Cost-Effective Adversarial Attacks against Scene Text Recognition
Mingkun Yang,
Haitian Zheng,
Xiang Bai,
Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; Adversarial Attacks on Scene Text Recognition
Similar papers
Transferable Adversarial Attacks for Deep Scene Text Detection
Shudeng Wu, Tao Dai, Guanghao Meng, Bin Chen, Jian Lu, Shutao Xia

Auto-TLDR; Robustness of DNN-based STD methods against Adversarial Attacks
IBN-STR: A Robust Text Recognizer for Irregular Text in Natural Scenes
Xiaoqian Li, Jie Liu, Shuwu Zhang
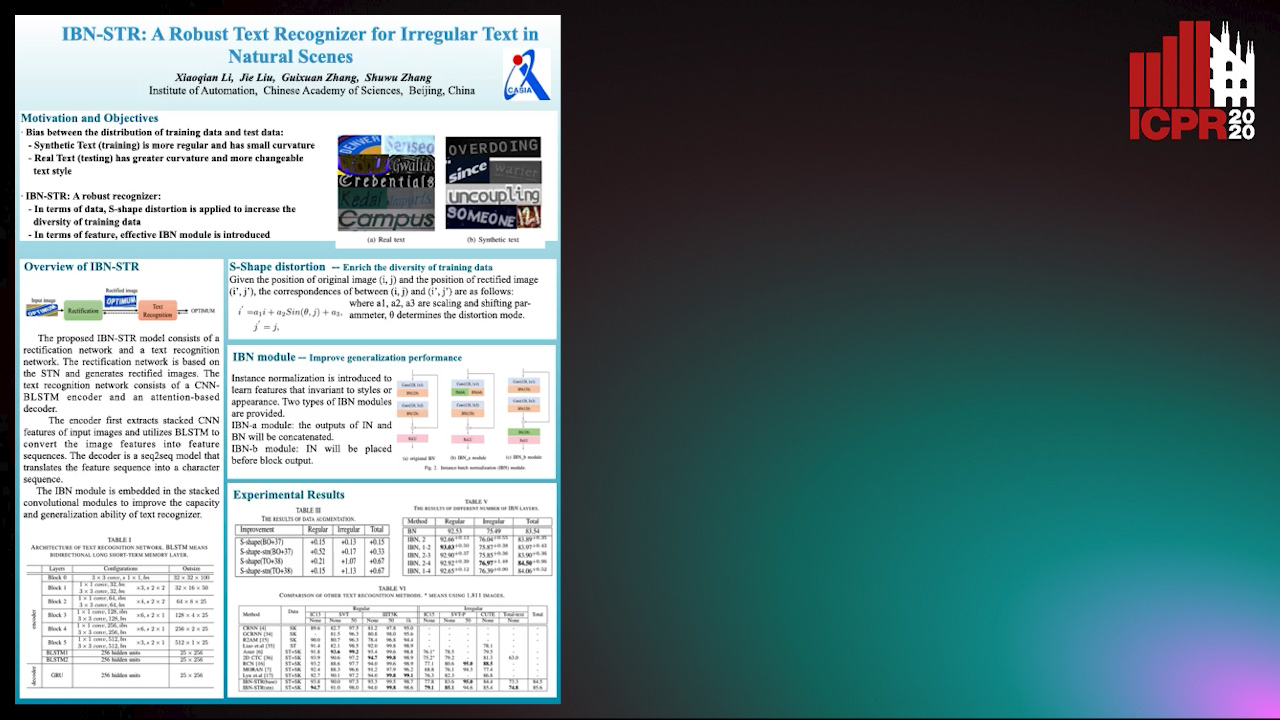
Auto-TLDR; IBN-STR: A Robust Text Recognition System Based on Data and Feature Representation
Gaussian Constrained Attention Network for Scene Text Recognition
Zhi Qiao, Xugong Qin, Yu Zhou, Fei Yang, Weiping Wang

Auto-TLDR; Gaussian Constrained Attention Network for Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ReADS: A Rectified Attentional Double Supervised Network for Scene Text Recognition
Qi Song, Qianyi Jiang, Xiaolin Wei, Nan Li, Rui Zhang

Auto-TLDR; ReADS: Rectified Attentional Double Supervised Network for General Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weakly Supervised Attention Rectification for Scene Text Recognition
Chengyu Gu, Shilin Wang, Yiwei Zhu, Zheng Huang, Kai Chen

Auto-TLDR; An auxiliary supervision branch for attention-based scene text recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recognizing Multiple Text Sequences from an Image by Pure End-To-End Learning
Zhenlong Xu, Shuigeng Zhou, Fan Bai, Cheng Zhanzhan, Yi Niu, Shiliang Pu

Auto-TLDR; Pure End-to-End Learning for Multiple Text Sequences Recognition from Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Multi-Head Self-Relation Network for Scene Text Recognition
Zhou Junwei, Hongchao Gao, Jiao Dai, Dongqin Liu, Jizhong Han
Auto-TLDR; Multi-head Self-relation Network for Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Text Recognition in Real Scenarios with a Few Labeled Samples
Jinghuang Lin, Cheng Zhanzhan, Fan Bai, Yi Niu, Shiliang Pu, Shuigeng Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Few-shot Adversarial Sequence Domain Adaptation for Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Text Recognition - Real World Data and Where to Find Them
Klára Janoušková, Lluis Gomez, Dimosthenis Karatzas, Jiri Matas

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Weakly Annotated Images for Text Extraction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
2D License Plate Recognition based on Automatic Perspective Rectification
Hui Xu, Zhao-Hong Guo, Da-Han Wang, Xiang-Dong Zhou, Yu Shi

Auto-TLDR; Perspective Rectification Network for License Plate Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MEAN: A Multi-Element Attention Based Network for Scene Text Recognition
Ruijie Yan, Liangrui Peng, Shanyu Xiao, Gang Yao, Jaesik Min

Auto-TLDR; Multi-element Attention Network for Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Sample-Aware Data Augmentor for Scene Text Recognition
Guanghao Meng, Tao Dai, Shudeng Wu, Bin Chen, Jian Lu, Yong Jiang, Shutao Xia
Auto-TLDR; Sample-Aware Data Augmentation for Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Stratified Multi-Task Learning for Robust Spotting of Scene Texts
Kinjal Dasgupta, Sudip Das, Ujjwal Bhattacharya

Auto-TLDR; Feature Representation Block for Multi-task Learning of Scene Text
Robust Lexicon-Free Confidence Prediction for Text Recognition
Qi Song, Qianyi Jiang, Rui Zhang, Xiaolin Wei

Auto-TLDR; Confidence Measurement for Optical Character Recognition using Single-Input Multi-Output Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Task-based Focal Loss for Adversarially Robust Meta-Learning
Yufan Hou, Lixin Zou, Weidong Liu

Auto-TLDR; Task-based Adversarial Focal Loss for Few-shot Meta-Learner
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-Lingual Text Image Recognition Via Multi-Task Sequence to Sequence Learning
Zhuo Chen, Fei Yin, Xu-Yao Zhang, Qing Yang, Cheng-Lin Liu

Auto-TLDR; Cross-Lingual Text Image Recognition with Multi-task Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Defense Mechanism against Adversarial Attacks Using Density-Based Representation of Images
Yen-Ting Huang, Wen-Hung Liao, Chen-Wei Huang

Auto-TLDR; Adversarial Attacks Reduction Using Input Recharacterization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adversarially Training for Audio Classifiers
Raymel Alfonso Sallo, Mohammad Esmaeilpour, Patrick Cardinal

Auto-TLDR; Adversarially Training for Robust Neural Networks against Adversarial Attacks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Noise Injection for Training Stochastic Student Networks from Deterministic Teachers
Yi Xiang Marcus Tan, Yuval Elovici, Alexander Binder

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Stochastic Networks for Adversarial Attacks
Variational Inference with Latent Space Quantization for Adversarial Resilience
Vinay Kyatham, Deepak Mishra, Prathosh A.P.

Auto-TLDR; A Generalized Defense Mechanism for Adversarial Attacks on Data Manifolds
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Polynomial Universal Adversarial Perturbations for Person Re-Identification
Wenjie Ding, Xing Wei, Rongrong Ji, Xiaopeng Hong, Yihong Gong

Auto-TLDR; Polynomial Universal Adversarial Perturbation for Re-identification Methods
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
F-Mixup: Attack CNNs from Fourier Perspective
Xiu-Chuan Li, Xu-Yao Zhang, Fei Yin, Cheng-Lin Liu

Auto-TLDR; F-Mixup: A novel black-box attack in frequency domain for deep neural networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attack Agnostic Adversarial Defense via Visual Imperceptible Bound
Saheb Chhabra, Akshay Agarwal, Richa Singh, Mayank Vatsa

Auto-TLDR; Robust Adversarial Defense with Visual Imperceptible Bound
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AdvHat: Real-World Adversarial Attack on ArcFace Face ID System
Stepan Komkov, Aleksandr Petiushko

Auto-TLDR; Adversarial Sticker Attack on ArcFace in Shooting Conditions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Optimal Transport As a Defense against Adversarial Attacks
Quentin Bouniot, Romaric Audigier, Angélique Loesch

Auto-TLDR; Sinkhorn Adversarial Training with Optimal Transport Theory
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual Path Multi-Modal High-Order Features for Textual Content Based Visual Question Answering
Yanan Li, Yuetan Lin, Hongrui Zhao, Donghui Wang

Auto-TLDR; TextVQA: An End-to-End Visual Question Answering Model for Text-Based VQA
CCA: Exploring the Possibility of Contextual Camouflage Attack on Object Detection
Shengnan Hu, Yang Zhang, Sumit Laha, Ankit Sharma, Hassan Foroosh

Auto-TLDR; Contextual camouflage attack for object detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On the Robustness of 3D Human Pose Estimation
Zerui Chen, Yan Huang, Liang Wang

Auto-TLDR; Robustness of 3D Human Pose Estimation Methods to Adversarial Attacks
Explain2Attack: Text Adversarial Attacks via Cross-Domain Interpretability
Mahmoud Hossam, Le Trung, He Zhao, Dinh Phung

Auto-TLDR; Transfer2Attack: A Black-box Adversarial Attack on Text Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Accuracy-Perturbation Curves for Evaluation of Adversarial Attack and Defence Methods
Auto-TLDR; Accuracy-perturbation Curve for Robustness Evaluation of Adversarial Examples
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Gradient Difference Based Mass Features for Classification of 2D-3D Natural Scene Text Images
Lokesh Nandanwar, Shivakumara Palaiahnakote, Raghavendra Ramachandra, Tong Lu, Umapada Pal, Daniel Lopresti, Nor Badrul Anuar
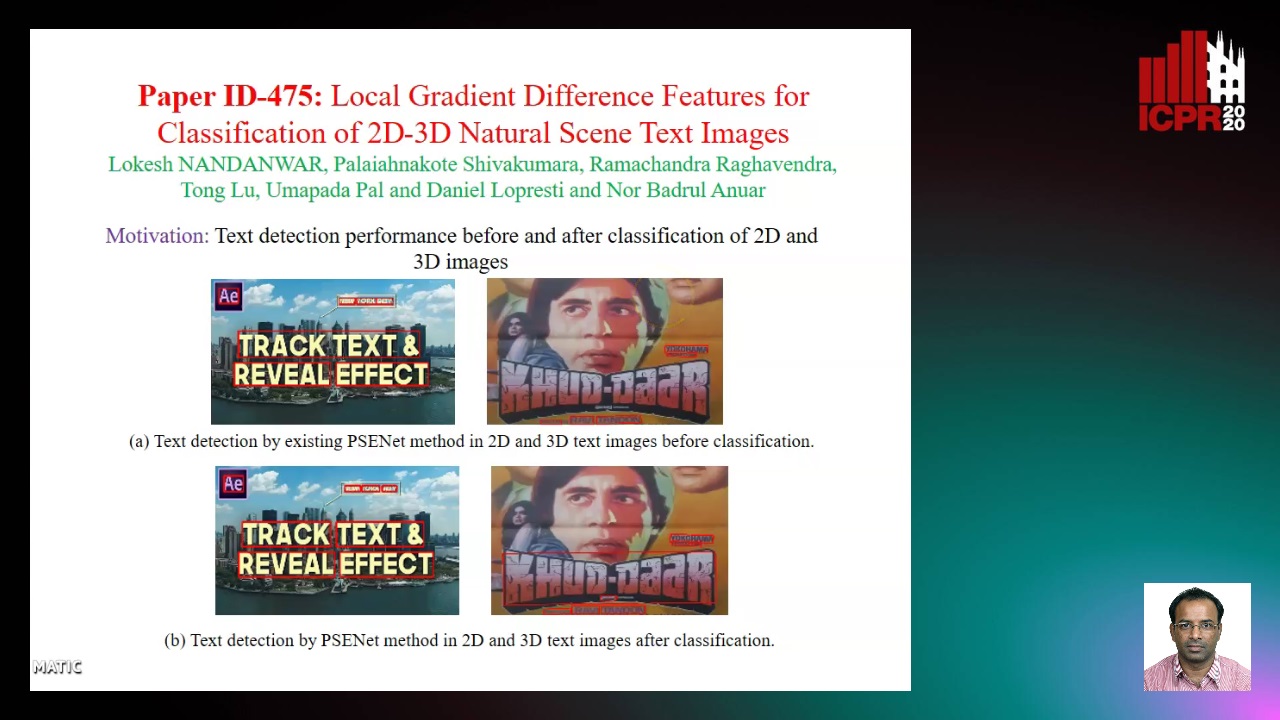
Auto-TLDR; Classification of 2D and 3D Natural Scene Images Using COLD
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Embedding Based Text Instance Grouping for Largely Spaced and Occluded Text Detection
Pan Gao, Qi Wan, Renwu Gao, Linlin Shen

Auto-TLDR; Text Instance Embedding Based Feature Embeddings for Multiple Text Instance Grouping
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Scene Text Detection with Selected Anchors
Anna Zhu, Hang Du, Shengwu Xiong

Auto-TLDR; AS-RPN: Anchor Selection-based Region Proposal Network for Scene Text Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Beyond Cross-Entropy: Learning Highly Separable Feature Distributions for Robust and Accurate Classification
Arslan Ali, Andrea Migliorati, Tiziano Bianchi, Enrico Magli

Auto-TLDR; Gaussian class-conditional simplex loss for adversarial robust multiclass classifiers
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Delayed Elastic-Net Approach for Performing Adversarial Attacks
Brais Cancela, Veronica Bolon-Canedo, Amparo Alonso-Betanzos

Auto-TLDR; Robustness of ImageNet Pretrained Models against Adversarial Attacks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DUET: Detection Utilizing Enhancement for Text in Scanned or Captured Documents
Eun-Soo Jung, Hyeonggwan Son, Kyusam Oh, Yongkeun Yun, Soonhwan Kwon, Min Soo Kim

Auto-TLDR; Text Detection for Document Images Using Synthetic and Real Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Accurate Threshold Insensitive Kernel Detector for Arbitrary Shaped Text
Xijun Qian, Yifan Liu, Yu-Bin Yang

Auto-TLDR; TIKD: threshold insensitive kernel detector for arbitrary shaped text
A Transformer-Based Radical Analysis Network for Chinese Character Recognition
Chen Yang, Qing Wang, Jun Du, Jianshu Zhang, Changjie Wu, Jiaming Wang

Auto-TLDR; Transformer-based Radical Analysis Network for Chinese Character Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TCATD: Text Contour Attention for Scene Text Detection
Ziling Hu, Wu Xingjiao, Jing Yang

Auto-TLDR; Text Contour Attention Text Detector
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Training for Domain Adaptive Scene Text Detection
Yudi Chen, Wei Wang, Yu Zhou, Fei Yang, Dongbao Yang, Weiping Wang

Auto-TLDR; A self-training framework for image-based scene text detection
Global Context-Based Network with Transformer for Image2latex
Nuo Pang, Chun Yang, Xiaobin Zhu, Jixuan Li, Xu-Cheng Yin

Auto-TLDR; Image2latex with Global Context block and Transformer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RLST: A Reinforcement Learning Approach to Scene Text Detection Refinement
Xuan Peng, Zheng Huang, Kai Chen, Jie Guo, Weidong Qiu
Auto-TLDR; Saccadic Eye Movements and Peripheral Vision for Scene Text Detection using Reinforcement Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
LODENet: A Holistic Approach to Offline Handwritten Chinese and Japanese Text Line Recognition
Huu Tin Hoang, Chun-Jen Peng, Hung Tran, Hung Le, Huy Hoang Nguyen

Auto-TLDR; Logographic DEComposition Encoding for Chinese and Japanese Text Line Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mutually Guided Dual-Task Network for Scene Text Detection
Mengbiao Zhao, Wei Feng, Fei Yin, Xu-Yao Zhang, Cheng-Lin Liu

Auto-TLDR; A dual-task network for word-level and line-level text detection
Killing Four Birds with One Gaussian Process: The Relation between Different Test-Time Attacks
Kathrin Grosse, Michael Thomas Smith, Michael Backes
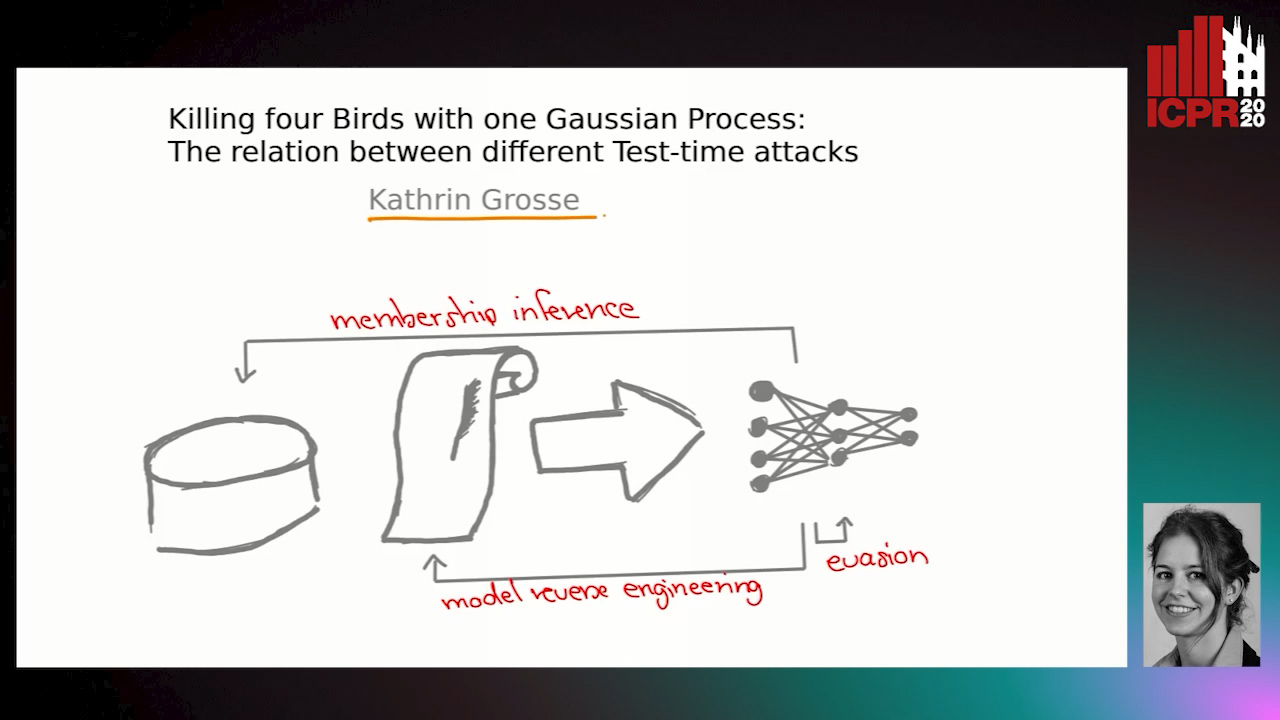
Auto-TLDR; Security of Gaussian Process Classifiers against Attack Algorithms
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boosting High-Level Vision with Joint Compression Artifacts Reduction and Super-Resolution
Xiaoyu Xiang, Qian Lin, Jan Allebach
Auto-TLDR; A Context-Aware Joint CAR and SR Neural Network for High-Resolution Text Recognition and Face Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Word Recognition Using Multiple Hypotheses and Deep Embeddings
Siddhant Bansal, Praveen Krishnan, C. V. Jawahar

Auto-TLDR; EmbedNet: fuse recognition-based and recognition-free approaches for word recognition using learning-based methods
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adversarial Training for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis with BERT
Akbar Karimi, Andrea Prati, Leonardo Rossi
Auto-TLDR; Adversarial Training of BERT for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar