Josef Kittler
Papers from this author
Adaptive Context-Aware Discriminative Correlation Filters for Robust Visual Object Tracking
Tianyang Xu, Zhenhua Feng, Xiaojun Wu, Josef Kittler

Auto-TLDR; ACA-DCF: Adaptive Context-Aware Discriminative Correlation Filter with complementary attention mechanisms
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Flatter Loss for Bias Mitigation in Cross-Dataset Facial Age Estimation
Ali Akbari, Muhammad Awais, Zhenhua Feng, Ammarah Farooq, Josef Kittler

Auto-TLDR; Cross-dataset Age Estimation for Neural Network Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Angular Sparsemax for Face Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Angular Sparsemax for Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fast Discrete Cross-Modal Hashing Based on Label Relaxation and Matrix Factorization
Donglin Zhang, Xiaojun Wu, Zhen Liu, Jun Yu, Josef Kittler

Auto-TLDR; LRMF: Label Relaxation and Discrete Matrix Factorization for Cross-Modal Retrieval
Subspace Clustering Via Joint Unsupervised Feature Selection
Wenhua Dong, Xiaojun Wu, Hui Li, Zhenhua Feng, Josef Kittler
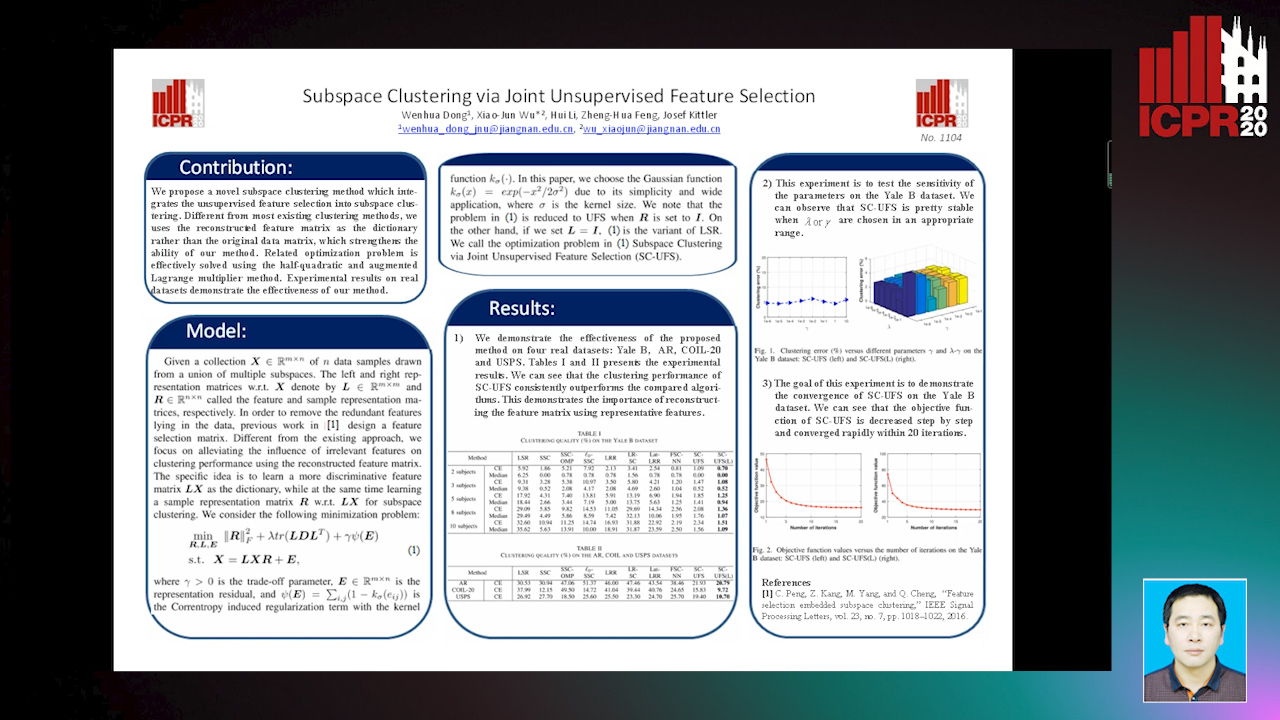
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Feature Selection for Subspace Clustering