Revisiting the Training of Very Deep Neural Networks without Skip Connections
Oyebade Kayode Oyedotun,
Abd El Rahman Shabayek,
Djamila Aouada,
Bjorn Ottersten

Auto-TLDR; Optimization of Very Deep PlainNets without shortcut connections with 'vanishing and exploding units' activations'
Similar papers
Improving Batch Normalization with Skewness Reduction for Deep Neural Networks
Pak Lun Kevin Ding, Martin Sarah, Baoxin Li
Auto-TLDR; Batch Normalization with Skewness Reduction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Norm Loss: An Efficient yet Effective Regularization Method for Deep Neural Networks
Theodoros Georgiou, Sebastian Schmitt, Thomas Baeck, Wei Chen, Michael Lew

Auto-TLDR; Weight Soft-Regularization with Oblique Manifold for Convolutional Neural Network Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
WeightAlign: Normalizing Activations by Weight Alignment
Xiangwei Shi, Yunqiang Li, Xin Liu, Jan Van Gemert

Auto-TLDR; WeightAlign: Normalization of Activations without Sample Statistics
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generalization Comparison of Deep Neural Networks Via Output Sensitivity
Mahsa Forouzesh, Farnood Salehi, Patrick Thiran
Auto-TLDR; Generalization of Deep Neural Networks using Sensitivity
MaxDropout: Deep Neural Network Regularization Based on Maximum Output Values
Claudio Filipi Gonçalves Santos, Danilo Colombo, Mateus Roder, Joao Paulo Papa

Auto-TLDR; MaxDropout: A Regularizer for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improved Residual Networks for Image and Video Recognition
Ionut Cosmin Duta, Li Liu, Fan Zhu, Ling Shao
Auto-TLDR; Residual Networks for Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention As Activation
Yimian Dai, Stefan Oehmcke, Fabian Gieseke, Yiquan Wu, Kobus Barnard

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Activation Units for Convolutional Networks
On the Information of Feature Maps and Pruning of Deep Neural Networks
Mohammadreza Soltani, Suya Wu, Jie Ding, Robert Ravier, Vahid Tarokh

Auto-TLDR; Compressing Deep Neural Models Using Mutual Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On Resource-Efficient Bayesian Network Classifiers and Deep Neural Networks
Wolfgang Roth, Günther Schindler, Holger Fröning, Franz Pernkopf

Auto-TLDR; Quantization-Aware Bayesian Network Classifiers for Small-Scale Scenarios
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Model Accuracy for Imbalanced Image Classification Tasks by Adding a Final Batch Normalization Layer: An Empirical Study
Veysel Kocaman, Ofer M. Shir, Thomas Baeck
Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Batch Normalization before the Output Layer in Deep Learning for Minority Class Detection in Imbalanced Data Sets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Filtered Batch Normalization
András Horváth, Jalal Al-Afandi

Auto-TLDR; Batch Normalization with Out-of-Distribution Activations in Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RNN Training along Locally Optimal Trajectories via Frank-Wolfe Algorithm
Yun Yue, Ming Li, Venkatesh Saligrama, Ziming Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Frank-Wolfe Algorithm for Efficient Training of RNNs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Close Look at Deep Learning with Small Data

Auto-TLDR; Low-Complex Neural Networks for Small Data Conditions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CQNN: Convolutional Quadratic Neural Networks

Auto-TLDR; Quadratic Neural Network for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Is the Meta-Learning Idea Able to Improve the Generalization of Deep Neural Networks on the Standard Supervised Learning?

Auto-TLDR; Meta-learning Based Training of Deep Neural Networks for Few-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploiting Non-Linear Redundancy for Neural Model Compression
Muhammad Ahmed Shah, Raphael Olivier, Bhiksha Raj
Auto-TLDR; Compressing Deep Neural Networks with Linear Dependency
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Slimming ResNet by Slimming Shortcut
Donggyu Joo, Doyeon Kim, Junmo Kim

Auto-TLDR; SSPruning: Slimming Shortcut Pruning on ResNet Based Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Sparse Deep Neural Networks Using Efficient Structured Projections on Convex Constraints for Green AI
Michel Barlaud, Frederic Guyard

Auto-TLDR; Constrained Deep Neural Network with Constrained Splitting Projection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Stable Deep Predictive Coding Networks with Weight Norm Supervision

Auto-TLDR; Stability of Predictive Coding Network with Weight Norm Supervision
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Quaternion Capsule Networks
Barış Özcan, Furkan Kınlı, Mustafa Furkan Kirac

Auto-TLDR; Quaternion Capsule Networks for Object Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Operation and Topology Aware Fast Differentiable Architecture Search
Shahid Siddiqui, Christos Kyrkou, Theocharis Theocharides

Auto-TLDR; EDARTS: Efficient Differentiable Architecture Search with Efficient Optimization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Probability Guided Maxout
Claudio Ferrari, Stefano Berretti, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Probability Guided Maxout for CNN Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature-Dependent Cross-Connections in Multi-Path Neural Networks
Dumindu Tissera, Kasun Vithanage, Rukshan Wijesinghe, Kumara Kahatapitiya, Subha Fernando, Ranga Rodrigo
Auto-TLDR; Multi-path Networks for Adaptive Feature Extraction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Neuron-Based Network Pruning Based on Majority Voting
Ali Alqahtani, Xianghua Xie, Ehab Essa, Mark W. Jones

Auto-TLDR; Large-Scale Neural Network Pruning using Majority Voting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Resource-efficient DNNs for Keyword Spotting using Neural Architecture Search and Quantization
David Peter, Wolfgang Roth, Franz Pernkopf

Auto-TLDR; Neural Architecture Search for Keyword Spotting in Limited Resource Environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Trainable Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations in Convolutional Neural Networks
Michele Alberti, Angela Botros, Schuetz Narayan, Rolf Ingold, Marcus Liwicki, Mathias Seuret

Auto-TLDR; Trainable and Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations for Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
From Early Biological Models to CNNs: Do They Look Where Humans Look?
Marinella Iole Cadoni, Andrea Lagorio, Enrico Grosso, Jia Huei Tan, Chee Seng Chan

Auto-TLDR; Comparing Neural Networks to Human Fixations for Semantic Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ResNet-Like Architecture with Low Hardware Requirements
Elena Limonova, Daniil Alfonso, Dmitry Nikolaev, Vladimir V. Arlazarov

Auto-TLDR; BM-ResNet: Bipolar Morphological ResNet for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Can Data Placement Be Effective for Neural Networks Classification Tasks? Introducing the Orthogonal Loss
Brais Cancela, Veronica Bolon-Canedo, Amparo Alonso-Betanzos

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Placement for Neural Network Training Loss Functions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fine-Tuning DARTS for Image Classification
Muhammad Suhaib Tanveer, Umar Karim Khan, Chong Min Kyung
Auto-TLDR; Fine-Tune Neural Architecture Search using Fixed Operations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Contextual Classification Using Self-Supervised Auxiliary Models for Deep Neural Networks
Sebastian Palacio, Philipp Engler, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel

Auto-TLDR; Self-Supervised Autogenous Learning for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Noise Injection for Training Stochastic Student Networks from Deterministic Teachers
Yi Xiang Marcus Tan, Yuval Elovici, Alexander Binder

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Stochastic Networks for Adversarial Attacks
Efficient Super Resolution by Recursive Aggregation
Zhengxiong Luo Zhengxiong Luo, Yan Huang, Shang Li, Liang Wang, Tieniu Tan

Auto-TLDR; Recursive Aggregation Network for Efficient Deep Super Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
How Does DCNN Make Decisions?
Yi Lin, Namin Wang, Xiaoqing Ma, Ziwei Li, Gang Bai

Auto-TLDR; Exploring Deep Convolutional Neural Network's Decision-Making Interpretability
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
InsideBias: Measuring Bias in Deep Networks and Application to Face Gender Biometrics
Ignacio Serna, Alejandro Peña Almansa, Aythami Morales, Julian Fierrez
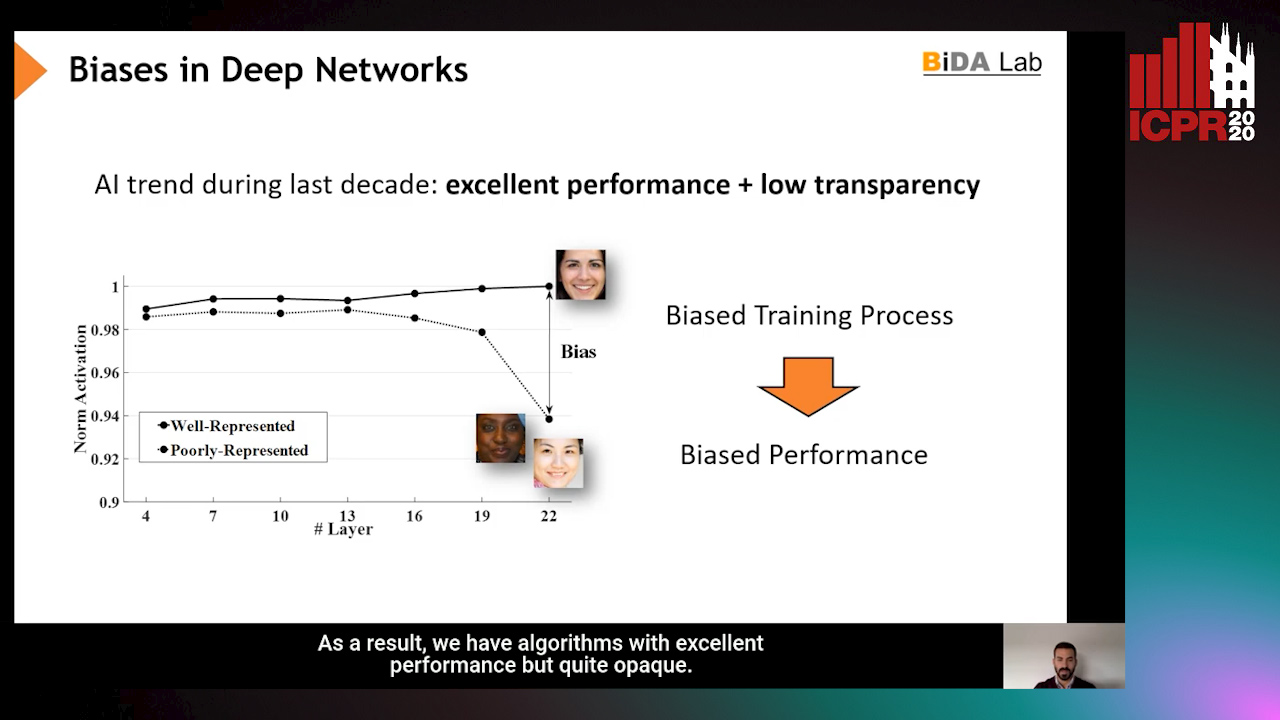
Auto-TLDR; InsideBias: Detecting Bias in Deep Neural Networks from Face Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Regularized Flexible Activation Function Combinations for Deep Neural Networks
Renlong Jie, Junbin Gao, Andrey Vasnev, Minh-Ngoc Tran
Auto-TLDR; Flexible Activation in Deep Neural Networks using ReLU and ELUs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ESResNet: Environmental Sound Classification Based on Visual Domain Models
Andrey Guzhov, Federico Raue, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel
Auto-TLDR; Environmental Sound Classification with Short-Time Fourier Transform Spectrograms
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamic Multi-Path Neural Network
Yingcheng Su, Yichao Wu, Ken Chen, Ding Liang, Xiaolin Hu

Auto-TLDR; Dynamic Multi-path Neural Network
P-DIFF: Learning Classifier with Noisy Labels Based on Probability Difference Distributions
Wei Hu, Qihao Zhao, Yangyu Huang, Fan Zhang

Auto-TLDR; P-DIFF: A Simple and Effective Training Paradigm for Deep Neural Network Classifier with Noisy Labels
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning to Prune in Training via Dynamic Channel Propagation
Shibo Shen, Rongpeng Li, Zhifeng Zhao, Honggang Zhang, Yugeng Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Dynamic Channel Propagation for Neural Network Pruning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rethinking of Deep Models Parameters with Respect to Data Distribution
Shitala Prasad, Dongyun Lin, Yiqun Li, Sheng Dong, Zaw Min Oo

Auto-TLDR; A progressive stepwise training strategy for deep neural networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Softer Pruning, Incremental Regularization
Linhang Cai, Zhulin An, Yongjun Xu

Auto-TLDR; Asymptotic SofteR Filter Pruning for Deep Neural Network Pruning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FatNet: A Feature-Attentive Network for 3D Point Cloud Processing
Chaitanya Kaul, Nick Pears, Suresh Manandhar

Auto-TLDR; Feature-Attentive Neural Networks for Point Cloud Classification and Segmentation
Second-Order Attention Guided Convolutional Activations for Visual Recognition
Shannan Chen, Qian Wang, Qiule Sun, Bin Liu, Jianxin Zhang, Qiang Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Second-order Attention Guided Network for Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Color, Edge, and Pixel-Wise Explanation of Predictions Based onInterpretable Neural Network Model

Auto-TLDR; Explainable Deep Neural Network with Edge Detecting Filters
Not All Domains Are Equally Complex: Adaptive Multi-Domain Learning
Ali Senhaji, Jenni Karoliina Raitoharju, Moncef Gabbouj, Alexandros Iosifidis

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Parameterization for Multi-Domain Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Robust Learning with Different Label Noise Distributions
Diego Ortego, Eric Arazo, Paul Albert, Noel E O'Connor, Kevin Mcguinness

Auto-TLDR; Distribution Robust Pseudo-Labeling with Semi-supervised Learning
On the Global Self-attention Mechanism for Graph Convolutional Networks
Auto-TLDR; Global Self-Attention Mechanism for Graph Convolutional Networks