Text Recognition in Real Scenarios with a Few Labeled Samples
Jinghuang Lin,
Cheng Zhanzhan,
Fan Bai,
Yi Niu,
Shiliang Pu,
Shuigeng Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Few-shot Adversarial Sequence Domain Adaptation for Scene Text Recognition
Similar papers
Recognizing Multiple Text Sequences from an Image by Pure End-To-End Learning
Zhenlong Xu, Shuigeng Zhou, Fan Bai, Cheng Zhanzhan, Yi Niu, Shiliang Pu

Auto-TLDR; Pure End-to-End Learning for Multiple Text Sequences Recognition from Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Gaussian Constrained Attention Network for Scene Text Recognition
Zhi Qiao, Xugong Qin, Yu Zhou, Fei Yang, Weiping Wang

Auto-TLDR; Gaussian Constrained Attention Network for Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weakly Supervised Attention Rectification for Scene Text Recognition
Chengyu Gu, Shilin Wang, Yiwei Zhu, Zheng Huang, Kai Chen

Auto-TLDR; An auxiliary supervision branch for attention-based scene text recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ReADS: A Rectified Attentional Double Supervised Network for Scene Text Recognition
Qi Song, Qianyi Jiang, Xiaolin Wei, Nan Li, Rui Zhang

Auto-TLDR; ReADS: Rectified Attentional Double Supervised Network for General Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Multi-Head Self-Relation Network for Scene Text Recognition
Zhou Junwei, Hongchao Gao, Jiao Dai, Dongqin Liu, Jizhong Han
Auto-TLDR; Multi-head Self-relation Network for Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MEAN: A Multi-Element Attention Based Network for Scene Text Recognition
Ruijie Yan, Liangrui Peng, Shanyu Xiao, Gang Yao, Jaesik Min

Auto-TLDR; Multi-element Attention Network for Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Text Recognition - Real World Data and Where to Find Them
Klára Janoušková, Lluis Gomez, Dimosthenis Karatzas, Jiri Matas

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Weakly Annotated Images for Text Extraction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cost-Effective Adversarial Attacks against Scene Text Recognition
Mingkun Yang, Haitian Zheng, Xiang Bai, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; Adversarial Attacks on Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-Lingual Text Image Recognition Via Multi-Task Sequence to Sequence Learning
Zhuo Chen, Fei Yin, Xu-Yao Zhang, Qing Yang, Cheng-Lin Liu

Auto-TLDR; Cross-Lingual Text Image Recognition with Multi-task Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Stratified Multi-Task Learning for Robust Spotting of Scene Texts
Kinjal Dasgupta, Sudip Das, Ujjwal Bhattacharya

Auto-TLDR; Feature Representation Block for Multi-task Learning of Scene Text
Sample-Aware Data Augmentor for Scene Text Recognition
Guanghao Meng, Tao Dai, Shudeng Wu, Bin Chen, Jian Lu, Yong Jiang, Shutao Xia
Auto-TLDR; Sample-Aware Data Augmentation for Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
IBN-STR: A Robust Text Recognizer for Irregular Text in Natural Scenes
Xiaoqian Li, Jie Liu, Shuwu Zhang
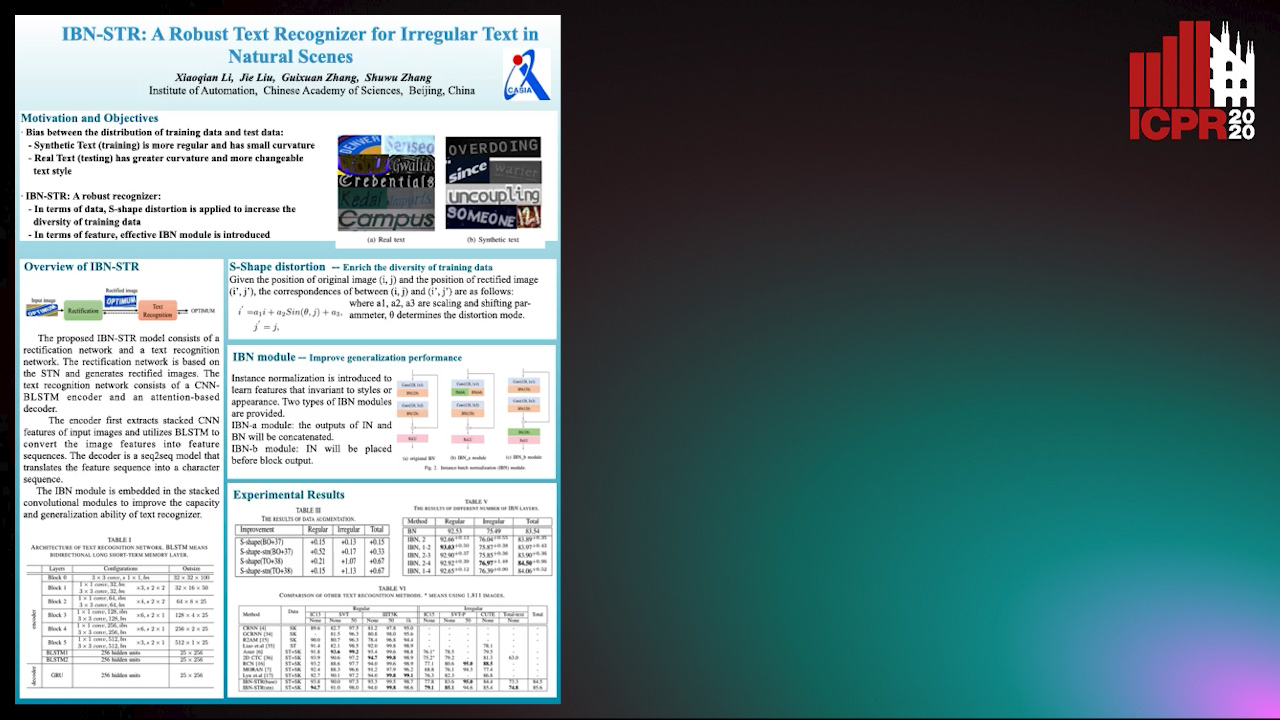
Auto-TLDR; IBN-STR: A Robust Text Recognition System Based on Data and Feature Representation
Self-Training for Domain Adaptive Scene Text Detection
Yudi Chen, Wei Wang, Yu Zhou, Fei Yang, Dongbao Yang, Weiping Wang

Auto-TLDR; A self-training framework for image-based scene text detection
Robust Lexicon-Free Confidence Prediction for Text Recognition
Qi Song, Qianyi Jiang, Rui Zhang, Xiaolin Wei

Auto-TLDR; Confidence Measurement for Optical Character Recognition using Single-Input Multi-Output Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
2D License Plate Recognition based on Automatic Perspective Rectification
Hui Xu, Zhao-Hong Guo, Da-Han Wang, Xiang-Dong Zhou, Yu Shi

Auto-TLDR; Perspective Rectification Network for License Plate Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Multiple Domain Discriminators and Adaptive Self-Training
Teo Spadotto, Marco Toldo, Umberto Michieli, Pietro Zanuttigh

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Scenes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation of Urban Scenes Via Multi-Level Feature Alignment
Bin Zhang, Shengjie Zhao, Rongqing Zhang
Auto-TLDR; Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation Using Generative Adversarial Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual Path Multi-Modal High-Order Features for Textual Content Based Visual Question Answering
Yanan Li, Yuetan Lin, Hongrui Zhao, Donghui Wang

Auto-TLDR; TextVQA: An End-to-End Visual Question Answering Model for Text-Based VQA
Learning Low-Shot Generative Networks for Cross-Domain Data
Hsuan-Kai Kao, Cheng-Che Lee, Wei-Chen Chiu
Auto-TLDR; Learning Generators for Cross-Domain Data under Low-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Shape Consistent 2D Keypoint Estimation under Domain Shift
Levi Vasconcelos, Massimiliano Mancini, Davide Boscaini, Barbara Caputo, Elisa Ricci

Auto-TLDR; Deep Adaptation for Keypoint Prediction under Domain Shift
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Spatial-Aware GAN for Unsupervised Person Re-Identification
Fangneng Zhan, Changgong Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Person Re-Identification
Open Set Domain Recognition Via Attention-Based GCN and Semantic Matching Optimization
Xinxing He, Yuan Yuan, Zhiyu Jiang

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based GCN and Semantic Matching Optimization for Open Set Domain Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enlarging Discriminative Power by Adding an Extra Class in Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Hai Tran, Sumyeong Ahn, Taeyoung Lee, Yung Yi

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation using Artificial Classes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Multi-Task Domain Adaptation

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Multi-task Learning for Image Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Embedding Based Text Instance Grouping for Largely Spaced and Occluded Text Detection
Pan Gao, Qi Wan, Renwu Gao, Linlin Shen

Auto-TLDR; Text Instance Embedding Based Feature Embeddings for Multiple Text Instance Grouping
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Class Conditional Alignment for Partial Domain Adaptation
Mohsen Kheirandishfard, Fariba Zohrizadeh, Farhad Kamangar
Auto-TLDR; Multi-class Adversarial Adaptation for Partial Domain Adaptation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Randomized Transferable Machine

Auto-TLDR; Randomized Transferable Machine for Suboptimal Feature-based Transfer Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DUET: Detection Utilizing Enhancement for Text in Scanned or Captured Documents
Eun-Soo Jung, Hyeonggwan Son, Kyusam Oh, Yongkeun Yun, Soonhwan Kwon, Min Soo Kim

Auto-TLDR; Text Detection for Document Images Using Synthetic and Real Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Foreground-Focused Domain Adaption for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Unsupervised Object Detection
DAPC: Domain Adaptation People Counting Via Style-Level Transfer Learning and Scene-Aware Estimation
Na Jiang, Xingsen Wen, Zhiping Shi

Auto-TLDR; Domain Adaptation People counting via Style-Level Transfer Learning and Scene-Aware Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
LODENet: A Holistic Approach to Offline Handwritten Chinese and Japanese Text Line Recognition
Huu Tin Hoang, Chun-Jen Peng, Hung Tran, Hung Le, Huy Hoang Nguyen

Auto-TLDR; Logographic DEComposition Encoding for Chinese and Japanese Text Line Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-People Mobile-Phone Based Airwriting Character Recognition
Yunzhe Li, Hui Zheng, He Zhu, Haojun Ai, Xiaowei Dong

Auto-TLDR; Cross-People Airwriting Recognition via Motion Sensor Signal via Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Teacher-Student Competition for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Ruixin Xiao, Zhilei Liu, Baoyuan Wu
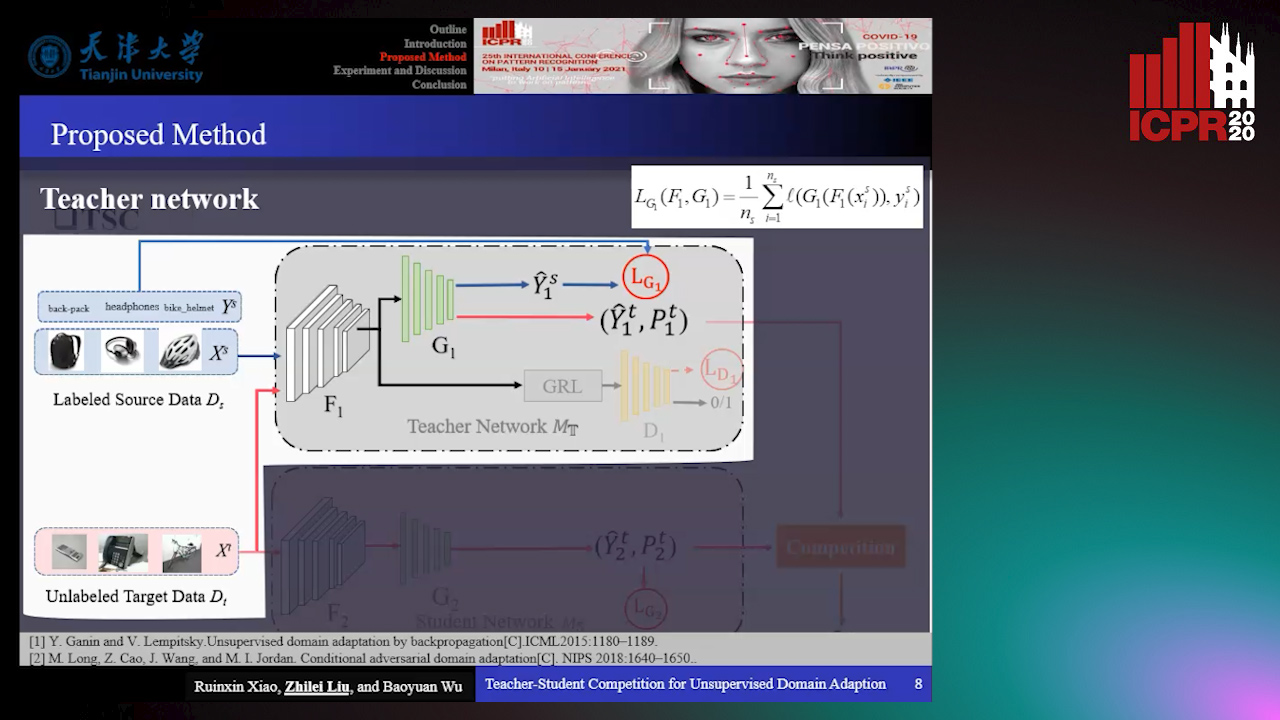
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaption with Teacher-Student Competition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Simple Domain Shifting Network for Generating Low Quality Images
Guruprasad Hegde, Avinash Nittur Ramesh, Kanchana Vaishnavi Gandikota, Michael Möller, Roman Obermaisser
Auto-TLDR; Robotic Image Classification Using Quality degrading networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Gradient Difference Based Mass Features for Classification of 2D-3D Natural Scene Text Images
Lokesh Nandanwar, Shivakumara Palaiahnakote, Raghavendra Ramachandra, Tong Lu, Umapada Pal, Daniel Lopresti, Nor Badrul Anuar
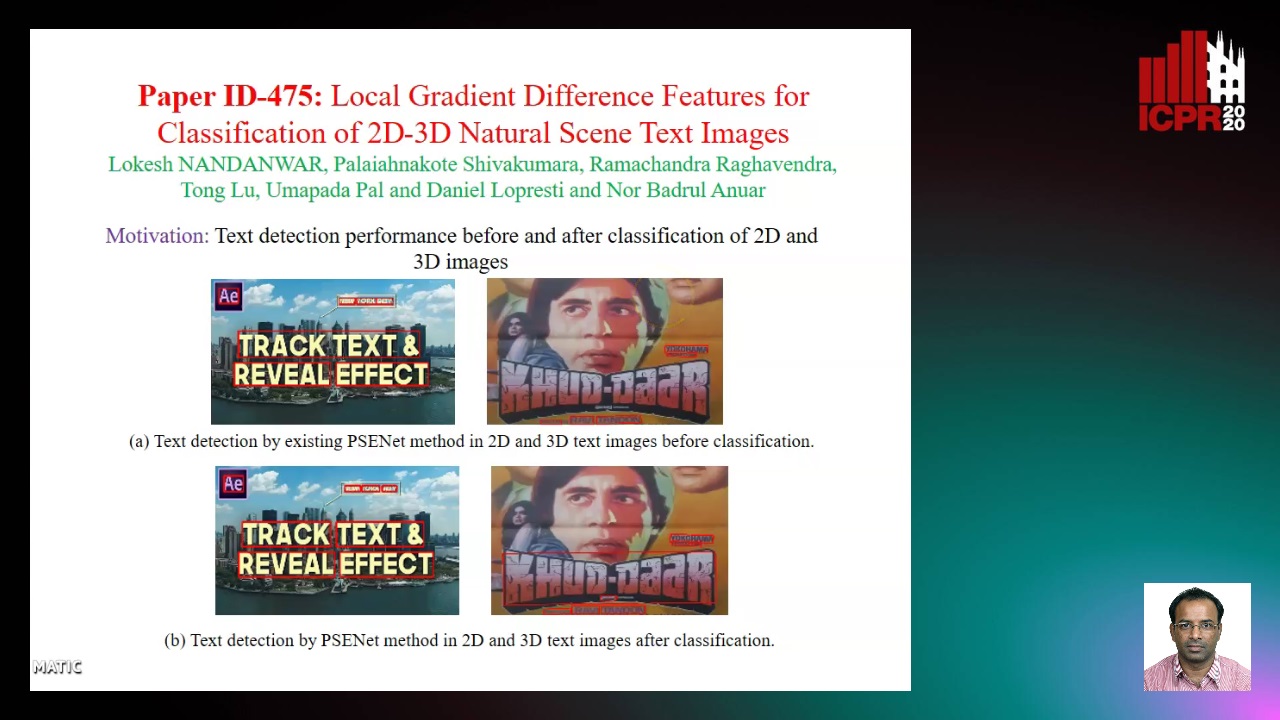
Auto-TLDR; Classification of 2D and 3D Natural Scene Images Using COLD
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semi-Supervised Domain Adaptation Via Selective Pseudo Labeling and Progressive Self-Training

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Domain Adaptation with Pseudo Labels
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Energy-Constrained Self-Training for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Xiaofeng Liu, Xiongchang Liu, Bo Hu, Jun Lu, Jonghye Woo, Jane You

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Energy Function Minimization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Transformer-Based Radical Analysis Network for Chinese Character Recognition
Chen Yang, Qing Wang, Jun Du, Jianshu Zhang, Changjie Wu, Jiaming Wang

Auto-TLDR; Transformer-based Radical Analysis Network for Chinese Character Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Supervised Domain Adaptation Using Graph Embedding
Lukas Hedegaard, Omar Ali Sheikh-Omar, Alexandros Iosifidis
Auto-TLDR; Domain Adaptation from the Perspective of Multi-view Graph Embedding and Dimensionality Reduction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Scene Text Detection with Selected Anchors
Anna Zhu, Hang Du, Shengwu Xiong

Auto-TLDR; AS-RPN: Anchor Selection-based Region Proposal Network for Scene Text Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TCATD: Text Contour Attention for Scene Text Detection
Ziling Hu, Wu Xingjiao, Jing Yang

Auto-TLDR; Text Contour Attention Text Detector
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adversarially Constrained Interpolation for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Mohamed Azzam, Aurele Tohokantche Gnanha, Hau-San Wong, Si Wu

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Domain Mixup Strategy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mutually Guided Dual-Task Network for Scene Text Detection
Mengbiao Zhao, Wei Feng, Fei Yin, Xu-Yao Zhang, Cheng-Lin Liu

Auto-TLDR; A dual-task network for word-level and line-level text detection
Global Context-Based Network with Transformer for Image2latex
Nuo Pang, Chun Yang, Xiaobin Zhu, Jixuan Li, Xu-Cheng Yin

Auto-TLDR; Image2latex with Global Context block and Transformer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Watch Your Strokes: Improving Handwritten Text Recognition with Deformable Convolutions
Iulian Cojocaru, Silvia Cascianelli, Lorenzo Baraldi, Massimiliano Corsini, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Deformable Convolutional Neural Networks for Handwritten Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Object Detection in Cultural Sites
Giovanni Pasqualino, Antonino Furnari, Giovanni Maria Farinella

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Object Detection in Cultural Sites
An Accurate Threshold Insensitive Kernel Detector for Arbitrary Shaped Text
Xijun Qian, Yifan Liu, Yu-Bin Yang

Auto-TLDR; TIKD: threshold insensitive kernel detector for arbitrary shaped text
Rethinking Domain Generalization Baselines
Francesco Cappio Borlino, Antonio D'Innocente, Tatiana Tommasi

Auto-TLDR; Style Transfer Data Augmentation for Domain Generalization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar