Assortative-Constrained Stochastic Block Models
Daniel Gribel,
Thibaut Vidal,
Michel Gendreau

Auto-TLDR; Constrained Stochastic Block Models for Assortative Communities in Neural Networks
Similar papers
Sketch-Based Community Detection Via Representative Node Sampling
Mahlagha Sedghi, Andre Beckus, George Atia
Auto-TLDR; Sketch-based Clustering of Community Detection Using a Small Sketch
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cluster-Size Constrained Network Partitioning
Maksim Mironov, Konstantin Avrachenkov
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Graph Clustering with Stochastic Block Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Temporal Pattern Detection in Time-Varying Graphical Models
Federico Tomasi, Veronica Tozzo, Annalisa Barla

Auto-TLDR; A dynamical network inference model that leverages on kernels to consider general temporal patterns
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Aggregating Dependent Gaussian Experts in Local Approximation

Auto-TLDR; A novel approach for aggregating the Gaussian experts by detecting strong violations of conditional independence
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Empirical Bayes Approach to Topic Modeling
Auto-TLDR; An Empirical Bayes Based Framework for Topic Modeling in Documents
Naturally Constrained Online Expectation Maximization
Daniela Pamplona, Antoine Manzanera
Auto-TLDR; Constrained Online Expectation-Maximization for Probabilistic Principal Components Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Scalable Direction-Search-Based Approach to Subspace Clustering

Auto-TLDR; Fast Direction-Search-Based Subspace Clustering
Constrained Spectral Clustering Network with Self-Training
Xinyue Liu, Shichong Yang, Linlin Zong

Auto-TLDR; Constrained Spectral Clustering Network: A Constrained Deep spectral clustering network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tensor Factorization of Brain Structural Graph for Unsupervised Classification in Multiple Sclerosis
Berardino Barile, Marzullo Aldo, Claudio Stamile, Françoise Durand-Dubief, Dominique Sappey-Marinier

Auto-TLDR; A Fully Automated Tensor-based Algorithm for Multiple Sclerosis Classification based on Structural Connectivity Graph of the White Matter Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3CS Algorithm for Efficient Gaussian Process Model Retrieval
Fabian Berns, Kjeld Schmidt, Ingolf Bracht, Christian Beecks

Auto-TLDR; Efficient retrieval of Gaussian Process Models for large-scale data using divide-&-conquer-based approach
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Sparse-Dense Subspace Clustering
Shuai Yang, Wenqi Zhu, Yuesheng Zhu

Auto-TLDR; Sparse-Dense Subspace Clustering with Piecewise Correlation Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Thermal Characterisation of Unweighted and Weighted Networks
Jianjia Wang, Hui Wu, Edwin Hancock
Auto-TLDR; Thermodynamic Characterisation of Networks as Particles of the Thermal System
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Connectivity with Graph Convolutional Networks
Auto-TLDR; Learning Graph Convolutional Networks Using Topological Properties of Graphs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Active Sampling for Pairwise Comparisons via Approximate Message Passing and Information Gain Maximization
Aliaksei Mikhailiuk, Clifford Wilmot, Maria Perez-Ortiz, Dingcheng Yue, Rafal Mantiuk

Auto-TLDR; ASAP: An Active Sampling Algorithm for Pairwise Comparison Data
FMRI Brain Networks As Statistical Mechanical Ensembles
Jianjia Wang, Hui Wu, Edwin Hancock
Auto-TLDR; Microcanonical Ensemble Methods for FMRI Brain Networks for Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A General Model for Learning Node and Graph Representations Jointly
Auto-TLDR; Joint Community Detection/Dynamic Routing for Graph Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Routing Mixture of Experts
Wenbo Zhao, Yang Gao, Shahan Ali Memon, Bhiksha Raj, Rita Singh

Auto-TLDR; A Binary Tree-structured Hierarchical Routing Mixture of Experts for Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On Learning Random Forests for Random Forest Clustering
Manuele Bicego, Francisco Escolano

Auto-TLDR; Learning Random Forests for Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Parameter Distributions to Detect Concept Drift in Data Streams
Johannes Haug, Gjergji Kasneci

Auto-TLDR; A novel framework for the detection of concept drift in streaming environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Region and Relations Based Multi Attention Network for Graph Classification
Manasvi Aggarwal, M. Narasimha Murty
Auto-TLDR; R2POOL: A Graph Pooling Layer for Non-euclidean Structures
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Bayesian Active Learning for Maximal Information Gain on Model Parameters
Kasra Arnavaz, Aasa Feragen, Oswin Krause, Marco Loog

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian assumptions for Bayesian classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Variational Deep Embedding Clustering by Augmented Mutual Information Maximization
Qiang Ji, Yanfeng Sun, Yongli Hu, Baocai Yin

Auto-TLDR; Clustering by Augmented Mutual Information maximization for Deep Embedding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Edge-Aware Graph Attention Network for Ratio of Edge-User Estimation in Mobile Networks
Jiehui Deng, Sheng Wan, Xiang Wang, Enmei Tu, Xiaolin Huang, Jie Yang, Chen Gong

Auto-TLDR; EAGAT: Edge-Aware Graph Attention Network for Automatic REU Estimation in Mobile Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Probabilistic Latent Factor Model for Collaborative Filtering with Bayesian Inference
Jiansheng Fang, Xiaoqing Zhang, Yan Hu, Yanwu Xu, Ming Yang, Jiang Liu

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian Latent Factor Model for Collaborative Filtering
Epitomic Variational Graph Autoencoder
Rayyan Ahmad Khan, Muhammad Umer Anwaar, Martin Kleinsteuber
Auto-TLDR; EVGAE: A Generative Variational Autoencoder for Graph Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Interpretable Structured Learning with Sparse Gated Sequence Encoder for Protein-Protein Interaction Prediction
Kishan K C, Feng Cui, Anne Haake, Rui Li

Auto-TLDR; Predicting Protein-Protein Interactions Using Sequence Representations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Graph Spectral Feature Learning for Mixed Data of Categorical and Numerical Type
Saswata Sahoo, Souradip Chakraborty

Auto-TLDR; Feature Learning in Mixed Type of Variable by an undirected graph
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature-Aware Unsupervised Learning with Joint Variational Attention and Automatic Clustering
Wang Ru, Lin Li, Peipei Wang, Liu Peiyu

Auto-TLDR; Deep Variational Attention Encoder-Decoder for Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Switching Dynamical Systems with Deep Neural Networks
Cesar Ali Ojeda Marin, Kostadin Cvejoski, Bogdan Georgiev, Ramses J. Sanchez

Auto-TLDR; Variational RNN for Switching Dynamics
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generative Deep-Neural-Network Mixture Modeling with Semi-Supervised MinMax+EM Learning
Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Deep Neural Networks for Generative Mixture Modeling and Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Convolutional Embedding for Digitized Painting Clustering
Giovanna Castellano, Gennaro Vessio

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Convolutional Embedding Model for Clustering Artworks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Motion Segmentation with Pairwise Matches and Unknown Number of Motions
Federica Arrigoni, Tomas Pajdla, Luca Magri

Auto-TLDR; Motion Segmentation using Multi-Modelfitting andpermutation synchronization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Intransitivity Model for Matchup and Pairwise Comparison
Yan Gu, Jiuding Duan, Hisashi Kashima

Auto-TLDR; Blade-Chest: A Low-Rank Matrix Approach for Probabilistic Ranking of Players
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Expectation-Maximization for Scheduling Problems in Satellite Communication
Werner Bailer, Martin Winter, Johannes Ebert, Joel Flavio, Karin Plimon

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Machine Learning for Satellite Communication Using Expectation-Maximization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GPSRL: Learning Semi-Parametric Bayesian Survival Rule Lists from Heterogeneous Patient Data
Ameer Hamza Shakur, Xiaoning Qian, Zhangyang Wang, Bobak Mortazavi, Shuai Huang

Auto-TLDR; Semi-parametric Bayesian Survival Rule List Model for Heterogeneous Survival Data
Automatically Mining Relevant Variable Interactions Via Sparse Bayesian Learning
Ryoichiro Yafune, Daisuke Sakuma, Yasuo Tabei, Noritaka Saito, Hiroto Saigo

Auto-TLDR; Sparse Bayes for Interpretable Non-linear Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Subspace Clustering Via Joint Unsupervised Feature Selection
Wenhua Dong, Xiaojun Wu, Hui Li, Zhenhua Feng, Josef Kittler
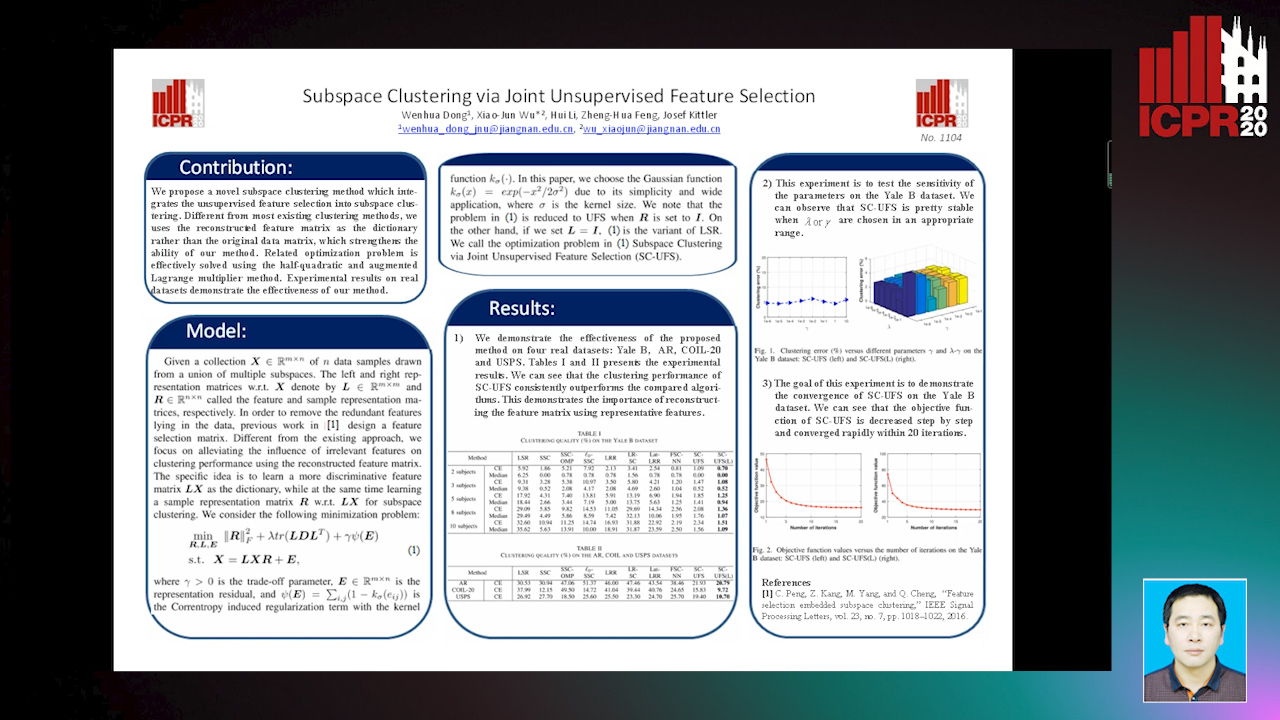
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Feature Selection for Subspace Clustering
A Multi-Task Multi-View Based Multi-Objective Clustering Algorithm

Auto-TLDR; MTMV-MO: Multi-task multi-view multi-objective optimization for multi-task clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Quantifying Model Uncertainty in Inverse Problems Via Bayesian Deep Gradient Descent
Riccardo Barbano, Chen Zhang, Simon Arridge, Bangti Jin

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian Neural Networks for Inverse Reconstruction via Bayesian Knowledge-Aided Computation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recursive Convolutional Neural Networks for Epigenomics
Aikaterini Symeonidi, Anguelos Nicolaou, Frank Johannes, Vincent Christlein
Auto-TLDR; Recursive Convolutional Neural Networks for Epigenomic Data Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Sign-Constrained Support Vector Machines
Kenya Tajima, Kouhei Tsuchida, Esmeraldo Ronnie Rey Zara, Naoya Ohta, Tsuyoshi Kato
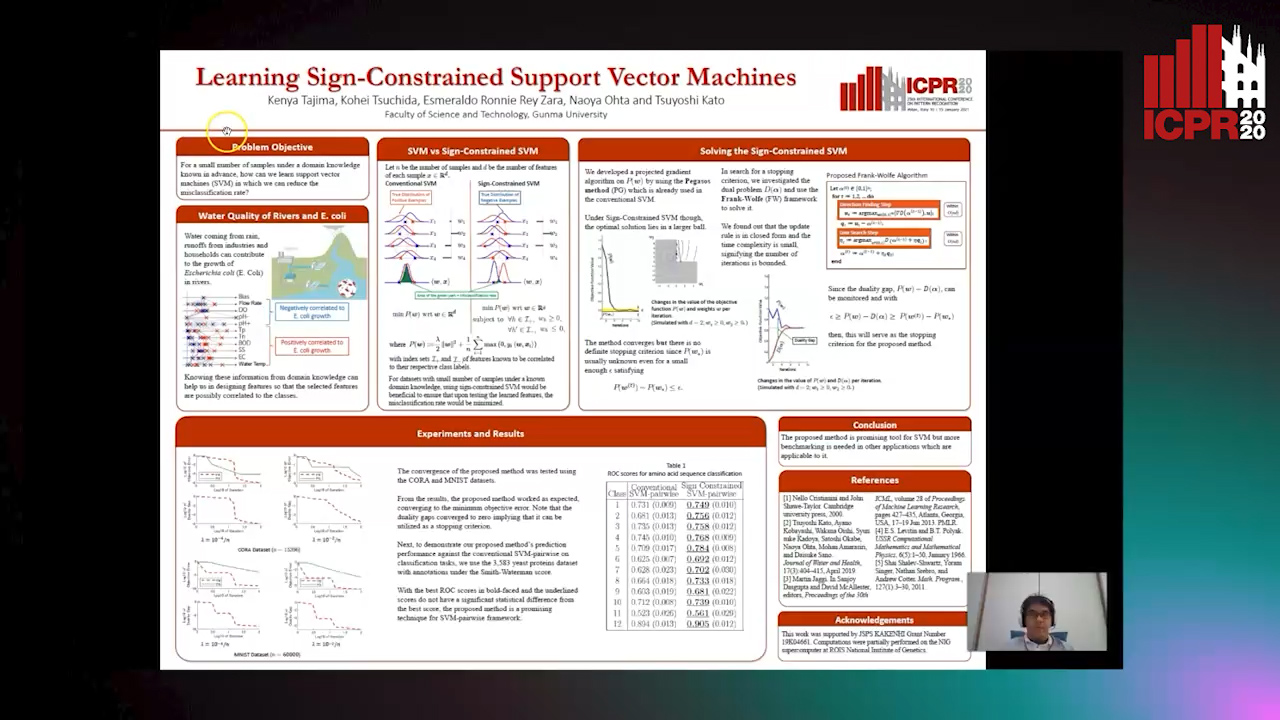
Auto-TLDR; Constrained Sign Constraints for Learning Linear Support Vector Machine
On Morphological Hierarchies for Image Sequences
Caglayan Tuna, Alain Giros, François Merciol, Sébastien Lefèvre

Auto-TLDR; Comparison of Hierarchies for Image Sequences
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Invariance-Guided Stability Criterion for Time Series Clustering Validation
Florent Forest, Alex Mourer, Mustapha Lebbah, Hanane Azzag, Jérôme Lacaille

Auto-TLDR; An invariance-guided method for clustering model selection in time series data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Map-Based Temporally Consistent Geolocalization through Learning Motion Trajectories

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Motion Trajectories for Geolocalization of Object on Topological Map using Recurrent Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-annotator Probabilistic Active Learning
Marek Herde, Daniel Kottke, Denis Huseljic, Bernhard Sick

Auto-TLDR; MaPAL: Multi-annotator Probabilistic Active Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Modal Deep Clustering: Unsupervised Partitioning of Images

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Modal Deep Clustering for Unlabeled Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AOAM: Automatic Optimization of Adjacency Matrix for Graph Convolutional Network
Yuhang Zhang, Hongshuai Ren, Jiexia Ye, Xitong Gao, Yang Wang, Kejiang Ye, Cheng-Zhong Xu

Auto-TLDR; Adjacency Matrix for Graph Convolutional Network in Non-Euclidean Space
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Seasonal Inhomogeneous Nonconsecutive Arrival Process Search and Evaluation
Kimberly Holmgren, Paul Gibby, Joseph Zipkin

Auto-TLDR; SINAPSE: Fitting a Sparse Time Series Model to Seasonal Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar