A Transformer-Based Radical Analysis Network for Chinese Character Recognition
Chen Yang,
Qing Wang,
Jun Du,
Jianshu Zhang,
Changjie Wu,
Jiaming Wang

Auto-TLDR; Transformer-based Radical Analysis Network for Chinese Character Recognition
Similar papers
Radical Counter Network for Robust Chinese Character Recognition
Yunqing Li, Yixing Zhu, Jun Du, Changjie Wu, Jianshu Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Radical Counter Network for Chinese Character Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Global Context-Based Network with Transformer for Image2latex
Nuo Pang, Chun Yang, Xiaobin Zhu, Jixuan Li, Xu-Cheng Yin

Auto-TLDR; Image2latex with Global Context block and Transformer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ConvMath : A Convolutional Sequence Network for Mathematical Expression Recognition
Zuoyu Yan, Xiaode Zhang, Liangcai Gao, Ke Yuan, Zhi Tang
Auto-TLDR; Convolutional Sequence Modeling for Mathematical Expressions Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Multi-Head Self-Relation Network for Scene Text Recognition
Zhou Junwei, Hongchao Gao, Jiao Dai, Dongqin Liu, Jizhong Han
Auto-TLDR; Multi-head Self-relation Network for Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
LODENet: A Holistic Approach to Offline Handwritten Chinese and Japanese Text Line Recognition
Huu Tin Hoang, Chun-Jen Peng, Hung Tran, Hung Le, Huy Hoang Nguyen

Auto-TLDR; Logographic DEComposition Encoding for Chinese and Japanese Text Line Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
IBN-STR: A Robust Text Recognizer for Irregular Text in Natural Scenes
Xiaoqian Li, Jie Liu, Shuwu Zhang
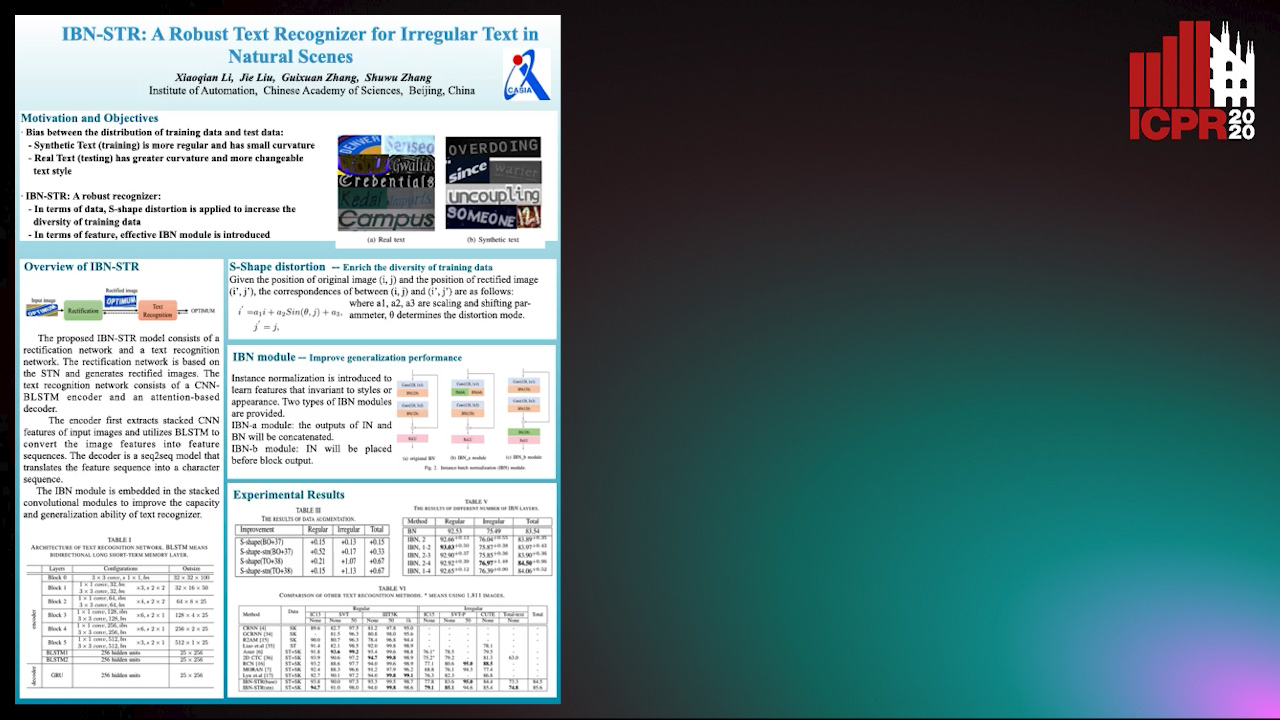
Auto-TLDR; IBN-STR: A Robust Text Recognition System Based on Data and Feature Representation
Stroke Based Posterior Attention for Online Handwritten Mathematical Expression Recognition
Changjie Wu, Qing Wang, Jianshu Zhang, Jun Du, Jiaming Wang, Jiajia Wu, Jin-Shui Hu

Auto-TLDR; Posterior Attention for Online Handwritten Mathematical Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MEAN: A Multi-Element Attention Based Network for Scene Text Recognition
Ruijie Yan, Liangrui Peng, Shanyu Xiao, Gang Yao, Jaesik Min

Auto-TLDR; Multi-element Attention Network for Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-Lingual Text Image Recognition Via Multi-Task Sequence to Sequence Learning
Zhuo Chen, Fei Yin, Xu-Yao Zhang, Qing Yang, Cheng-Lin Liu

Auto-TLDR; Cross-Lingual Text Image Recognition with Multi-task Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Task Learning Based Traditional Mongolian Words Recognition
Hongxi Wei, Hui Zhang, Jing Zhang, Kexin Liu

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Learning for Mongolian Words Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weakly Supervised Attention Rectification for Scene Text Recognition
Chengyu Gu, Shilin Wang, Yiwei Zhu, Zheng Huang, Kai Chen

Auto-TLDR; An auxiliary supervision branch for attention-based scene text recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Gaussian Constrained Attention Network for Scene Text Recognition
Zhi Qiao, Xugong Qin, Yu Zhou, Fei Yang, Weiping Wang

Auto-TLDR; Gaussian Constrained Attention Network for Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ReADS: A Rectified Attentional Double Supervised Network for Scene Text Recognition
Qi Song, Qianyi Jiang, Xiaolin Wei, Nan Li, Rui Zhang

Auto-TLDR; ReADS: Rectified Attentional Double Supervised Network for General Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
2D License Plate Recognition based on Automatic Perspective Rectification
Hui Xu, Zhao-Hong Guo, Da-Han Wang, Xiang-Dong Zhou, Yu Shi

Auto-TLDR; Perspective Rectification Network for License Plate Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Online Trajectory Recovery from Offline Handwritten Japanese Kanji Characters of Multiple Strokes
Hung Tuan Nguyen, Tsubasa Nakamura, Cuong Tuan Nguyen, Masaki Nakagawa

Auto-TLDR; Recovering Dynamic Online Trajectories from Offline Japanese Kanji Character Images for Handwritten Character Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Watch Your Strokes: Improving Handwritten Text Recognition with Deformable Convolutions
Iulian Cojocaru, Silvia Cascianelli, Lorenzo Baraldi, Massimiliano Corsini, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Deformable Convolutional Neural Networks for Handwritten Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recursive Recognition of Offline Handwritten Mathematical Expressions
Marco Cotogni, Claudio Cusano, Antonino Nocera

Auto-TLDR; Online Handwritten Mathematical Expression Recognition with Recurrent Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Sample-Aware Data Augmentor for Scene Text Recognition
Guanghao Meng, Tao Dai, Shudeng Wu, Bin Chen, Jian Lu, Yong Jiang, Shutao Xia
Auto-TLDR; Sample-Aware Data Augmentation for Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context Matters: Self-Attention for Sign Language Recognition
Fares Ben Slimane, Mohamed Bouguessa

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Network for Continuous Sign Language Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Robust Lexicon-Free Confidence Prediction for Text Recognition
Qi Song, Qianyi Jiang, Rui Zhang, Xiaolin Wei

Auto-TLDR; Confidence Measurement for Optical Character Recognition using Single-Input Multi-Output Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Text Recognition in Real Scenarios with a Few Labeled Samples
Jinghuang Lin, Cheng Zhanzhan, Fan Bai, Yi Niu, Shiliang Pu, Shuigeng Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Few-shot Adversarial Sequence Domain Adaptation for Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cost-Effective Adversarial Attacks against Scene Text Recognition
Mingkun Yang, Haitian Zheng, Xiang Bai, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; Adversarial Attacks on Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recognizing Multiple Text Sequences from an Image by Pure End-To-End Learning
Zhenlong Xu, Shuigeng Zhou, Fan Bai, Cheng Zhanzhan, Yi Niu, Shiliang Pu

Auto-TLDR; Pure End-to-End Learning for Multiple Text Sequences Recognition from Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Few-Shot Learning Approach for Historical Ciphered Manuscript Recognition
Mohamed Ali Souibgui, Alicia Fornés, Yousri Kessentini, Crina Tudor

Auto-TLDR; Handwritten Ciphers Recognition Using Few-Shot Object Detection
Predicting Chemical Properties Using Self-Attention Multi-Task Learning Based on SMILES Representation

Auto-TLDR; Self-attention based Transformer-Variant Model for Chemical Compound Properties Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
VTT: Long-Term Visual Tracking with Transformers
Tianling Bian, Yang Hua, Tao Song, Zhengui Xue, Ruhui Ma, Neil Robertson, Haibing Guan

Auto-TLDR; Visual Tracking Transformer with transformers for long-term visual tracking
TAAN: Task-Aware Attention Network for Few-Shot Classification

Auto-TLDR; TAAN: Task-Aware Attention Network for Few-Shot Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Progressive Scene Segmentation Based on Self-Attention Mechanism
Yunyi Pan, Yuan Gan, Kun Liu, Yan Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stage Semantic Scene Segmentation with Self-Attention
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PICK: Processing Key Information Extraction from Documents Using Improved Graph Learning-Convolutional Networks
Wenwen Yu, Ning Lu, Xianbiao Qi, Ping Gong, Rong Xiao

Auto-TLDR; PICK: A Graph Learning Framework for Key Information Extraction from Documents
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual Path Multi-Modal High-Order Features for Textual Content Based Visual Question Answering
Yanan Li, Yuetan Lin, Hongrui Zhao, Donghui Wang

Auto-TLDR; TextVQA: An End-to-End Visual Question Answering Model for Text-Based VQA
A Novel Attention-Based Aggregation Function to Combine Vision and Language
Matteo Stefanini, Marcella Cornia, Lorenzo Baraldi, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Fully-Attentive Reduction for Vision and Language
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mutual Alignment between Audiovisual Features for End-To-End Audiovisual Speech Recognition
Hong Liu, Yawei Wang, Bing Yang

Auto-TLDR; Mutual Iterative Attention for Audio Visual Speech Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recognizing Bengali Word Images - A Zero-Shot Learning Perspective
Sukalpa Chanda, Daniël Arjen Willem Haitink, Prashant Kumar Prasad, Jochem Baas, Umapada Pal, Lambert Schomaker
Auto-TLDR; Zero-Shot Learning for Word Recognition in Bengali Script
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Text Recognition - Real World Data and Where to Find Them
Klára Janoušková, Lluis Gomez, Dimosthenis Karatzas, Jiri Matas

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Weakly Annotated Images for Text Extraction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AttendAffectNet: Self-Attention Based Networks for Predicting Affective Responses from Movies
Thi Phuong Thao Ha, Bt Balamurali, Herremans Dorien, Roig Gemma

Auto-TLDR; AttendAffectNet: A Self-Attention Based Network for Emotion Prediction from Movies
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Embedding Based Text Instance Grouping for Largely Spaced and Occluded Text Detection
Pan Gao, Qi Wan, Renwu Gao, Linlin Shen

Auto-TLDR; Text Instance Embedding Based Feature Embeddings for Multiple Text Instance Grouping
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Collaborative Human Machine Attention Module for Character Recognition
Chetan Ralekar, Tapan Gandhi, Santanu Chaudhury

Auto-TLDR; A Collaborative Human-Machine Attention Module for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhancing Handwritten Text Recognition with N-Gram Sequencedecomposition and Multitask Learning
Vasiliki Tassopoulou, George Retsinas, Petros Maragos

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Learning for Handwritten Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context Visual Information-Based Deliberation Network for Video Captioning
Min Lu, Xueyong Li, Caihua Liu
Auto-TLDR; Context visual information-based deliberation network for video captioning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enriching Video Captions with Contextual Text
Philipp Rimle, Pelin Dogan, Markus Gross
Auto-TLDR; Contextualized Video Captioning Using Contextual Text
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Word Recognition Using Multiple Hypotheses and Deep Embeddings
Siddhant Bansal, Praveen Krishnan, C. V. Jawahar

Auto-TLDR; EmbedNet: fuse recognition-based and recognition-free approaches for word recognition using learning-based methods
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploiting the Logits: Joint Sign Language Recognition and Spell-Correction
Christina Runkel, Stefan Dorenkamp, Hartmut Bauermeister, Michael Möller

Auto-TLDR; A Convolutional Neural Network for Spell-correction in Sign Language Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Stratified Multi-Task Learning for Robust Spotting of Scene Texts
Kinjal Dasgupta, Sudip Das, Ujjwal Bhattacharya

Auto-TLDR; Feature Representation Block for Multi-task Learning of Scene Text
Attention-Driven Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Bappaditya Debnath, Swagat Kumar, Marry O'Brien, Ardhendu Behera

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Modal Contextual Graph Neural Network for Text Visual Question Answering
Yaoyuan Liang, Xin Wang, Xuguang Duan, Wenwu Zhu

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Contextual Graph Neural Network for Text Visual Question Answering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MAGNet: Multi-Region Attention-Assisted Grounding of Natural Language Queries at Phrase Level
Amar Shrestha, Krittaphat Pugdeethosapol, Haowen Fang, Qinru Qiu

Auto-TLDR; MAGNet: A Multi-Region Attention-Aware Grounding Network for Free-form Textual Queries
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Integrating Historical States and Co-Attention Mechanism for Visual Dialog
Tianling Jiang, Yi Ji, Chunping Liu
Auto-TLDR; Integrating Historical States and Co-attention for Visual Dialog
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient-Receptive Field Block with Group Spatial Attention Mechanism for Object Detection
Jiacheng Zhang, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; E-RFB: Efficient-Receptive Field Block for Deep Neural Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar