Confidence Calibration for Deep Renal Biopsy Immunofluorescence Image Classification
Federico Pollastri,
Juan Maroñas,
Federico Bolelli,
Giulia Ligabue,
Roberto Paredes,
Riccardo Magistroni,
Costantino Grana

Auto-TLDR; A Probabilistic Convolutional Neural Network for Immunofluorescence Classification in Renal Biopsy
Similar papers
Supporting Skin Lesion Diagnosis with Content-Based Image Retrieval
Stefano Allegretti, Federico Bolelli, Federico Pollastri, Sabrina Longhitano, Giovanni Pellacani, Costantino Grana

Auto-TLDR; Skin Images Retrieval Using Convolutional Neural Networks for Skin Lesion Classification and Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Systematic Investigation on Deep Architectures for Automatic Skin Lesions Classification
Pierluigi Carcagni, Marco Leo, Andrea Cuna, Giuseppe Celeste, Cosimo Distante

Auto-TLDR; RegNet: Deep Investigation of Convolutional Neural Networks for Automatic Classification of Skin Lesions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Uncertainty-Sensitive Activity Recognition: A Reliability Benchmark and the CARING Models
Alina Roitberg, Monica Haurilet, Manuel Martinez, Rainer Stiefelhagen

Auto-TLDR; CARING: Calibrated Action Recognition with Input Guidance
On-Manifold Adversarial Data Augmentation Improves Uncertainty Calibration
Kanil Patel, William Beluch, Dan Zhang, Michael Pfeiffer, Bin Yang

Auto-TLDR; On-Manifold Adversarial Data Augmentation for Uncertainty Estimation
A Systematic Investigation on End-To-End Deep Recognition of Grocery Products in the Wild
Marco Leo, Pierluigi Carcagni, Cosimo Distante

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Recognition of Products on grocery shelf images using Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Investigating and Exploiting Image Resolution for Transfer Learning-Based Skin Lesion Classification
Amirreza Mahbod, Gerald Schaefer, Chunliang Wang, Rupert Ecker, Georg Dorffner, Isabella Ellinger

Auto-TLDR; Fine-tuned Neural Networks for Skin Lesion Classification Using Dermoscopic Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Comparison of Neural Network Approaches for Melanoma Classification
Maria Frasca, Michele Nappi, Michele Risi, Genoveffa Tortora, Alessia Auriemma Citarella
Auto-TLDR; Classification of Melanoma Using Deep Neural Network Methodologies
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Model Accuracy for Imbalanced Image Classification Tasks by Adding a Final Batch Normalization Layer: An Empirical Study
Veysel Kocaman, Ofer M. Shir, Thomas Baeck
Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Batch Normalization before the Output Layer in Deep Learning for Minority Class Detection in Imbalanced Data Sets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Bridging the Gap between Natural and Medical Images through Deep Colorization
Lia Morra, Luca Piano, Fabrizio Lamberti, Tatiana Tommasi

Auto-TLDR; Transfer Learning for Diagnosis on X-ray Images Using Color Adaptation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Planar 3D Transfer Learning for End to End Unimodal MRI Unbalanced Data Segmentation
Martin Kolarik, Radim Burget, Carlos M. Travieso-Gonzalez, Jan Kocica

Auto-TLDR; Planar 3D Res-U-Net Network for Unbalanced 3D Image Segmentation using Fluid Attenuation Inversion Recover
Quasibinary Classifier for Images with Zero and Multiple Labels
Liao Shuai, Efstratios Gavves, Changyong Oh, Cees Snoek

Auto-TLDR; Quasibinary Classifiers for Zero-label and Multi-label Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fine-Tuning Convolutional Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Guide and Benchmark Analysis for Glaucoma Screening
Amed Mvoulana, Rostom Kachouri, Mohamed Akil
Auto-TLDR; Fine-tuning Convolutional Neural Networks for Glaucoma Screening
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Attribute Learning with Highly Imbalanced Data
Lady Viviana Beltran Beltran, Mickaël Coustaty, Nicholas Journet, Juan C. Caicedo, Antoine Doucet
Auto-TLDR; Data Imbalance in Multi-Attribute Deep Learning Models: Adaptation to face each one of the problems derived from imbalance
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learn to Segment Retinal Lesions and Beyond
Qijie Wei, Xirong Li, Weihong Yu, Xiao Zhang, Yongpeng Zhang, Bojie Hu, Bin Mo, Di Gong, Ning Chen, Dayong Ding, Youxin Chen

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Lesion Segmentation and Disease Classification for Diabetic Retinopathy Grading
Deep Learning in the Ultrasound Evaluation of Neonatal Respiratory Status
Michela Gravina, Diego Gragnaniello, Giovanni Poggi, Luisa Verdoliva, Carlo Sansone, Iuri Corsini, Carlo Dani, Fabio Meneghin, Gianluca Lista, Salvatore Aversa, Migliaro Migliaro, Raimondi Francesco

Auto-TLDR; Lung Ultrasound Imaging with Deep Learning Networks and Training Strategies: An Analysis and Adaptation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Semantic Segmentation of Structural Elements related to the Spinal Cord in the Lumbar Region by Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Jhon Jairo Sáenz Gamboa, Maria De La Iglesia-Vaya, Jon Ander Gómez

Auto-TLDR; Semantic Segmentation of Lumbar Spine Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Modeling the Distribution of Normal Data in Pre-Trained Deep Features for Anomaly Detection
Oliver Rippel, Patrick Mertens, Dorit Merhof

Auto-TLDR; Deep Feature Representations for Anomaly Detection in Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Trainable Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations in Convolutional Neural Networks
Michele Alberti, Angela Botros, Schuetz Narayan, Rolf Ingold, Marcus Liwicki, Mathias Seuret

Auto-TLDR; Trainable and Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations for Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Robust Learning with Different Label Noise Distributions
Diego Ortego, Eric Arazo, Paul Albert, Noel E O'Connor, Kevin Mcguinness

Auto-TLDR; Distribution Robust Pseudo-Labeling with Semi-supervised Learning
Attack-Agnostic Adversarial Detection on Medical Data Using Explainable Machine Learning
Matthew Watson, Noura Al Moubayed

Auto-TLDR; Explainability-based Detection of Adversarial Samples on EHR and Chest X-Ray Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Separation of Aleatoric and Epistemic Uncertainty in Deterministic Deep Neural Networks
Denis Huseljic, Bernhard Sick, Marek Herde, Daniel Kottke

Auto-TLDR; AE-DNN: Modeling Uncertainty in Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dealing with Scarce Labelled Data: Semi-Supervised Deep Learning with Mix Match for Covid-19 Detection Using Chest X-Ray Images
Saúl Calderón Ramirez, Raghvendra Giri, Shengxiang Yang, Armaghan Moemeni, Mario Umaña, David Elizondo, Jordina Torrents-Barrena, Miguel A. Molina-Cabello

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Deep Learning for Covid-19 Detection using Chest X-rays
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generalization Comparison of Deep Neural Networks Via Output Sensitivity
Mahsa Forouzesh, Farnood Salehi, Patrick Thiran
Auto-TLDR; Generalization of Deep Neural Networks using Sensitivity
Dual Stream Network with Selective Optimization for Skin Disease Recognition in Consumer Grade Images
Krishnam Gupta, Jaiprasad Rampure, Monu Krishnan, Ajit Narayanan, Nikhil Narayan
Auto-TLDR; A Deep Network Architecture for Skin Disease Localisation and Classification on Consumer Grade Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Probability Guided Maxout
Claudio Ferrari, Stefano Berretti, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Probability Guided Maxout for CNN Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The Color Out of Space: Learning Self-Supervised Representations for Earth Observation Imagery
Stefano Vincenzi, Angelo Porrello, Pietro Buzzega, Marco Cipriano, Pietro Fronte, Roberto Cuccu, Carla Ippoliti, Annamaria Conte, Simone Calderara

Auto-TLDR; Satellite Image Representation Learning for Remote Sensing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Skin Lesion Classification Using Weakly-Supervised Fine-Grained Method
Xi Xue, Sei-Ichiro Kamata, Daming Luo

Auto-TLDR; Different Region proposal module for skin lesion classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Learning-Based Type Identification of Volumetric MRI Sequences
Jean Pablo De Mello, Thiago Paixão, Rodrigo Berriel, Mauricio Reyes, Alberto F. De Souza, Claudine Badue, Thiago Oliveira-Santos

Auto-TLDR; Deep Learning for Brain MRI Sequences Identification Using Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Close Look at Deep Learning with Small Data

Auto-TLDR; Low-Complex Neural Networks for Small Data Conditions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Can Data Placement Be Effective for Neural Networks Classification Tasks? Introducing the Orthogonal Loss
Brais Cancela, Veronica Bolon-Canedo, Amparo Alonso-Betanzos

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Placement for Neural Network Training Loss Functions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Stochastic Label Refinery: Toward Better Target Label Distribution
Xi Fang, Jiancheng Yang, Bingbing Ni

Auto-TLDR; Stochastic Label Refinery for Deep Supervised Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Tackling Multi-Label Imbalances in Remote Sensing Imagery
Dominik Koßmann, Thorsten Wilhelm, Gernot Fink

Auto-TLDR; Class imbalance in land cover datasets using attribute encoding schemes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Convolutional Embedding for Digitized Painting Clustering
Giovanna Castellano, Gennaro Vessio

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Convolutional Embedding Model for Clustering Artworks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MaxDropout: Deep Neural Network Regularization Based on Maximum Output Values
Claudio Filipi Gonçalves Santos, Danilo Colombo, Mateus Roder, Joao Paulo Papa

Auto-TLDR; MaxDropout: A Regularizer for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Face Manipulation Detection through Ensemble of CNNs
Nicolo Bonettini, Edoardo Daniele Cannas, Sara Mandelli, Luca Bondi, Paolo Bestagini, Stefano Tubaro

Auto-TLDR; Face Manipulation Detection in Video Sequences Using Convolutional Neural Networks
A Delayed Elastic-Net Approach for Performing Adversarial Attacks
Brais Cancela, Veronica Bolon-Canedo, Amparo Alonso-Betanzos

Auto-TLDR; Robustness of ImageNet Pretrained Models against Adversarial Attacks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Merged 1D-2D Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Nerve Detection in Ultrasound Images
Mohammad Alkhatib, Adel Hafiane, Pierre Vieyres

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Neural Network for Deep Neural Networks to Detect Median Nerve in Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Multi-Task Contextual Atrous Residual Network for Brain Tumor Detection & Segmentation
Ngan Le, Kashu Yamazaki, Quach Kha Gia, Thanh-Dat Truong, Marios Savvides

Auto-TLDR; Contextual Brain Tumor Segmentation Using 3D atrous Residual Networks and Cascaded Structures
Iterative Label Improvement: Robust Training by Confidence Based Filtering and Dataset Partitioning
Christian Haase-Schütz, Rainer Stal, Heinz Hertlein, Bernhard Sick

Auto-TLDR; Meta Training and Labelling for Unlabelled Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Tuberculosis Detection Using Chest X-Ray Analysis with Position Enhanced Structural Information
Hermann Jepdjio Nkouanga, Szilard Vajda
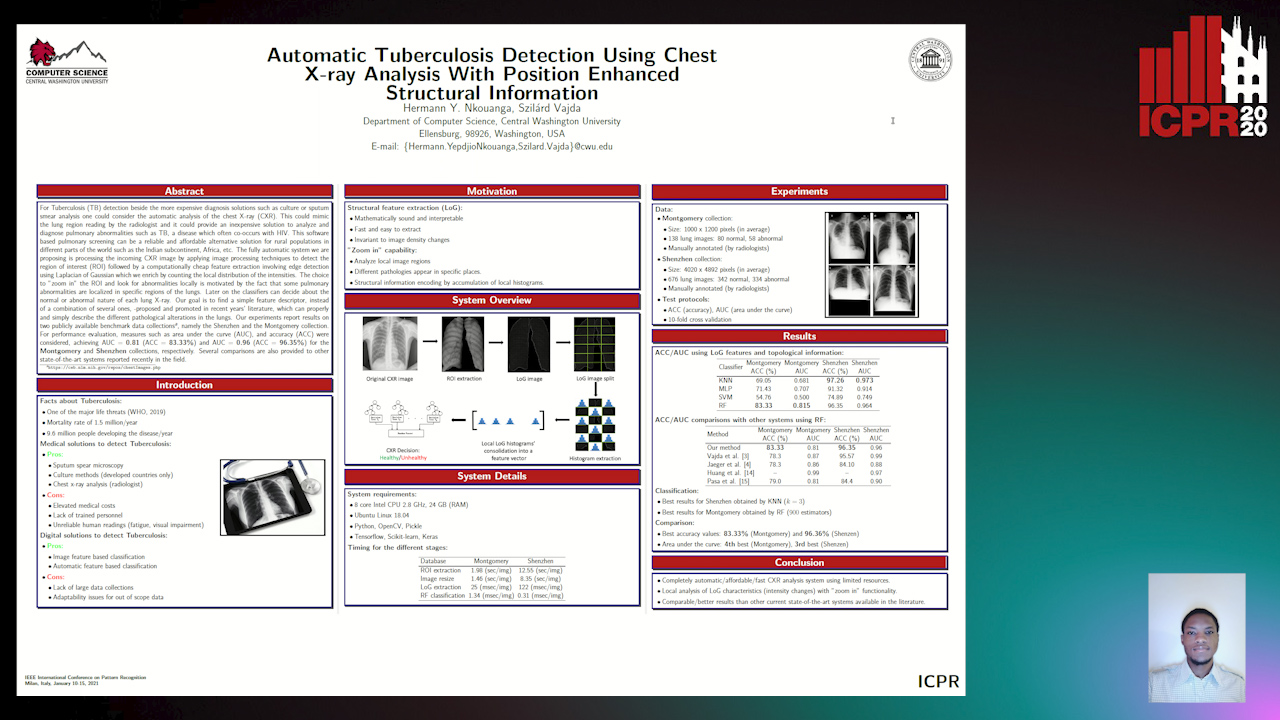
Auto-TLDR; Automatic Chest X-ray Screening for Tuberculosis in Rural Population using Localized Region on Interest
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
End-To-End Multi-Task Learning for Lung Nodule Segmentation and Diagnosis
Wei Chen, Qiuli Wang, Dan Yang, Xiaohong Zhang, Chen Liu, Yucong Li
Auto-TLDR; A novel multi-task framework for lung nodule diagnosis based on deep learning and medical features
Automatic Classification of Human Granulosa Cells in Assisted Reproductive Technology Using Vibrational Spectroscopy Imaging
Marina Paolanti, Emanuele Frontoni, Giorgia Gioacchini, Giorgini Elisabetta, Notarstefano Valentina, Zacà Carlotta, Carnevali Oliana, Andrea Borini, Marco Mameli

Auto-TLDR; Predicting Oocyte Quality in Assisted Reproductive Technology Using Machine Learning Techniques
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semi-Supervised Generative Adversarial Networks with a Pair of Complementary Generators for Retinopathy Screening
Yingpeng Xie, Qiwei Wan, Hai Xie, En-Leng Tan, Yanwu Xu, Baiying Lei

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Networks for Retinopathy Diagnosis via Fundus Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Verifying the Causes of Adversarial Examples
Honglin Li, Yifei Fan, Frieder Ganz, Tony Yezzi, Payam Barnaghi

Auto-TLDR; Exploring the Causes of Adversarial Examples in Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Contextual Classification Using Self-Supervised Auxiliary Models for Deep Neural Networks
Sebastian Palacio, Philipp Engler, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel

Auto-TLDR; Self-Supervised Autogenous Learning for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Estimation of Abundance and Distribution of SaltMarsh Plants from Images Using Deep Learning
Jayant Parashar, Suchendra Bhandarkar, Jacob Simon, Brian Hopkinson, Steven Pennings
Auto-TLDR; CNN-based approaches to automated plant identification and localization in salt marsh images
The eXPose Approach to Crosslier Detection
Antonio Barata, Frank Takes, Hendrik Van Den Herik, Cor Veenman

Auto-TLDR; EXPose: Crosslier Detection Based on Supervised Category Modeling
Abstract Slides Poster Similar