Deeply-Fused Attentive Network for Stereo Matching
Zuliu Yang,
Xindong Ai,
Weida Yang,
Yong Zhao,
Qifei Dai,
Fuchi Li

Auto-TLDR; DF-Net: Deep Learning-based Network for Stereo Matching
Similar papers
Attention Stereo Matching Network
Doudou Zhang, Jing Cai, Yanbing Xue, Zan Gao, Hua Zhang

Auto-TLDR; ASM-Net: Attention Stereo Matching with Disparity Refinement
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Suppressing Features That Contain Disparity Edge for Stereo Matching
Xindong Ai, Zuliu Yang, Weida Yang, Yong Zhao, Zhengzhong Yu, Fuchi Li

Auto-TLDR; SDE-Attention: A Novel Attention Mechanism for Stereo Matching
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Stereo Matchability in Disparity Regression Networks
Jingyang Zhang, Yao Yao, Zixin Luo, Shiwei Li, Tianwei Shen, Tian Fang, Long Quan

Auto-TLDR; Deep Stereo Matchability for Weakly Matchable Regions
Two-Stage Adaptive Object Scene Flow Using Hybrid CNN-CRF Model
Congcong Li, Haoyu Ma, Qingmin Liao

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive object scene flow estimation using a hybrid CNN-CRF model and adaptive iteration
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Movement-Induced Priors for Deep Stereo
Yuxin Hou, Muhammad Kamran Janjua, Juho Kannala, Arno Solin

Auto-TLDR; Fusing Stereo Disparity Estimation with Movement-induced Prior Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FC-DCNN: A Densely Connected Neural Network for Stereo Estimation
Dominik Hirner, Friedrich Fraundorfer

Auto-TLDR; FC-DCNN: A Lightweight Network for Stereo Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ResFPN: Residual Skip Connections in Multi-Resolution Feature Pyramid Networks for Accurate Dense Pixel Matching
Rishav ., René Schuster, Ramy Battrawy, Oliver Wasenmüler, Didier Stricker

Auto-TLDR; Resolution Feature Pyramid Networks for Dense Pixel Matching
Multi-Scale Residual Pyramid Attention Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Jing Liu, Xiaona Zhang, Zhaoxin Li, Tianlu Mao
Auto-TLDR; Multi-scale Residual Pyramid Attention Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Leveraging a Weakly Adversarial Paradigm for Joint Learning of Disparity and Confidence Estimation
Matteo Poggi, Fabio Tosi, Filippo Aleotti, Stefano Mattoccia

Auto-TLDR; Joint Training of Deep-Networks for Outlier Detection from Stereo Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Transitional Asymmetric Non-Local Neural Networks for Real-World Dirt Road Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Transitional Asymmetric Non-Local Neural Networks for Semantic Segmentation on Dirt Roads
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Delivering Meaningful Representation for Monocular Depth Estimation
Doyeon Kim, Donggyu Joo, Junmo Kim

Auto-TLDR; Monocular Depth Estimation by Bridging the Context between Encoding and Decoding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Progressive Scene Segmentation Based on Self-Attention Mechanism
Yunyi Pan, Yuan Gan, Kun Liu, Yan Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stage Semantic Scene Segmentation with Self-Attention
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
HMFlow: Hybrid Matching Optical Flow Network for Small and Fast-Moving Objects
Suihanjin Yu, Youmin Zhang, Chen Wang, Xiao Bai, Liang Zhang, Edwin Hancock

Auto-TLDR; Hybrid Matching Optical Flow Network with Global Matching Component
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Global-Local Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation in Aerial Images
Minglong Li, Lianlei Shan, Weiqiang Wang

Auto-TLDR; GLANet: Global-Local Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real-Time Monocular Depth Estimation with Extremely Light-Weight Neural Network
Mian Jhong Chiu, Wei-Chen Chiu, Hua-Tsung Chen, Jen-Hui Chuang
Auto-TLDR; Real-Time Light-Weight Depth Prediction for Obstacle Avoidance and Environment Sensing with Deep Learning-based CNN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PSDNet: A Balanced Architecture of Accuracy and Parameters for Semantic Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Pyramid Pooling Module with SE1Cblock and D2SUpsample Network (PSDNet)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Extending Single Beam Lidar to Full Resolution by Fusing with Single Image Depth Estimation
Yawen Lu, Yuxing Wang, Devarth Parikh, Guoyu Lu

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised LIDAR for Low-Cost Depth Estimation
Real-Time Semantic Segmentation Via Region and Pixel Context Network
Yajun Li, Yazhou Liu, Quansen Sun
Auto-TLDR; A Dual Context Network for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GSTO: Gated Scale-Transfer Operation for Multi-Scale Feature Learning in Semantic Segmentation
Zhuoying Wang, Yongtao Wang, Zhi Tang, Yangyan Li, Ying Chen, Haibin Ling, Weisi Lin

Auto-TLDR; Gated Scale-Transfer Operation for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Mucong Ye, Ouyang Jinpeng, Ge Chen, Jing Zhang, Xiaogang Yu
Auto-TLDR; EFPN: Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamic Guided Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Xiaoxia Xing, Yinghao Cai, Yiping Yang, Dayong Wen

Auto-TLDR; DGNet: Dynamic Guidance Upsampling for Self-attention-Decoding for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Domain Siamese CNNs for Sparse Multispectral Disparity Estimation
David-Alexandre Beaupre, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau

Auto-TLDR; Multispectral Disparity Estimation between Thermal and Visible Images using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CT-UNet: An Improved Neural Network Based on U-Net for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images
Huanran Ye, Sheng Liu, Kun Jin, Haohao Cheng
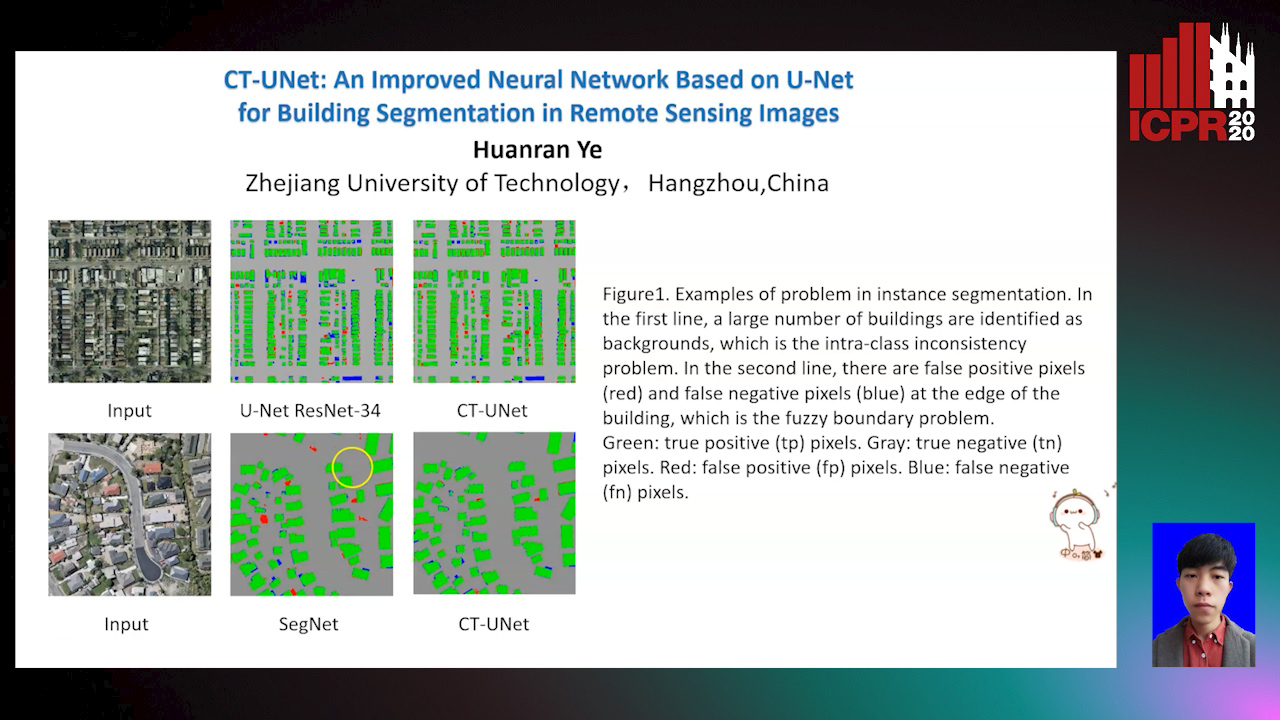
Auto-TLDR; Context-Transfer-UNet: A UNet-based Network for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
STaRFlow: A SpatioTemporal Recurrent Cell for Lightweight Multi-Frame Optical Flow Estimation
Pierre Godet, Alexandre Boulch, Aurélien Plyer, Guy Le Besnerais
Auto-TLDR; STaRFlow: A lightweight CNN-based algorithm for optical flow estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhancing Depth Quality of Stereo Vision Using Deep Learning-Based Prior Information of the Driving Environment
Weifu Li, Vijay John, Seiichi Mita

Auto-TLDR; A Novel Post-processing Mathematical Framework for Stereo Vision
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boundary-Aware Graph Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Hanzhe Hu, Jinshi Cui, Jinshi Hongbin Zha
Auto-TLDR; Boundary-Aware Graph Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Ordinal Depth Classification Using Region-Based Self-Attention
Minh Hieu Phan, Son Lam Phung, Abdesselam Bouzerdoum

Auto-TLDR; Region-based Self-Attention for Multi-scale Depth Estimation from a Single 2D Image
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient-Receptive Field Block with Group Spatial Attention Mechanism for Object Detection
Jiacheng Zhang, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; E-RFB: Efficient-Receptive Field Block for Deep Neural Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
P2D: A Self-Supervised Method for Depth Estimation from Polarimetry
Marc Blanchon, Desire Sidibe, Olivier Morel, Ralph Seulin, Daniel Braun, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; Polarimetric Regularization for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Encoder-Decoder Based Convolutional Neural Networks with Multi-Scale-Aware Modules for Crowd Counting
Pongpisit Thanasutives, Ken-Ichi Fukui, Masayuki Numao, Boonserm Kijsirikul

Auto-TLDR; M-SFANet and M-SegNet for Crowd Counting Using Multi-Scale Fusion Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Lightweight Network to Learn Optical Flow from Event Data

Auto-TLDR; A lightweight pyramid network with attention mechanism to learn optical flow from events data
Attention Based Coupled Framework for Road and Pothole Segmentation
Shaik Masihullah, Ritu Garg, Prerana Mukherjee, Anupama Ray
Auto-TLDR; Few Shot Learning for Road and Pothole Segmentation on KITTI and IDD
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention Pyramid Module for Scene Recognition
Zhinan Qiao, Xiaohui Yuan, Chengyuan Zhuang, Abolfazl Meyarian

Auto-TLDR; Attention Pyramid Module for Multi-Scale Scene Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Spatial-Related and Scale-Aware Network for Crowd Counting
Lei Li, Yuan Dong, Hongliang Bai

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Attention for Crowd Counting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Direction Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Dehui Li, Zhiguo Cao, Ke Xian, Xinyuan Qi, Chao Zhang, Hao Lu

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Direction Convolution for Contextual Segmentation
Context-Aware Residual Module for Image Classification
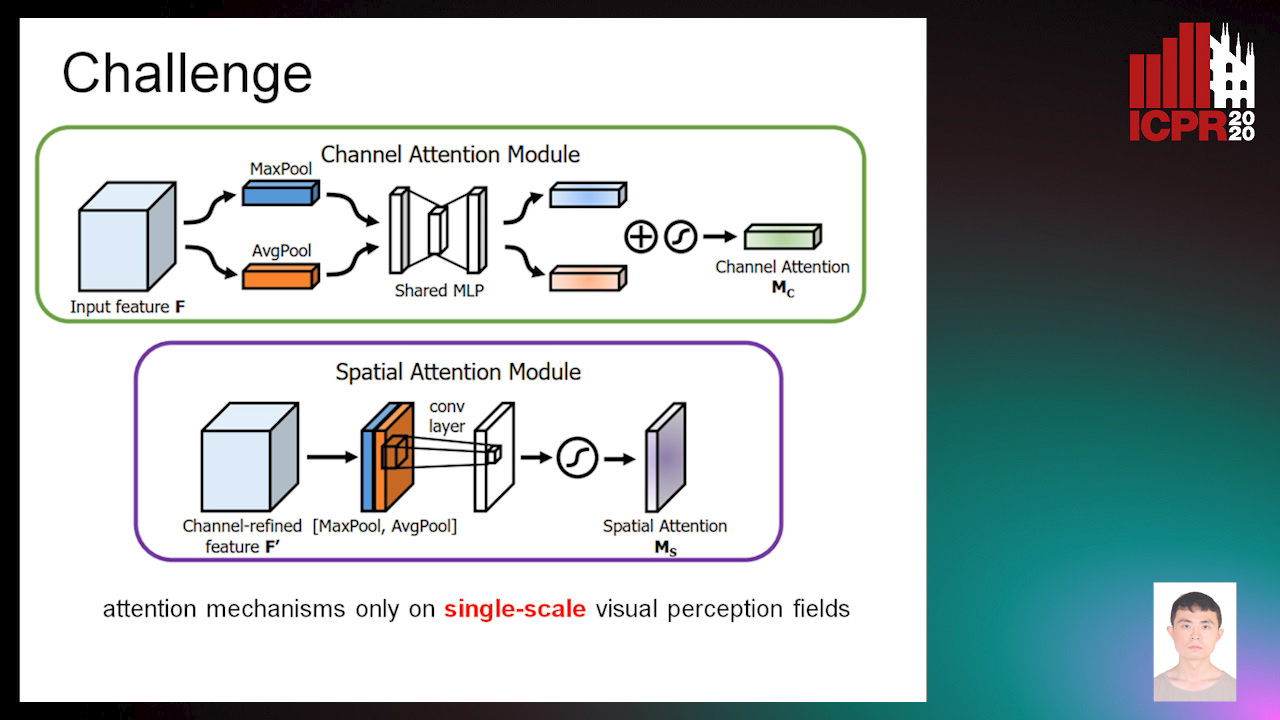
Auto-TLDR; Context-Aware Residual Module for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single Image Deblurring Using Bi-Attention Network

Auto-TLDR; Bi-Attention Neural Network for Single Image Deblurring
NetCalib: A Novel Approach for LiDAR-Camera Auto-Calibration Based on Deep Learning
Shan Wu, Amnir Hadachi, Damien Vivet, Yadu Prabhakar

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Calibration of LiDAR and Cameras using Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchically Aggregated Residual Transformation for Single Image Super Resolution

Auto-TLDR; HARTnet: Hierarchically Aggregated Residual Transformation for Multi-Scale Super-resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Selective Kernel and Motion-Emphasized Loss Based Attention-Guided Network for HDR Imaging of Dynamic Scenes
Yipeng Deng, Qin Liu, Takeshi Ikenaga

Auto-TLDR; SK-AHDRNet: A Deep Network with attention module and motion-emphasized loss function to produce ghost-free HDR images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Point Matching in Cross-Spectral Images with Cycle Consistency Learning
Ryosuke Furuta, Naoaki Noguchi, Xueting Wang, Toshihiko Yamasaki

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Learning for General Feature Point Matching in Cross-Spectral Settings
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fast and Accurate Real-Time Semantic Segmentation with Dilated Asymmetric Convolutions
Leonel Rosas-Arias, Gibran Benitez-Garcia, Jose Portillo-Portillo, Gabriel Sanchez-Perez, Keiji Yanai
Auto-TLDR; FASSD-Net: Dilated Asymmetric Pyramidal Fusion for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ACRM: Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix-NMS for Metallic Surface Defect Detection
Junting Fang, Xiaoyang Tan, Yuhui Wang

Auto-TLDR; Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix Non-Maximum Suppression for Robust Metal Defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Novel Region of Interest Extraction Layer for Instance Segmentation
Leonardo Rossi, Akbar Karimi, Andrea Prati

Auto-TLDR; Generic RoI Extractor for Two-Stage Neural Network for Instance Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Global Context-Based Network with Transformer for Image2latex
Nuo Pang, Chun Yang, Xiaobin Zhu, Jixuan Li, Xu-Cheng Yin

Auto-TLDR; Image2latex with Global Context block and Transformer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Coarse-To-Fine Foreground Segmentation Based on Co-Occurrence Pixel-Block and Spatio-Temporal Attention Model
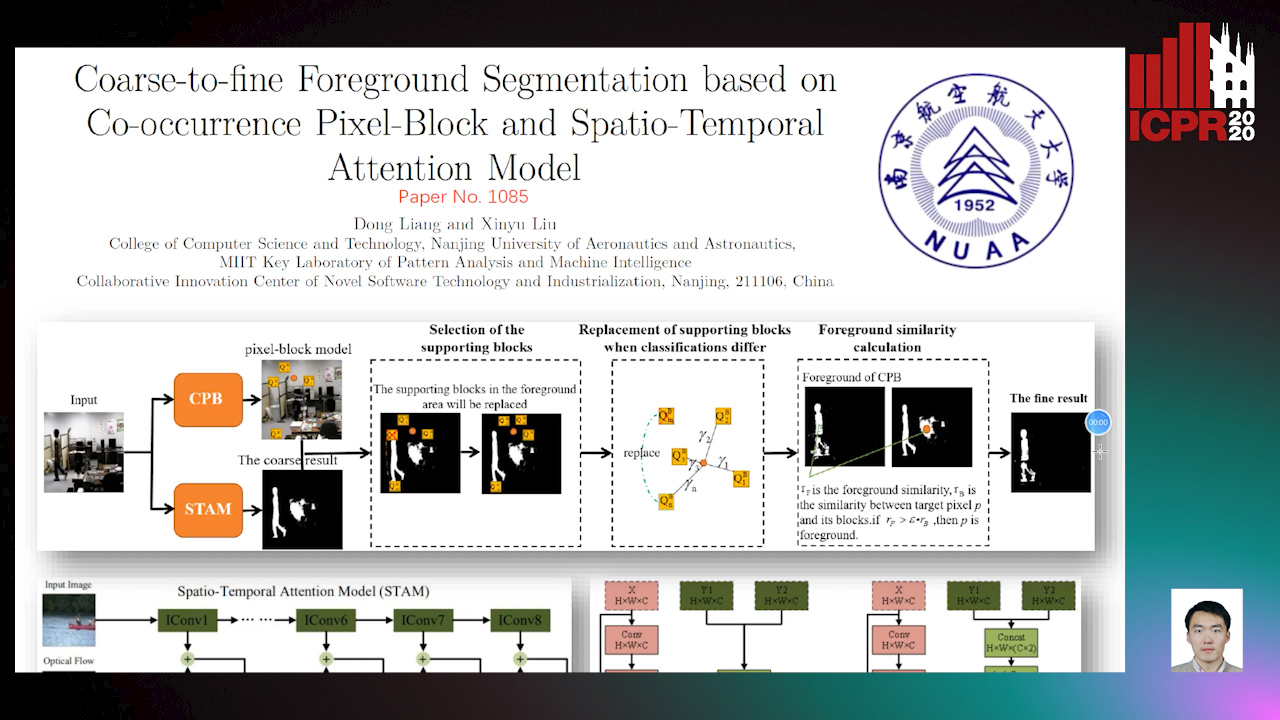
Auto-TLDR; Foreground Segmentation from coarse to Fine Using Co-occurrence Pixel-Block Model for Dynamic Scene
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Forground-Guided Vehicle Perception Framework
Kun Tian, Tong Zhou, Shiming Xiang, Chunhong Pan

Auto-TLDR; A foreground segmentation branch for vehicle detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
EDD-Net: An Efficient Defect Detection Network
Tianyu Guo, Linlin Zhang, Runwei Ding, Ge Yang

Auto-TLDR; EfficientNet: Efficient Network for Mobile Phone Surface defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar