Adaptive Image Compression Using GAN Based Semantic-Perceptual Residual Compensation
Ruojing Wang,
Zitang Sun,
Sei-Ichiro Kamata,
Weili Chen
Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Image Compression using GAN based Semantic-Perceptual Residual Compensation
Similar papers
Boosting High-Level Vision with Joint Compression Artifacts Reduction and Super-Resolution
Xiaoyu Xiang, Qian Lin, Jan Allebach
Auto-TLDR; A Context-Aware Joint CAR and SR Neural Network for High-Resolution Text Recognition and Face Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fidelity-Controllable Extreme Image Compression with Generative Adversarial Networks
Shoma Iwai, Tomo Miyazaki, Yoshihiro Sugaya, Shinichiro Omachi
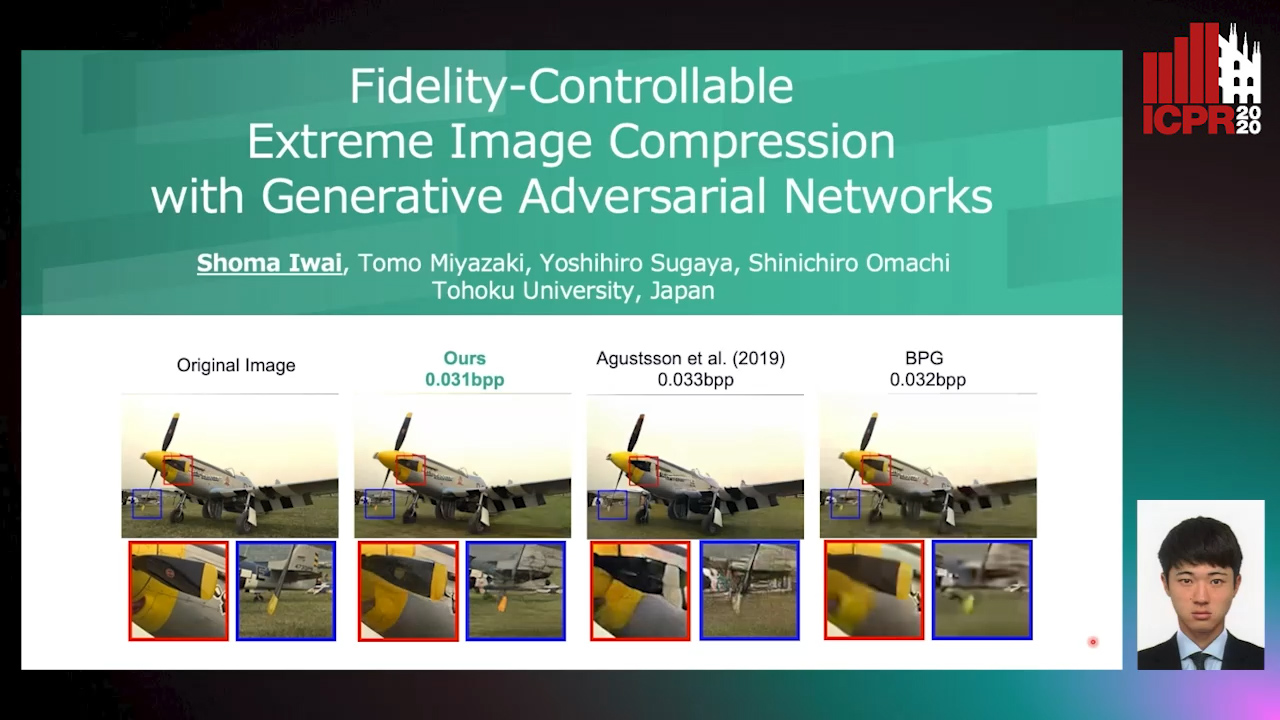
Auto-TLDR; GAN-based Image Compression at Low Bitrates
A NoGAN Approach for Image and Video Restoration and Compression Artifact Removal
Mameli Filippo, Marco Bertini, Leonardo Galteri, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Deep Neural Network for Image and Video Compression Artifact Removal and Restoration
SIDGAN: Single Image Dehazing without Paired Supervision
Pan Wei, Xin Wang, Lei Wang, Ji Xiang, Zihan Wang

Auto-TLDR; DehazeGAN: An End-to-End Generative Adversarial Network for Image Dehazing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Continuous Learning of Face Attribute Synthesis
Ning Xin, Shaohui Xu, Fangzhe Nan, Xiaoli Dong, Weijun Li, Yuanzhou Yao

Auto-TLDR; Continuous Learning for Face Attribute Synthesis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semantic Segmentation Refinement Using Entropy and Boundary-guided Monte Carlo Sampling and Directed Regional Search
Zitang Sun, Sei-Ichiro Kamata, Ruojing Wang, Weili Chen
Auto-TLDR; Directed Region Search and Refinement for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Thermal Image Enhancement Using Generative Adversarial Network for Pedestrian Detection
Mohamed Amine Marnissi, Hajer Fradi, Anis Sahbani, Najoua Essoukri Ben Amara
Auto-TLDR; Improving Visual Quality of Infrared Images for Pedestrian Detection Using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Laplacian GAN with Edge Enhancement for Face Super Resolution
Auto-TLDR; Face Image Super-Resolution with Enhanced Edge Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Residual Fractal Network for Single Image Super Resolution by Widening and Deepening
Jiahang Gu, Zhaowei Qu, Xiaoru Wang, Jiawang Dan, Junwei Sun
Auto-TLDR; Residual fractal convolutional network for single image super-resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Dual-Branch Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion

Auto-TLDR; Image Fusion Using Autoencoder for Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MBD-GAN: Model-Based Image Deblurring with a Generative Adversarial Network

Auto-TLDR; Model-Based Deblurring GAN for Inverse Imaging
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Facial Attribute Transfer through Inpainting
Ricard Durall, Franz-Josef Pfreundt, Janis Keuper

Auto-TLDR; Attribute Transfer Inpainting Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Free-Form Image Inpainting Via Contrastive Attention Network
Xin Ma, Xiaoqiang Zhou, Huaibo Huang, Zhenhua Chai, Xiaolin Wei, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Siamese inference for image inpainting
Image Inpainting with Contrastive Relation Network
Xiaoqiang Zhou, Junjie Li, Zilei Wang, Ran He, Tieniu Tan

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stage Inpainting with Graph-based Relation Network
Learning Disentangled Representations for Identity Preserving Surveillance Face Camouflage
Jingzhi Li, Lutong Han, Hua Zhang, Xiaoguang Han, Jingguo Ge, Xiaochu Cao

Auto-TLDR; Individual Face Privacy under Surveillance Scenario with Multi-task Loss Function
Joint Compressive Autoencoders for Full-Image-To-Image Hiding
Xiyao Liu, Ziping Ma, Xingbei Guo, Jialu Hou, Lei Wang, Gerald Schaefer, Hui Fang

Auto-TLDR; J-CAE: Joint Compressive Autoencoder for Image Hiding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Joint Representation Learning and Feature Modeling Approach for One-Class Recognition
Pramuditha Perera, Vishal Patel
Auto-TLDR; Combining Generative Features and One-Class Classification for Effective One-class Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single Image Deblurring Using Bi-Attention Network

Auto-TLDR; Bi-Attention Neural Network for Single Image Deblurring
LFIEM: Lightweight Filter-Based Image Enhancement Model
Oktai Tatanov, Aleksei Samarin
Auto-TLDR; Image Retouching Using Semi-supervised Learning for Mobile Devices
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Progressive Splitting and Upscaling Structure for Super-Resolution

Auto-TLDR; PSUS: Progressive and Upscaling Layer for Single Image Super-Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Explorable Tone Mapping Operators
Su Chien-Chuan, Yu-Lun Liu, Hung Jin Lin, Ren Wang, Chia-Ping Chen, Yu-Lin Chang, Soo-Chang Pei

Auto-TLDR; Learning-based multimodal tone-mapping from HDR images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Mucong Ye, Ouyang Jinpeng, Ge Chen, Jing Zhang, Xiaogang Yu
Auto-TLDR; EFPN: Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MedZip: 3D Medical Images Lossless Compressor Using Recurrent Neural Network (LSTM)
Omniah Nagoor, Joss Whittle, Jingjing Deng, Benjamin Mora, Mark W. Jones

Auto-TLDR; Recurrent Neural Network for Lossless Medical Image Compression using Long Short-Term Memory
Small Object Detection by Generative and Discriminative Learning
Yi Gu, Jie Li, Chentao Wu, Weijia Jia, Jianping Chen

Auto-TLDR; Generative and Discriminative Learning for Small Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RSAN: Residual Subtraction and Attention Network for Single Image Super-Resolution
Shuo Wei, Xin Sun, Haoran Zhao, Junyu Dong

Auto-TLDR; RSAN: Residual subtraction and attention network for super-resolution
Towards Artifacts-Free Image Defogging
Gabriele Graffieti, Davide Maltoni

Auto-TLDR; CurL-Defog: Learning Based Defogging with CycleGAN and HArD
GAN-Based Image Deblurring Using DCT Discriminator
Hiroki Tomosada, Takahiro Kudo, Takanori Fujisawa, Masaaki Ikehara
Auto-TLDR; DeblurDCTGAN: A Discrete Cosine Transform for Image Deblurring
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchically Aggregated Residual Transformation for Single Image Super Resolution

Auto-TLDR; HARTnet: Hierarchically Aggregated Residual Transformation for Multi-Scale Super-resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamic Guided Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Xiaoxia Xing, Yinghao Cai, Yiping Yang, Dayong Wen

Auto-TLDR; DGNet: Dynamic Guidance Upsampling for Self-attention-Decoding for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CSpA-DN: Channel and Spatial Attention Dense Network for Fusing PET and MRI Images
Bicao Li, Zhoufeng Liu, Shan Gao, Jenq-Neng Hwang, Jun Sun, Zongmin Wang

Auto-TLDR; CSpA-DN: Unsupervised Fusion of PET and MR Images with Channel and Spatial Attention
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Zoom-CAM: Generating Fine-Grained Pixel Annotations from Image Labels
Xiangwei Shi, Seyran Khademi, Yunqiang Li, Jan Van Gemert
Auto-TLDR; Zoom-CAM for Weakly Supervised Object Localization and Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient-Receptive Field Block with Group Spatial Attention Mechanism for Object Detection
Jiacheng Zhang, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; E-RFB: Efficient-Receptive Field Block for Deep Neural Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context-Aware Residual Module for Image Classification
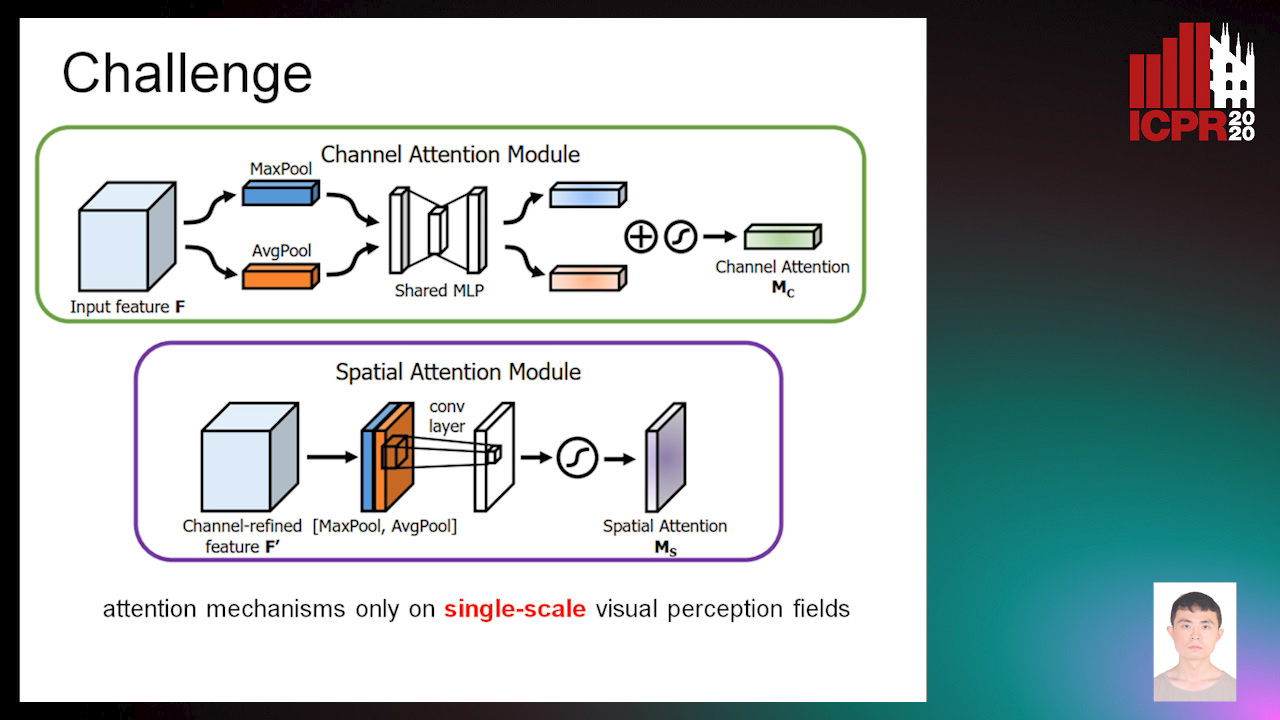
Auto-TLDR; Context-Aware Residual Module for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MFPP: Morphological Fragmental Perturbation Pyramid for Black-Box Model Explanations
Qing Yang, Xia Zhu, Jong-Kae Fwu, Yun Ye, Ganmei You, Yuan Zhu

Auto-TLDR; Morphological Fragmental Perturbation Pyramid for Explainable Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SECI-GAN: Semantic and Edge Completion for Dynamic Objects Removal
Francesco Pinto, Andrea Romanoni, Matteo Matteucci, Phil Torr

Auto-TLDR; SECI-GAN: Semantic and Edge Conditioned Inpainting Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
High Resolution Face Age Editing
Xu Yao, Gilles Puy, Alasdair Newson, Yann Gousseau, Pierre Hellier
Auto-TLDR; An Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Face Age editing on High Resolution Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Few-Shot Font Generation with Deep Metric Learning
Haruka Aoki, Koki Tsubota, Hikaru Ikuta, Kiyoharu Aizawa
Auto-TLDR; Deep Metric Learning for Japanese Typographic Font Synthesis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detail-Revealing Deep Low-Dose CT Reconstruction
Xinchen Ye, Yuyao Xu, Rui Xu, Shoji Kido, Noriyuki Tomiyama

Auto-TLDR; A Dual-branch Aggregation Network for Low-Dose CT Reconstruction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boundary Guided Image Translation for Pose Estimation from Ultra-Low Resolution Thermal Sensor
Kohei Kurihara, Tianren Wang, Teng Zhang, Brian Carrington Lovell
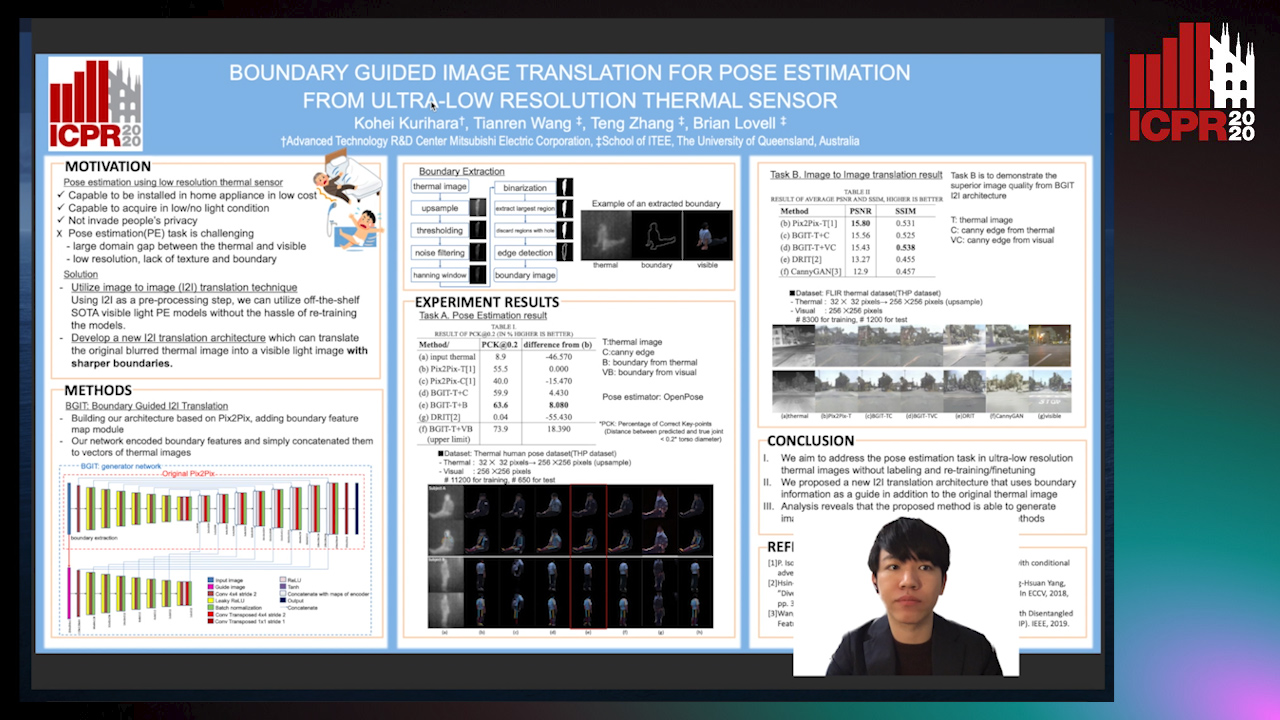
Auto-TLDR; Pose Estimation on Low-Resolution Thermal Images Using Image-to-Image Translation Architecture
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Coarse to Fine: Progressive and Multi-Task Learning for Salient Object Detection
Dong-Goo Kang, Sangwoo Park, Joonki Paik
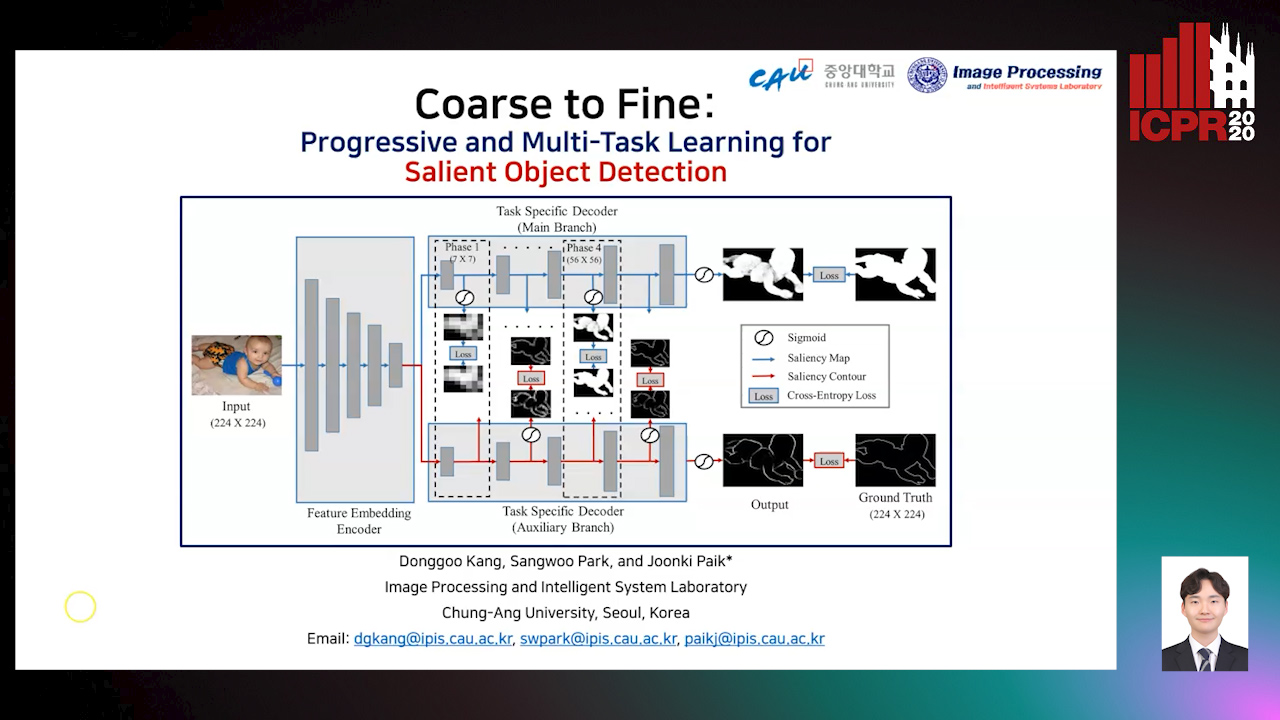
Auto-TLDR; Progressive and mutl-task learning scheme for salient object detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mobile Phone Surface Defect Detection Based on Improved Faster R-CNN
Tao Wang, Can Zhang, Runwei Ding, Ge Yang

Auto-TLDR; Faster R-CNN for Mobile Phone Surface Defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detail Fusion GAN: High-Quality Translation for Unpaired Images with GAN-Based Data Augmentation
Ling Li, Yaochen Li, Chuan Wu, Hang Dong, Peilin Jiang, Fei Wang

Auto-TLDR; Data Augmentation with GAN-based Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention2AngioGAN: Synthesizing Fluorescein Angiography from Retinal Fundus Images Using Generative Adversarial Networks
Sharif Amit Kamran, Khondker Fariha Hossain, Alireza Tavakkoli, Stewart Lee Zuckerbrod
Auto-TLDR; Fluorescein Angiography from Fundus Images using Attention-based Generative Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
From Early Biological Models to CNNs: Do They Look Where Humans Look?
Marinella Iole Cadoni, Andrea Lagorio, Enrico Grosso, Jia Huei Tan, Chee Seng Chan

Auto-TLDR; Comparing Neural Networks to Human Fixations for Semantic Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Combining GANs and AutoEncoders for Efficient Anomaly Detection
Fabio Carrara, Giuseppe Amato, Luca Brombin, Fabrizio Falchi, Claudio Gennaro
Auto-TLDR; CBIGAN: Anomaly Detection in Images with Consistency Constrained BiGAN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PSDNet: A Balanced Architecture of Accuracy and Parameters for Semantic Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Pyramid Pooling Module with SE1Cblock and D2SUpsample Network (PSDNet)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Image Representation Learning by Transformation Regression
Xifeng Guo, Jiyuan Liu, Sihang Zhou, En Zhu, Shihao Dong

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Image Representation Learning using Continuous Parameter Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
LiNet: A Lightweight Network for Image Super Resolution
Armin Mehri, Parichehr Behjati Ardakani, Angel D. Sappa

Auto-TLDR; LiNet: A Compact Dense Network for Lightweight Super Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar