Knowledge Distillation with a Precise Teacher and Prediction with Abstention

Auto-TLDR; Knowledge Distillation using Deep gambler loss and selective classification framework
Similar papers
Efficient Online Subclass Knowledge Distillation for Image Classification
Maria Tzelepi, Nikolaos Passalis, Anastasios Tefas
Auto-TLDR; OSKD: Online Subclass Knowledge Distillation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Distilling Spikes: Knowledge Distillation in Spiking Neural Networks
Ravi Kumar Kushawaha, Saurabh Kumar, Biplab Banerjee, Rajbabu Velmurugan

Auto-TLDR; Knowledge Distillation in Spiking Neural Networks for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Knowledge Distillation Beyond Model Compression
Fahad Sarfraz, Elahe Arani, Bahram Zonooz

Auto-TLDR; Knowledge Distillation from Teacher to Student
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Stochastic Label Refinery: Toward Better Target Label Distribution
Xi Fang, Jiancheng Yang, Bingbing Ni

Auto-TLDR; Stochastic Label Refinery for Deep Supervised Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Fusion for Online Mutual Knowledge Distillation
Jangho Kim, Minsung Hyun, Inseop Chung, Nojun Kwak

Auto-TLDR; Feature Fusion Learning Using Fusion of Sub-Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Compact CNN Structure Learning by Knowledge Distillation
Waqar Ahmed, Andrea Zunino, Pietro Morerio, Vittorio Murino

Auto-TLDR; Knowledge Distillation for Compressing Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Channel Planting for Deep Neural Networks Using Knowledge Distillation
Kakeru Mitsuno, Yuichiro Nomura, Takio Kurita

Auto-TLDR; Incremental Training for Deep Neural Networks with Knowledge Distillation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Student Network Search for Knowledge Distillation
Zhexi Zhang, Wei Zhu, Junchi Yan, Peng Gao, Guotong Xie

Auto-TLDR; NAS-KD: Knowledge Distillation for BERT
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Clustering with Mean Teacher for Semi-Supervised Learning
Zexi Chen, Benjamin Dutton, Bharathkumar Ramachandra, Tianfu Wu, Ranga Raju Vatsavai

Auto-TLDR; Local Clustering for Semi-supervised Learning
Towards Low-Bit Quantization of Deep Neural Networks with Limited Data
Yong Yuan, Chen Chen, Xiyuan Hu, Silong Peng

Auto-TLDR; Low-Precision Quantization of Deep Neural Networks with Limited Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Noise Injection for Training Stochastic Student Networks from Deterministic Teachers
Yi Xiang Marcus Tan, Yuval Elovici, Alexander Binder

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Stochastic Networks for Adversarial Attacks
Can Data Placement Be Effective for Neural Networks Classification Tasks? Introducing the Orthogonal Loss
Brais Cancela, Veronica Bolon-Canedo, Amparo Alonso-Betanzos

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Placement for Neural Network Training Loss Functions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boundary Optimised Samples Training for Detecting Out-Of-Distribution Images
Luca Marson, Vladimir Li, Atsuto Maki
Auto-TLDR; Boundary Optimised Samples for Out-of-Distribution Input Detection in Deep Convolutional Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Boundary-Aware Distillation Network for Compressed Video Semantic Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; A Boundary-Aware Distillation Network for Video Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Class-Incremental Learning with Topological Schemas of Memory Spaces
Xinyuan Chang, Xiaoyu Tao, Xiaopeng Hong, Xing Wei, Wei Ke, Yihong Gong

Auto-TLDR; Class-incremental Learning with Topological Schematic Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FastSal: A Computationally Efficient Network for Visual Saliency Prediction

Auto-TLDR; MobileNetV2: A Convolutional Neural Network for Saliency Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Iterative Label Improvement: Robust Training by Confidence Based Filtering and Dataset Partitioning
Christian Haase-Schütz, Rainer Stal, Heinz Hertlein, Bernhard Sick

Auto-TLDR; Meta Training and Labelling for Unlabelled Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Is the Meta-Learning Idea Able to Improve the Generalization of Deep Neural Networks on the Standard Supervised Learning?

Auto-TLDR; Meta-learning Based Training of Deep Neural Networks for Few-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adversarial Knowledge Distillation for a Compact Generator
Hideki Tsunashima, Shigeo Morishima, Junji Yamato, Qiu Chen, Hirokatsu Kataoka

Auto-TLDR; Adversarial Knowledge Distillation for Generative Adversarial Nets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Quasibinary Classifier for Images with Zero and Multiple Labels
Liao Shuai, Efstratios Gavves, Changyong Oh, Cees Snoek

Auto-TLDR; Quasibinary Classifiers for Zero-label and Multi-label Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Smart Inference for Multidigit Convolutional Neural Network Based Barcode Decoding
Duy-Thao Do, Tolcha Yalew, Tae Joon Jun, Daeyoung Kim

Auto-TLDR; Smart Inference for Barcode Decoding using Deep Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Contextual Classification Using Self-Supervised Auxiliary Models for Deep Neural Networks
Sebastian Palacio, Philipp Engler, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel

Auto-TLDR; Self-Supervised Autogenous Learning for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Distillation for Decentralized Learning from Heterogeneous Clients
Jiaxin Ma, Ryo Yonetani, Zahid Iqbal

Auto-TLDR; Decentralized Learning via Adaptive Distillation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Teacher-Student Competition for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Ruixin Xiao, Zhilei Liu, Baoyuan Wu
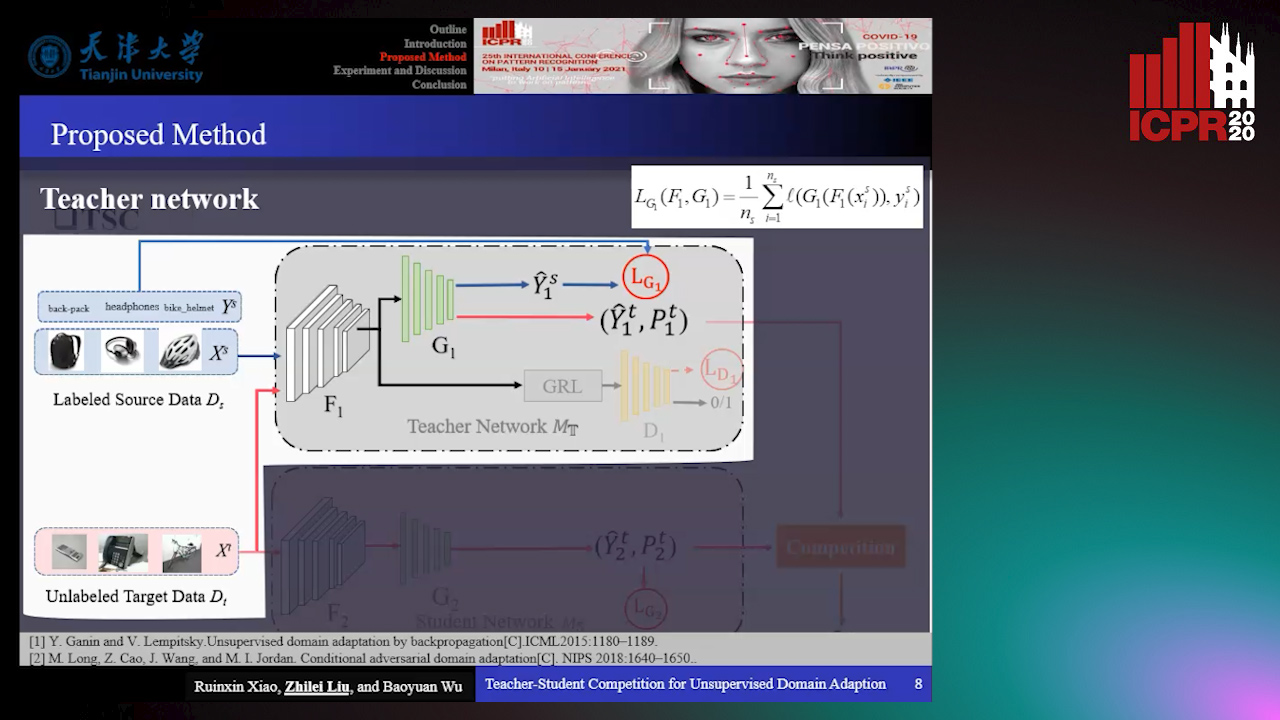
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaption with Teacher-Student Competition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Order Feature Statistical Model for Fine-Grained Visual Categorization
Qingtao Wang, Ke Zhang, Shaoli Huang, Lianbo Zhang, Jin Fan

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Order Feature Statistical Method for Fine-Grained Visual Categorization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Delayed Elastic-Net Approach for Performing Adversarial Attacks
Brais Cancela, Veronica Bolon-Canedo, Amparo Alonso-Betanzos

Auto-TLDR; Robustness of ImageNet Pretrained Models against Adversarial Attacks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Meta Soft Label Generation for Noisy Labels

Auto-TLDR; MSLG: Meta-Learning for Noisy Label Generation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Teacher-Student Training and Triplet Loss for Facial Expression Recognition under Occlusion
Mariana-Iuliana Georgescu, Radu Ionescu

Auto-TLDR; Knowledge Distillation for Facial Expression Recognition under Occlusion
Image Representation Learning by Transformation Regression
Xifeng Guo, Jiyuan Liu, Sihang Zhou, En Zhu, Shihao Dong

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Image Representation Learning using Continuous Parameter Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Beyond Cross-Entropy: Learning Highly Separable Feature Distributions for Robust and Accurate Classification
Arslan Ali, Andrea Migliorati, Tiziano Bianchi, Enrico Magli

Auto-TLDR; Gaussian class-conditional simplex loss for adversarial robust multiclass classifiers
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Verifying the Causes of Adversarial Examples
Honglin Li, Yifei Fan, Frieder Ganz, Tony Yezzi, Payam Barnaghi

Auto-TLDR; Exploring the Causes of Adversarial Examples in Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
P-DIFF: Learning Classifier with Noisy Labels Based on Probability Difference Distributions
Wei Hu, Qihao Zhao, Yangyu Huang, Fan Zhang

Auto-TLDR; P-DIFF: A Simple and Effective Training Paradigm for Deep Neural Network Classifier with Noisy Labels
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Revisiting ImprovedGAN with Metric Learning for Semi-Supervised Learning
Jaewoo Park, Yoon Gyo Jung, Andrew Teoh

Auto-TLDR; Improving ImprovedGAN with Metric Learning for Semi-supervised Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rethinking Experience Replay: A Bag of Tricks for Continual Learning
Pietro Buzzega, Matteo Boschini, Angelo Porrello, Simone Calderara

Auto-TLDR; Experience Replay for Continual Learning: A Practical Approach
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Norm Loss: An Efficient yet Effective Regularization Method for Deep Neural Networks
Theodoros Georgiou, Sebastian Schmitt, Thomas Baeck, Wei Chen, Michael Lew

Auto-TLDR; Weight Soft-Regularization with Oblique Manifold for Convolutional Neural Network Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
IDA-GAN: A Novel Imbalanced Data Augmentation GAN
Auto-TLDR; IDA-GAN: Generative Adversarial Networks for Imbalanced Data Augmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MetaMix: Improved Meta-Learning with Interpolation-based Consistency Regularization
Yangbin Chen, Yun Ma, Tom Ko, Jianping Wang, Qing Li

Auto-TLDR; MetaMix: A Meta-Agnostic Meta-Learning Algorithm for Few-Shot Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rethinking of Deep Models Parameters with Respect to Data Distribution
Shitala Prasad, Dongyun Lin, Yiqun Li, Sheng Dong, Zaw Min Oo

Auto-TLDR; A progressive stepwise training strategy for deep neural networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pretraining Image Encoders without Reconstruction Via Feature Prediction Loss
Gustav Grund Pihlgren, Fredrik Sandin, Marcus Liwicki

Auto-TLDR; Feature Prediction Loss for Autoencoder-based Pretraining of Image Encoders
Exploiting Knowledge Embedded Soft Labels for Image Recognition
Lixian Yuan, Riquan Chen, Hefeng Wu, Tianshui Chen, Wentao Wang, Pei Chen

Auto-TLDR; A Soft Label Vector for Image Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
NeuralFP: Out-Of-Distribution Detection Using Fingerprints of Neural Networks
Wei-Han Lee, Steve Millman, Nirmit Desai, Mudhakar Srivatsa, Changchang Liu
Auto-TLDR; NeuralFP: Detecting Out-of-Distribution Records Using Neural Network Models
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Knowledge Distillation for Action Anticipation Via Label Smoothing
Guglielmo Camporese, Pasquale Coscia, Antonino Furnari, Giovanni Maria Farinella, Lamberto Ballan

Auto-TLDR; A Multi-Modal Framework for Action Anticipation using Long Short-Term Memory Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Probability Guided Maxout
Claudio Ferrari, Stefano Berretti, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Probability Guided Maxout for CNN Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploiting Distilled Learning for Deep Siamese Tracking
Chengxin Liu, Zhiguo Cao, Wei Li, Yang Xiao, Shuaiyuan Du, Angfan Zhu

Auto-TLDR; Distilled Learning Framework for Siamese Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fine-Tuning DARTS for Image Classification
Muhammad Suhaib Tanveer, Umar Karim Khan, Chong Min Kyung
Auto-TLDR; Fine-Tune Neural Architecture Search using Fixed Operations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generalization Comparison of Deep Neural Networks Via Output Sensitivity
Mahsa Forouzesh, Farnood Salehi, Patrick Thiran
Auto-TLDR; Generalization of Deep Neural Networks using Sensitivity
Improving Batch Normalization with Skewness Reduction for Deep Neural Networks
Pak Lun Kevin Ding, Martin Sarah, Baoxin Li
Auto-TLDR; Batch Normalization with Skewness Reduction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adversarially Constrained Interpolation for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Mohamed Azzam, Aurele Tohokantche Gnanha, Hau-San Wong, Si Wu

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Domain Mixup Strategy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar