Combining GANs and AutoEncoders for Efficient Anomaly Detection
Fabio Carrara,
Giuseppe Amato,
Luca Brombin,
Fabrizio Falchi,
Claudio Gennaro
Auto-TLDR; CBIGAN: Anomaly Detection in Images with Consistency Constrained BiGAN
Similar papers
Improved anomaly detection by training an autoencoder with skip connections on images corrupted with Stain-shaped noise
Anne-Sophie Collin, Christophe De Vleeschouwer
Auto-TLDR; Autoencoder with Skip Connections for Anomaly Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Evaluation of Anomaly Detection Algorithms for the Real-World Applications
Marija Ivanovska, Domen Tabernik, Danijel Skocaj, Janez Pers

Auto-TLDR; Evaluating Anomaly Detection Algorithms for Practical Applications
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Discriminative Multi-Level Reconstruction under Compact Latent Space for One-Class Novelty Detection
Jaewoo Park, Yoon Gyo Jung, Andrew Teoh

Auto-TLDR; Discriminative Compact AE for One-Class novelty detection and Adversarial Example Detection
Modeling the Distribution of Normal Data in Pre-Trained Deep Features for Anomaly Detection
Oliver Rippel, Patrick Mertens, Dorit Merhof

Auto-TLDR; Deep Feature Representations for Anomaly Detection in Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AVAE: Adversarial Variational Auto Encoder
Antoine Plumerault, Hervé Le Borgne, Celine Hudelot

Auto-TLDR; Combining VAE and GAN for Realistic Image Generation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Anomaly Detection by Estimating Likelihood of Representations

Auto-TLDR; Video Anomaly Detection in the latent feature space using a deep probabilistic model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Joint Representation Learning and Feature Modeling Approach for One-Class Recognition
Pramuditha Perera, Vishal Patel
Auto-TLDR; Combining Generative Features and One-Class Classification for Effective One-class Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Detection of Stationary Waves in the Venus’ Atmosphere Using Deep Generative Models
Minori Narita, Daiki Kimura, Takeshi Imamura
Auto-TLDR; Anomaly Detection of Large Bow-shaped Structures on the Venus Clouds using Variational Auto-encoder and Attention Maps
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Anomaly Detection, Localization and Classification for Railway Inspection
Riccardo Gasparini, Andrea D'Eusanio, Guido Borghi, Stefano Pini, Giuseppe Scaglione, Simone Calderara, Eugenio Fedeli, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Anomaly Detection and Localization using thermal images in the lowlight environment
Local Facial Attribute Transfer through Inpainting
Ricard Durall, Franz-Josef Pfreundt, Janis Keuper

Auto-TLDR; Attribute Transfer Inpainting Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
IDA-GAN: A Novel Imbalanced Data Augmentation GAN
Auto-TLDR; IDA-GAN: Generative Adversarial Networks for Imbalanced Data Augmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
JUMPS: Joints Upsampling Method for Pose Sequences
Lucas Mourot, Francois Le Clerc, Cédric Thébault, Pierre Hellier

Auto-TLDR; JUMPS: Increasing the Number of Joints in 2D Pose Estimation and Recovering Occluded or Missing Joints
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Phase Retrieval Using Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks
Tobias Uelwer, Alexander Oberstraß, Stefan Harmeling

Auto-TLDR; Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks for Phase Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Detection of Pulmonary Opacities for Computer-Aided Diagnosis of COVID-19 on CT Images
Rui Xu, Xiao Cao, Yufeng Wang, Yen-Wei Chen, Xinchen Ye, Lin Lin, Wenchao Zhu, Chao Chen, Fangyi Xu, Yong Zhou, Hongjie Hu, Shoji Kido, Noriyuki Tomiyama
Auto-TLDR; A computer-aided diagnosis of COVID-19 from CT images using unsupervised pulmonary opacity detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Galaxy Image Translation with Semi-Supervised Noise-Reconstructed Generative Adversarial Networks
Qiufan Lin, Dominique Fouchez, Jérôme Pasquet
Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Image Translation with Generative Adversarial Networks Using Paired and Unpaired Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Reducing the Variance of Variational Estimates of Mutual Information by Limiting the Critic's Hypothesis Space to RKHS
Aditya Sreekar P, Ujjwal Tiwari, Anoop Namboodiri

Auto-TLDR; Mutual Information Estimation from Variational Lower Bounds Using a Critic's Hypothesis Space
Mutual Information Based Method for Unsupervised Disentanglement of Video Representation
Aditya Sreekar P, Ujjwal Tiwari, Anoop Namboodiri

Auto-TLDR; MIPAE: Mutual Information Predictive Auto-Encoder for Video Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Variational Deep Embedding Clustering by Augmented Mutual Information Maximization
Qiang Ji, Yanfeng Sun, Yongli Hu, Baocai Yin

Auto-TLDR; Clustering by Augmented Mutual Information maximization for Deep Embedding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PIF: Anomaly detection via preference embedding
Filippo Leveni, Luca Magri, Giacomo Boracchi, Cesare Alippi

Auto-TLDR; PIF: Anomaly Detection with Preference Embedding for Structured Patterns
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Self-Supervised GAN for Unsupervised Few-Shot Object Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Few-Shot Object Recognition with a Triplet GAN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semi-Supervised Generative Adversarial Networks with a Pair of Complementary Generators for Retinopathy Screening
Yingpeng Xie, Qiwei Wan, Hai Xie, En-Leng Tan, Yanwu Xu, Baiying Lei

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Networks for Retinopathy Diagnosis via Fundus Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Variational Capsule Encoder
Harish Raviprakash, Syed Anwar, Ulas Bagci

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian Capsule Networks for Representation Learning in latent space
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Clustering with Mean Teacher for Semi-Supervised Learning
Zexi Chen, Benjamin Dutton, Bharathkumar Ramachandra, Tianfu Wu, Ranga Raju Vatsavai

Auto-TLDR; Local Clustering for Semi-supervised Learning
SAGE: Sequential Attribute Generator for Analyzing Glioblastomas Using Limited Dataset
Padmaja Jonnalagedda, Brent Weinberg, Jason Allen, Taejin Min, Shiv Bhanu, Bir Bhanu

Auto-TLDR; SAGE: Generative Adversarial Networks for Imaging Biomarker Detection and Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fidelity-Controllable Extreme Image Compression with Generative Adversarial Networks
Shoma Iwai, Tomo Miyazaki, Yoshihiro Sugaya, Shinichiro Omachi
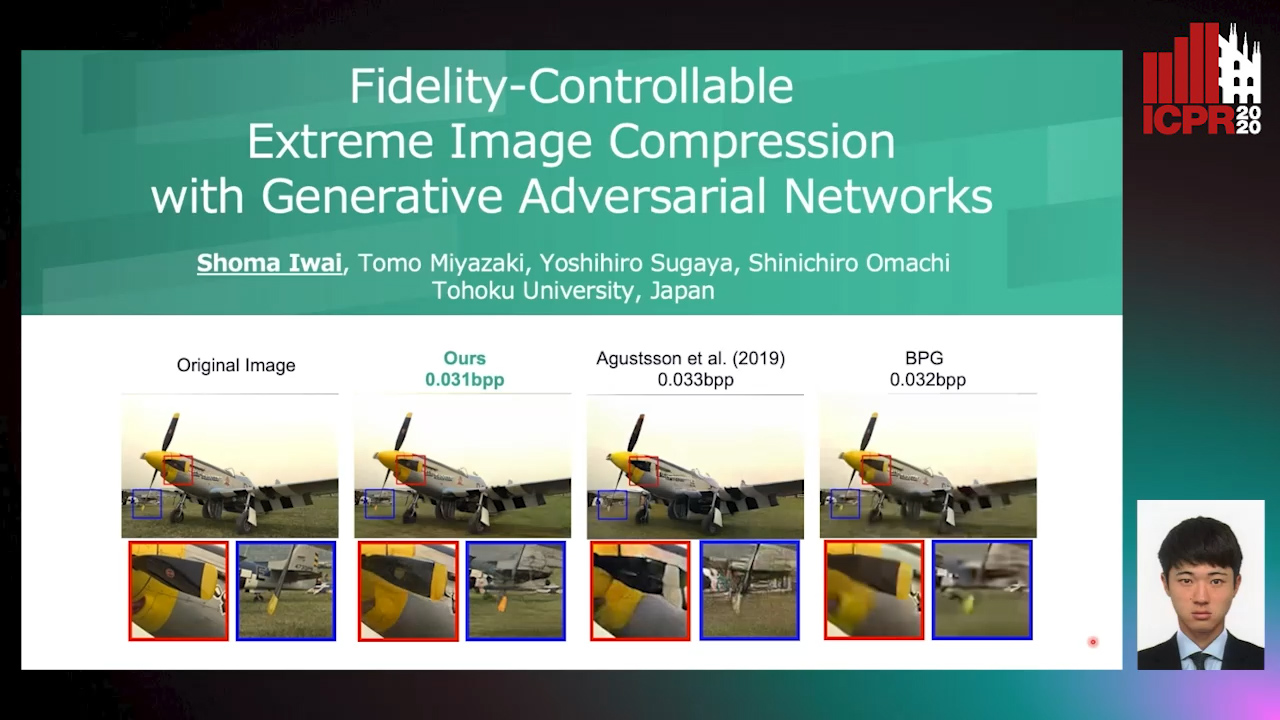
Auto-TLDR; GAN-based Image Compression at Low Bitrates
Image Representation Learning by Transformation Regression
Xifeng Guo, Jiyuan Liu, Sihang Zhou, En Zhu, Shihao Dong

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Image Representation Learning using Continuous Parameter Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adversarial Encoder-Multi-Task-Decoder for Multi-Stage Processes
Andre Mendes, Julian Togelius, Leandro Dos Santos Coelho

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Task Learning and Semi-Supervised Learning for Multi-Stage Processes
Generative Latent Implicit Conditional Optimization When Learning from Small Sample
Auto-TLDR; GLICO: Generative Latent Implicit Conditional Optimization for Small Sample Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GAN-Based Gaussian Mixture Model Responsibility Learning
Wanming Huang, Yi Da Xu, Shuai Jiang, Xuan Liang, Ian Oppermann

Auto-TLDR; Posterior Consistency Module for Gaussian Mixture Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Image Compression Using GAN Based Semantic-Perceptual Residual Compensation
Ruojing Wang, Zitang Sun, Sei-Ichiro Kamata, Weili Chen
Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Image Compression using GAN based Semantic-Perceptual Residual Compensation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ARCADe: A Rapid Continual Anomaly Detector
Ahmed Frikha, Denis Krompass, Volker Tresp

Auto-TLDR; ARCADe: A Meta-Learning Approach for Continuous Anomaly Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Future Urban Scenes Generation through Vehicles Synthesis
Alessandro Simoni, Luca Bergamini, Andrea Palazzi, Simone Calderara, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Predicting the Future of an Urban Scene with a Novel View Synthesis Paradigm
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pretraining Image Encoders without Reconstruction Via Feature Prediction Loss
Gustav Grund Pihlgren, Fredrik Sandin, Marcus Liwicki

Auto-TLDR; Feature Prediction Loss for Autoencoder-based Pretraining of Image Encoders
Motion and Region Aware Adversarial Learning for Fall Detection with Thermal Imaging
Vineet Mehta, Abhinav Dhall, Sujata Pal, Shehroz Khan

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Fall Detection with Adversarial Network using Thermal Imaging Camera
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The eXPose Approach to Crosslier Detection
Antonio Barata, Frank Takes, Hendrik Van Den Herik, Cor Veenman

Auto-TLDR; EXPose: Crosslier Detection Based on Supervised Category Modeling
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PoseCVAE: Anomalous Human Activity Detection
Yashswi Jain, Ashvini Kumar Sharma, Rajbabu Velmurugan, Biplab Banerjee

Auto-TLDR; PoseCVAE: Anomalous Human Activity Detection Using Generative Modeling
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Few-Shot Font Generation with Deep Metric Learning
Haruka Aoki, Koki Tsubota, Hikaru Ikuta, Kiyoharu Aizawa
Auto-TLDR; Deep Metric Learning for Japanese Typographic Font Synthesis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semantics-Guided Representation Learning with Applications to Visual Synthesis
Jia-Wei Yan, Ci-Siang Lin, Fu-En Yang, Yu-Jhe Li, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang

Auto-TLDR; Learning Interpretable and Interpolatable Latent Representations for Visual Synthesis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Interpretable Representation for 3D Point Clouds
Feng-Guang Su, Ci-Siang Lin, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang

Auto-TLDR; Disentangling Body-type and Pose Information from 3D Point Clouds Using Adversarial Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
High Resolution Face Age Editing
Xu Yao, Gilles Puy, Alasdair Newson, Yann Gousseau, Pierre Hellier
Auto-TLDR; An Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Face Age editing on High Resolution Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semantic-Guided Inpainting Network for Complex Urban Scenes Manipulation
Pierfrancesco Ardino, Yahui Liu, Elisa Ricci, Bruno Lepri, Marco De Nadai

Auto-TLDR; Semantic-Guided Inpainting of Complex Urban Scene Using Semantic Segmentation and Generation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Leveraging a Weakly Adversarial Paradigm for Joint Learning of Disparity and Confidence Estimation
Matteo Poggi, Fabio Tosi, Filippo Aleotti, Stefano Mattoccia

Auto-TLDR; Joint Training of Deep-Networks for Outlier Detection from Stereo Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Variational Inference with Latent Space Quantization for Adversarial Resilience
Vinay Kyatham, Deepak Mishra, Prathosh A.P.

Auto-TLDR; A Generalized Defense Mechanism for Adversarial Attacks on Data Manifolds
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks and Fast Adaptive Bi-Dimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition for Style Transfer
Elissavet Batziou, Petros Alvanitopoulos, Konstantinos Ioannidis, Ioannis Patras, Stefanos Vrochidis, Ioannis Kompatsiaris

Auto-TLDR; FABEMD: Fast and Adaptive Bidimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition for Style Transfer on Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Disentangled Representations for Identity Preserving Surveillance Face Camouflage
Jingzhi Li, Lutong Han, Hua Zhang, Xiaoguang Han, Jingguo Ge, Xiaochu Cao

Auto-TLDR; Individual Face Privacy under Surveillance Scenario with Multi-task Loss Function
CardioGAN: An Attention-Based Generative Adversarial Network for Generation of Electrocardiograms
Subhrajyoti Dasgupta, Sudip Das, Ujjwal Bhattacharya

Auto-TLDR; CardioGAN: Generative Adversarial Network for Synthetic Electrocardiogram Signals
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Multi-Task Domain Adaptation

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Multi-task Learning for Image Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Quantifying the Use of Domain Randomization
Mohammad Ani, Hector Basevi, Ales Leonardis

Auto-TLDR; Evaluating Domain Randomization for Synthetic Image Generation by directly measuring the difference between realistic and synthetic data distributions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar