Local Clustering with Mean Teacher for Semi-Supervised Learning
Zexi Chen,
Benjamin Dutton,
Bharathkumar Ramachandra,
Tianfu Wu,
Ranga Raju Vatsavai

Auto-TLDR; Local Clustering for Semi-supervised Learning
Similar papers
Learning with Multiplicative Perturbations

Auto-TLDR; XAT and xVAT: A Multiplicative Adversarial Training Algorithm for Robust DNN Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Revisiting ImprovedGAN with Metric Learning for Semi-Supervised Learning
Jaewoo Park, Yoon Gyo Jung, Andrew Teoh

Auto-TLDR; Improving ImprovedGAN with Metric Learning for Semi-supervised Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adversarially Constrained Interpolation for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Mohamed Azzam, Aurele Tohokantche Gnanha, Hau-San Wong, Si Wu

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Domain Mixup Strategy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enlarging Discriminative Power by Adding an Extra Class in Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Hai Tran, Sumyeong Ahn, Taeyoung Lee, Yung Yi

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation using Artificial Classes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generative Latent Implicit Conditional Optimization When Learning from Small Sample
Auto-TLDR; GLICO: Generative Latent Implicit Conditional Optimization for Small Sample Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Constrained Spectral Clustering Network with Self-Training
Xinyue Liu, Shichong Yang, Linlin Zong

Auto-TLDR; Constrained Spectral Clustering Network: A Constrained Deep spectral clustering network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Beyond Cross-Entropy: Learning Highly Separable Feature Distributions for Robust and Accurate Classification
Arslan Ali, Andrea Migliorati, Tiziano Bianchi, Enrico Magli

Auto-TLDR; Gaussian class-conditional simplex loss for adversarial robust multiclass classifiers
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Modal Deep Clustering: Unsupervised Partitioning of Images

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Modal Deep Clustering for Unlabeled Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Embeddings for Image Clustering: An Empirical Study of Triplet Loss Approaches
Kalun Ho, Janis Keuper, Franz-Josef Pfreundt, Margret Keuper
Auto-TLDR; Clustering Objectives for K-means and Correlation Clustering Using Triplet Loss
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rethinking Deep Active Learning: Using Unlabeled Data at Model Training
Oriane Siméoni, Mateusz Budnik, Yannis Avrithis, Guillaume Gravier

Auto-TLDR; Unlabeled Data for Active Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semi-Supervised Generative Adversarial Networks with a Pair of Complementary Generators for Retinopathy Screening
Yingpeng Xie, Qiwei Wan, Hai Xie, En-Leng Tan, Yanwu Xu, Baiying Lei

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Networks for Retinopathy Diagnosis via Fundus Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Knowledge Distillation Beyond Model Compression
Fahad Sarfraz, Elahe Arani, Bahram Zonooz

Auto-TLDR; Knowledge Distillation from Teacher to Student
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adversarial Encoder-Multi-Task-Decoder for Multi-Stage Processes
Andre Mendes, Julian Togelius, Leandro Dos Santos Coelho

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Task Learning and Semi-Supervised Learning for Multi-Stage Processes
Teacher-Student Competition for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Ruixin Xiao, Zhilei Liu, Baoyuan Wu
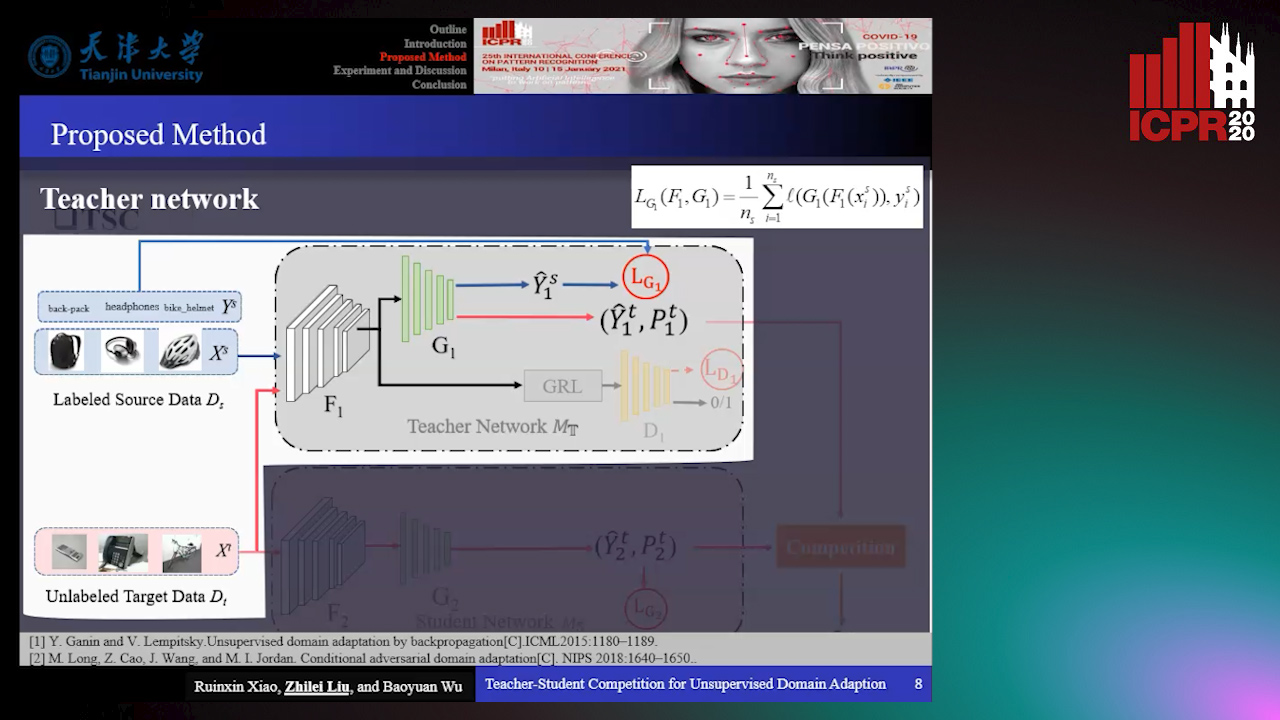
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaption with Teacher-Student Competition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Knowledge Distillation with a Precise Teacher and Prediction with Abstention

Auto-TLDR; Knowledge Distillation using Deep gambler loss and selective classification framework
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Image Representation Learning by Transformation Regression
Xifeng Guo, Jiyuan Liu, Sihang Zhou, En Zhu, Shihao Dong

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Image Representation Learning using Continuous Parameter Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Noise Injection for Training Stochastic Student Networks from Deterministic Teachers
Yi Xiang Marcus Tan, Yuval Elovici, Alexander Binder

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Stochastic Networks for Adversarial Attacks
IDA-GAN: A Novel Imbalanced Data Augmentation GAN
Auto-TLDR; IDA-GAN: Generative Adversarial Networks for Imbalanced Data Augmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Robust Learning with Different Label Noise Distributions
Diego Ortego, Eric Arazo, Paul Albert, Noel E O'Connor, Kevin Mcguinness

Auto-TLDR; Distribution Robust Pseudo-Labeling with Semi-supervised Learning
Graph-Based Interpolation of Feature Vectors for Accurate Few-Shot Classification
Yuqing Hu, Vincent Gripon, Stéphane Pateux

Auto-TLDR; Transductive Learning for Few-Shot Classification using Graph Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Combining GANs and AutoEncoders for Efficient Anomaly Detection
Fabio Carrara, Giuseppe Amato, Luca Brombin, Fabrizio Falchi, Claudio Gennaro
Auto-TLDR; CBIGAN: Anomaly Detection in Images with Consistency Constrained BiGAN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Variational Deep Embedding Clustering by Augmented Mutual Information Maximization
Qiang Ji, Yanfeng Sun, Yongli Hu, Baocai Yin

Auto-TLDR; Clustering by Augmented Mutual Information maximization for Deep Embedding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On-Manifold Adversarial Data Augmentation Improves Uncertainty Calibration
Kanil Patel, William Beluch, Dan Zhang, Michael Pfeiffer, Bin Yang

Auto-TLDR; On-Manifold Adversarial Data Augmentation for Uncertainty Estimation
Meta Soft Label Generation for Noisy Labels

Auto-TLDR; MSLG: Meta-Learning for Noisy Label Generation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Domain Adaptation with Consistency Training
Liang Xiao, Jiaolong Xu, Dawei Zhao, Zhiyu Wang, Li Wang, Yiming Nie, Bin Dai

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Close Look at Deep Learning with Small Data

Auto-TLDR; Low-Complex Neural Networks for Small Data Conditions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient Online Subclass Knowledge Distillation for Image Classification
Maria Tzelepi, Nikolaos Passalis, Anastasios Tefas
Auto-TLDR; OSKD: Online Subclass Knowledge Distillation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Joint Representation Learning and Feature Modeling Approach for One-Class Recognition
Pramuditha Perera, Vishal Patel
Auto-TLDR; Combining Generative Features and One-Class Classification for Effective One-class Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generalization Comparison of Deep Neural Networks Via Output Sensitivity
Mahsa Forouzesh, Farnood Salehi, Patrick Thiran
Auto-TLDR; Generalization of Deep Neural Networks using Sensitivity
Pretraining Image Encoders without Reconstruction Via Feature Prediction Loss
Gustav Grund Pihlgren, Fredrik Sandin, Marcus Liwicki

Auto-TLDR; Feature Prediction Loss for Autoencoder-based Pretraining of Image Encoders
Improved Deep Classwise Hashing with Centers Similarity Learning for Image Retrieval

Auto-TLDR; Deep Classwise Hashing for Image Retrieval Using Center Similarity Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Verifying the Causes of Adversarial Examples
Honglin Li, Yifei Fan, Frieder Ganz, Tony Yezzi, Payam Barnaghi

Auto-TLDR; Exploring the Causes of Adversarial Examples in Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Self-Supervised GAN for Unsupervised Few-Shot Object Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Few-Shot Object Recognition with a Triplet GAN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
N2D: (Not Too) Deep Clustering Via Clustering the Local Manifold of an Autoencoded Embedding
Ryan Mcconville, Raul Santos-Rodriguez, Robert Piechocki, Ian Craddock

Auto-TLDR; Local Manifold Learning for Deep Clustering on Autoencoded Embeddings
Boundary Optimised Samples Training for Detecting Out-Of-Distribution Images
Luca Marson, Vladimir Li, Atsuto Maki
Auto-TLDR; Boundary Optimised Samples for Out-of-Distribution Input Detection in Deep Convolutional Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Stochastic Label Refinery: Toward Better Target Label Distribution
Xi Fang, Jiancheng Yang, Bingbing Ni

Auto-TLDR; Stochastic Label Refinery for Deep Supervised Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TAAN: Task-Aware Attention Network for Few-Shot Classification

Auto-TLDR; TAAN: Task-Aware Attention Network for Few-Shot Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Soft Label and Discriminant Embedding Estimation for Semi-Supervised Classification
Fadi Dornaika, Abdullah Baradaaji, Youssof El Traboulsi
Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Semi-Supervised Learning for Linear Feature Extraction and Label Propagation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Separation of Aleatoric and Epistemic Uncertainty in Deterministic Deep Neural Networks
Denis Huseljic, Bernhard Sick, Marek Herde, Daniel Kottke

Auto-TLDR; AE-DNN: Modeling Uncertainty in Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Supervised Domain Adaptation Using Graph Embedding
Lukas Hedegaard, Omar Ali Sheikh-Omar, Alexandros Iosifidis
Auto-TLDR; Domain Adaptation from the Perspective of Multi-view Graph Embedding and Dimensionality Reduction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Is the Meta-Learning Idea Able to Improve the Generalization of Deep Neural Networks on the Standard Supervised Learning?

Auto-TLDR; Meta-learning Based Training of Deep Neural Networks for Few-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AVAE: Adversarial Variational Auto Encoder
Antoine Plumerault, Hervé Le Borgne, Celine Hudelot

Auto-TLDR; Combining VAE and GAN for Realistic Image Generation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Class-Incremental Learning with Topological Schemas of Memory Spaces
Xinyuan Chang, Xiaoyu Tao, Xiaopeng Hong, Xing Wei, Wei Ke, Yihong Gong

Auto-TLDR; Class-incremental Learning with Topological Schematic Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Convolutional Embedding for Digitized Painting Clustering
Giovanna Castellano, Gennaro Vessio

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Convolutional Embedding Model for Clustering Artworks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Multi-Task Domain Adaptation

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Multi-task Learning for Image Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On the Evaluation of Generative Adversarial Networks by Discriminative Models
Amirsina Torfi, Mohammadreza Beyki, Edward Alan Fox
Auto-TLDR; Domain-agnostic GAN Evaluation with Siamese Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MaxDropout: Deep Neural Network Regularization Based on Maximum Output Values
Claudio Filipi Gonçalves Santos, Danilo Colombo, Mateus Roder, Joao Paulo Papa

Auto-TLDR; MaxDropout: A Regularizer for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semi-Supervised Class Incremental Learning
Alexis Lechat, Stéphane Herbin, Frederic Jurie

Auto-TLDR; incremental class learning with non-annotated batches
Abstract Slides Poster Similar