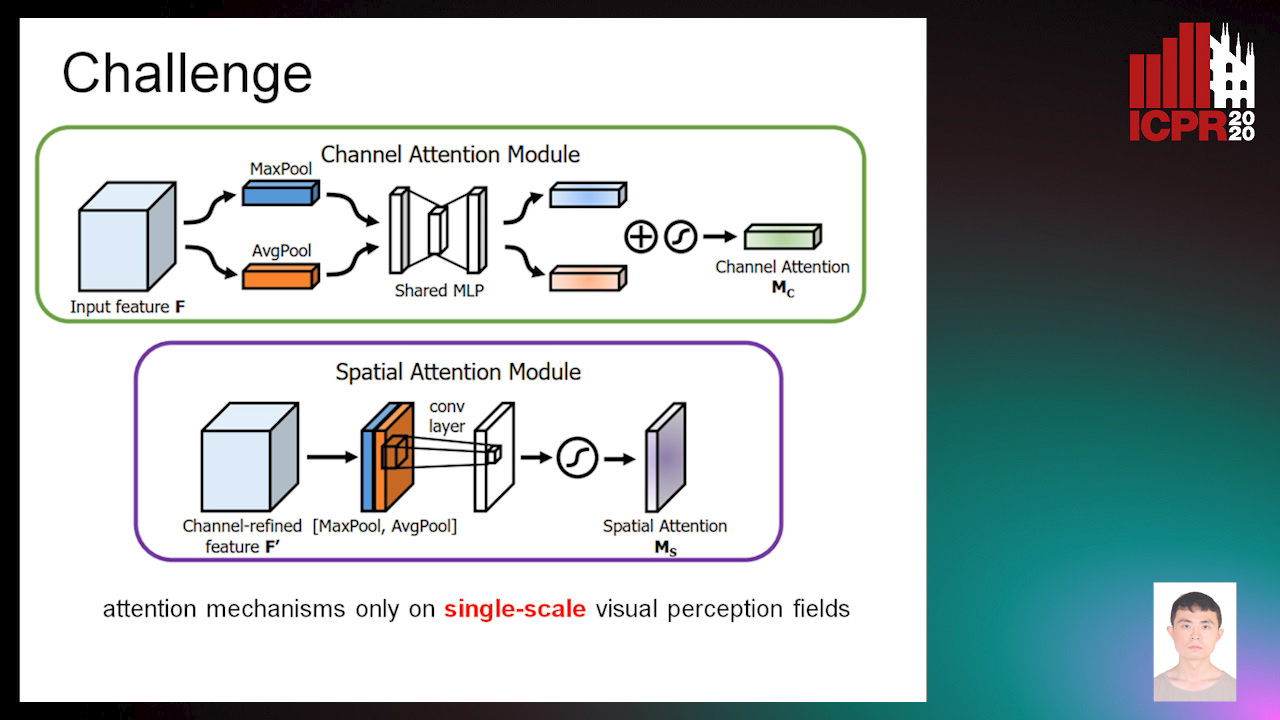
Auto-TLDR; Context-Aware Residual Module for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention Stereo Matching Network
Doudou Zhang, Jing Cai, Yanbing Xue, Zan Gao, Hua Zhang

Auto-TLDR; ASM-Net: Attention Stereo Matching with Disparity Refinement
Abstract Slides Poster Similar