Constrained Spectral Clustering Network with Self-Training
Xinyue Liu,
Shichong Yang,
Linlin Zong

Auto-TLDR; Constrained Spectral Clustering Network: A Constrained Deep spectral clustering network
Similar papers
Feature-Aware Unsupervised Learning with Joint Variational Attention and Automatic Clustering
Wang Ru, Lin Li, Peipei Wang, Liu Peiyu

Auto-TLDR; Deep Variational Attention Encoder-Decoder for Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
N2D: (Not Too) Deep Clustering Via Clustering the Local Manifold of an Autoencoded Embedding
Ryan Mcconville, Raul Santos-Rodriguez, Robert Piechocki, Ian Craddock

Auto-TLDR; Local Manifold Learning for Deep Clustering on Autoencoded Embeddings
Variational Deep Embedding Clustering by Augmented Mutual Information Maximization
Qiang Ji, Yanfeng Sun, Yongli Hu, Baocai Yin

Auto-TLDR; Clustering by Augmented Mutual Information maximization for Deep Embedding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Clustering with Mean Teacher for Semi-Supervised Learning
Zexi Chen, Benjamin Dutton, Bharathkumar Ramachandra, Tianfu Wu, Ranga Raju Vatsavai

Auto-TLDR; Local Clustering for Semi-supervised Learning
Sparse-Dense Subspace Clustering
Shuai Yang, Wenqi Zhu, Yuesheng Zhu

Auto-TLDR; Sparse-Dense Subspace Clustering with Piecewise Correlation Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Modal Deep Clustering: Unsupervised Partitioning of Images

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Modal Deep Clustering for Unlabeled Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
JECL: Joint Embedding and Cluster Learning for Image-Text Pairs
Sean Yang, Kuan-Hao Huang, Bill Howe
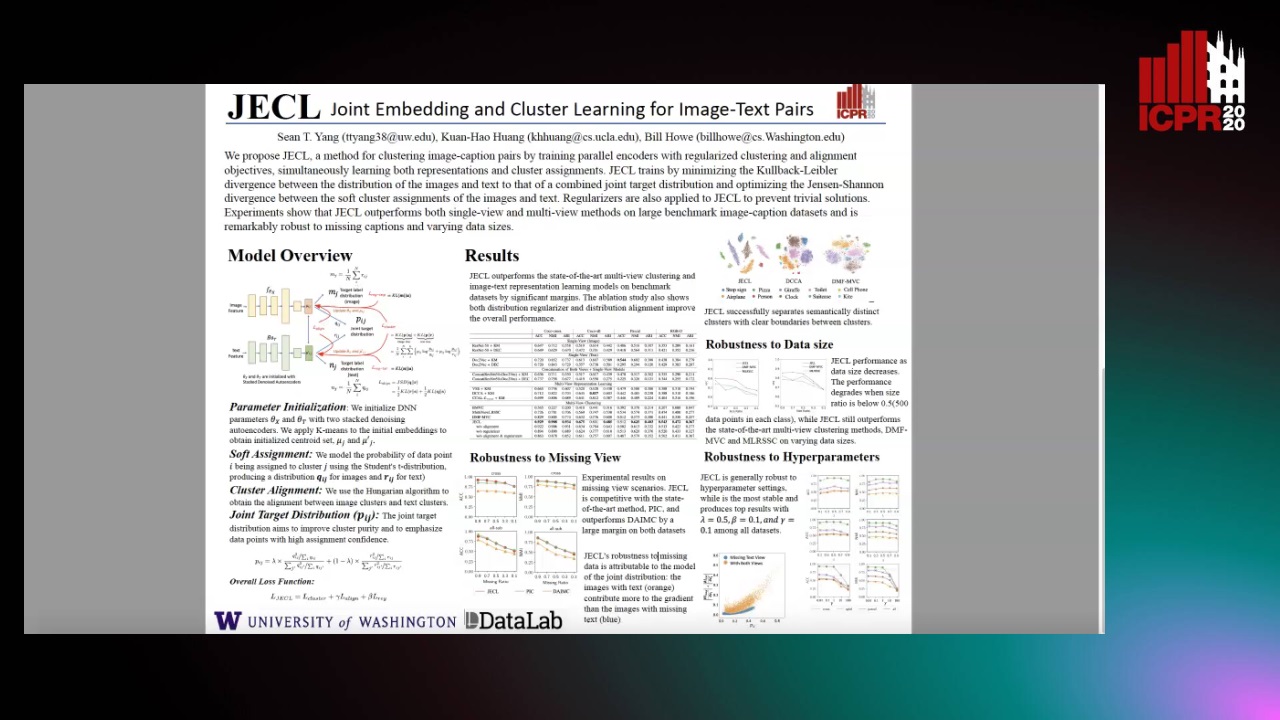
Auto-TLDR; JECL: Clustering Image-Caption Pairs with Parallel Encoders and Regularized Clusters
Deep Convolutional Embedding for Digitized Painting Clustering
Giovanna Castellano, Gennaro Vessio

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Convolutional Embedding Model for Clustering Artworks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Soft Label and Discriminant Embedding Estimation for Semi-Supervised Classification
Fadi Dornaika, Abdullah Baradaaji, Youssof El Traboulsi
Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Semi-Supervised Learning for Linear Feature Extraction and Label Propagation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Embeddings for Image Clustering: An Empirical Study of Triplet Loss Approaches
Kalun Ho, Janis Keuper, Franz-Josef Pfreundt, Margret Keuper
Auto-TLDR; Clustering Objectives for K-means and Correlation Clustering Using Triplet Loss
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generative Deep-Neural-Network Mixture Modeling with Semi-Supervised MinMax+EM Learning
Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Deep Neural Networks for Generative Mixture Modeling and Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Unified Framework for Distance-Aware Domain Adaptation
Fei Wang, Youdong Ding, Huan Liang, Yuzhen Gao, Wenqi Che

Auto-TLDR; distance-aware domain adaptation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Scalable Direction-Search-Based Approach to Subspace Clustering

Auto-TLDR; Fast Direction-Search-Based Subspace Clustering
Subspace Clustering Via Joint Unsupervised Feature Selection
Wenhua Dong, Xiaojun Wu, Hui Li, Zhenhua Feng, Josef Kittler
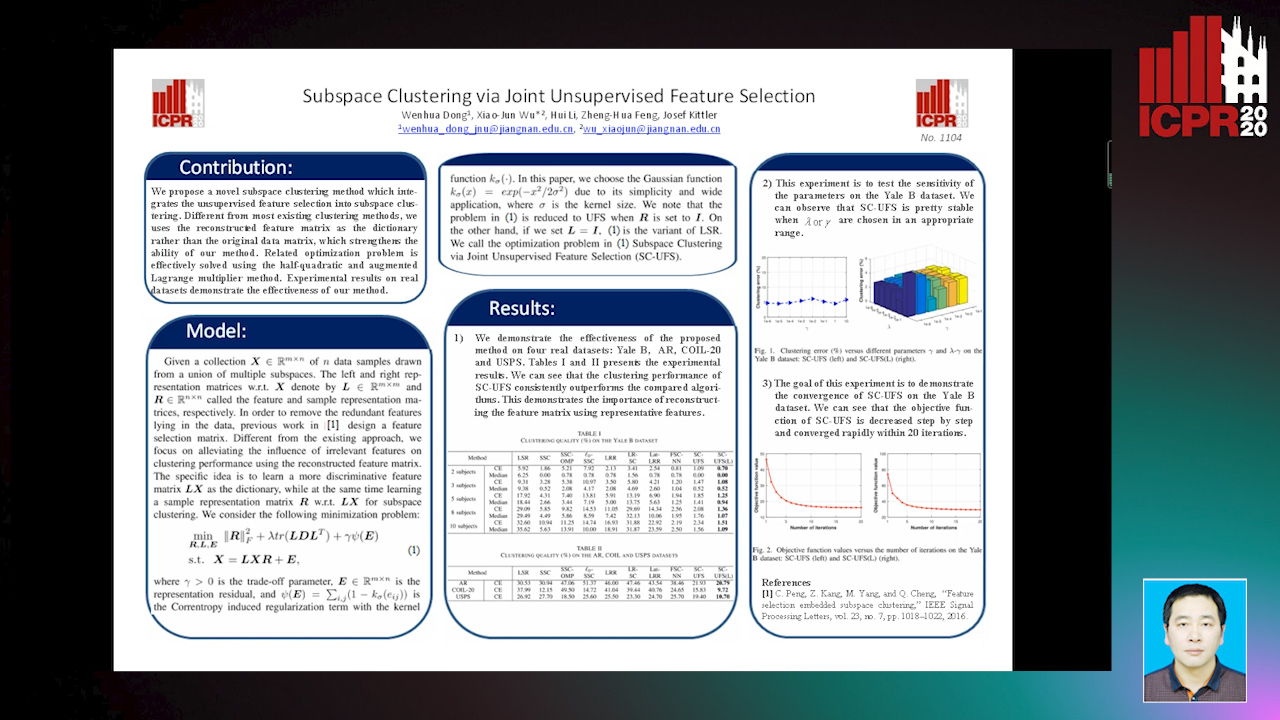
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Feature Selection for Subspace Clustering
Low Rank Representation on Product Grassmann Manifolds for Multi-viewSubspace Clustering
Jipeng Guo, Yanfeng Sun, Junbin Gao, Yongli Hu, Baocai Yin

Auto-TLDR; Low Rank Representation on Product Grassmann Manifold for Multi-View Data Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adversarial Encoder-Multi-Task-Decoder for Multi-Stage Processes
Andre Mendes, Julian Togelius, Leandro Dos Santos Coelho

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Task Learning and Semi-Supervised Learning for Multi-Stage Processes
Nonlinear Ranking Loss on Riemannian Potato Embedding
Byung Hyung Kim, Yoonje Suh, Honggu Lee, Sungho Jo

Auto-TLDR; Riemannian Potato for Rank-based Metric Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improved Deep Classwise Hashing with Centers Similarity Learning for Image Retrieval

Auto-TLDR; Deep Classwise Hashing for Image Retrieval Using Center Similarity Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Label Self-Adaption Hashing for Image Retrieval
Jianglin Lu, Zhihui Lai, Hailing Wang, Jie Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Label Self-Adaption Hashing for Large-Scale Image Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Supervised Domain Adaptation Using Graph Embedding
Lukas Hedegaard, Omar Ali Sheikh-Omar, Alexandros Iosifidis
Auto-TLDR; Domain Adaptation from the Perspective of Multi-view Graph Embedding and Dimensionality Reduction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rethinking Deep Active Learning: Using Unlabeled Data at Model Training
Oriane Siméoni, Mateusz Budnik, Yannis Avrithis, Guillaume Gravier

Auto-TLDR; Unlabeled Data for Active Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Double Manifolds Regularized Non-Negative Matrix Factorization for Data Representation
Jipeng Guo, Shuai Yin, Yanfeng Sun, Yongli Hu

Auto-TLDR; Double Manifolds Regularized Non-negative Matrix Factorization for Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Paced Bottom-Up Clustering Network with Side Information for Person Re-Identification
Mingkun Li, Chun-Guang Li, Ruo-Pei Guo, Jun Guo

Auto-TLDR; Self-Paced Bottom-up Clustering Network with Side Information for Unsupervised Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Progressive Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Image-Based Person Re-Identification
Mingliang Yang, Da Huang, Jing Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Progressive Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Person Re-Identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A General Model for Learning Node and Graph Representations Jointly
Auto-TLDR; Joint Community Detection/Dynamic Routing for Graph Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fast Subspace Clustering Based on the Kronecker Product
Lei Zhou, Xiao Bai, Liang Zhang, Jun Zhou, Edwin Hancock

Auto-TLDR; Subspace Clustering with Kronecker Product for Large Scale Datasets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Uniform and Non-Uniform Sampling Methods for Sub-Linear Time K-Means Clustering

Auto-TLDR; Sub-linear Time Clustering with Constant Approximation Ratio for K-Means Problem
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Progressive Cluster Purification for Unsupervised Feature Learning
Yifei Zhang, Chang Liu, Yu Zhou, Wei Wang, Weiping Wang, Qixiang Ye

Auto-TLDR; Progressive Cluster Purification for Unsupervised Feature Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Q-SNE: Visualizing Data Using Q-Gaussian Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding
Motoshi Abe, Junichi Miyao, Takio Kurita
Auto-TLDR; Q-Gaussian distributed stochastic neighbor embedding for 2-dimensional mapping and classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Assortative-Constrained Stochastic Block Models
Daniel Gribel, Thibaut Vidal, Michel Gendreau

Auto-TLDR; Constrained Stochastic Block Models for Assortative Communities in Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semi-Supervised Class Incremental Learning
Alexis Lechat, Stéphane Herbin, Frederic Jurie

Auto-TLDR; incremental class learning with non-annotated batches
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Spectral Clustering on Grassmann Manifold Via Double Low Rank Constraint
Xinglin Piao, Yongli Hu, Junbin Gao, Yanfeng Sun, Xin Yang, Baocai Yin

Auto-TLDR; Double Low Rank Representation for High-Dimensional Data Clustering on Grassmann Manifold
Deep Topic Modeling by Multilayer Bootstrap Network and Lasso
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Deep Topic Modeling with Multilayer Bootstrap Network and Lasso
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Subspace Clustering for Action Recognition with Covariance Representations and Temporal Pruning
Giancarlo Paoletti, Jacopo Cavazza, Cigdem Beyan, Alessio Del Bue

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Learning for Human Action Recognition from Skeletal Data
RSAC: Regularized Subspace Approximation Classifier for Lightweight Continuous Learning

Auto-TLDR; Regularized Subspace Approximation Classifier for Lightweight Continuous Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Aggregating Dependent Gaussian Experts in Local Approximation

Auto-TLDR; A novel approach for aggregating the Gaussian experts by detecting strong violations of conditional independence
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Superpixel Cut for Unsupervised Image Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Deep Superpixel Cut for Deep Unsupervised Image Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single-Modal Incremental Terrain Clustering from Self-Supervised Audio-Visual Feature Learning
Reina Ishikawa, Ryo Hachiuma, Akiyoshi Kurobe, Hideo Saito

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Variational Autoencoder for Terrain Type Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Sparse Deep Neural Networks Using Efficient Structured Projections on Convex Constraints for Green AI
Michel Barlaud, Frederic Guyard

Auto-TLDR; Constrained Deep Neural Network with Constrained Splitting Projection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adversarially Constrained Interpolation for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Mohamed Azzam, Aurele Tohokantche Gnanha, Hau-San Wong, Si Wu

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Domain Mixup Strategy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weakly Supervised Learning through Rank-Based Contextual Measures
João Gabriel Camacho Presotto, Lucas Pascotti Valem, Nikolas Gomes De Sá, Daniel Carlos Guimaraes Pedronette, Joao Paulo Papa

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Unlabeled Data for Weakly Supervised Classification of Multimedia Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Graph Spectral Feature Learning for Mixed Data of Categorical and Numerical Type
Saswata Sahoo, Souradip Chakraborty

Auto-TLDR; Feature Learning in Mixed Type of Variable by an undirected graph
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Stochastic Label Refinery: Toward Better Target Label Distribution
Xi Fang, Jiancheng Yang, Bingbing Ni

Auto-TLDR; Stochastic Label Refinery for Deep Supervised Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Wasserstein k-Means with Sparse Simplex Projection
Takumi Fukunaga, Hiroyuki Kasai
Auto-TLDR; SSPW $k$-means: Sparse Simplex Projection-based Wasserstein $ k$-Means Algorithm
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Few-Shot Font Generation with Deep Metric Learning
Haruka Aoki, Koki Tsubota, Hikaru Ikuta, Kiyoharu Aizawa
Auto-TLDR; Deep Metric Learning for Japanese Typographic Font Synthesis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Region and Relations Based Multi Attention Network for Graph Classification
Manasvi Aggarwal, M. Narasimha Murty
Auto-TLDR; R2POOL: A Graph Pooling Layer for Non-euclidean Structures
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Variational Capsule Encoder
Harish Raviprakash, Syed Anwar, Ulas Bagci

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian Capsule Networks for Representation Learning in latent space
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Beyond Cross-Entropy: Learning Highly Separable Feature Distributions for Robust and Accurate Classification
Arslan Ali, Andrea Migliorati, Tiziano Bianchi, Enrico Magli

Auto-TLDR; Gaussian class-conditional simplex loss for adversarial robust multiclass classifiers
Abstract Slides Poster Similar