Multi-Scale Residual Pyramid Attention Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Jing Liu,
Xiaona Zhang,
Zhaoxin Li,
Tianlu Mao
Auto-TLDR; Multi-scale Residual Pyramid Attention Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Similar papers
Dynamic Guided Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Xiaoxia Xing, Yinghao Cai, Yiping Yang, Dayong Wen

Auto-TLDR; DGNet: Dynamic Guidance Upsampling for Self-attention-Decoding for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Ordinal Depth Classification Using Region-Based Self-Attention
Minh Hieu Phan, Son Lam Phung, Abdesselam Bouzerdoum

Auto-TLDR; Region-based Self-Attention for Multi-scale Depth Estimation from a Single 2D Image
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Delivering Meaningful Representation for Monocular Depth Estimation
Doyeon Kim, Donggyu Joo, Junmo Kim

Auto-TLDR; Monocular Depth Estimation by Bridging the Context between Encoding and Decoding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention Stereo Matching Network
Doudou Zhang, Jing Cai, Yanbing Xue, Zan Gao, Hua Zhang

Auto-TLDR; ASM-Net: Attention Stereo Matching with Disparity Refinement
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Global-Local Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation in Aerial Images
Minglong Li, Lianlei Shan, Weiqiang Wang

Auto-TLDR; GLANet: Global-Local Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real-Time Monocular Depth Estimation with Extremely Light-Weight Neural Network
Mian Jhong Chiu, Wei-Chen Chiu, Hua-Tsung Chen, Jen-Hui Chuang
Auto-TLDR; Real-Time Light-Weight Depth Prediction for Obstacle Avoidance and Environment Sensing with Deep Learning-based CNN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real-Time Semantic Segmentation Via Region and Pixel Context Network
Yajun Li, Yazhou Liu, Quansen Sun
Auto-TLDR; A Dual Context Network for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Extending Single Beam Lidar to Full Resolution by Fusing with Single Image Depth Estimation
Yawen Lu, Yuxing Wang, Devarth Parikh, Guoyu Lu

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised LIDAR for Low-Cost Depth Estimation
Deeply-Fused Attentive Network for Stereo Matching
Zuliu Yang, Xindong Ai, Weida Yang, Yong Zhao, Qifei Dai, Fuchi Li

Auto-TLDR; DF-Net: Deep Learning-based Network for Stereo Matching
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DARN: Deep Attentive Refinement Network for Liver Tumor Segmentation from 3D CT Volume
Yao Zhang, Jiang Tian, Cheng Zhong, Yang Zhang, Zhongchao Shi, Zhiqiang He

Auto-TLDR; Deep Attentive Refinement Network for Liver Tumor Segmentation from 3D Computed Tomography Using Multi-Level Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Mucong Ye, Ouyang Jinpeng, Ge Chen, Jing Zhang, Xiaogang Yu
Auto-TLDR; EFPN: Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PSDNet: A Balanced Architecture of Accuracy and Parameters for Semantic Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Pyramid Pooling Module with SE1Cblock and D2SUpsample Network (PSDNet)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single Image Deblurring Using Bi-Attention Network

Auto-TLDR; Bi-Attention Neural Network for Single Image Deblurring
Spatial-Related and Scale-Aware Network for Crowd Counting
Lei Li, Yuan Dong, Hongliang Bai

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Attention for Crowd Counting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Stereo Matchability in Disparity Regression Networks
Jingyang Zhang, Yao Yao, Zixin Luo, Shiwei Li, Tianwei Shen, Tian Fang, Long Quan

Auto-TLDR; Deep Stereo Matchability for Weakly Matchable Regions
Progressive Scene Segmentation Based on Self-Attention Mechanism
Yunyi Pan, Yuan Gan, Kun Liu, Yan Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stage Semantic Scene Segmentation with Self-Attention
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Partially Supervised Multi-Task Network for Single-View Dietary Assessment
Ya Lu, Thomai Stathopoulou, Stavroula Mougiakakou
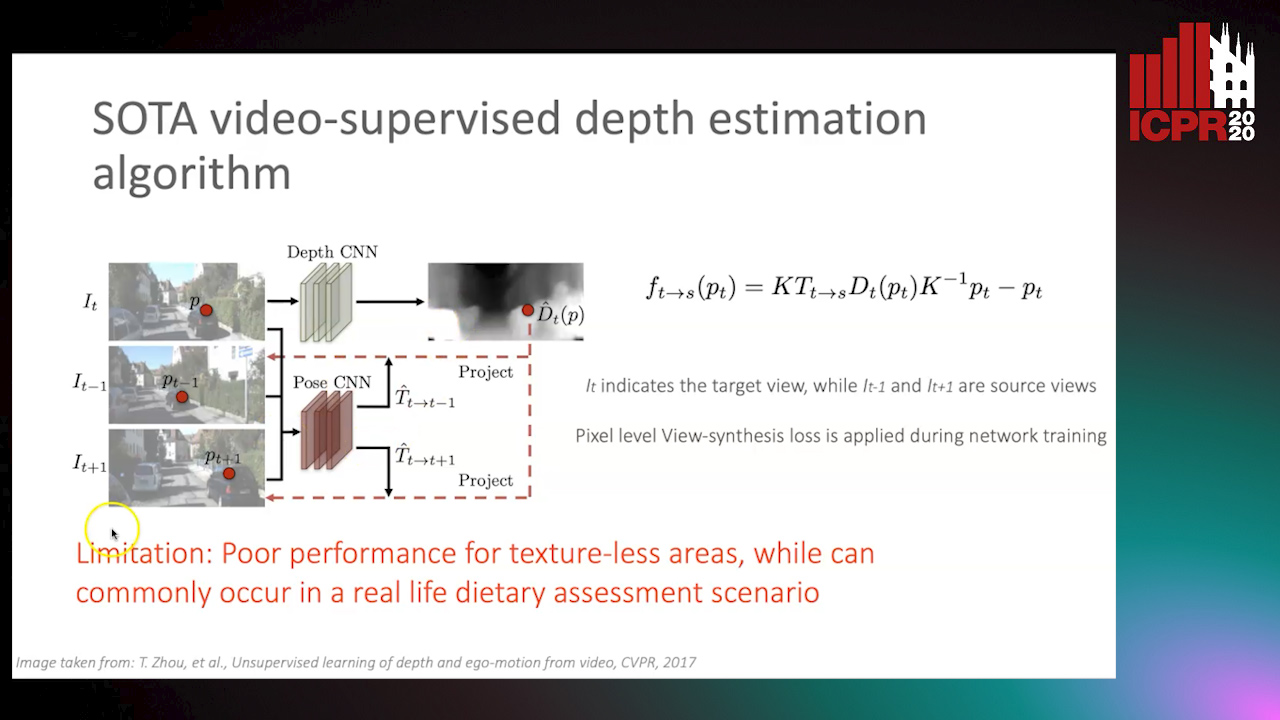
Auto-TLDR; Food Volume Estimation from a Single Food Image via Geometric Understanding and Semantic Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Encoder-Decoder Based Convolutional Neural Networks with Multi-Scale-Aware Modules for Crowd Counting
Pongpisit Thanasutives, Ken-Ichi Fukui, Masayuki Numao, Boonserm Kijsirikul

Auto-TLDR; M-SFANet and M-SegNet for Crowd Counting Using Multi-Scale Fusion Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Direction Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Dehui Li, Zhiguo Cao, Ke Xian, Xinyuan Qi, Chao Zhang, Hao Lu

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Direction Convolution for Contextual Segmentation
Towards Efficient 3D Point Cloud Scene Completion Via Novel Depth View Synthesis
Haiyan Wang, Liang Yang, Xuejian Rong, Ying-Li Tian

Auto-TLDR; 3D Point Cloud Completion with Depth View Synthesis and Depth View synthesis
Attention Pyramid Module for Scene Recognition
Zhinan Qiao, Xiaohui Yuan, Chengyuan Zhuang, Abolfazl Meyarian

Auto-TLDR; Attention Pyramid Module for Multi-Scale Scene Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
P2D: A Self-Supervised Method for Depth Estimation from Polarimetry
Marc Blanchon, Desire Sidibe, Olivier Morel, Ralph Seulin, Daniel Braun, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; Polarimetric Regularization for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Transitional Asymmetric Non-Local Neural Networks for Real-World Dirt Road Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Transitional Asymmetric Non-Local Neural Networks for Semantic Segmentation on Dirt Roads
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GSTO: Gated Scale-Transfer Operation for Multi-Scale Feature Learning in Semantic Segmentation
Zhuoying Wang, Yongtao Wang, Zhi Tang, Yangyan Li, Ying Chen, Haibin Ling, Weisi Lin

Auto-TLDR; Gated Scale-Transfer Operation for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boundary-Aware Graph Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Hanzhe Hu, Jinshi Cui, Jinshi Hongbin Zha
Auto-TLDR; Boundary-Aware Graph Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context-Aware Residual Module for Image Classification
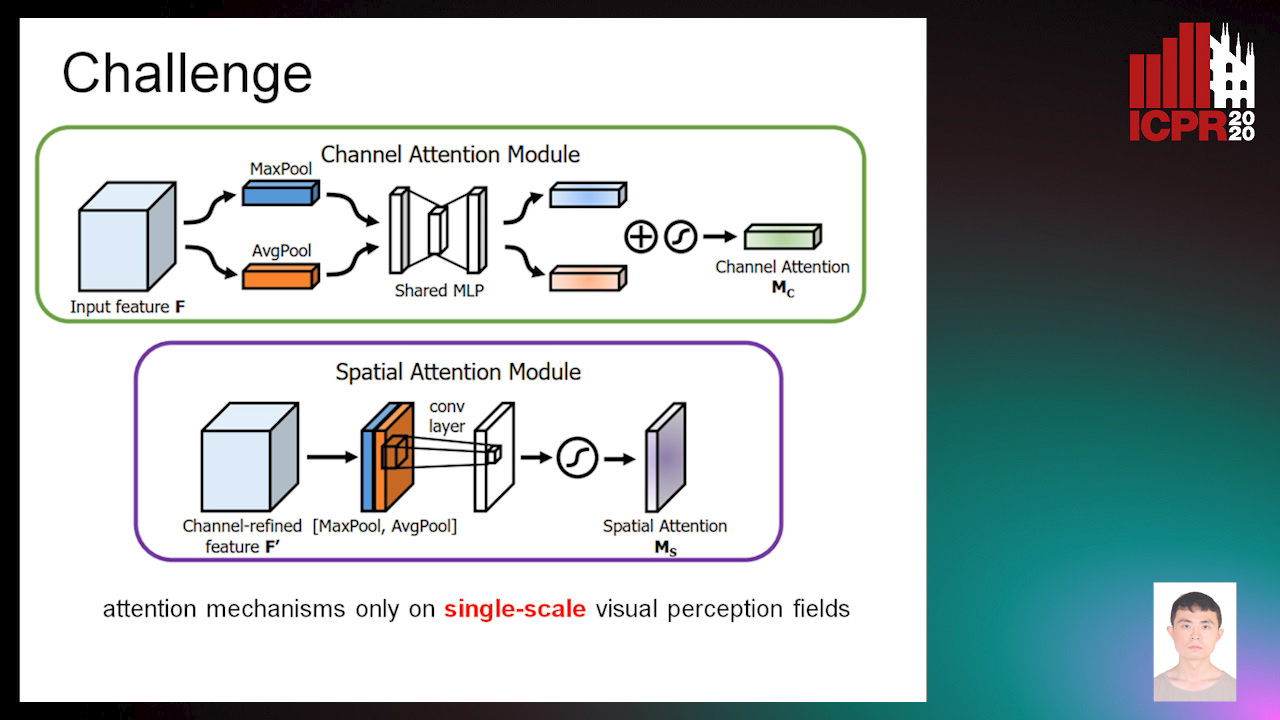
Auto-TLDR; Context-Aware Residual Module for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FastCompletion: A Cascade Network with Multiscale Group-Fused Inputs for Real-Time Depth Completion
Ang Li, Zejian Yuan, Yonggen Ling, Wanchao Chi, Shenghao Zhang, Chong Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Efficient Depth Completion with Clustered Hourglass Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient-Receptive Field Block with Group Spatial Attention Mechanism for Object Detection
Jiacheng Zhang, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; E-RFB: Efficient-Receptive Field Block for Deep Neural Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Leveraging a Weakly Adversarial Paradigm for Joint Learning of Disparity and Confidence Estimation
Matteo Poggi, Fabio Tosi, Filippo Aleotti, Stefano Mattoccia

Auto-TLDR; Joint Training of Deep-Networks for Outlier Detection from Stereo Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DE-Net: Dilated Encoder Network for Automated Tongue Segmentation
Hui Tang, Bin Wang, Jun Zhou, Yongsheng Gao

Auto-TLDR; Automated Tongue Image Segmentation using De-Net
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Accurate Cell Segmentation in Digital Pathology Images Via Attention Enforced Networks
Zeyi Yao, Kaiqi Li, Guanhong Zhang, Yiwen Luo, Xiaoguang Zhou, Muyi Sun

Auto-TLDR; AENet: Attention Enforced Network for Automatic Cell Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DEN: Disentangling and Exchanging Network for Depth Completion
You-Feng Wu, Vu-Hoang Tran, Ting-Wei Chang, Wei-Chen Chiu, Ching-Chun Huang

Auto-TLDR; Disentangling and Exchanging Network for Depth Completion
Selective Kernel and Motion-Emphasized Loss Based Attention-Guided Network for HDR Imaging of Dynamic Scenes
Yipeng Deng, Qin Liu, Takeshi Ikenaga

Auto-TLDR; SK-AHDRNet: A Deep Network with attention module and motion-emphasized loss function to produce ghost-free HDR images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Detection Model Based on Scene-Level Region Proposal Self-Attention
Yu Quan, Zhixin Li, Canlong Zhang, Huifang Ma

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Semantic Informations for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Free-Form Image Inpainting Via Contrastive Attention Network
Xin Ma, Xiaoqiang Zhou, Huaibo Huang, Zhenhua Chai, Xiaolin Wei, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Siamese inference for image inpainting
Object Detection on Monocular Images with Two-Dimensional Canonical Correlation Analysis

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Task Object Detection from Monocular Images Using Multimodal RGB and Depth Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TSMSAN: A Three-Stream Multi-Scale Attentive Network for Video Saliency Detection
Jingwen Yang, Guanwen Zhang, Wei Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Three-stream Multi-scale attentive network for video saliency detection in dynamic scenes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semantic Segmentation Refinement Using Entropy and Boundary-guided Monte Carlo Sampling and Directed Regional Search
Zitang Sun, Sei-Ichiro Kamata, Ruojing Wang, Weili Chen
Auto-TLDR; Directed Region Search and Refinement for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention Based Coupled Framework for Road and Pothole Segmentation
Shaik Masihullah, Ritu Garg, Prerana Mukherjee, Anupama Ray
Auto-TLDR; Few Shot Learning for Road and Pothole Segmentation on KITTI and IDD
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
6D Pose Estimation with Correlation Fusion
Yi Cheng, Hongyuan Zhu, Ying Sun, Cihan Acar, Wei Jing, Yan Wu, Liyuan Li, Cheston Tan, Joo-Hwee Lim

Auto-TLDR; Intra- and Inter-modality Fusion for 6D Object Pose Estimation with Attention Mechanism
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhanced Vote Network for 3D Object Detection in Point Clouds

Auto-TLDR; A Vote Feature Enhancement Network for 3D Bounding Box Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock Module for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Junhui Yin, Siqing Zhang, Dongliang Chang, Zhanyu Ma, Jun Guo
Auto-TLDR; Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Do Not Treat Boundaries and Regions Differently: An Example on Heart Left Atrial Segmentation
Zhou Zhao, Elodie Puybareau, Nicolas Boutry, Thierry Geraud
Auto-TLDR; Attention Full Convolutional Network for Atrial Segmentation using ResNet-101 Architecture
CSpA-DN: Channel and Spatial Attention Dense Network for Fusing PET and MRI Images
Bicao Li, Zhoufeng Liu, Shan Gao, Jenq-Neng Hwang, Jun Sun, Zongmin Wang

Auto-TLDR; CSpA-DN: Unsupervised Fusion of PET and MR Images with Channel and Spatial Attention
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SFPN: Semantic Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; SFPN: Semantic Feature Pyramid Network to Address Information Dilution Issue in FPN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Aggregating Object Features Based on Attention Weights for Fine-Grained Image Retrieval
Hongli Lin, Yongqi Song, Zixuan Zeng, Weisheng Wang

Auto-TLDR; DSAW: Unsupervised Dual-selection for Fine-Grained Image Retrieval
DA-RefineNet: Dual-Inputs Attention RefineNet for Whole Slide Image Segmentation
Ziqiang Li, Rentuo Tao, Qianrun Wu, Bin Li

Auto-TLDR; DA-RefineNet: A dual-inputs attention network for whole slide image segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CT-UNet: An Improved Neural Network Based on U-Net for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images
Huanran Ye, Sheng Liu, Kun Jin, Haohao Cheng
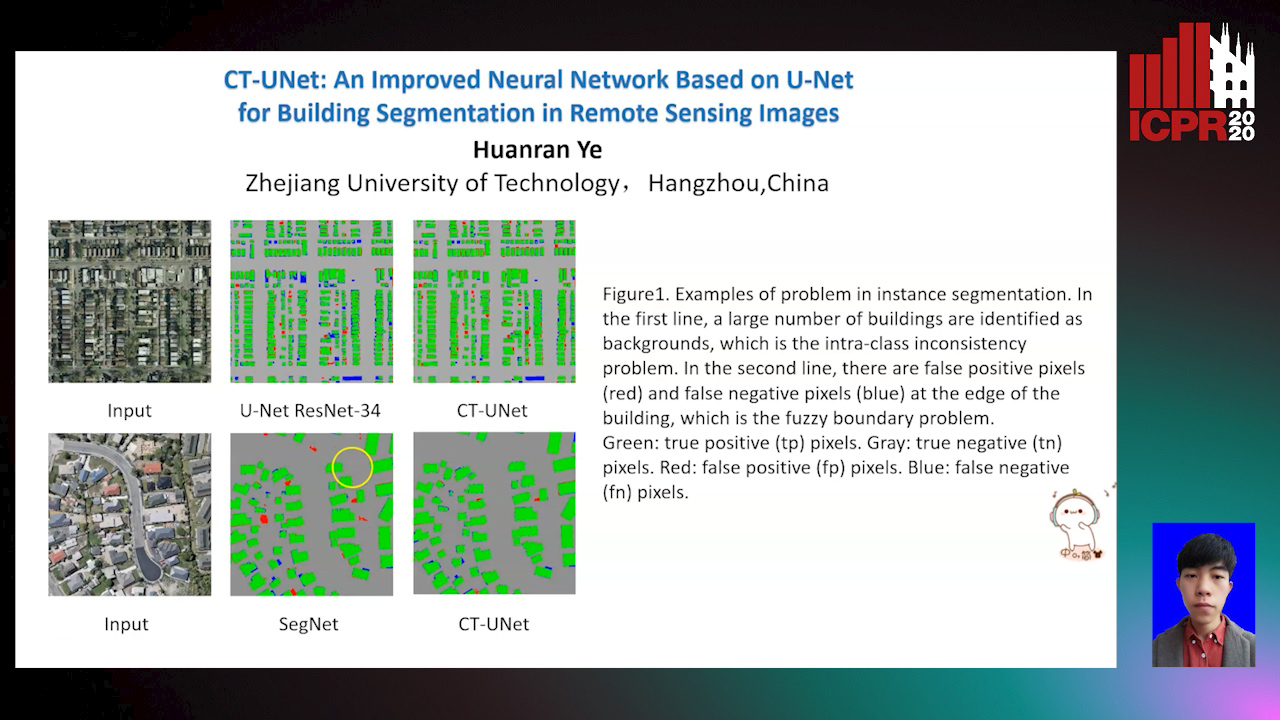
Auto-TLDR; Context-Transfer-UNet: A UNet-based Network for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar