Nonlinear Ranking Loss on Riemannian Potato Embedding
Byung Hyung Kim,
Yoonje Suh,
Honggu Lee,
Sungho Jo

Auto-TLDR; Riemannian Potato for Rank-based Metric Learning
Similar papers
Batch-Incremental Triplet Sampling for Training Triplet Networks Using Bayesian Updating Theorem
Milad Sikaroudi, Benyamin Ghojogh, Fakhri Karray, Mark Crowley, Hamid Reza Tizhoosh
Auto-TLDR; Bayesian Updating Triplet Mining with Bayesian updating
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Embeddings for Image Clustering: An Empirical Study of Triplet Loss Approaches
Kalun Ho, Janis Keuper, Franz-Josef Pfreundt, Margret Keuper
Auto-TLDR; Clustering Objectives for K-means and Correlation Clustering Using Triplet Loss
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generalized Local Attention Pooling for Deep Metric Learning
Carlos Roig Mari, David Varas, Issey Masuda, Juan Carlos Riveiro, Elisenda Bou-Balust

Auto-TLDR; Generalized Local Attention Pooling for Deep Metric Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SL-DML: Signal Level Deep Metric Learning for Multimodal One-Shot Action Recognition
Raphael Memmesheimer, Nick Theisen, Dietrich Paulus

Auto-TLDR; One-Shot Action Recognition using Metric Learning
Deep Top-Rank Counter Metric for Person Re-Identification
Chen Chen, Hao Dou, Xiyuan Hu, Silong Peng

Auto-TLDR; Deep Top-Rank Counter Metric for Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improved Deep Classwise Hashing with Centers Similarity Learning for Image Retrieval

Auto-TLDR; Deep Classwise Hashing for Image Retrieval Using Center Similarity Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Level Deep Learning Vehicle Re-Identification Using Ranked-Based Loss Functions
Eleni Kamenou, Jesus Martinez-Del-Rincon, Paul Miller, Patricia Devlin - Hill
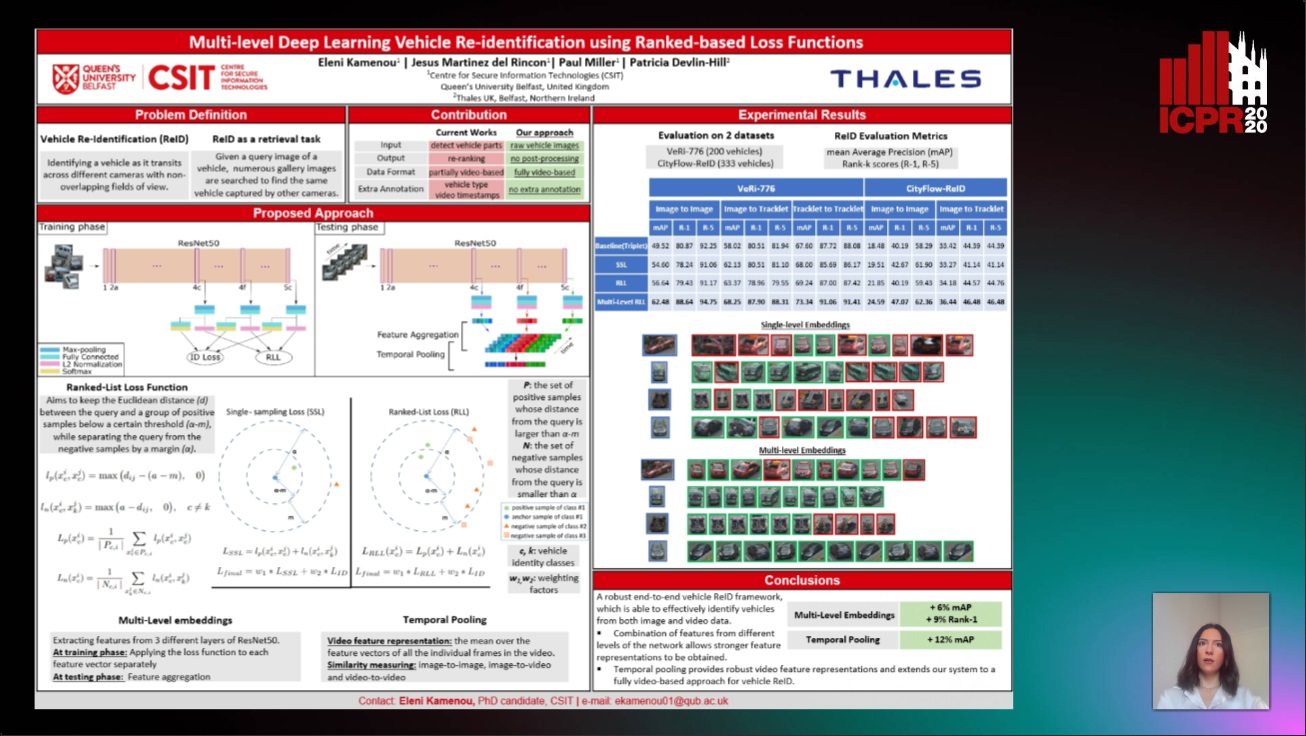
Auto-TLDR; Multi-Level Re-identification Network for Vehicle Re-Identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Progressive Learning Algorithm for Efficient Person Re-Identification
Zhen Li, Hanyang Shao, Liang Niu, Nian Xue

Auto-TLDR; Progressive Learning Algorithm for Large-Scale Person Re-Identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Label Contrastive Focal Loss for Pedestrian Attribute Recognition
Xiaoqiang Zheng, Zhenxia Yu, Lin Chen, Fan Zhu, Shilong Wang

Auto-TLDR; Multi-label Contrastive Focal Loss for Pedestrian Attribute Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Not 3D Re-ID: Simple Single Stream 2D Convolution for Robust Video Re-Identification

Auto-TLDR; ResNet50-IBN for Video-based Person Re-Identification using Single Stream 2D Convolution Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Temporally Coherent Embeddings for Self-Supervised Video Representation Learning
Joshua Knights, Ben Harwood, Daniel Ward, Anthony Vanderkop, Olivia Mackenzie-Ross, Peyman Moghadam

Auto-TLDR; Temporally Coherent Embeddings for Self-supervised Video Representation Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Revisiting ImprovedGAN with Metric Learning for Semi-Supervised Learning
Jaewoo Park, Yoon Gyo Jung, Andrew Teoh

Auto-TLDR; Improving ImprovedGAN with Metric Learning for Semi-supervised Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Facial Matching by Spiral Convolutional Metric Learning and a Biometric Fusion-Net of Demographic Properties
Soha Sadat Mahdi, Nele Nauwelaers, Philip Joris, Giorgos Bouritsas, Imperial London, Sergiy Bokhnyak, Susan Walsh, Mark Shriver, Michael Bronstein, Peter Claes

Auto-TLDR; Multi-biometric Fusion for Biometric Verification using 3D Facial Mesures
Rotation Invariant Aerial Image Retrieval with Group Convolutional Metric Learning
Hyunseung Chung, Woo-Jeoung Nam, Seong-Whan Lee

Auto-TLDR; Robust Remote Sensing Image Retrieval Using Group Convolution with Attention Mechanism and Metric Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Encoding Brain Networks through Geodesic Clustering of Functional Connectivity for Multiple Sclerosis Classification
Muhammad Abubakar Yamin, Valsasina Paola, Michael Dayan, Sebastiano Vascon, Tessadori Jacopo, Filippi Massimo, Vittorio Murino, A Rocca Maria, Diego Sona

Auto-TLDR; Geodesic Clustering of Connectivity Matrices for Multiple Sclerosis Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Constrained Spectral Clustering Network with Self-Training
Xinyue Liu, Shichong Yang, Linlin Zong

Auto-TLDR; Constrained Spectral Clustering Network: A Constrained Deep spectral clustering network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Supervised Domain Adaptation Using Graph Embedding
Lukas Hedegaard, Omar Ali Sheikh-Omar, Alexandros Iosifidis
Auto-TLDR; Domain Adaptation from the Perspective of Multi-view Graph Embedding and Dimensionality Reduction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SSDL: Self-Supervised Domain Learning for Improved Face Recognition
Samadhi Poornima Kumarasinghe Wickrama Arachchilage, Ebroul Izquierdo

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Domain Learning for Face Recognition in unconstrained environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Few-Shot Font Generation with Deep Metric Learning
Haruka Aoki, Koki Tsubota, Hikaru Ikuta, Kiyoharu Aizawa
Auto-TLDR; Deep Metric Learning for Japanese Typographic Font Synthesis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Based Deep Metric Learning for Near-Duplicate Video Retrieval
Kuan-Hsun Wang, Chia Chun Cheng, Yi-Ling Chen, Yale Song, Shang-Hong Lai

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Deep Metric Learning for Near-duplicate Video Retrieval
A Unified Framework for Distance-Aware Domain Adaptation
Fei Wang, Youdong Ding, Huan Liang, Yuzhen Gao, Wenqi Che

Auto-TLDR; distance-aware domain adaptation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DAIL: Dataset-Aware and Invariant Learning for Face Recognition
Gaoang Wang, Chen Lin, Tianqiang Liu, Mingwei He, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; DAIL: Dataset-Aware and Invariant Learning for Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Subspace Clustering for Action Recognition with Covariance Representations and Temporal Pruning
Giancarlo Paoletti, Jacopo Cavazza, Cigdem Beyan, Alessio Del Bue

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Learning for Human Action Recognition from Skeletal Data
Soft Label and Discriminant Embedding Estimation for Semi-Supervised Classification
Fadi Dornaika, Abdullah Baradaaji, Youssof El Traboulsi
Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Semi-Supervised Learning for Linear Feature Extraction and Label Propagation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Recurrent High-Order Statistics for Skeleton-Based Hand Gesture Recognition
Xuan Son Nguyen, Luc Brun, Olivier Lezoray, Sébastien Bougleux
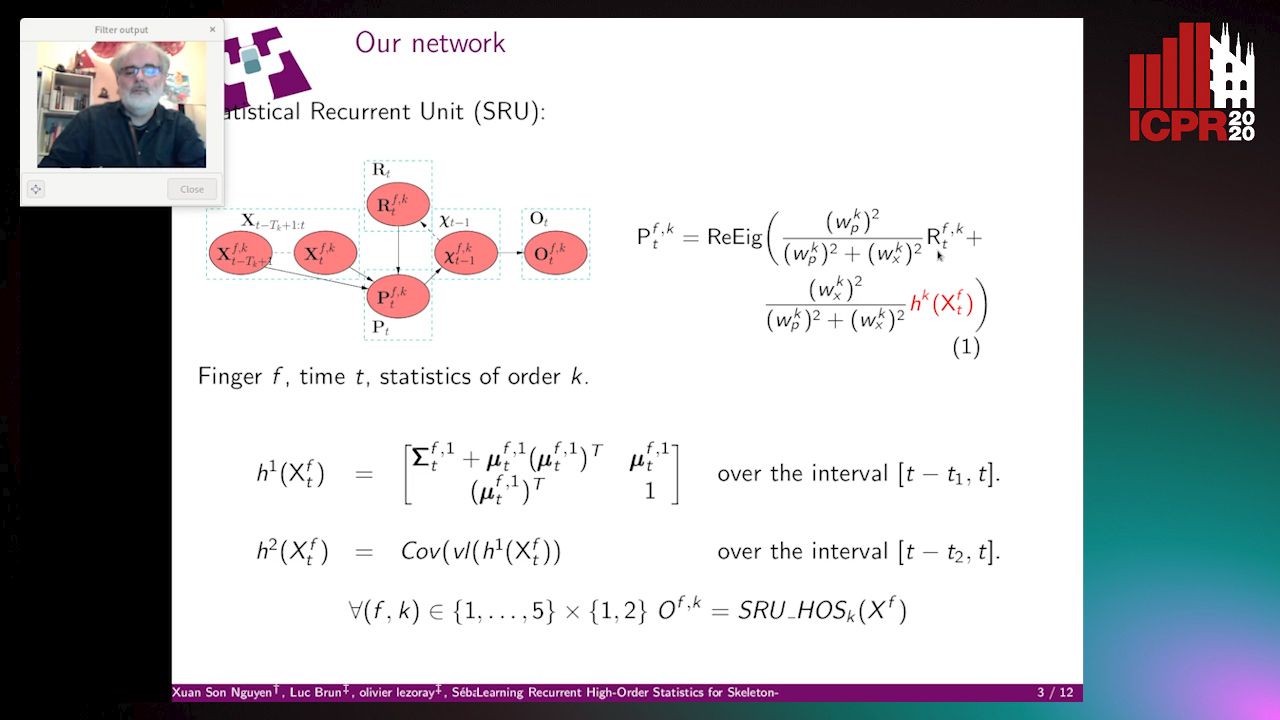
Auto-TLDR; Exploiting High-Order Statistics in Recurrent Neural Networks for Hand Gesture Recog-nition
End-To-End Triplet Loss Based Emotion Embedding System for Speech Emotion Recognition
Puneet Kumar, Sidharth Jain, Balasubramanian Raman, Partha Pratim Roy, Masakazu Iwamura

Auto-TLDR; End-to-End Neural Embedding System for Speech Emotion Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
One-Shot Representational Learning for Joint Biometric and Device Authentication

Auto-TLDR; Joint Biometric and Device Recognition from a Single Biometric Image
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Loop-closure detection by LiDAR scan re-identification
Jukka Peltomäki, Xingyang Ni, Jussi Puura, Joni-Kristian Kamarainen, Heikki Juhani Huttunen

Auto-TLDR; Loop-Closing Detection from LiDAR Scans Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Equation Attention Relationship Network (EARN) : A Geometric Deep Metric Framework for Learning Similar Math Expression Embedding
Saleem Ahmed, Kenny Davila, Srirangaraj Setlur, Venu Govindaraju

Auto-TLDR; Representational Learning for Similarity Based Retrieval of Mathematical Expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
N2D: (Not Too) Deep Clustering Via Clustering the Local Manifold of an Autoencoded Embedding
Ryan Mcconville, Raul Santos-Rodriguez, Robert Piechocki, Ian Craddock

Auto-TLDR; Local Manifold Learning for Deep Clustering on Autoencoded Embeddings
Angular Sparsemax for Face Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Angular Sparsemax for Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Kernel-based Graph Convolutional Networks
Auto-TLDR; Spatial Graph Convolutional Networks in Recurrent Kernel Hilbert Space
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Total Whitening for Online Signature Verification Based on Deep Representation
Xiaomeng Wu, Akisato Kimura, Kunio Kashino, Seiichi Uchida

Auto-TLDR; Total Whitening for Online Signature Verification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Comparison of Stacking-Based Classifier Ensembles Using Euclidean and Riemannian Geometries
Vitaliy Tayanov, Adam Krzyzak, Ching Y Suen
Auto-TLDR; Classifier Stacking in Riemannian Geometries using Cascades of Random Forest and Extra Trees
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cam-Softmax for Discriminative Deep Feature Learning
Tamas Suveges, Stephen James Mckenna

Auto-TLDR; Cam-Softmax: A Generalisation of Activations and Softmax for Deep Feature Spaces
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Neural Textual Representations for Citation Recommendation
Thanh Binh Kieu, Inigo Jauregi Unanue, Son Bao Pham, Xuan-Hieu Phan, M. Piccardi

Auto-TLDR; Sentence-BERT cascaded with Siamese and triplet networks for citation recommendation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Probabilistic Word Embeddings in Kinematic Space
Adarsh Jamadandi, Rishabh Tigadoli, Ramesh Ashok Tabib, Uma Mudenagudi

Auto-TLDR; Kinematic Space for Hierarchical Representation Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Spectral Clustering on Grassmann Manifold Via Double Low Rank Constraint
Xinglin Piao, Yongli Hu, Junbin Gao, Yanfeng Sun, Xin Yang, Baocai Yin

Auto-TLDR; Double Low Rank Representation for High-Dimensional Data Clustering on Grassmann Manifold
Supporting Skin Lesion Diagnosis with Content-Based Image Retrieval
Stefano Allegretti, Federico Bolelli, Federico Pollastri, Sabrina Longhitano, Giovanni Pellacani, Costantino Grana

Auto-TLDR; Skin Images Retrieval Using Convolutional Neural Networks for Skin Lesion Classification and Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Beyond the Deep Metric Learning: Enhance the Cross-Modal Matching with Adversarial Discriminative Domain Regularization
Li Ren, Kai Li, Liqiang Wang, Kien Hua

Auto-TLDR; Adversarial Discriminative Domain Regularization for Efficient Cross-Modal Matching
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Extraction by Joint Robust Discriminant Analysis and Inter-Class Sparsity
Auto-TLDR; Robust Discriminant Analysis with Feature Selection and Inter-class Sparsity (RDA_FSIS)
Rethinking ReID:Multi-Feature Fusion Person Re-Identification Based on Orientation Constraints
Mingjing Ai, Guozhi Shan, Bo Liu, Tianyang Liu
Auto-TLDR; Person Re-identification with Orientation Constrained Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Clustering with Mean Teacher for Semi-Supervised Learning
Zexi Chen, Benjamin Dutton, Bharathkumar Ramachandra, Tianfu Wu, Ranga Raju Vatsavai

Auto-TLDR; Local Clustering for Semi-supervised Learning
Learning Connectivity with Graph Convolutional Networks
Auto-TLDR; Learning Graph Convolutional Networks Using Topological Properties of Graphs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cc-Loss: Channel Correlation Loss for Image Classification
Zeyu Song, Dongliang Chang, Zhanyu Ma, Li Xiaoxu, Zheng-Hua Tan

Auto-TLDR; Channel correlation loss for ad- dressing image classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A New Geodesic-Based Feature for Characterization of 3D Shapes: Application to Soft Tissue Organ Temporal Deformations
Karim Makki, Amine Bohi, Augustin Ogier, Marc-Emmanuel Bellemare

Auto-TLDR; Spatio-Temporal Feature Descriptors for 3D Shape Characterization from Point Clouds
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-spectrum Face Recognition Using Subspace Projection Hashing
Hanrui Wang, Xingbo Dong, Jin Zhe, Jean-Luc Dugelay, Massimo Tistarelli

Auto-TLDR; Subspace Projection Hashing for Cross-Spectrum Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
More Correlations Better Performance: Fully Associative Networks for Multi-Label Image Classification

Auto-TLDR; Fully Associative Network for Fully Exploiting Correlation Information in Multi-Label Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar