Probability Guided Maxout
Claudio Ferrari,
Stefano Berretti,
Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Probability Guided Maxout for CNN Training
Similar papers
MaxDropout: Deep Neural Network Regularization Based on Maximum Output Values
Claudio Filipi Gonçalves Santos, Danilo Colombo, Mateus Roder, Joao Paulo Papa

Auto-TLDR; MaxDropout: A Regularizer for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Model Accuracy for Imbalanced Image Classification Tasks by Adding a Final Batch Normalization Layer: An Empirical Study
Veysel Kocaman, Ofer M. Shir, Thomas Baeck
Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Batch Normalization before the Output Layer in Deep Learning for Minority Class Detection in Imbalanced Data Sets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generalization Comparison of Deep Neural Networks Via Output Sensitivity
Mahsa Forouzesh, Farnood Salehi, Patrick Thiran
Auto-TLDR; Generalization of Deep Neural Networks using Sensitivity
Neuron-Based Network Pruning Based on Majority Voting
Ali Alqahtani, Xianghua Xie, Ehab Essa, Mark W. Jones

Auto-TLDR; Large-Scale Neural Network Pruning using Majority Voting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Close Look at Deep Learning with Small Data

Auto-TLDR; Low-Complex Neural Networks for Small Data Conditions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Can Data Placement Be Effective for Neural Networks Classification Tasks? Introducing the Orthogonal Loss
Brais Cancela, Veronica Bolon-Canedo, Amparo Alonso-Betanzos

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Placement for Neural Network Training Loss Functions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Batch Normalization with Skewness Reduction for Deep Neural Networks
Pak Lun Kevin Ding, Martin Sarah, Baoxin Li
Auto-TLDR; Batch Normalization with Skewness Reduction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Uncertainty-Sensitive Activity Recognition: A Reliability Benchmark and the CARING Models
Alina Roitberg, Monica Haurilet, Manuel Martinez, Rainer Stiefelhagen

Auto-TLDR; CARING: Calibrated Action Recognition with Input Guidance
InsideBias: Measuring Bias in Deep Networks and Application to Face Gender Biometrics
Ignacio Serna, Alejandro Peña Almansa, Aythami Morales, Julian Fierrez
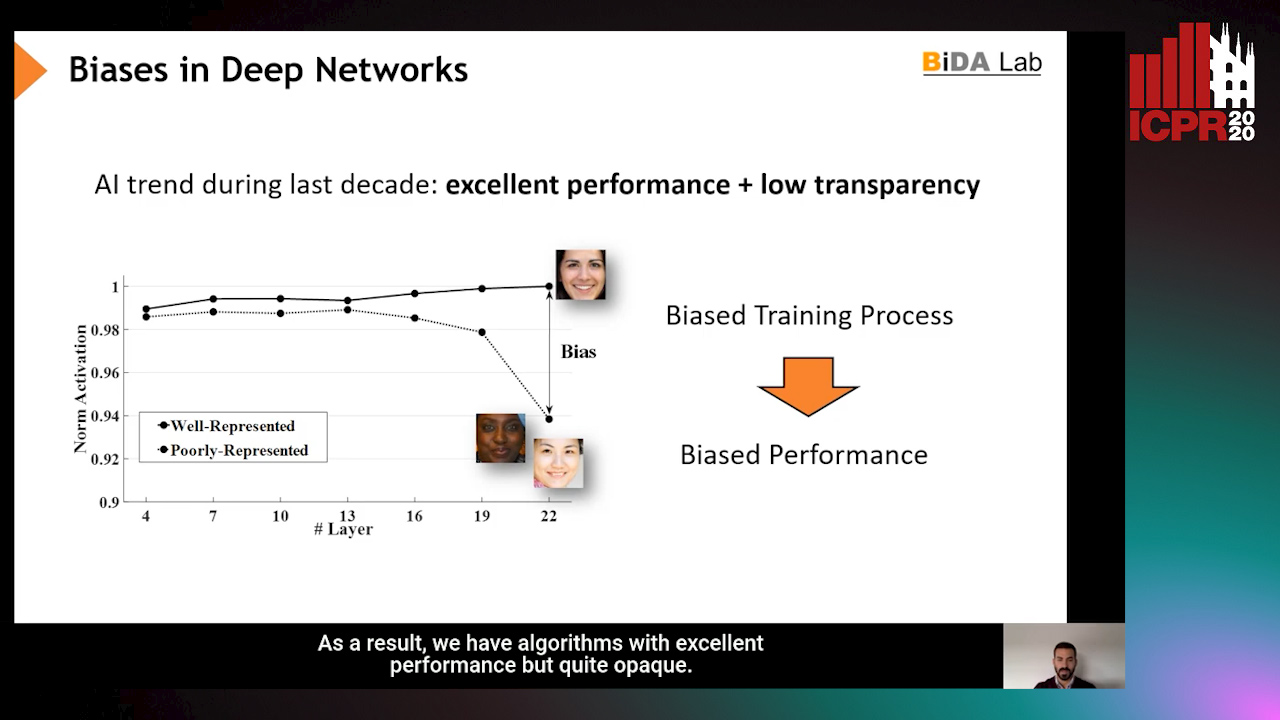
Auto-TLDR; InsideBias: Detecting Bias in Deep Neural Networks from Face Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Confidence Calibration for Deep Renal Biopsy Immunofluorescence Image Classification
Federico Pollastri, Juan Maroñas, Federico Bolelli, Giulia Ligabue, Roberto Paredes, Riccardo Magistroni, Costantino Grana

Auto-TLDR; A Probabilistic Convolutional Neural Network for Immunofluorescence Classification in Renal Biopsy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Verifying the Causes of Adversarial Examples
Honglin Li, Yifei Fan, Frieder Ganz, Tony Yezzi, Payam Barnaghi

Auto-TLDR; Exploring the Causes of Adversarial Examples in Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Iterative Label Improvement: Robust Training by Confidence Based Filtering and Dataset Partitioning
Christian Haase-Schütz, Rainer Stal, Heinz Hertlein, Bernhard Sick

Auto-TLDR; Meta Training and Labelling for Unlabelled Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On the Information of Feature Maps and Pruning of Deep Neural Networks
Mohammadreza Soltani, Suya Wu, Jie Ding, Robert Ravier, Vahid Tarokh

Auto-TLDR; Compressing Deep Neural Models Using Mutual Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock Module for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Junhui Yin, Siqing Zhang, Dongliang Chang, Zhanyu Ma, Jun Guo
Auto-TLDR; Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Contextual Classification Using Self-Supervised Auxiliary Models for Deep Neural Networks
Sebastian Palacio, Philipp Engler, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel

Auto-TLDR; Self-Supervised Autogenous Learning for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Revisiting the Training of Very Deep Neural Networks without Skip Connections
Oyebade Kayode Oyedotun, Abd El Rahman Shabayek, Djamila Aouada, Bjorn Ottersten

Auto-TLDR; Optimization of Very Deep PlainNets without shortcut connections with 'vanishing and exploding units' activations'
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning to Prune in Training via Dynamic Channel Propagation
Shibo Shen, Rongpeng Li, Zhifeng Zhao, Honggang Zhang, Yugeng Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Dynamic Channel Propagation for Neural Network Pruning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Locality-Promoting Representation Learning
Auto-TLDR; Locality-promoting Regularization for Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Uncertainty-Aware Data Augmentation for Food Recognition
Eduardo Aguilar, Bhalaji Nagarajan, Rupali Khatun, Marc Bolaños, Petia Radeva

Auto-TLDR; Data Augmentation for Food Recognition Using Epistemic Uncertainty
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Face Manipulation Detection through Ensemble of CNNs
Nicolo Bonettini, Edoardo Daniele Cannas, Sara Mandelli, Luca Bondi, Paolo Bestagini, Stefano Tubaro

Auto-TLDR; Face Manipulation Detection in Video Sequences Using Convolutional Neural Networks
On-Manifold Adversarial Data Augmentation Improves Uncertainty Calibration
Kanil Patel, William Beluch, Dan Zhang, Michael Pfeiffer, Bin Yang

Auto-TLDR; On-Manifold Adversarial Data Augmentation for Uncertainty Estimation
Beyond Cross-Entropy: Learning Highly Separable Feature Distributions for Robust and Accurate Classification
Arslan Ali, Andrea Migliorati, Tiziano Bianchi, Enrico Magli

Auto-TLDR; Gaussian class-conditional simplex loss for adversarial robust multiclass classifiers
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cam-Softmax for Discriminative Deep Feature Learning
Tamas Suveges, Stephen James Mckenna

Auto-TLDR; Cam-Softmax: A Generalisation of Activations and Softmax for Deep Feature Spaces
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Norm Loss: An Efficient yet Effective Regularization Method for Deep Neural Networks
Theodoros Georgiou, Sebastian Schmitt, Thomas Baeck, Wei Chen, Michael Lew

Auto-TLDR; Weight Soft-Regularization with Oblique Manifold for Convolutional Neural Network Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Noise Injection for Training Stochastic Student Networks from Deterministic Teachers
Yi Xiang Marcus Tan, Yuval Elovici, Alexander Binder

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Stochastic Networks for Adversarial Attacks
Separation of Aleatoric and Epistemic Uncertainty in Deterministic Deep Neural Networks
Denis Huseljic, Bernhard Sick, Marek Herde, Daniel Kottke

Auto-TLDR; AE-DNN: Modeling Uncertainty in Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Trainable Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations in Convolutional Neural Networks
Michele Alberti, Angela Botros, Schuetz Narayan, Rolf Ingold, Marcus Liwicki, Mathias Seuret

Auto-TLDR; Trainable and Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations for Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Is the Meta-Learning Idea Able to Improve the Generalization of Deep Neural Networks on the Standard Supervised Learning?

Auto-TLDR; Meta-learning Based Training of Deep Neural Networks for Few-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Speeding-Up Pruning for Artificial Neural Networks: Introducing Accelerated Iterative Magnitude Pruning
Marco Zullich, Eric Medvet, Felice Andrea Pellegrino, Alessio Ansuini

Auto-TLDR; Iterative Pruning of Artificial Neural Networks with Overparametrization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Building Computationally Efficient and Well-Generalizing Person Re-Identification Models with Metric Learning
Vladislav Sovrasov, Dmitry Sidnev

Auto-TLDR; Cross-Domain Generalization in Person Re-identification using Omni-Scale Network
On the Minimal Recognizable Image Patch
Mark Fonaryov, Michael Lindenbaum

Auto-TLDR; MIRC: A Deep Neural Network for Minimal Recognition on Partially Occluded Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Quasibinary Classifier for Images with Zero and Multiple Labels
Liao Shuai, Efstratios Gavves, Changyong Oh, Cees Snoek

Auto-TLDR; Quasibinary Classifiers for Zero-label and Multi-label Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Sparse Deep Neural Networks Using Efficient Structured Projections on Convex Constraints for Green AI
Michel Barlaud, Frederic Guyard

Auto-TLDR; Constrained Deep Neural Network with Constrained Splitting Projection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Force Banner for the Recognition of Spatial Relations
Robin Deléarde, Camille Kurtz, Laurent Wendling, Philippe Dejean

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Relation Recognition using Force Banners
CQNN: Convolutional Quadratic Neural Networks

Auto-TLDR; Quadratic Neural Network for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploiting Non-Linear Redundancy for Neural Model Compression
Muhammad Ahmed Shah, Raphael Olivier, Bhiksha Raj
Auto-TLDR; Compressing Deep Neural Networks with Linear Dependency
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Convolutional STN for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Akhil Meethal, Marco Pedersoli, Soufiane Belharbi, Eric Granger

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Localization for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
A Joint Representation Learning and Feature Modeling Approach for One-Class Recognition
Pramuditha Perera, Vishal Patel
Auto-TLDR; Combining Generative Features and One-Class Classification for Effective One-class Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On Resource-Efficient Bayesian Network Classifiers and Deep Neural Networks
Wolfgang Roth, Günther Schindler, Holger Fröning, Franz Pernkopf

Auto-TLDR; Quantization-Aware Bayesian Network Classifiers for Small-Scale Scenarios
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Image Representation Learning by Transformation Regression
Xifeng Guo, Jiyuan Liu, Sihang Zhou, En Zhu, Shihao Dong

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Image Representation Learning using Continuous Parameter Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Delayed Elastic-Net Approach for Performing Adversarial Attacks
Brais Cancela, Veronica Bolon-Canedo, Amparo Alonso-Betanzos

Auto-TLDR; Robustness of ImageNet Pretrained Models against Adversarial Attacks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
P-DIFF: Learning Classifier with Noisy Labels Based on Probability Difference Distributions
Wei Hu, Qihao Zhao, Yangyu Huang, Fan Zhang

Auto-TLDR; P-DIFF: A Simple and Effective Training Paradigm for Deep Neural Network Classifier with Noisy Labels
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Bridging the Gap between Natural and Medical Images through Deep Colorization
Lia Morra, Luca Piano, Fabrizio Lamberti, Tatiana Tommasi

Auto-TLDR; Transfer Learning for Diagnosis on X-ray Images Using Color Adaptation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature-Dependent Cross-Connections in Multi-Path Neural Networks
Dumindu Tissera, Kasun Vithanage, Rukshan Wijesinghe, Kumara Kahatapitiya, Subha Fernando, Ranga Rodrigo
Auto-TLDR; Multi-path Networks for Adaptive Feature Extraction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Robust Learning with Different Label Noise Distributions
Diego Ortego, Eric Arazo, Paul Albert, Noel E O'Connor, Kevin Mcguinness

Auto-TLDR; Distribution Robust Pseudo-Labeling with Semi-supervised Learning
Knowledge Distillation for Action Anticipation Via Label Smoothing
Guglielmo Camporese, Pasquale Coscia, Antonino Furnari, Giovanni Maria Farinella, Lamberto Ballan

Auto-TLDR; A Multi-Modal Framework for Action Anticipation using Long Short-Term Memory Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rank-Based Ordinal Classification

Auto-TLDR; Ordinal Classification with Order
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Regularized Flexible Activation Function Combinations for Deep Neural Networks
Renlong Jie, Junbin Gao, Andrey Vasnev, Minh-Ngoc Tran
Auto-TLDR; Flexible Activation in Deep Neural Networks using ReLU and ELUs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar