JECL: Joint Embedding and Cluster Learning for Image-Text Pairs
Sean Yang,
Kuan-Hao Huang,
Bill Howe
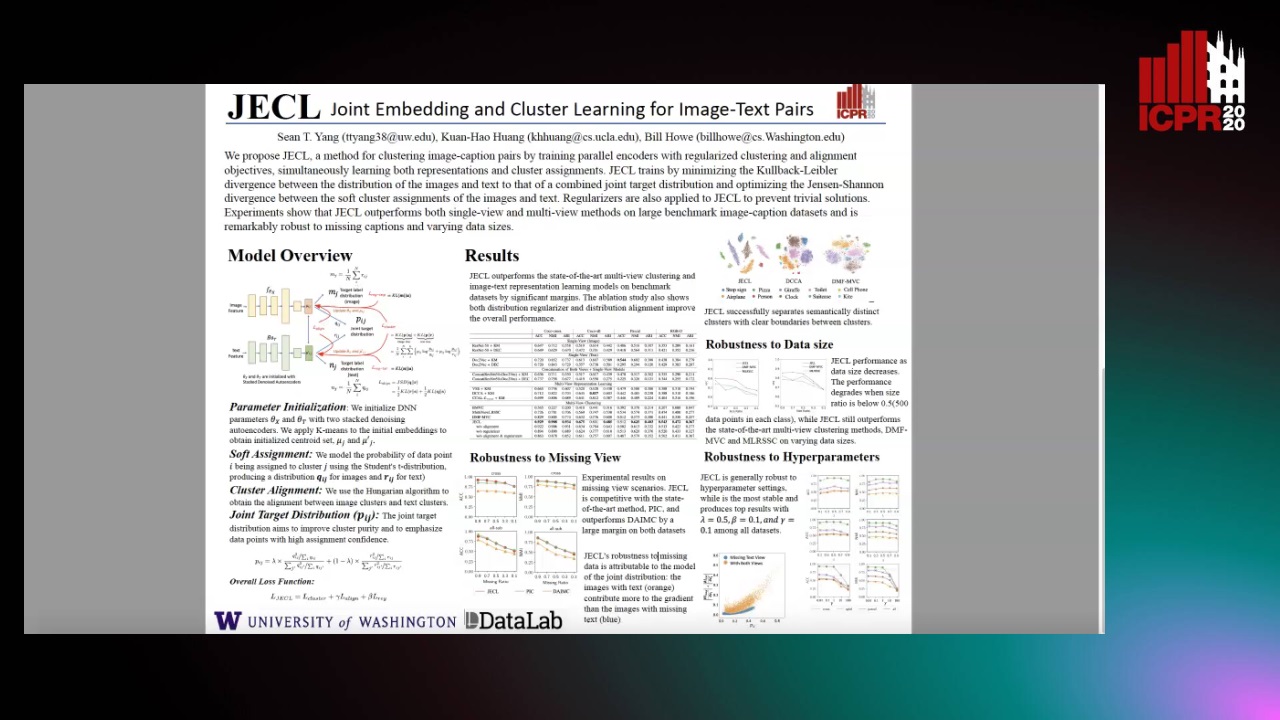
Auto-TLDR; JECL: Clustering Image-Caption Pairs with Parallel Encoders and Regularized Clusters
Similar papers
Deep Convolutional Embedding for Digitized Painting Clustering
Giovanna Castellano, Gennaro Vessio

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Convolutional Embedding Model for Clustering Artworks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Webly Supervised Image-Text Embedding with Noisy Tag Refinement
Niluthpol Mithun, Ravdeep Pasricha, Evangelos Papalexakis, Amit Roy-Chowdhury
Auto-TLDR; Robust Joint Embedding for Image-Text Retrieval Using Web Images
Multi-Modal Deep Clustering: Unsupervised Partitioning of Images

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Modal Deep Clustering for Unlabeled Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Constrained Spectral Clustering Network with Self-Training
Xinyue Liu, Shichong Yang, Linlin Zong

Auto-TLDR; Constrained Spectral Clustering Network: A Constrained Deep spectral clustering network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature-Aware Unsupervised Learning with Joint Variational Attention and Automatic Clustering
Wang Ru, Lin Li, Peipei Wang, Liu Peiyu

Auto-TLDR; Deep Variational Attention Encoder-Decoder for Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Variational Deep Embedding Clustering by Augmented Mutual Information Maximization
Qiang Ji, Yanfeng Sun, Yongli Hu, Baocai Yin

Auto-TLDR; Clustering by Augmented Mutual Information maximization for Deep Embedding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
N2D: (Not Too) Deep Clustering Via Clustering the Local Manifold of an Autoencoded Embedding
Ryan Mcconville, Raul Santos-Rodriguez, Robert Piechocki, Ian Craddock

Auto-TLDR; Local Manifold Learning for Deep Clustering on Autoencoded Embeddings
Beyond the Deep Metric Learning: Enhance the Cross-Modal Matching with Adversarial Discriminative Domain Regularization
Li Ren, Kai Li, Liqiang Wang, Kien Hua

Auto-TLDR; Adversarial Discriminative Domain Regularization for Efficient Cross-Modal Matching
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Embeddings for Image Clustering: An Empirical Study of Triplet Loss Approaches
Kalun Ho, Janis Keuper, Franz-Josef Pfreundt, Margret Keuper
Auto-TLDR; Clustering Objectives for K-means and Correlation Clustering Using Triplet Loss
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Multi-Task Multi-View Based Multi-Objective Clustering Algorithm

Auto-TLDR; MTMV-MO: Multi-task multi-view multi-objective optimization for multi-task clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Low Rank Representation on Product Grassmann Manifolds for Multi-viewSubspace Clustering
Jipeng Guo, Yanfeng Sun, Junbin Gao, Yongli Hu, Baocai Yin

Auto-TLDR; Low Rank Representation on Product Grassmann Manifold for Multi-View Data Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Double Manifolds Regularized Non-Negative Matrix Factorization for Data Representation
Jipeng Guo, Shuai Yin, Yanfeng Sun, Yongli Hu

Auto-TLDR; Double Manifolds Regularized Non-negative Matrix Factorization for Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-Media Hash Retrieval Using Multi-head Attention Network
Zhixin Li, Feng Ling, Chuansheng Xu, Canlong Zhang, Huifang Ma

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Cross-Media Hash Retrieval Using Multi-Head Attention Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
VSR++: Improving Visual Semantic Reasoning for Fine-Grained Image-Text Matching
Hui Yuan, Yan Huang, Dongbo Zhang, Zerui Chen, Wenlong Cheng, Liang Wang

Auto-TLDR; Improving Visual Semantic Reasoning for Fine-Grained Image-Text Matching
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generative Deep-Neural-Network Mixture Modeling with Semi-Supervised MinMax+EM Learning
Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Deep Neural Networks for Generative Mixture Modeling and Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Paced Bottom-Up Clustering Network with Side Information for Person Re-Identification
Mingkun Li, Chun-Guang Li, Ruo-Pei Guo, Jun Guo

Auto-TLDR; Self-Paced Bottom-up Clustering Network with Side Information for Unsupervised Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Sparse-Dense Subspace Clustering
Shuai Yang, Wenqi Zhu, Yuesheng Zhu

Auto-TLDR; Sparse-Dense Subspace Clustering with Piecewise Correlation Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Transformer Reasoning Network for Image-Text Matching and Retrieval
Nicola Messina, Fabrizio Falchi, Andrea Esuli, Giuseppe Amato

Auto-TLDR; A Transformer Encoder Reasoning Network for Image-Text Matching in Large-Scale Information Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Scalable Direction-Search-Based Approach to Subspace Clustering

Auto-TLDR; Fast Direction-Search-Based Subspace Clustering
Subspace Clustering Via Joint Unsupervised Feature Selection
Wenhua Dong, Xiaojun Wu, Hui Li, Zhenhua Feng, Josef Kittler
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Feature Selection for Subspace Clustering
A Novel Attention-Based Aggregation Function to Combine Vision and Language
Matteo Stefanini, Marcella Cornia, Lorenzo Baraldi, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Fully-Attentive Reduction for Vision and Language
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single-Modal Incremental Terrain Clustering from Self-Supervised Audio-Visual Feature Learning
Reina Ishikawa, Ryo Hachiuma, Akiyoshi Kurobe, Hideo Saito

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Variational Autoencoder for Terrain Type Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Clustering with Mean Teacher for Semi-Supervised Learning
Zexi Chen, Benjamin Dutton, Bharathkumar Ramachandra, Tianfu Wu, Ranga Raju Vatsavai

Auto-TLDR; Local Clustering for Semi-supervised Learning
Deep Topic Modeling by Multilayer Bootstrap Network and Lasso
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Deep Topic Modeling with Multilayer Bootstrap Network and Lasso
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Person Recognition with HGR Maximal Correlation on Multimodal Data
Yihua Liang, Fei Ma, Yang Li, Shao-Lun Huang
Auto-TLDR; A correlation-based multimodal person recognition framework that learns discriminative embeddings of persons by joint learning visual features and audio features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fast Discrete Cross-Modal Hashing Based on Label Relaxation and Matrix Factorization
Donglin Zhang, Xiaojun Wu, Zhen Liu, Jun Yu, Josef Kittler

Auto-TLDR; LRMF: Label Relaxation and Discrete Matrix Factorization for Cross-Modal Retrieval
Respecting Domain Relations: Hypothesis Invariance for Domain Generalization
Ziqi Wang, Marco Loog, Jan Van Gemert

Auto-TLDR; Learning Hypothesis Invariant Representations for Domain Generalization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Progressive Cluster Purification for Unsupervised Feature Learning
Yifei Zhang, Chang Liu, Yu Zhou, Wei Wang, Weiping Wang, Qixiang Ye

Auto-TLDR; Progressive Cluster Purification for Unsupervised Feature Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Embedding Shared Low-Rank and Feature Correlation for Multi-View Data Analysis
Zhan Wang, Lizhi Wang, Hua Huang

Auto-TLDR; embedding shared low-rank and feature correlation for multi-view data analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fast Subspace Clustering Based on the Kronecker Product
Lei Zhou, Xiao Bai, Liang Zhang, Jun Zhou, Edwin Hancock

Auto-TLDR; Subspace Clustering with Kronecker Product for Large Scale Datasets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Discrete Semantic Matrix Factorization Hashing for Cross-Modal Retrieval
Jianyang Qin, Lunke Fei, Shaohua Teng, Wei Zhang, Genping Zhao, Haoliang Yuan

Auto-TLDR; Discrete Semantic Matrix Factorization Hashing for Cross-Modal Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Class Conditional Alignment for Partial Domain Adaptation
Mohsen Kheirandishfard, Fariba Zohrizadeh, Farhad Kamangar
Auto-TLDR; Multi-class Adversarial Adaptation for Partial Domain Adaptation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Making Every Label Count: Handling Semantic Imprecision by Integrating Domain Knowledge
Clemens-Alexander Brust, Björn Barz, Joachim Denzler

Auto-TLDR; Class Hierarchies for Imprecise Label Learning and Annotation eXtrapolation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Text Synopsis Generation for Egocentric Videos
Aidean Sharghi, Niels Lobo, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; Egocentric Video Summarization Using Multi-task Learning for End-to-End Learning
Wasserstein k-Means with Sparse Simplex Projection
Takumi Fukunaga, Hiroyuki Kasai
Auto-TLDR; SSPW $k$-means: Sparse Simplex Projection-based Wasserstein $ k$-Means Algorithm
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Natural Thresholds for Image Ranking
Somayeh Keshavarz, Quang Nhat Tran, Richard Souvenir

Auto-TLDR; Image Representation Learning and Label Discretization for Natural Image Ranking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GuCNet: A Guided Clustering-Based Network for Improved Classification
Ushasi Chaudhuri, Syomantak Chaudhuri, Subhasis Chaudhuri
Auto-TLDR; Semantic Classification of Challenging Dataset Using Guide Datasets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Subspace Clustering for Action Recognition with Covariance Representations and Temporal Pruning
Giancarlo Paoletti, Jacopo Cavazza, Cigdem Beyan, Alessio Del Bue

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Learning for Human Action Recognition from Skeletal Data
Enriching Video Captions with Contextual Text
Philipp Rimle, Pelin Dogan, Markus Gross
Auto-TLDR; Contextualized Video Captioning Using Contextual Text
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Contextual Classification Using Self-Supervised Auxiliary Models for Deep Neural Networks
Sebastian Palacio, Philipp Engler, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel

Auto-TLDR; Self-Supervised Autogenous Learning for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On the Information of Feature Maps and Pruning of Deep Neural Networks
Mohammadreza Soltani, Suya Wu, Jie Ding, Robert Ravier, Vahid Tarokh

Auto-TLDR; Compressing Deep Neural Models Using Mutual Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Motion Segmentation with Pairwise Matches and Unknown Number of Motions
Federica Arrigoni, Tomas Pajdla, Luca Magri

Auto-TLDR; Motion Segmentation using Multi-Modelfitting andpermutation synchronization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentive Visual Semantic Specialized Network for Video Captioning
Jesus Perez-Martin, Benjamin Bustos, Jorge Pérez

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Visual Semantic Specialized Network for Video Captioning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CANU-ReID: A Conditional Adversarial Network for Unsupervised Person Re-IDentification
Guillaume Delorme, Yihong Xu, Stéphane Lathuiliere, Radu Horaud, Xavier Alameda-Pineda

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Person Re-Identification with Clustering and Adversarial Learning
Cross-spectrum Face Recognition Using Subspace Projection Hashing
Hanrui Wang, Xingbo Dong, Jin Zhe, Jean-Luc Dugelay, Massimo Tistarelli

Auto-TLDR; Subspace Projection Hashing for Cross-Spectrum Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context Visual Information-Based Deliberation Network for Video Captioning
Min Lu, Xueyong Li, Caihua Liu
Auto-TLDR; Context visual information-based deliberation network for video captioning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Picture-To-Amount (PITA): Predicting Relative Ingredient Amounts from Food Images
Jiatong Li, Fangda Han, Ricardo Guerrero, Vladimir Pavlovic

Auto-TLDR; PITA: A Deep Learning Architecture for Predicting the Relative Amount of Ingredients from Food Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RGB-Infrared Person Re-Identification Via Image Modality Conversion
Huangpeng Dai, Qing Xie, Yanchun Ma, Yongjian Liu, Shengwu Xiong

Auto-TLDR; CE2L: A Novel Network for Cross-Modality Re-identification with Feature Alignment
Abstract Slides Poster Similar