TAAN: Task-Aware Attention Network for Few-Shot Classification

Auto-TLDR; TAAN: Task-Aware Attention Network for Few-Shot Classification
Similar papers
Meta Generalized Network for Few-Shot Classification
Wei Wu, Shanmin Pang, Zhiqiang Tian, Yaochen Li

Auto-TLDR; Meta Generalized Network for Few-Shot Classification
Complementing Representation Deficiency in Few-Shot Image Classification: A Meta-Learning Approach
Xian Zhong, Cheng Gu, Wenxin Huang, Lin Li, Shuqin Chen, Chia-Wen Lin

Auto-TLDR; Meta-learning with Complementary Representations Network for Few-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MetaMix: Improved Meta-Learning with Interpolation-based Consistency Regularization
Yangbin Chen, Yun Ma, Tom Ko, Jianping Wang, Qing Li

Auto-TLDR; MetaMix: A Meta-Agnostic Meta-Learning Algorithm for Few-Shot Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Augmented Bi-Path Network for Few-Shot Learning
Baoming Yan, Chen Zhou, Bo Zhao, Kan Guo, Yang Jiang, Xiaobo Li, Zhang Ming, Yizhou Wang

Auto-TLDR; Augmented Bi-path Network for Few-shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Explanation-Guided Training for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Classification
Jiamei Sun, Sebastian Lapuschkin, Wojciech Samek, Yunqing Zhao, Ngai-Man Cheung, Alexander Binder

Auto-TLDR; Explaination-Guided Training for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Propagation for Few-Shot Learning
Yann Lifchitz, Yannis Avrithis, Sylvaine Picard

Auto-TLDR; Local Propagation for Few-Shot Inference
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Few-Shot Few-Shot Learning and the Role of Spatial Attention
Yann Lifchitz, Yannis Avrithis, Sylvaine Picard

Auto-TLDR; Few-shot Learning with Pre-trained Classifier on Large-Scale Datasets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Graph-Based Interpolation of Feature Vectors for Accurate Few-Shot Classification
Yuqing Hu, Vincent Gripon, Stéphane Pateux

Auto-TLDR; Transductive Learning for Few-Shot Classification using Graph Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Few-Shot Learning Based on Metric Learning Using Class Augmentation
Susumu Matsumi, Keiichi Yamada

Auto-TLDR; Metric Learning for Few-shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multiscale Attention-Based Prototypical Network for Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Yifei Zhang, Desire Sidibe, Olivier Morel, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; Few-shot Semantic Segmentation with Multiscale Feature Attention
Directed Variational Cross-encoder Network for Few-Shot Multi-image Co-segmentation
Sayan Banerjee, Divakar Bhat S, Subhasis Chaudhuri, Rajbabu Velmurugan
Auto-TLDR; Directed Variational Inference Cross Encoder for Class Agnostic Co-Segmentation of Multiple Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Self-Supervised GAN for Unsupervised Few-Shot Object Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Few-Shot Object Recognition with a Triplet GAN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
IFSM: An Iterative Feature Selection Mechanism for Few-Shot Image Classification
Chunhao Cai, Minglei Yuan, Tong Lu

Auto-TLDR; Iterative Feature Selection Mechanism for Few-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self and Channel Attention Network for Person Re-Identification
Asad Munir, Niki Martinel, Christian Micheloni

Auto-TLDR; SCAN: Self and Channel Attention Network for Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
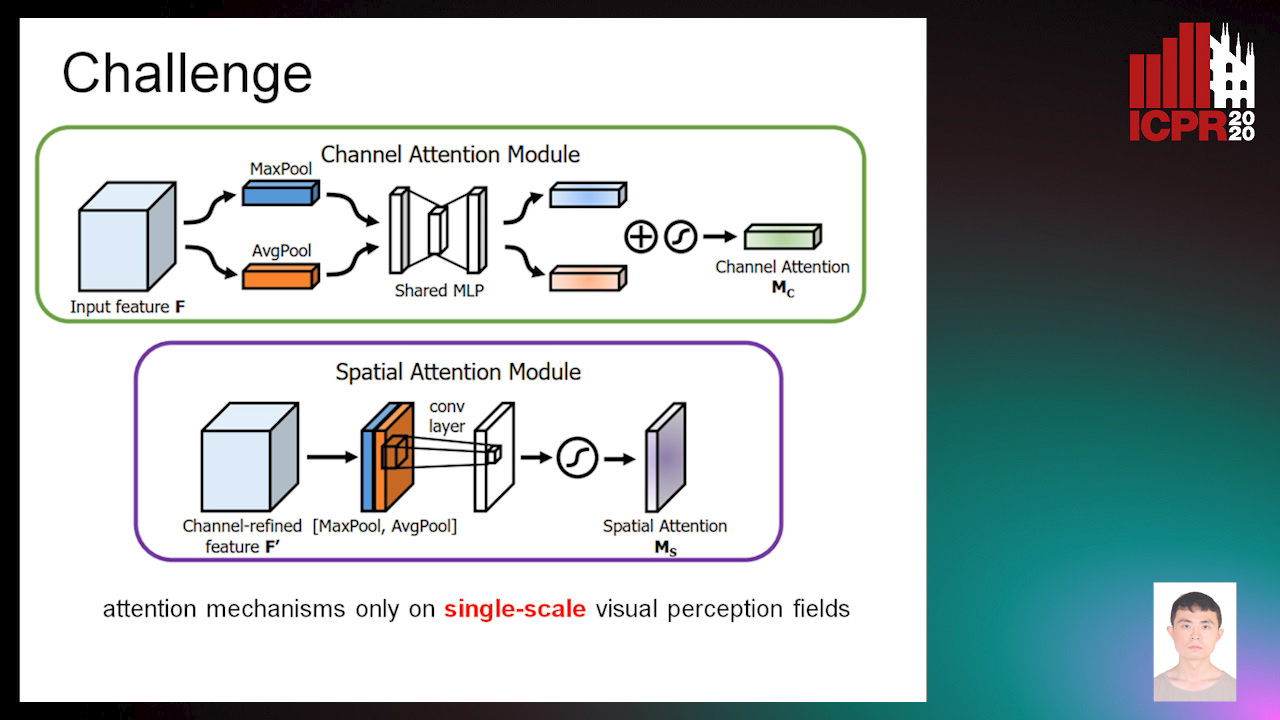
Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock Module for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Junhui Yin, Siqing Zhang, Dongliang Chang, Zhanyu Ma, Jun Guo
Auto-TLDR; Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Incorporating Depth Information into Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Yifei Zhang, Desire Sidibe, Olivier Morel, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; RDNet: A Deep Neural Network for Few-shot Segmentation Using Depth Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose-Robust Face Recognition by Deep Meta Capsule Network-Based Equivariant Embedding
Fangyu Wu, Jeremy Simon Smith, Wenjin Lu, Bailing Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Deep Meta Capsule Network-based Equivariant Embedding Model for Pose-Robust Face Recognition
Aggregating Object Features Based on Attention Weights for Fine-Grained Image Retrieval
Hongli Lin, Yongqi Song, Zixuan Zeng, Weisheng Wang

Auto-TLDR; DSAW: Unsupervised Dual-selection for Fine-Grained Image Retrieval
Free-Form Image Inpainting Via Contrastive Attention Network
Xin Ma, Xiaoqiang Zhou, Huaibo Huang, Zhenhua Chai, Xiaolin Wei, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Siamese inference for image inpainting
Global Context-Based Network with Transformer for Image2latex
Nuo Pang, Chun Yang, Xiaobin Zhu, Jixuan Li, Xu-Cheng Yin

Auto-TLDR; Image2latex with Global Context block and Transformer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ACRM: Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix-NMS for Metallic Surface Defect Detection
Junting Fang, Xiaoyang Tan, Yuhui Wang

Auto-TLDR; Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix Non-Maximum Suppression for Robust Metal Defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
VTT: Long-Term Visual Tracking with Transformers
Tianling Bian, Yang Hua, Tao Song, Zhengui Xue, Ruhui Ma, Neil Robertson, Haibing Guan

Auto-TLDR; Visual Tracking Transformer with transformers for long-term visual tracking
Attentive Part-Aware Networks for Partial Person Re-Identification
Lijuan Huo, Chunfeng Song, Zhengyi Liu, Zhaoxiang Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Part-Aware Learning for Partial Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context Matters: Self-Attention for Sign Language Recognition
Fares Ben Slimane, Mohamed Bouguessa

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Network for Continuous Sign Language Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context-Aware Residual Module for Image Classification
Auto-TLDR; Context-Aware Residual Module for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boundary-Aware Graph Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Hanzhe Hu, Jinshi Cui, Jinshi Hongbin Zha
Auto-TLDR; Boundary-Aware Graph Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Order Feature Statistical Model for Fine-Grained Visual Categorization
Qingtao Wang, Ke Zhang, Shaoli Huang, Lianbo Zhang, Jin Fan

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Order Feature Statistical Method for Fine-Grained Visual Categorization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Prototype-Based Generalized Zero-Shot Learning Framework for Hand Gesture Recognition
Jinting Wu, Yujia Zhang, Xiao-Guang Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Generalized Zero-Shot Learning for Hand Gesture Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
VSB^2-Net: Visual-Semantic Bi-Branch Network for Zero-Shot Hashing
Xin Li, Xiangfeng Wang, Bo Jin, Wenjie Zhang, Jun Wang, Hongyuan Zha
Auto-TLDR; VSB^2-Net: inductive zero-shot hashing for image retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention Pyramid Module for Scene Recognition
Zhinan Qiao, Xiaohui Yuan, Chengyuan Zhuang, Abolfazl Meyarian

Auto-TLDR; Attention Pyramid Module for Multi-Scale Scene Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Task-based Focal Loss for Adversarially Robust Meta-Learning
Yufan Hou, Lixin Zou, Weidong Liu

Auto-TLDR; Task-based Adversarial Focal Loss for Few-shot Meta-Learner
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Is the Meta-Learning Idea Able to Improve the Generalization of Deep Neural Networks on the Standard Supervised Learning?

Auto-TLDR; Meta-learning Based Training of Deep Neural Networks for Few-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Large-Scale Historical Watermark Recognition: Dataset and a New Consistency-Based Approach
Xi Shen, Ilaria Pastrolin, Oumayma Bounou, Spyros Gidaris, Marc Smith, Olivier Poncet, Mathieu Aubry

Auto-TLDR; Historical Watermark Recognition with Fine-Grained Cross-Domain One-Shot Instance Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Progressive Learning Algorithm for Efficient Person Re-Identification
Zhen Li, Hanyang Shao, Liang Niu, Nian Xue

Auto-TLDR; Progressive Learning Algorithm for Large-Scale Person Re-Identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Global-Local Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation in Aerial Images
Minglong Li, Lianlei Shan, Weiqiang Wang

Auto-TLDR; GLANet: Global-Local Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MANet: Multimodal Attention Network Based Point-View Fusion for 3D Shape Recognition
Yaxin Zhao, Jichao Jiao, Ning Li
Auto-TLDR; Fusion Network for 3D Shape Recognition based on Multimodal Attention Mechanism
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rotation Invariant Aerial Image Retrieval with Group Convolutional Metric Learning
Hyunseung Chung, Woo-Jeoung Nam, Seong-Whan Lee

Auto-TLDR; Robust Remote Sensing Image Retrieval Using Group Convolution with Attention Mechanism and Metric Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Open Set Domain Recognition Via Attention-Based GCN and Semantic Matching Optimization
Xinxing He, Yuan Yuan, Zhiyu Jiang

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based GCN and Semantic Matching Optimization for Open Set Domain Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Zero-Shot Text Classification with Semantically Extended Graph Convolutional Network
Tengfei Liu, Yongli Hu, Junbin Gao, Yanfeng Sun, Baocai Yin

Auto-TLDR; Semantically Extended Graph Convolutional Network for Zero-shot Text Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Progressive Scene Segmentation Based on Self-Attention Mechanism
Yunyi Pan, Yuan Gan, Kun Liu, Yan Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stage Semantic Scene Segmentation with Self-Attention
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Transformer-Based Radical Analysis Network for Chinese Character Recognition
Chen Yang, Qing Wang, Jun Du, Jianshu Zhang, Changjie Wu, Jiaming Wang

Auto-TLDR; Transformer-based Radical Analysis Network for Chinese Character Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generalized Local Attention Pooling for Deep Metric Learning
Carlos Roig Mari, David Varas, Issey Masuda, Juan Carlos Riveiro, Elisenda Bou-Balust

Auto-TLDR; Generalized Local Attention Pooling for Deep Metric Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention As Activation
Yimian Dai, Stefan Oehmcke, Fabian Gieseke, Yiquan Wu, Kobus Barnard

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Activation Units for Convolutional Networks
Local Clustering with Mean Teacher for Semi-Supervised Learning
Zexi Chen, Benjamin Dutton, Bharathkumar Ramachandra, Tianfu Wu, Ranga Raju Vatsavai

Auto-TLDR; Local Clustering for Semi-supervised Learning
Cc-Loss: Channel Correlation Loss for Image Classification
Zeyu Song, Dongliang Chang, Zhanyu Ma, Li Xiaoxu, Zheng-Hua Tan

Auto-TLDR; Channel correlation loss for ad- dressing image classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Multi-Head Self-Relation Network for Scene Text Recognition
Zhou Junwei, Hongchao Gao, Jiao Dai, Dongqin Liu, Jizhong Han
Auto-TLDR; Multi-head Self-relation Network for Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Prior Knowledge about Attributes: Learning a More Effective Potential Space for Zero-Shot Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Attribute Correlation Potential Space Generation for Zero-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Parallel Network to Learn Novelty from the Known
Shuaiyuan Du, Chaoyi Hong, Zhiyu Pan, Chen Feng, Zhiguo Cao
Auto-TLDR; Trainable Parallel Network for Pseudo-Novel Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar